The inflammatory process on the skin, especially on the face, is a great stress for the body. Various pimples and pustules bring a lot of inconvenience to a person. But their reasons can be completely different. Some are less dangerous, others can lead to serious consequences. Accordingly, they all require a different treatment approach. Let's look at how to distinguish a boil from a pimple by location, appearance, pain, ripening time and other manifestations, and try to understand the reasons for their appearance.
How to distinguish a pimple from a boil
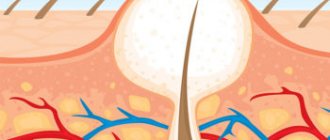
During the first stage of these two developing processes, the skin becomes red and sore. If the cause of a pimple is a blockage of the sebaceous duct, then this formation will be called a boil or furuncle. It is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle and develops when staphylococcus gets into the wound.
Most often, boils occur under the influence of such factors:
- excessive sweating,
- disordered diet,
- deterioration of metabolic processes,
- decrease in the body's defenses,
- failure to comply with hygiene rules,
- skin wounds,
- wearing underwear made of synthetic fabrics,
- hypothermia,
- squeezing out a boil with dirty hands.
Differences between a boil and a pimple
Usually pimples do not hurt and look smaller in size than boils. They do not always become inflamed and may be white. Their inflammatory appearance is characterized by the formation of small red bumps with a pustular formation on the surface.
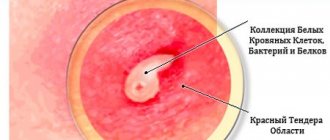
At the initial stage of boil formation, a small red cone with a white abscess in the center appears. Associated symptoms include swelling of the surrounding tissues. After a few days, the size of the boil becomes larger, which entails the beginning of the process of suppuration, and after two weeks it breaks through.
If boils form throughout the body, this indicates the presence of Staphylococcus aureus. This disease is called furunculosis.
Differences by location
Acne most often appears only on the face, less often on the chest, back or shoulder. Such formations are not hazardous to health.
Boils pose a danger to the body as a whole. The main places where boils appear:
- face,
- back of the neck
- hips,
- back,
- groin area,
- gluteal region.
Furuncle or pimple?
Furuncle or pimple?
A strange formation appeared on the tip of my nose, like a large pimple. It hurts a lot when I touch it. I heard that such pimples are called boils and they definitely need to be removed. Is it so?
T.S. GLEBOVA, Nizhny Novgorod.
Otorhinolaryngologist, doctor of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences Petr Aleksandrovich KOCHETKOV (Moscow) explains.
— As you know, there are hairs on human skin. Each hair has a hair follicle - a follicle. Small hairs grow in people's noses, protecting the sinuses from dust, cold and other irritants.
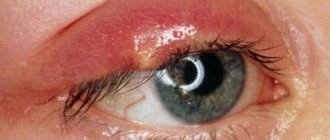
A furuncle (an inflammatory process of the skin of the nose) occurs due to the penetration of infection into the hair follicle. When bacteria multiply, a purulent focus is formed, which, increasing, rises above the surface of the skin - this is how a boil appears. It can form both in the vestibule of the nose and on its back or wings.
The onset of the disease is acute . There is slight discomfort in the area of the vestibule of the nose, which gradually increases and turns into pain. Pain is often absent at rest and appears when touching the nose, sharp inhalation or exhalation. Upon visual examination, you can notice swelling in the vestibule of the nose, the skin acquires a reddish tint (inflammatory hyperemia).
This condition lasts from several hours to 2-3 days, after which an area of pus breakthrough becomes noticeable at the top of the pimple. However, with boils, purulent discharge can break out not only outside, but also into the tissue. In this case, swelling and soreness of the cheek, upper lip and even eyelids appear. The listed symptoms are an absolute indication for an autopsy of the boil in a specialized ENT office.
There can be many reasons for the development of the disease . The main ones are the following:
- introduction of infection into soft tissues by contact - through dirty hands, hygiene items, poor-quality water;
- the presence of chronic foci of infection, such as adenoids, adenoiditis, sinusitis;
— decrease in the body’s immune forces (immunodeficiency states lead to a reduction in the activity of protective substances on the surface of the skin);
— parasitosis (giardiasis, enterobiasis, opisthorchiasis cause allergies and reduce immunity).
Why are boils dangerous? It would seem that ordinary acne, which can periodically appear on different parts of the skin, should not cause concern. Squeezed out - and order. However, not all so simple.
Firstly, we must not forget that a boil is a purulent-inflammatory process in the soft tissues of the head.
Secondly, there is a peculiarity of the blood supply to soft tissues. The fact is that in the human body, blood from the entire body is directed through the veins to the heart. The blood supply in the head proceeds according to a different pattern: here the blood rushes into the cavity of the skull. This means that an infection in the tissues of the facial skin can travel through the veins to the brain.
What to do if you find a boil? First of all, do not try to open it yourself. The best option is to consult an ENT doctor.
Opening a boil is usually performed under local anesthesia and is painless for the patient. In young children, it is advisable to perform a mini-operation under general anesthesia, since after it it is necessary to do dressings for several days. If the child negatively perceives the autopsy procedure itself, then it will be more difficult to persuade him to bandage it.
The purpose of treating a boil is to drain the pus and ensure constant drainage from the wound. The simplest treatment is a 10% hypertonic sodium chloride solution, a bandage with which is applied to the area of the boil after opening.
Pimple development and removal
Around the formed core of a simple formation, an area of inflammation is noticeable, in place of which a white spot forms. It is painless upon palpation.
You can open such a pimple yourself, following the rules of hygiene. A small amount of pus and blood may come out.
The most favorable time for its removal is the maturation and formation of the rod. First, the pimple needs to be treated with an antiseptic, then pierced with a sterilized needle and after this manipulation, lubricate the damaged area with hydrogen peroxide.
How to distinguish a boil from a pimple by appearance
Pimples and boils can have a fairly similar appearance, especially if the inflammation is just beginning to form. Both pimples, boils, and boils can have the same red and raised appearance at the beginning of their formation. Over time, such inflammations can become much larger than the pimples. Boils can even unite and form one large carbuncle shape, which is a group of boils that connect and form a group of such large pimples. Typically, the difference between a boil and a pimple also lies in the fact that the former is much more painful when contacting it, unlike a regular pimple.
Development of boils
The main reason for the formation of a boil is a staphylococcal infection that has entered the body.
The follicle fills with pus due to the activation of the immune system and the direction of leukocytes to the affected area, and after 10-14 days it can rupture. During this time, the person experiences pain and discomfort.
If the infection is carried through the bloodstream, it can cause the formation of furunculosis.
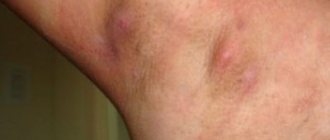
Then boils appear throughout the body. Most often, these formations form on the chin, nose, neck and back. Sometimes the lesion affects the armpits, groin, butt and thighs.
Acne pimples, boil - boil
Definition:
Acne is a skin condition that occurs due to excessive oil clogging in the pores of the skin and is characterized by the presence of pimples, blackheads, blackheads and whiteheads.
A boil is a skin outbreak in the form of a swollen bump caused by an infected hair follicle.
Most common areas of appearance on the skin
Face, neck, chest, back, shoulders and arms.
Face, neck, armpits, chest, groin and buttocks.
Develops in
Typically in teenagers.
Any age.
Affect
Skin surface.
Deeper areas of the skin.
Bacteria causing inflammation
Pacnes.
Staphylococcus.
Treatment
Includes keratolytics (sulfur-based treatments), antibiotics and antibacterials (benzoyl peroxide), Azelaic acid preparation, topical antiseptic washes, chemical treatments, retinoids, etc.
They may go away on their own when they first appear, but warm compresses on boils, surgery for deep or large boils, over-the-counter medications such as Terrasil, bacitracin for soft boils can also help in getting rid of them.
Symptoms
Pus filled under skin tissue about 5mm in diameter - very painful, papules (small red bumps), pustules, redness around skin rashes, skin splinters.
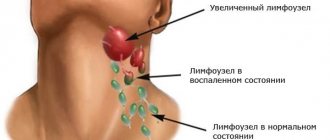
The onset of a severe, red, painful swelling that is usually less than 4 cm. Later, a swelling occurs that becomes softer, larger and painful. Then a pocket of pus forms at the top of the boil, an increased temperature appears, and nearby lymph nodes (glands) may become swollen.
How to treat inflammation
When a boil or boil develops, it is recommended to treat it with an antiseptic (iodine) and apply ichthyol ointment to it. It is better to use alcohol or chlorhexidine to treat the skin around it.
If a common pimple is inflamed, then Levomekol is used to treat it. Compared to ointment for boils, this remedy will not clog the sebaceous duct and will not aggravate the situation.
Attention! Doctors do not recommend getting rid of pimples and boils on your own by squeezing, as there is a risk of infection in the wound. In the worst situation, even the most harmless skin defect can increase in size and subsequently spread throughout the body.
Possible reasons for the formation of boils
This not very pleasant problem does not depend on the age category of people. Inflammation can appear in both an adult and a child. Boils themselves do not harm health. The bacteria that provoke them is dangerous - staphylococcus or streptococcus. Therefore, purulent acne cannot be ignored and it is important to start treatment in a timely manner.
Among the reasons that provoke purulent rashes are the following:
- Various microorganisms enter the hair follicle and a pimple appears. Most often, such problems occur immediately after the end of the winter months. It is well known that when spring comes, the human body weakens. He lacks vitamins and his immune system fails. A fragile body is not able to cope with bacteria. The consequence of this is the appearance of a rash on the skin.
- The occurrence of pimples is especially affected by metabolic disorders;
- If a person has oily skin, he cannot avoid inflammation.
- Acne often appears in those who almost never rest, are subject to various kinds of stress and anxiety, and are in constant nervous tension.
- Another common cause of boils is small abrasions and wounds.
- Acne also occurs due to overheating or hypothermia of the body.
There are many reasons that provoke skin reactions. It is impossible to insure against everyone, therefore the main preventive measures are reasonable hygiene and increasing immunity.
Common features and differences between a boil and a regular pimple
It is easy to distinguish a boil from a pimple; the main thing is to know the main signs of the disease. Similar features and differences between purulent processes are presented in the table.
| Type of education | Furuncle | Acne |
| Localization | Hair follicle. | Hair follicle, sebaceous gland. |
| Formation of pus | Present. | Present. |
| Kernel | Present. | Absent. |
| Stages of maturation | Similar. | Acne occurs more rapidly. |
| Pathogen | Staphylococcus aureus. | Propionibacterium acnes. |
| Inflammation | Always observed with a boil. | Whiteheads and millet acne can occur without inflammation. |
| Pain when squeezing | Significant. | Slight, closer to discomfort. |
| Hereditary factor | Boils are absent. | Present. |
| Cold factor | Present. | Absent. |
| Hormonal dysfunction | It is a provoking factor. | Main role. |
| Treatment | Spontaneous autopsy is possible, but more often surgical. | Conservative. The main focus is hormonal correction and hygiene. |
| Age factor | The occurrence of a boil does not depend. | Mainly in adolescence. |
| Complications | High risk. | Minor risk. |
| Diagnostics | In case of single and rare cases, no research is carried out. | In case of multiple lesions, blood tests and bacterial cultures are indicated. |
It is easy to distinguish a boil from a pimple by external signs; they pose a health hazard and have ulcers. If the process is widespread or there are frequent relapses of the disease, you need to consult a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Signs of a boil
A staphylococcal infection in combination with a pathological factor, exogenous or endogenous (external or internal origin), leads to the development of a boil and the appearance of its symptoms. When the disease manifests itself in the form of multiple foci of inflammation, a type of pyoderma called furunculosis develops.
A tendency to inflammatory purulent lesions of the hair follicle is observed with:
- heavy sweating;
- general fatigue of the body;
- impaired protective function of the skin, the appearance of severe symptoms;
- minor skin damage (abrasions, scratches);
- metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, malnutrition, vitamin deficiency);
- contact with secretions from an infectious disease;
- failure to comply with hygiene standards;
- weakness of the immune system;
- hormonal imbalance.
The main symptom of a boil is the appearance of inflammation in the form of a red lump with a hair follicle in the center. The boil has signs such as pain, tingling, and swelling of nearby tissues.
Nature of pain and itching
A patient suffering from furunculosis complains of symptoms: pain and itching in the area of inflammation. The pain is pulsating (twitching) in nature. When pressing on the boil, the manifestations intensify and can radiate (the pain radiates to nearby tissues).
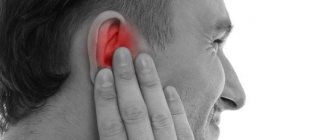
The severity of painful manifestations and swelling with a boil is determined by the stage of the disease. The size of the focus of inflammation and its location also matter. The most painful manifestations of purulent formations formed on the mucous membrane of the nasal passages or auditory canals, in the area of the external genitalia. The symptom intensifies as the abscess matures. In rare cases, a boil may grow without being very painful.
Skin appearance
More often, abscesses form in the nose, cheeks, ears, and neck. The skin on the face is abundantly supplied with sebaceous glands, through which pathogenic bacteria and viruses penetrate the body. Furunculosis affects the shoulders, elbows and armpits, thighs, and buttocks. The most unpleasant manifestations of boils forming in intimate places and the groin area. It is characterized by severe pain.
Need advice from an experienced doctor? Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Small boils that appear on the cheeks or forehead resemble acne. When squeezing them out, severe pain is felt. This is a distinctive symptom indicating that the purulent formation is a boil and not a large pimple.
At the initial stage, a compaction appears on the skin. The manifestation of the pathological process boils down to the fact that the skin at the site of inflammation acquires a bright red tint. This is the first symptom of the appearance of pyoderma. The boil looks like a small reddish bump in the first days.
As the boil abscesses, the appearance of the affected area will worsen and the symptoms will become more severe.
The second stage is characterized by the appearance of a necrotic core in the center of the compaction. Manifestations of a boil are complemented by severe swelling of nearby tissues. The skin at the site of inflammation tightens and becomes bluish. The pain intensifies.
At the third stage, the abscess heals after it is opened and the purulent contents are released. The symptom is the formation of a crater at the site of inflammation. It will gradually become covered with granulation tissue. After 4 days, a scar will remain from the boil. At first, the manifestations of scarring are reddish-blue in color. Over time, its manifestations will become less noticeable. The scar will lighten.
Temperature increase
The temperature during a boil can be raised to 38°C. This symptom is provoked by an inflammatory process that affects the hair follicle and nearby tissues. The manifestations are complemented by a feeling of general weakness and weakness.
The symptom of a boil in the form of elevated temperature often occurs against a background of weakened immunity, hypovitaminosis, and anemia. The manifestation indicates the need for antibiotic therapy and surgical intervention.
If a purulent formation gives a temperature above +38.5 ° C and the general condition worsens, you must seek medical help. There is a risk of infection entering the bloodstream, which can lead to bacteremia and even sepsis. Symptoms are complemented by a feeling of chills and fever.
What is recurrent furunculosis
Within a year, boils reappear in about 10% of people who have suffered furunculosis or soft tissue abscess. Recurrent furunculosis is said to occur when boils appear at least three times within 12 months. Domestic sources consider furunculosis to be recurrent (in a mild form), if relapses occur once a year, without intoxication, possibly with enlargement of local lymph nodes.
The disease can be severe
With severe furunculosis, multiple foci of boils appear in different areas of the skin. General intoxication, weakness, headache, fever, and sweating develop. A violent inflammatory reaction is characteristic of a moderately severe disease: boils reach large sizes, and inflammation of the lymph nodes develops. After furunculosis, scars may remain on the skin.
How to eliminate boils?
Since it is quite simple to distinguish a pimple from a boil by the extent of the process, anyone can determine the degree of danger of an abscess developing under the skin. When examining the affected area of the skin, the presence of severe redness and swelling is immediately revealed. The skin where the boil forms becomes very thick to the touch after a few days. When such a formation appears, it is best to immediately consult a doctor, since in some cases the purulent contents will not be able to find a way out, and the necessary measure is prompt opening of the abscess. To prevent the development of various complications and restore the health of the skin, the following drugs are prescribed;
- antibiotics;
- multivitamin complexes;
- immunomodulators.
After opening a large boil, compresses are also required to help heal the existing wound. In cases where the cavity of the boil and the volume of purulent contents is small, in order to eliminate the formation, the affected area is first treated with an antiseptic, for example salicylic alcohol or furacilin. Next, apply a compress with Ichthyol ointment. This ointment promotes the formation and breakthrough of the boil shaft.
In order to remove all the pus from the existing cavity, compresses are applied with Vishnevsky ointment, which helps draw out the pus from the wound. Bandages need to be changed at least 2 times a day. Throughout the entire period of treatment, a person suffering from furunculosis must take broad-spectrum antibiotics. The course of antibiotic treatment is prescribed by a doctor individually and can last from 7 to 14 days. The most commonly used antibiotics include the following:
- Tetracycline.
- Levomycetin.
- Erythromycin.
- Minocycline.
Before applying a new compress, it is necessary to thoroughly wash off the remaining ointment and purulent contents with a soap solution and treat with antiseptic agents. It is necessary to apply compresses with Vishnevsky ointment until the color of the skin is normalized and the healing of the existing wound begins. After the boil begins to heal, it is necessary to continue treating the skin with antiseptics and undergo a course of antibiotic treatment.
Treatment methods
Localization of a boil on the face is already grounds for hospitalization of the patient, so treatment of furunculosis should be carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist, surgeon or therapist.
Sometimes the therapist gives a referral for a consultation with a dentist, especially in severe cases of furunculosis, because if treated incorrectly, the facial nerves can be affected.
The patient is prescribed bed rest; if the boil is located on the ears or neck, then friction of the abscess on clothing should be avoided. It is worth avoiding fatty, fried and spicy foods during treatment, and eliminating alcohol.
Local antiseptic treatment
For processing you can use:
- 70% alcohol;
- salicylic alcohol;
- hydrogen peroxide (3%);
- furatsilin solution.
It is not recommended to treat boils with iodine, since its action is directed not to the upper layers of the skin, but inside - this can lead to the reverse development of the disease.
When wiping the skin, do not rub the boil, disinfect the inflammation site several times a day, change pillowcases more often and do not touch the boil with your hands.
Physiotherapy
These procedures are painless; medical practice has shown that after several procedures the pain disappears and the inflammatory process stops increasing.
Physiotherapy can be prescribed at all stages of furunculosis. To increase the body's resistance, ozone therapy is prescribed - saturation of tissue with oxygen to stimulate the immune and barrier properties of the skin.
Antibiotics for boils on the face
Antibiotics are also prescribed to prevent furunculosis from becoming chronic and reappearing. The drug is selected individually depending on the patient’s condition and clinical picture of the disease.
The most commonly prescribed drugs are Cephalexin, Amoxiclav, and Fuzidin sodium. If the boil occurs against the background of other diseases, and the general condition of the body is depleted, antibiotics are prescribed in the form of intramuscular injections.
Compresses with anti-inflammatory drugs and ointments with antibiotic components are applied locally: Tetracycline ointment, Erythromycin, Bactroban, Baneocin.
Apply a thin layer of ointment to a cotton pad and apply it to the boil twice a day. After opening the abscess, you can also apply compresses, but to the area around the boil.
Surgery
After removing the purulent-necrotic masses, the wound is washed and a bandage with an antibiotic is applied.
Often the doctor simply pierces the boil in several places, so there is no scar left after such a procedure.
It is recommended to talk as little as possible and eat only soft food.
For prevention and treatment, you can use Galavit, Estifan, Echinacea, Arbidol.
Autohemotherapy
Autohemotherapy is a common method of treating inflammatory processes, in which the patient is injected subcutaneously or intramuscularly with blood taken from his own vein.
When administered again, the blood finds the source of the disease and destroys it, as a result the procedure stimulates the immune system and improves metabolic processes.
Absorbable ointments
There are many brands of drugs in the pharmacy; almost all absorbable gels are based on heparin and silicone - agents that activate blood flow.
The most popular remedies for scars: Strataderm, Mederma, Contratubeks, Heparin ointment, Bodyaga.
Advice: after opening the boil (not earlier!), bandages with drugs that draw out pus are prescribed: Levosin, Ichthyol ointment, Vishnevsky ointment. Compresses with such ointments will also speed up healing.
Why do boils recur?
Many scientists call the tendency of family members to furunculosis to be the most significant risk factor for both “simple” boils and the recurrent course of the disease. In recurring furunculosis, colonization of the nose or other parts of the body by staphylococcus plays an important role (this can be the inguinal folds, ears, folds under the mammary glands).
Risk factors for recurrent furunculosis include:
- anemia;
- use of antibiotics the day before;
- diabetes;
- hospitalization;
- multiple lesions on the skin;
- concomitant skin diseases (wounds, atopic dermatitis);
- poor personal hygiene skills;
- obesity;
- diseases of the blood system and hematopoietic organs;
- suppressed immunity (but scientists believe this is rarely the main cause).
In many cases of furunculosis, doctors cannot detect any of these risk factors; anyone can develop the disease. Scientists emphasize that many risk factors for relapse are modifiable, that is, they can be influenced in order to prevent the disease.