Who should I contact if I suspect demodicosis?
If you have symptoms of a skin disease, you should immediately consult a doctor. The sooner treatment is started, the easier it will be to get rid of parasites and restore the condition of the skin.
An appointment for analysis to detect Demodex mites can be obtained from a therapist, dermatologist, or from doctors such as a mycologist or parasitologist. When the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment is carried out:
- dermatologist (for skin form);
- trichologist (if the scalp is affected by subcutaneous mites);
- ophthalmologist (for the eye form of the disease).
Visit to a specialist
Attention! Only a specialist can correctly interpret the analysis results and determine a treatment regimen.
When to get tested for ticks
Indications for testing are:
- itching and redness of the skin;
- pustules and red spots on the body and face;
- rashes similar to insect bites or long “bursts”;
- inflammation of the eyelids, accompanied by the appearance of whitish scales, loss of eyelashes and eyebrows;
- acne that does not go away with treatment;
- expansion of capillary vessels;
- “stye” in the eyes, lacrimation and photophobia.
Laboratory diagnostics are especially necessary for erased and atypical forms of the disease, as well as to determine the type of pathogen.
When is the study scheduled?
The Demodex mite belongs to the category of opportunistic organisms. It exists on human skin without being active. But in case of weakened immunity, metabolic disorders, hormonal imbalances, autoimmune diseases, or under the influence of certain external factors (for example, regular exposure to high temperatures in a sauna or solarium), the parasite begins to multiply, affecting more and more areas of the skin.
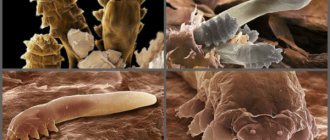
Subcutaneous mites settle in hair follicles, sebaceous glands and feed on keratin, sebum, and dead skin particles.
An analysis for demodicosis is prescribed if the following symptoms appear:
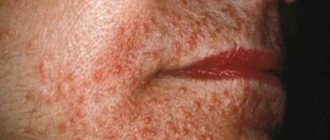
- redness of the skin of the face or eyelids;
- the appearance of pustules, pimples, nodules, blackheads;
- oily facial skin;
- changes in the appearance of the skin (it becomes lumpy, compactions appear);
- swelling and inflammation of the eyelids;
- eyelashes stick together and fall out;
- in the evenings and at night, the affected areas begin to itch very much;
- flaky spots appear on the skin.
Signs of demodicosis are usually noticeable in the area of the cheeks, forehead, chin, wings of the nose, eyelids, and eyebrows. Since the symptoms are nonspecific, tests are needed to help differentiate the disease. The biomaterial for study is tissue from the affected area.
Skin scraping for demodex
Analysis for the identification of subcutaneous skin mites is also carried out using laboratory diagnostics. Most often, a superficial biopsy is performed. First, a small amount of special cyanoacrylate glue is applied to the cleaned and prepared glass. After this, it sticks to the affected area on the surface of the face for 50-60 seconds.
Sometimes, to carry out this study, tape is used, which is glued to a special piece of glass. After the required time has elapsed, they are removed from the face. A small upper layer of the epidermis remains on their surface, as well as the substance contained in the affected sebaceous glands. Next, the resulting material is examined for the presence of a pathological pathogen under microscopy (at low magnification). An important disadvantage of this research method is that some areas of the face are difficult to access for collecting material. It is most inconvenient to remove material from the surface of the wings of the nose.
Also, to diagnose demodicosis, you can take not only the contents of the acne, but also a small piece of the gland for analysis. At the same time, it is examined by histological method. In the affected area of the skin, not only adult parasites can be found; non-physiological tissue proliferation and thickening of the walls of blood vessels are also taken into account. At the same time, the cells of the hair follicles are visualized destroyed.
Where can I get tested?
An analysis for the presence of subcutaneous mites can be taken at a public medical institution if it sees a dermatologist and has a laboratory. You can also be diagnosed for demodicosis at a skin and venereal disease clinic or any private medical center.
The cost of analysis in a private clinic will be slightly more expensive, but it is still better to choose this option. The fact is that Demodex does not tolerate ultraviolet radiation and during daylight hours it gets deeper into the skin, showing practically no activity. Therefore, it is better to take the test after 18.00, when ticks are active and it is easier to detect them.
However, in public clinics, biomaterial collection is most often carried out in the morning. In a commercial institution, you can adjust the time for taking the analysis.
What is demodicosis?
Demodicosis - description
The term demodicosis refers to an acariatic disease that appears in the body under the activity of a parasitic mite - the acne gland. This pathogenic organism is quite small in size (up to 0.5 millimeters), settling in the sebaceous ducts of the skin. In addition to this habitat, the acne gland can be found in the meibomian area, as well as hair follicles.
This parasite causes discomfort associated with scabies and the development of a disease such as demodicosis. Another peculiarity of this parasite is that it parasitizes exclusively in the skin of the human body, bypassing other organisms.
As soon as such a mite enters the human body, it immediately begins to feed on the secretions of the sebaceous glands and dead exfoliated skin particles. This is how he exists throughout his life. In appearance, an adult tick is quite oblong in shape with a transparent body, which is covered with small scales.
A special examination, for which a scraping is performed, will help identify the presence of this parasite in the body.
This examination is carried out in a laboratory using special equipment and the necessary equipment. According to medical studies conducted on numerous populations, it was found that only two percent of the population does not have this parasite in their skin. This means that the tick is in close contact with the majority of the inhabitants of our planet.
More information about demodicosis can be found in the video.
Why don't many people suffer from such contact? It turns out that these mites are symbiotic organisms that cohabit with humans. Moreover, not all people suffer from such a neighborhood, and most practically do not notice it. Therefore, such ticks do not cause harm to the majority of the inhabitants of our planet.
Recent results of laboratory tests have proven such cohabitation, demonstrating the presence of several individuals in one cell. Nevertheless, such cohabitation can cause the development of demodicosis in humans through unlimited reproduction of the parasite.
This happens when a person has:
- Frequent stress
- Nervous breakdowns
- Diseases of the digestive organs
- Endocrine system diseases
- Malfunctions of the immune system
Therefore, if a person does not want to turn his symbiotic neighbor into a malicious enemy, he must avoid the factors described above.
Preparing for analysis
Testing for Demodex mites requires preliminary preparation. 3-5 days before the procedure you should stop using decorative cosmetics. You should also not use creams, ointments, medicinal cosmetics, wash your face with products containing a high alkali content, or wash your hair (if the scalp is affected). If signs of ophthalmodicosis (damage to the eye area or eyelids) are detected, it is necessary to temporarily interrupt the use of eye drops, with the exception of those prescribed for the treatment of serious eye pathologies. But it is better to refuse them at least a day before the test.
All these measures are necessary in order to obtain the most reliable research results. This also includes the advisability of carrying out the procedure in the evening. If the biomaterial is submitted during the day, the parasite may not be detected. Then you will need a repeat analysis, and possibly several.
Causes of development and symptoms of demodicosis
Scientists today cannot say with 100% accuracy when and why Demodex mites become pathogenic. It is most likely that in most cases the triggering factor is the altered microflora of the skin - due to age-related, immune changes, concomitant diseases: gastrointestinal dysfunction, chronic infections. others.
The functioning of the sebaceous glands and the composition of sebum change, the composition of the skin microbiocenosis changes, skin dysbacteriosis develops, and the amount of opportunistic microflora increases.
Many scientists believe that mites themselves are not pathogenic, but simply carry microbes and viruses (for example, Pityrosporum spp., pathogenic pyococci) deep into the sebaceous glands and hair follicles, resulting in inflammatory processes. Symptoms of demodicosis:
- itching in the area of eyelashes, eyelids, eyebrows (demodectic blepharitis);
- plaque along the edge of the eyelid, thickening of the eyelid;
- sticky eyelashes, eyelash loss;
- in advanced cases - conjunctivitis, decreased vision;
- rough, scaly patches on the skin;
- redness around the eyes;
- burning;
- manifestations of rosacea, dermatitis.
Indications for testing for demodicosis:
- redness of the eyelids, itching, burning in the area of the eyelids, brow ridges;
- with frequent styes;
- for chronic inflammation, facial skin diseases;
- for recurrent rosacea, acne;
- to control therapy.
The disease develops quickly and suddenly. There is a burning sensation and heat. The skin in the affected area becomes like papyrus paper and acquires a grayish tint. If the eyes are affected, hyperkeratosis of the ciliary margin is noted, and there is a sensation of foreign bodies in the eyes. If the disease is not treated or is treated ineffectively, the skin thickens, “tightens”, loses elasticity, softness, and becomes covered with serous, bloody-purulent crusts. Often in this case, D. is accompanied by a secondary pyococcal infection, in which large pustules and microabscesses appear, which, in turn, can lead to facial disfigurement.
If the scalp is affected, itching occurs, hair loss increases, sometimes multiple times, and dandruff comes off in large flakes.
Preparing for the study:
- if a scraping is used to detect a tick, the skin should not be wetted or lubricated with cream for 3 days or 24 hours (depending on the laboratory) before collecting the biomaterial;
- do not use decorative cosmetics for 24 hours;
- the day before the analysis, do not use detergents with a high alkali content.
How is the analysis carried out?
Biomaterial for testing for the presence of subcutaneous mites is taken from the area that the parasite usually affects - from the skin of the face, eyelids, eyebrows.
Conducting research
The selection of biomaterial can be carried out in the following ways:
- scraping the skin using a scalpel (you can also use the contents of acne, which is obtained using a special device, to analyze for demodicosis);
- eyelash test - 3-4 eyelashes are taken from the upper and lower eyelids of each eye.
The procedure is completely painless; in rare cases, the patient experiences slight discomfort. The resulting material is placed in an alkaline or glycerin solution and examined under a microscope.
Since the likelihood of detecting ticks in the evening is much higher, you can take a Demodex test using independently selected biomaterial. To do this, in the evening before going to bed, apply a piece of special transparent tape to the affected area. In the morning, the tape is removed and placed between two glass slides. In this form, the material is sent to the laboratory.
Also, to establish the possible cause of the appearance of demodicosis on the face, as well as to identify concomitant pathologies, it is recommended to take a general blood test.
Indications for examination
Analysis for demodex must be carried out if there is:
The doctor's or patient's assumption of infection.- Clinical manifestations in the form of:
- affected ciliary margin;
- redness and inflammation;
- gluing eyelashes;
- severe scabies at the affected area;
- heaviness in the eyes;
- eyelash loss, which usually falls out without a root;
- the appearance of plaque or white scales on the eyelashes.
The danger is not the tick itself, but the products of its vital activity; it does not live long (up to 18 days in the larval stage and 5 days as an adult). When the tick dies, it begins to disintegrate, releasing toxins that subsequently lead to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms.
Decoding the results
The test result for demodicosis is considered positive if eggs, larvae or adult mites of the genus Demodex were found in the biomaterial being tested. If only empty shells are detected, re-analysis is necessary.
The number of parasites detected also matters. If 5 or more adult mites are found on a skin area of 1 cm2, the diagnosis is confirmed. A smaller number is considered a conditionally negative result, which requires a repeat study after some time.
It is important not only to verify the presence of parasites, but also to identify the species. Demodicosis is caused by 2 types of mites - Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis. The first usually causes ciliary demodicosis, and also settles in the follicles of the eyebrows and hair. The second mainly lives in the sebaceous glands, provoking the development of the skin form of the disease. Determining the type of tick helps in the future to select the most effective treatment regimen.
The result of a test for demodicosis in a private laboratory can be obtained within an hour, in a public medical institution the result is given within 24 hours.
How does the procedure work?
Diagnosis of demodicosis consists of detecting a parasitic organism in a scraping from an area of the affected epithelium, secretion of hair follicles from hair, or examination of eyelashes. The analysis does not cause pain or discomfort to the patient. Results can be obtained within 3 days; in some clinics, the doctor conducts them during the patient’s appointment.
Eyelash analysis
Eyelash analysis is one of the leading methods for identifying the parasite. You will need to pull out 8 hairs from each eye with tweezers, 4 from the lower and upper eyelids. The material under study is placed on a glass plate, an alkali solution or a glycerin composition with saline solution (1 ml and 9 ml, respectively) is added to it, after which the eyelashes are examined under a microscope.
Scraping
A scraping for demodicosis is taken when the inflammatory process covers areas of the skin and head. The biomaterial is removed from the affected surface of the epithelium. If there are no obvious symptoms, tissue is collected randomly from several places on the skin:
- heads;
- ears;
- backs;
- breasts;
- groin;
- hips
The dermatologist's tool is a special scalpel, with which he carefully removes part of the patient's epidermis. The purulent contents of the inflamed follicle are also collected with a spoon. To carry out the test, a 10% alkali solution is required, and the skin tissue is also examined under a microscope.
A negative analysis means that not only mites, but also no traces of their presence or egg shells were found. A positive verdict is given if the mites themselves, their eggs and membranes are found. If only empty shells are identified, a repeat test is scheduled.
If the test result is positive, it is important to determine the type of parasite; the duration of treatment and therapeutic measures will depend on this. Long types of Demodex folliculorum require less duration of treatment, but if a short variety is detected, the recovery process will take longer.
Skin scraping is removed with a special scalpel