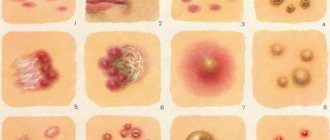
Intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland is a benign neoplasm that is located in the ducts of the mammary gland. A tumor occurs due to the proliferation of epithelial cells.
There are several reasons for this process, but they are all associated with changes in hormonal balance. The formation itself does not pose a threat to the woman’s body, but there is a possibility that it will develop into a malignant growth. For this reason, the disease cannot be ignored. It is important to identify the pathology in time and begin treatment, which can only be prescribed by a doctor after appropriate research.
What is pathology?
Intraductal papilloma has similar features to a cyst. In the absence of qualified treatment, tissue cell death occurs around the formation and bleeding occurs.
Intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland has very thin walls. For this reason, the slightest mechanical impact leads to injury. As a result, the woman begins to ooze discharge from her breast nipples. They are of a moderate nature. Discharge from the nipples of the breast is ichor, and if the mechanical impact was too strong, then blood may begin to ooze from the nipples of the breast, but in small quantities. There is no threat of hemorrhage.
Intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland, photos of which are posted by doctors on the Internet, has different sizes. Dimensions can be only a few millimeters, or they can reach several centimeters.
The neoplasm does not cause deformation of the shape of a woman’s breasts. For this reason, it is difficult to detect, especially if the tumor is small.
Intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland occurs in patients, regardless of social status and number of years lived.
Cases have been recorded in which pathology developed in a girl entering puberty and in a woman experiencing menopause. However, middle-aged women are most susceptible to the disease. During this period, the risk of developing formations that have a malignant form also increases. In order to diagnose pathology in a timely manner, you should monitor the condition of your body and see a doctor every six months.
Classification
The disease has the following classification:
- Papillary papillomas of the breast . Such formations form and grow in any part of the ducts. There are peripheral and central papillomas. Division occurs at the place of growth of the formation. The latter are located in the area of the areola of the breast, and the former can be located in any part of the ducts.
- Intraductal papillomas of the mammary gland . There are also two types of the disease. The first is solitary papillomas of the mammary gland. They are single formations. They are usually found in the subareolar zone. The second type is multiple mammary papillomas. Localized in the peripheral area of the chest. Multiple formations more often than others develop into tumors that have a malignant form.
Causes
Intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland occurs against the background of hormonal imbalance. An imbalance occurs for the following reasons:
- inflammation of the appendages;
- infectious pathologies of the reproductive system;
- multiple abortions;
- surgical intervention performed on the organs of the reproductive system;
- excess weight;
- unstable emotional background;
- puberty;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- menopause;
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- period of bearing a baby;
- lactation;
- mastopathy, which is diffuse and nodular in nature;
- use of oral contraceptives;
- genetic predisposition;
- harmful addictions.
Causes and symptoms
Etiological and risk factors for the development and stimulation of papilloma in the mammary gland are divided into the following categories:
- hormonal imbalance in the body against the background of pathology of the endocrine glands or external influences: thyroid pathology, polycystic ovary syndrome, autoimmune aggression, diabetes mellitus, history of abortions, miscarriages, obesity;
- weakened immunity during pregnancy;
- prolonged depression, stress and emotional outburst contribute to the appearance of growths (juvenile);
- bad habits: alcohol abuse, smoking, drug use;
- long-term fibrocystic changes against the background of nodular or diffuse mastopathy;
- menopause;
- breast surgery;
- heredity.
Symptoms
It is difficult to determine the presence of intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland during external examination. You can understand that a lump has appeared on your own before seeing a doctor. The main symptom is discharge from the nipples. They are sudden in nature and appear on their own or ooze at the moment when mechanical force (pressure) is applied to the chest.
Discharge from the nipple varies in thickness. Their consistency does not indicate the stage of development of the pathology. Shade: pale yellow or white.
Discharge from the nipple comes out both with and without blood. They are usually of a moderate nature. Large blood loss is not typical for the pathology. If the discharge from the nipple is thick and contains admixtures of pus, this indicates the development of an inflammatory process occurring in the ducts.
There are several other symptoms characteristic of intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland:
- pain in the breast area, which appears both at rest and during mechanical action (stroking, pressing);
- swelling of the mammary gland;
- slight redness, the origin of which is puzzling;
- causeless weakness even after a long rest;
- an increase in body temperature, while it may increase slightly, or it may rise by several degrees, until a fever occurs.
If any sign of breast papilloma located inside the ducts occurs, it is recommended to consult a doctor. The sooner the diagnosis is made, the sooner therapy will begin. Timely treatment will help avoid complications and the development of more serious diseases.
What is cystadenopapilloma of the breast?
In medicine, the pathology is also referred to as “papillary cystadenoma” and is included in the section of fibrocystic mastopathy.
This disease is popularly called “breast bleeding” because when you press on the chest, light or dark liquid similar to blood clots can be released from the nipples. In the first stages of development, the disease may not manifest itself in any way and may not bother you in any way. However, over time, as the milk ducts dilate and grow, women experience severe breast pain and may feel cyst-like formations.
Cystic formations during the course of this disease are formed from the epithelial tissue of the excretory ducts of the breast in the papillary region and are easily palpable as formations with a diameter of up to two centimeters.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is performed by a specialist mammologist . It is recommended to contact this doctor for any problems related to the mammary glands.
To make a diagnosis, the doctor needs to examine the mammary glands. The specialist determines the presence of a compaction by the discharge.
Diagnostics is also based on relevant studies:
- A smear of discharge, which allows you to determine the presence or absence of cytology. The analysis shows the presence or absence of atypical cells. If any are detected, a study is ordered to determine the nature of the pathology and exclude the presence of malignant tumors. If no atypical cells are found, but discharge does occur, the specialist will prescribe a repeat analysis to rule out errors.
- Ductography. This is a type of x-ray examination. The bottom line is to scan all the ducts of the mammary gland to detect papillomas and determine their location, the number of tumors and their size.
- Histology. The study shows the presence or absence of dead tissue and cancerous tumors.
- MRI, mammography, ultrasound. Such studies can reveal the presence or absence of other seals.
Etiology of the disease
Before getting rid of papillomas, it is important to determine the cause of their appearance. Hormonal dysfunction is a general term. Experts call the main factors of failure:
- inflammatory processes in the appendages;
- malfunction of one or both ovaries;
- stress or depression;
- obesity of any degree;
- poor metabolism;
- history of miscarriages or abortions;
- tumors of the reproductive system;
- menopause.
During adolescence, when puberty occurs, hormone surges can lead to the formation of ductal papilloma. A similar picture is observed during pregnancy.
Doctors consider women at risk:
- with a genetic predisposition;
- with a diagnosis of fibrocystic mastopathy.
Mastopathy leads to dilation of the ducts, which becomes a suitable environment for the growth of papillary neoplasms. Favorable factors for the development of mammary duct papilloma are smoking and lack of childbirth.
Types of cystadenomas
An annual examination by a doctor is an excellent preventive measure for the development of cystadenoma.
The classification of breast papilloma is based on the characteristics of neoplasms and location:
- Papillary. It grows in ducts, affecting any part of the system. Depending on the location, it can be atypical, peripheral or central.
- Intraductal. It grows in single papillomas or groups. The maximum size can reach 20 mm. The larger the group of formed cystadenomas, the smaller their size. Massive accumulation can be observed in the peripheral zone of the milk ducts. Single papillomas are larger and located closer to the nipple.
Cystadenomas, which provoke the appearance of a malignant tumor, are dangerous. If they are detected, only surgical treatment is prescribed.
Symptoms
Small papillomas at the initial stage are not determined by palpation or visually. The danger is that symptoms do not appear until the tumor in the mammary gland increases to a certain size. A woman may be concerned about:
- Nipple discharge. The color of the discharge varies from clear to green and brown. If blood or pus is present, this indicates inflammation. The amount of discharge can be moderate, scanty or abundant.
- Fever and weakness. Symptoms indicate damage to the neoplasm, which entails the development of an inflammatory process. Visually, you can notice redness and swelling of the area of the skin where the damage occurred. The compaction can be felt and painful sensations occur upon contact.
- The presence of elastic nodes in the nipple area. If you palpate the areola at home, you can feel a new formation. Pressure is accompanied by pain, discomfort and serous-bloody discharge from the nipple.
The longer the inflammation lasts, the denser the intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland becomes. There is swelling around the problem area and purulent discharge. You should not delay your visit to the doctor, so as not to complicate the situation.
Normally, a woman should be examined by a mammologist once a year, and if alarming symptoms are detected, seek medical help.
Diagnostic methods
Characteristic symptoms are not enough to make a correct diagnosis without examination. High-precision hardware techniques allow you to identify intraductal papillomas:
- Mammography. X-rays are used to detect a tumor in any part of the breast. The disadvantages include the pain of the method: additional compression of the chest is performed during photography. It is prescribed to women over the age of 40, since it is difficult to see the milky canal in the dense gland of a young woman. Errors and incorrect results may occur.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound). New growths as small as 5 mm are detected, so the technique is productive at the asymptomatic stage of the disease. The advantage of the examination is its accuracy: the device allows you to clearly see the structure of the tumor. If the cyst has fluid inside, then the papilloma is a dense node. Advantages include simultaneous examination of the lymph nodes around the breast.
- Ductography. The method differs from x-rays by using a contrast agent, which allows you to carefully examine the ducts in the mammary gland from the inside. It is considered the most reliable of all existing studies. A contrast liquid is injected using a special catheter. The resulting x-ray shows the outline of the tumor and its location. The specialist determines the degree of oncogenicity of the tumor from the image. In case of discharge from the nipple, ductography is mandatory.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Using the technique, it is possible to identify neoplasms in the thoracic ducts by assessing their size and shape. Refers to painless and safe methods of examination. Difficulties may arise for people suffering from claustrophobia.
In Moscow, you can do any of the listed diagnostics. Before the examination, you cannot specifically express pathological discharge so as not to distort the results. The doctor may additionally prescribe a cytological examination of a smear of discharge and a blood test for tumor markers of breast cancer.
Therapy
When an intraductal papilloma is detected, treatment most often involves surgical removal if the tumors are multiple. If the tumors are single, then they can disappear on their own without any treatment, but this happens infrequently.
If papillomas are found in the internal ducts of the mammary gland, it is recommended to make an appointment with a surgeon. He will not necessarily prescribe surgery right away. If research results show that the tumors are small in size and there is no inflammatory process, the doctor may prescribe drug therapy for the pathology.
When a pathology is detected in a woman during pregnancy, treatment is carried out only after childbirth. The exception is when the papilloma inside the mammary ducts risks developing into a malignant compaction. In this case, the expectant mother is scheduled for surgery. After this, drug treatment is effective.
At what age can cystadenopapilloma of the breast occur?
Despite the fact that this disease is diagnosed quite rarely, it can develop in women of any age: from puberty to menopause. Papillary cystadenoma is most often observed in nulliparous women and patients who already have breast diseases or inflammatory processes. According to the observations of doctors, 10 percent out of 100, that benign formations of cystadenopapilloma of the mammary gland can turn into malignant diseases.
Read also: How to get rid of calluses on feet?
Surgical intervention
Surgery to remove intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland is prescribed for the vast majority of women. This is the preferred method of treating pathology. The essence of the procedure is surgical removal of the tumor. The operation is performed under local anesthesia if the lump is located in close proximity to the nipple. If it is located deep in the chest, general anesthesia is performed. Not only the tumor is amputated, but also blood clots located in the tissues around the tumor.
Diagnostic methods
Examination of the patient must begin with a medical history. It is important to establish exactly when the first symptoms of the pathology began.
You also need to ask whether there have been cases of breast cancer in the patient’s immediate relatives. All patients with suspected neoplasm should be examined by an experienced mammologist.
He examines and palpates the mammary glands, and also immediately refers you for a mammogram. An additional method at the first stage of diagnosis is a cytological examination of breast discharge.
This test can detect changes in secretions characteristic of cancer or bacterial infection.
In the laboratory, the patient undergoes general and biochemical blood tests. Of particular importance is the determination of the breast cancer tumor marker CA 15-3. This makes it possible to switch off the malignant process without a biopsy with a high degree of probability.
After determining the location of the tumor, an ultrasound examination is prescribed, and then magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Ductography is also highly informative - the study with contrasting of the structure and patency of the thoracic ducts.
Additionally, it allows you to determine the location of papillomas, which provides important information for planning surgical intervention.
Mandatory in case of a doubtful diagnosis is a biopsy of the tumor. Further research allows not only to determine the benignity of the tumor, but also to determine its histological type. The prognosis of the course of the disease for the patient and the choice of possible treatment tactics depend on this.
Treatment tactics for intraductal papilloma After the diagnosis of intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland, as well as the localization of the tumor, patients are offered radical treatment - surgery with the removal of all altered tissues.
Unfortunately, no other method has such performance indicators.
Many patients have a certain fear of possible aesthetic changes in the mammary gland. Therefore, the doctor must explain that for this pathology, organ-preserving surgery is used, in which the surgeon removes only a small part affected by the pathological process.
Before the operation, the surgeon must explain to the patient the planned intervention. The presence of allergies to medications is checked, and a general examination of the functional state of the body is carried out (ECG, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, biochemical blood test, coagulogram, chest x-ray).
Surgical technique
The preferred option for surgery is sectoral resection of the mammary gland. Its essence is that part of the organ is removed in the form of a sector, which contains pathologically altered tissue. The operation is usually performed under general anesthesia (except for cases where the tumor is located directly under the areola).
The intervention begins with the surgeon, under ultrasound control, using a special pencil to mark the locations of future incisions on the skin. The tissue is then cut along two radial lines radially from the areola.
Next, the surgeon makes another incision from 2 cm from the edge of the tumor to the border of the pectoralis major muscle. After separation of the skin from adjacent tissues and hemostasis, the tumor is removed.
Its sample is necessarily sent for histological examination.
Before closing the wound, the bleeding is again stopped by electrocoagulation of the vessels and the surgical field is sanitized. The surgeon closes and stitches the wound in layers. Drainage must be installed for several days.
Conservative method of treatment
Therapy based on the use of traditional medicine is not an independent method of treatment. There are no drugs that can stop the development of pathology. The use of medications is advisable after cutting out the seal. This helps the body recover faster and avoid complications.
After the operation, the patient is prescribed multivitamin complexes. They will generally improve the condition of the body and contribute to rapid recovery after manipulation.
After surgery, the doctor also prescribes medications that help strengthen the immune system and antiviral drugs. This therapy serves to prevent complications.
If after surgery, tests show a hormonal imbalance, the doctor prescribes the patient to take medications made on the basis of hormones. They will help solve this problem.
To make the scar heal faster after an incision, it is recommended to use topical therapy. These include ointments and gels that accelerate healing and have anti-inflammatory properties.
Negative consequences
After surgery, a course of restorative procedures prescribed by the attending physician is required. The duration is determined taking into account the stage at which the operation was performed and the condition of the operated patient.
If a relapse occurs, repeated surgery is prescribed, which consists of complete removal of the mammary gland.
In this case, complications develop:
- edema;
- mental state disturbance caused by a change in appearance;
- development of postural disorders.
How to prevent the formation of a growth and what is the prognosis
To prevent the formation of tumors in the breast area, it is recommended to undergo control examinations of the thoracic region at least 2 times a year by a mammologist and gynecologist.
If alarming symptoms occur, there is no need to self-medicate, which often causes additional health problems.
It is also possible for papillomas to appear on the labia or even in the vaginal mucosa in women.
Preventive measures against intraductal neoplasms:
- avoiding bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol, taking drugs);
- exclusion of stressful situations;
- wearing underwear that fits properly (not squeezing the chest);
- exclude the use of other people's underwear and other personal belongings;
- promptly identify and treat provoking diseases.
Conclusion
In most cases, the prognosis is favorable. This applies to both single and multiple neoplasms. If pathology is identified at an early stage and appropriate therapy is started immediately, one can hope for a complete recovery.
Folk remedies
Non-traditional therapeutic methods do not stop the development of papilloma located in the ducts of the mammary gland. For this reason, alternative medicine is not a treatment option. If such drugs are used to treat the disease, the formation will develop into a malignant tumor, which is more difficult to get rid of and will require not only surgery, but also chemotherapy.
Traditional methods of treatment can be used in the postoperative period to strengthen the immune system and restore the body, but only as prescribed by a doctor.
Prevention of intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland
Intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland is one of the few pathologies that do not have methods of prevention. It is impossible to prevent the development of the disease. The only thing that experts advise is to regularly attend scheduled examinations with doctors. Tests will help determine hormonal imbalance, and then it will be easier to determine the presence of pathology. External examinations by a mammologist are also a guarantee of timely diagnosis of pathology.
Doctors also recommend eliminating all risks of the disease. Women who have given birth to a baby should not give up breastfeeding. This will not only help to avoid pathology, but will also have a positive effect on the baby’s condition.
Doctors also advise representatives of the fair sex to give up bad addictions, since they push the body to the occurrence of papillomas. Weight control is another measure that excludes women from the risk group. Experts do not advise forgetting about proper nutrition. Eating fresh seasonal vegetables, fruits and berries increases the body's defenses and helps it resist the occurrence of tumors, both benign and malignant.
If intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland appears, it is not recommended to delay treatment. If the disease is started, tissue cells around the formation will die, and bleeding will begin.