It is possible to defeat parasites!
If you are reading these lines, it means that you still think that it is impossible to quickly remove parasites. Have you already tried various anti-parasitic agents that are sold in pharmacies, followed the recommendations of your grandmothers and are completely desperate?
Are parasites still living in your body and continuing to multiply, killing you from the inside? Or do you want to undergo a preventive course of treatment and protect yourself and your family? Then you will be interested to know what the famous TV presenter Elena Malysheva recommends, and what modern means she suggests using...
Read article »
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is established on the basis of anamnesis, clinical picture, and laboratory test results. When treating elderly patients, the possible interaction of systemic antimycotic drugs with chronically taken medications should be taken into account.
Before making a diagnosis, it is not recommended to treat the affected areas of the skin with antiseptic solutions, as this can blur the clinical picture and lead to a diagnostic error.
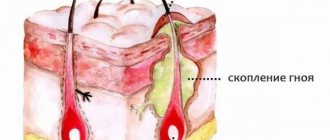
During microscopy of biological material taken from lesions (epidermal scales, hair, horny masses from the nail bed, etc.), mycelium, hyphae or spores of the pathogen are detected. Sowing scrapings from the affected area on nutrient media (universal and selective) allows you to identify the infectious agent and determine its sensitivity to antifungal drugs. Laboratory determination of antibodies to the pathogen in the patient's blood may be required.
An informative method for diagnosing some dermatomycosis is to examine the skin under a Wood's lamp - a greenish-blue, reddish, brown or golden-yellow glow of scales in the affected areas is revealed.
Before prescribing systemic therapy for dermatomycosis, especially for elderly patients, a general blood and urine test, a biochemical blood test (liver transaminases, bilirubin, creatinine), as well as an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs and kidneys, and electrocardiography are prescribed. This allows us to identify patients for whom systemic therapy is contraindicated.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with psoriasis, eczema, neurodermatitis, vitiligo, seborrhea, syphilitic leukoderma.
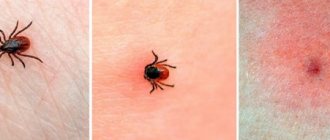
Where do they come from?
Hypodermic mites are common inhabitants of human skin. Their small numbers are unnoticeable because the immune system keeps the natural mite population in check. That is why treatment of subcutaneous mites on the face must be carried out against the background of drugs that support the weakened immunity of the patient or relieve the stressful state of the body.
Immunity
main reasons for the appearance of subcutaneous mites are a violation of the immune or hormonal status of the body, due to which their rapid reproduction occurs. It most often affects teenagers, pregnant women, and people with a weakened immune response (for example, those who have been treated with immunosuppressants). There are also seasonal variations in incidence - in winter and spring, when human immunity weakens, demodicosis appears much more often.
Symptoms of human subcutaneous mites can also occur in the presence of chronic diseases, prolonged infections, immunodeficiency states, various intoxications and poor nutrition.
Demodexes are necessarily transmitted from mother to newborn child. In cases of generalized infection, intrauterine infection may occur.
Prevention of recurrence
Those who have decided on how to cure subcutaneous mites on the face are unlikely to want to encounter this unpleasant insect again. To prevent its reappearance, you should follow a diet, filling your diet with useful minerals and trace elements and avoiding high-calorie, spicy and fatty foods, regularly using preventive cosmetics or homemade mixtures against ticks, changing them so that the parasites do not have time to adapt and get used to it.
It is useful to get pillows with synthetic filling; you should not overcool your face or use cosmetics. It is also useful to regularly wash your face with tar soap or special products containing acaricides. You should unlearn the habit of touching your face with your hands.
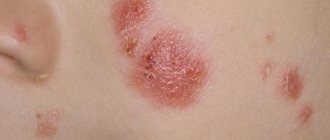
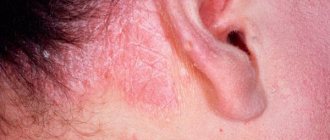
Demodectic mange on the face - symptoms
the edges of the affected areas are clearly visible; swelling of the wings and back of the nose; localization of lumpy and purulent manifestations on the forehead, cheeks and nose.
All other symptoms of the disease are also present.
Demodectic mange of the head is also common. The following factors can be considered its manifestations:
itching of the scalp; small ulcers and redness of the skin; formation of white scales; hair loss; hair loss.
Sometimes demodicosis spreads to the eyes. Demodicosis of the eyelids is the most severe form of the disease. Its symptoms include the following:
hyperemia (redness) of the edges of the eyelids; inflammation of the eyelids; swelling of the eyelids; the appearance of white-yellow foamy discharge from the eyes; white scales at the base of the cilia; itching, feeling of a foreign object in the eyes; eye sensitivity to light; severe eyelash loss; the occurrence of blepharitis; conjunctivitis and other diseases; frequent occurrence of styes.
Treatment of demodicosis: drugs
Treatment of demodicosis is carried out with the help of such drugs belonging to the group of antibiotics, antihistamines, and antiparasitic (acaricidal) agents.
Antibiotics include tetracycline ointment, clindovit, demalan, and so on.
Acaricidal agents are benzyl benzoate and its analogues.
As for antihistamines, you can use any second or third generation drugs (they do not cause drowsiness).
Sulfur ointment, ichthyol ointment, and permethrin ointment are also used to treat demodicosis.
You can often hear reviews about good results when using metronidazole (in tablets or in the form of gels and ointments). But this fact has not been proven.
It would be best if you consult with an experienced doctor about the use of medications (tablets, ointments, gels, etc.).
Treatment of demodicosis
How to recover from this disease quickly and painlessly? To begin with, it should be understood that therapy should be comprehensive and include the use of medications, folk remedies, a psychological attitude toward a good result, and so on.
The first step in the treatment of this disease should be the complete abolition of any cosmetic products and increased personal hygiene. Also, during treatment it is necessary to follow a special diet. The speed of recovery from demodicosis depends on how correctly the medications were selected for you and on how you follow the doctor’s instructions.
How to get rid of subcutaneous mites
Treatment of demodicosis is a complex undertaking. The victim must not only treat the affected areas externally, but also take antiparasitic agents internally. To obtain a long-term effect, it is necessary to exclude factors that provoke the development of the disease.
It is impossible to say clearly how long demodicosis can be treated. It all depends on the treatment used and the degree of neglect of the disease. At the initial stage, improvement may occur within a week, at the last stage - only after several months.
There are several main areas of treatment for subcutaneous mites.
Drug treatment
The most effective remedies for subcutaneous mites include::
- pills. Metrogyl and Trichopolum tablets are considered effective broad-spectrum antimicrobial drugs. To calm irritation and relieve redness, doctors prescribe antihistamines Suprastin, Zyrtec, Zodak. As additional therapy, agents are prescribed to strengthen the immune system.
- Ointments, gels, creams. Sulfur ointment has a pronounced therapeutic effect. It stimulates the regeneration of the skin and helps eliminate subcutaneous parasites, but has a pungent, unpleasant odor. Benzyl benzoate and permethrin ointment are effective against subcutaneous mites. The active substance of the drugs is able to penetrate the chitinous membrane of the parasite, destroying it.
Of course, before treating demodex with medications, you should consult a doctor to determine the optimal dosage and make sure there are no contraindications.
Antiparasitic drugs
In addition to the listed ointments and creams, a number of antiparasitic and medicinal drugs are used as an adjuvant for the treatment of subcutaneous demodex mites:
- Aerosol "Spregal". Spray on the body before bed, apply to the face using a cotton pad. The main active ingredient has a detrimental effect on both subcutaneous mites and laid eggs.
- Cream-gel "Dexomed Phyto". It has an antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, cleansing effect, it refreshes and soothes damaged skin.
- "Demazol". Accelerates skin regeneration, reduces inflammation caused by demodex mites.
- "Chlorhexidine." Inexpensive antiseptic drug with a wide spectrum of action.
- "Azogel". Restores the functioning of the sebaceous glands due to the azelaic acid included in its composition. It has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
- "Crotamiton." Used after a shower, relieves irritation, destroys parasites.
It should be noted that the listed drugs are used as part of complex therapy. If they are used as an independent means of treatment, the effect produced will be short-lived.
Antibiotics
These drugs are used as adjuvant therapy when ulcers appear. The demodex mite will not die from the effects of antibiotics, but the development of a secondary infection will be prevented. Thus, the process of healing and tissue regeneration will accelerate.
Antibiotics have quite a few disadvantages. They contribute to a decrease in immunity, disruption of the kidneys and liver, destroy beneficial microflora in the intestines, and provoke allergies.
Therefore, antibiotics are used only in advanced cases, when effective treatment of demodicosis is of paramount importance and the benefit brought by the medicine exceeds the harm caused.
Vascular strengthening agents
Such remedies cannot cure demodicosis. The purpose of the drugs is to strengthen the walls of the capillaries so that they cannot be damaged by subcutaneous mites. A treatment regimen for demodicosis using vascular strengthening agents should be developed by a doctor.
As additional support measures, you can use:
- ascorbic acid;
- fat-soluble vitamin E, which increases the strength of blood vessel walls;
- vitamin P, which reduces capillary fragility.
The use of vascular strengthening agents will remove redness of the skin.
Application of medicinal cosmetics
The use of professional cosmetics helps eliminate external signs of the disease. The main task of such preparations is to moisturize the skin, reduce sebum production without drying the surface, and relieve irritation. Also, cosmetics against demodicosis have a sunscreen effect.
Before getting rid of subcutaneous mites using medications, you can undergo a number of cosmetic procedures.
Deep peeling
To treat the skin, trichloroacetic acid is used, which dissolves the upper keratinized layer of the epidermis. Within a week, the scales with dead parasites and their metabolic products peel off and are replaced by new, healthy cells.
Demodicosis in humans can go away after deep peeling in the initial stages of the disease. If the parasite has penetrated into the lower layers of the skin, into which the acid does not penetrate, the procedure must be combined with drug treatment (only after consultation with your doctor).
Cryomassage
You can get rid of demodex in the upper layers of the skin using low-temperature treatment. During the procedure, the specialist uses a roller soaked in liquid nitrogen. As a result, the top layer of skin freezes and dies. The damaged epidermis peels off and a new layer is formed to replace it.
Laser removal
The procedure involves treating the body surface with directed light rays. Before being cured of demodicosis using laser treatment, you must undergo thorough preparation: stop using cosmetics for a week, exclude fatty foods, as well as foods that can cause allergies.
The course of maintenance therapy may include 5–15 sessions and be repeated 2–3 times a year, depending on the severity of the disease .
Laser therapy not only gets rid of acne, it relieves swelling, increases blood circulation, and has an anti-inflammatory and decongestant effect.