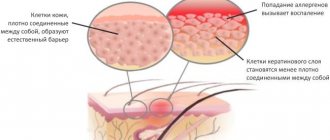
Causes of allergic dermatitis
Allergic dermatitis is a multifactorial disease, that is, the culprits of the disease can be very different. In addition to the immediate causes, the development of dermatosis is largely determined by genetic inheritance and the state of the immune system.
The trigger for skin allergies is the penetration of an irritant into the body, which triggers the process of activation of T-lymphocytes. Defender cells begin to attack the intruder, thereby causing inflammation in the upper layers of the skin.
The main culprits of allergic dermatitis:
- plant pollen;
- citrus;
- cosmetics, perfumes and care products;
- medications (both tablets and injections);
- paints, polymers and metals;
- synthetic clothing, bed linen;
- dust, especially book dust;
- latex materials.
This is not a complete list of sensitizers (irritants) that can activate the immune response. Allergy as a disease can arise from contact with absolutely any compound. In this case, the determining factor is not the chemical composition of the stimulus, but the sensitivity of the body to it in each individual case.
Allergic dermatitis in pregnant women usually appears against the background of hormonal changes in the body and reduced immunity, and the above sensitizers play the role of provocateurs. During this period, acute sensitivity to many foods, cosmetics and household chemicals occurs even in those who have never suffered from allergies before.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Photo: Seborrheic dermatitis on the face
This type of dermatitis occurs on the scalp (dermatitis on the head, face, sternum, in the area between the shoulder blades) and occurs due to excessive attack of these areas by the fungus malassezia furfur. This fungus likes to live where there is increased activity of the sebaceous glands.
Causes of seborrheic type dermatitis
The fungus, the excessive colonization of the skin of which causes seborrheic dermatitis in children and adults, lives in almost every person. However, not everyone gets seborrhea. The causes of the development of the disease are the following factors:
- hormonal changes;
- bad habits;
- individual characteristics of sebum of a hereditary nature;
- poor nutrition, diets;
- adolescence (period of hormonal surges);
- other conditions favorable for the development of fungus.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis appear the same in both children and adults. There is always abundant dandruff on the scalp due to very strong peeling of the skin. Reddened areas are visible on the head. A spring-autumn exacerbation of seborrhea is also considered a symptom.
For diagnosis, a visual examination is almost always sufficient, but sometimes there is a need to conduct additional analysis to differentiate seborrhea from psoriasis, rosacea, acne, which can also progress together.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis
Most often, topical anti-inflammatory and sedative drugs are prescribed for seborrheic dermatitis. Equally important in treatment are diet, giving up bad habits and proper skin care.
As an effective treatment for seborrheic dermatitis, dermatologists consider phototherapy sessions, which speed up the recovery process and prolong remission periods. Phototherapy is carried out as intensive therapy (3-4 times a week) and as maintenance therapy (up to 2 times a week).
Skin care for this type of dermatitis must include the following:
- hydration;
- exfoliating procedures;
- the use of anti-inflammatory cosmetics, such as antifungal shampoo, cream, anti-inflammatory mask, etc.
At-risk groups
Very often, allergic dermatitis is diagnosed in representatives of a particular specialty. This type of disease got its name - occupational dermatitis.
Several risk groups can be distinguished:
- builders;
- specialists in hazardous industries;
- medical workers;
- hairdressers, manicurists, cosmetologists;
- archivists.
All these people daily encounter irritant allergens: dust, chemicals, formaldehyde, industrial products.
Symptoms of allergic dermatitis
Allergic dermatosis differs from ordinary irritation arising from mechanical (friction) or chemical (alkali/acid) effects in the speed of development. In the first case, the skin reaction after contact occurs instantly, in the second - delayed, after 2-3 weeks.
What does an allergic lesion look like? As a rule, the manifestation of symptoms depends on the patient’s age, the state of the immune system, the presence of concomitant pathologies, and the duration of the disease.
In general, allergic dermatitis on the body manifests itself as follows:
- itching, redness and burning of the skin;
- rash in the form of blisters;
- swelling of the affected areas;
- Ulcers and erosions appear at the site of rupture of pustules.
A severe form of dermatosis is accompanied by signs of intoxication of the body:
- headache;
- weakness, drowsiness, lethargy;
- chills;
- temperature increase;
- skin peeling;
- nausea, vomiting.
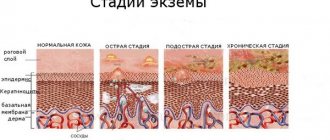
The severity of symptoms depends on the stage of dermatitis. The acute phase appears much brighter than the subacute phase. Signs of chronic damage develop in different forms and variations; foci of inflammation appear in places that have not been in any contact with the irritant.
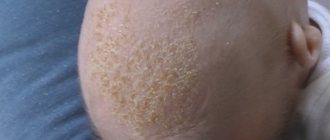
Diaper dermatitis
Photo: Diaper dermatitis
Diaper dermatitis, as the name of this type of skin disease implies, occurs only in infants. The disease can develop into more serious skin diseases and develop into chronic and severe allergies.
You need to know that diaper dermatitis in infants occurs more often in girls, as well as in bottle-fed infants of both sexes (60-65% of infants). The duration of diaper dermatitis is conditionally normal - up to the age of three, while the baby is still not able to control his bowel movements.
Together with diaper dermatitis, a child may be susceptible to dermatitis with other localizations, for example, eczema, gneiss, atopic dermatitis.
There are also types of film dermatitis in children:
- perianal childhood dermatitis - only the skin near the anus is inflamed. The appearance of this type of diaper dermatitis is associated with the baby’s nutrition and the activity of enzymes in his feces;
- limited inflammation of the skin in the folds of the groin;
- isolated inflammation of the genital organs, which occurs due to the characteristic features of the child’s urine.
Causes of diaper dermatitis in newborns
Factors that provoke the appearance of this skin disease are:
- mechanical effects (clothing fabric rubs delicate skin);
- chemical effects (when using rinses and powders when washing children's clothes, as skin reactions to baby cream or milk, as well as exposure to feces and urine of a baby);
- microbial factors;
- high humidity;
- too sensitive skin;
- unsatisfactory food quality.
The main thing to remember when considering the causes of diaper dermatitis is the quality of care for the baby.
You can look at a photo of diaper dermatitis to understand how the disease manifests itself
Symptoms of diaper dermatitis
Diaper dermatitis is manifested by the following characteristic signs:
- the appearance of redness and abrasions in the groin area;
- the presence of red spots of different shapes and sizes on the skin of the baby’s entire body, which can unite and cause discomfort;
- the appearance of intradermal vesicles with transparent filling on a red background (if the filling of the vesicles becomes cloudy, this indicates advanced inflammation);
- flaky areas of skin, the appearance of crusts, small erosions and wounds.
The skin of a baby affected by inflammation can be either general or local in nature (only on the buttocks and groin or only in the neck area if the child regurgitates frequently).
Treatment of diaper dermatitis
Photo: Treatment of diaper dermatitis
The prescribed treatment for diaper dermatitis may include recommendations for performing hygiene procedures with the use of light medications.
Recommendations that can help resolve the problem:
- keep inflamed skin areas clean;
- ensure dry and clean baby's skin;
- select diapers for the child according to his size, so that too small ones do not squeeze the skin and do not rub too large ones;
- change diapers in a timely manner, and with each change, wipe the affected areas of the skin with a gauze pad soaked in a decoction of string, chamomile or oak bark;
- give the baby air baths more often;
- use healing powders and talcum powders before putting on a clean diaper.
Medicinal creams and ointments for the treatment of diaper dermatitis:
- Drapolene;
- Bepanthen or D-panthenol;
- Desitin;
- Sudocrem;
- Miconazole or clotrimazole may be prescribed for fungal types of dermatitis.
Types of allergic dermatitis
An allergic reaction is a very individual process. Its manifestations in adults depend on the type of irritant, cause and location. On this basis, it is customary to distinguish several types of allergic dermatitis.
Phytodermatitis
Develops after contact with pollen and milky sap of certain plants: buttercups, euphorbias, lilies. Citrus fruits are especially aggressive in this regard. Often the pathological process occurs as a reaction to indoor plants.
In addition to itching and redness of the skin, allergic dermatitis is accompanied by severe runny nose, tearing, and sneezing. During an exacerbation, a rash appears on the extensor surfaces, in the neck and groin area.
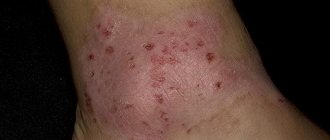
Contact dermatitis
The second most common type of allergic dermatitis. It develops in direct contact with an irritating substance: detergents, hard water, household chemicals, cosmetics, industrial preparations.
The contact form most often affects the skin of the palms and face. Women especially suffer from this disease, since they constantly use care products and household cleaners.
Dermatitis on the elbows can be caused by various reasons. Contact irritation most often occurs on the internal area, and food irritation occurs on the external area. The main symptom of this dermatosis is a urticaria-type rash.
Very often, the cause of contact scalp allergies is various hair dyes, incorrectly selected shampoos and rinses. In addition, synthetic hats, insufficient care, or constant wearing of a hat can cause allergic dermatitis on the head.
Toxidermy
Occurs when an irritant enters the body through the gastrointestinal tract or injection. This type of allergy is triggered by medications or food. The manifestations of such dermatitis are very diverse and depend on the sensitizer.
For example, antibacterial medications cause peeling and rashes. Sulfonamides typically cause local redness of the hands, groin area and irritation of the oral cavity. The food reaction causes numerous areas of inflammation throughout the body.
A severe form of toxic-allergic damage under the influence of unfavorable factors can develop into Lyell's syndrome. Acute epidermal necrolysis is manifested by a sharp deterioration in the patient's condition. Blisters form in the inguinal and axillary folds, in the place of which, after opening, ulcers form.
Childhood dermatitis
Allergic dermatitis in a baby develops in a slightly different scenario. The severity of symptoms in children depends on age. According to this principle, it is customary to distinguish the following forms of childhood dermatitis:
- exudative. Develops in the first months after birth;
- vesicular-crustic. Affects children under six months of age;
- erythematous-squamous. Appears up to 2 years of age.
In adolescence, the lichenoid form is registered, which is accompanied by itching and the appearance of painful scabs.
How long does allergic dermatitis last? It all depends on the cause of the disease. The faster the irritant can be detected and eliminated, the sooner the symptoms of the disease will disappear.
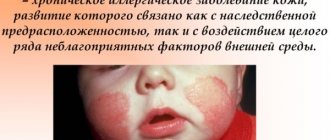
Atopic dermatitis
Photo: Atopic dermatitis in children
The chronic skin disease atopic dermatitis (AD), always accompanied by excessive dry skin, itching and inflammatory lesions with redness, is the most common skin disease in children. Thus, one-year-old children develop AD in approximately 60% of cases, and young children – in 90% of cases. At the same time, it is possible to completely get rid of an uncomfortable disease only in adolescence. Often the disease remains a constant companion of a person forever.
But parents who are faced with a problem have every chance to correctly help their child pass this test and cure atopic dermatitis.
Causes of blood pressure in children
Atopic dermatitis in children can manifest itself after drinking milk. You need to know that most often signs appear precisely when formula is introduced into the child’s diet. Products that can provoke disease (diathesis) also include eggs, strawberries, strawberries, citrus fruits, oatmeal and other cereals. Moreover, even with breastfeeding, babies can get diathesis if the listed products were consumed by the nursing mother.
The reason for the appearance of AD, which is not so common, is the use of washing powder when washing children's clothes.
The disease can also be caused by a seemingly banal change in weather conditions. In this case, dermatitis in children is often accompanied by other diseases, such as dysbiosis. However, if the climate is changed to maritime, the disease noticeably weakens and the child becomes better.
The main symptoms of atypical dermatitis in children:
- dryness and redness of the cheeks, which can be either permanent or “disappearing” (for example, when going out into cold air, redness may go away, but then return);
- dry skin all over the body from a very early age;
- Diaper rash that occurs in a baby takes a long time and is difficult to disappear, the symptom is especially noticeable in the folds on the legs and arms;
- the appearance of strong gneiss on the hairline (scales stuck together by the secretion of the sebaceous glands);
- the appearance of a rash on the baby’s skin;
- the appearance of weeping areas on the child’s skin;
- itchy nodules filled with clear liquid (strophulus);
- the presence of plaque on the tongue in the form of patterns and lines;
- the appearance of problems with stool (diarrhea or constipation).
AD may go away completely before the age of two, but sometimes the disease can develop into more serious diseases such as asthma and chronic allergic rhinitis.
How to treat atopic dermatitis in children
The pediatrician’s choice of medications depends on the nature of blood pressure, the location of the outbreak and the degree of its manifestation. Treatment of atopic dermatitis:
- taking medications orally (drops or tablets);
- local application (ointments and mash applied to the lesions).
When taking any medications prescribed by a pediatrician, you must first make sure exactly how, how often and in what dosage they should be used.
Medicines available without a doctor's prescription:
- topical steroids such as hydrocortisone. Relieves itchy symptoms. Effective for mild forms of blood pressure;
- fast-acting antihistamines for external and oral use. Relieves dry skin and itching. They have practically no side effects. Sometimes topical preparations can cause a slight burning sensation of the skin (if they contain alcohol). Oral medications may cause drowsiness.
Prescription drugs:
- some topical steroids that relieve swelling and itching. Side effects may include acne, thinning of the skin and stretch marks (if used incorrectly or intolerant);
- immunomodulators of oral or local action. Reduce inflammatory reactions, relieve itching and irritation;
- antibiotics. Prescribed to patients for use in the presence of repeated infection;
- oral steroids. They are prescribed extremely rarely by pediatricians because they are unsafe for the child’s body.
Which doctor treats allergic dermatitis?
At the first signs of dermatosis in the form of itching, rash, redness of the skin, you should visit an allergist. This relatively new specialty is becoming increasingly popular today among patients with an autoimmune nature. Unfortunately, their number is steadily growing. Timely consultation will protect you from serious complications and speed up recovery. A qualified specialist will identify the cause of dermatosis and prescribe the optimal treatment, as well as advise on further preventive measures.
Symptoms in teenage boys and girls
Atopic dermatitis affects the skin of the face, neck, back, and chest. There are also inflammatory lesions on the soft tissues of the lower and upper extremities. Characteristic symptoms:
- intense itching that intensifies at night;
- possible formation of seborrheic scales on the scalp;
- redness, swelling;
- excessive drying of the skin;
- formation of cracks;
- dryness may alternate with weeping;
- scratch marks appear on the body;
- sleep problems;
- the psycho-emotional state of the teenager becomes unstable.
The disease is local in nature and can affect any part of the body. In some cases, the formation of pustules may occur. Their appearance often causes secondary infection, which significantly complicates the course of the disease.
The affected skin may become thicker and its pattern may change. The erosive areas become covered with dense crusts, which may cause bleeding when removed.
Diagnosis of allergic dermatosis
The process of diagnosing allergic dermatitis, as a rule, does not cause difficulties. During the initial conversation, the doctor collects an anamnesis (history of the disease) and conducts a visual examination of the patient’s skin. During the examination, manifestations characteristic of dermatosis are identified and a diagnosis is made.
To confirm the initial conclusion, the doctor prescribes additional tests:
- skin allergy tests;
- testing for sensitivity to irritants;
- hemoscanning.
In order to differentiate (distinguish) allergic dermatitis from other skin diseases, computer diagnostics of the body is prescribed. A tissue biopsy is performed for the same purpose.
Oral dermatitis
Photo: Oral dermatitis
Another name is perioral dermatitis.
This type of dermatitis is characterized by the fact that the location of its manifestation is the area around the mouth and chin. A papular-spotted rash appears in these places.
Reasons for appearance
There is no clear etiology for oral dermatitis, but some factors are still identified that contribute to the onset of the disease. Among them are the following:
- Mostly girls and women are affected by the disease (risk group);
- simultaneous use of two or more cosmetics in facial skin care;
- long-term use of hormone-containing ointments (in particular glucocorticoids and their fluorinated compounds, such as flucinar, fluorocort);
- immune imbalance;
- gastrointestinal diseases.
Symptoms of oral dermatitis
The oral type of dermatitis may have very similar symptoms to other types of dermatitis, but there are also characteristic features. Thus, oral dermatitis never has manifestations of general reactions of the body, but only manifestations of a local nature.
Localization of rashes - near the mouth, around the lips, on the chin, in the area of the nasolabial triangle. Peroral dermatitis never spreads further, which is also a distinctive feature of this particular type of dermatitis. Between the lip line and the beginning of the rash area there is always a white stripe of skin that has not undergone any changes. This is also a characteristic sign of oral dermatitis.
The rashes also have characteristic features in a quantitative aspect: at first there will be individual papules, like pimples, and over time there are more of them, and they begin to create islands, uniting with each other locally. Polymorphism of rashes acts as the main sign for verification of the diagnosis. A small pimple of 2-3 mm at first, filled with liquid at the end, forms a crust over time and the skin peels off.
Oral dermatitis in children
Children are less susceptible to this disease (only in 5-8% of cases) than adults, and this fact is attributed precisely to the fact that the child does not use cosmetics.
This does not only apply to teenagers, in whom this type of dermatitis occurs quite often.
Treatment of allergic dermatitis
The disease requires timely and adequate therapy. Treatment should be carried out in 2 directions:
- Eliminate any contact with the irritant.
- Direct fight against unpleasant symptoms.
In some cases, it is enough to remove the sensitizer for the signs of the disease to disappear. But more often you have to use medications.
Treatment of skin lesions at home is carried out with mandatory adherence to a diet. This is one of the main points of care for the patient.
In newborns
Allergic dermatitis develops much more often in newborns than in adults. The cause of the disease is usually a food allergen. The main symptom of dermatosis is a small, bright rash on the baby’s cheeks.
If the disease is not treated, blisters appear at the site of irritation, which burst and form ulcers. When scratching and introducing dirt, a bacterial infection may occur.
So, how to treat allergic dermatitis in a newborn? Therapy for young children has its own characteristics. To combat the disease, an integrated approach is used based on the following measures:
- control over the nutrition of the baby and mother;
- exclusion of possible irritants from the child’s environment;
- creating comfortable external conditions.
In addition to symptomatic measures, for allergic dermatosis, treatment with local agents (Ichthyol ointment) and oral antihistamines (Suprastin, Zyrtek) are prescribed. Valerian tablets are used to reduce itching. All medications are prescribed only by a pediatrician and are used under strict supervision.
In children
How to treat allergic dermatitis in preschool and primary school children? The childhood form of the disease is registered in children under 12 years of age and is popularly called diathesis. They fight it using standard methods - identify and exclude the allergen from the environment, and then relieve symptoms with medications:
- oral antihistamines - Erius, Zyrtec, Cetrin;
- local means - Bepanten, D-Panthenol, Elobaze, Cynovit.
If a bacterial infection is associated with allergic dermatitis, the child is prescribed antimicrobial tablets (Cefuroxime, Cefazolin, Cefepime), but this is done extremely rarely. External antiseptics are most often used:
- Miramistin;
- Fukortsin;
- Chlorhexidine.
To eliminate the symptoms of dermatosis, ointments are used - Levosin or Bactroban. Apply them in a thin layer strictly to the affected areas 1-2 times a day.
Allergic dermatitis in adults
Treatment of allergic dermatitis in adults is carried out using physiotherapeutic procedures: laser therapy, infrared radiation. Otherwise, the fight against dermatosis is not new. Also, first of all, the irritant is eliminated and symptomatic therapy is prescribed.
Drugs for the treatment of allergic dermatitis:
- antihistamine tablets - Erius, Zyrtec, Fenkarol;
- antipruritics - tincture of Motherwort, Valerian, Novopassit;
- detoxification medications - activated carbon, Enterogel;
- enzymes - Mezim-Forte, Linex;
- corticosteroid creams and gels - Elidel, Fucicort, Advantan, Flucinar, Lokoid, Akriderm.
Treatment of allergic dermatitis with folk remedies gives good results, but herbal medicine should be used only after consultation with a doctor, since many herbs are allergenic. To wash the affected areas, you can use infusions of soothing and anti-inflammatory plants: string, oak bark, chamomile, calendula.
In pregnant women
How to cure allergic dermatitis during pregnancy? Only a doctor can prescribe tablets and ointments during this period, guided by the severity of the symptoms and the danger of the pathological condition for the child.
For mild dermatosis, a hypoallergenic diet and external ointments are used: Bepanten, D-Panthenol, Skin-Cap. For moderate skin allergies, sorbents (activated carbon, Polysorb) and antihistamines (Loratadine, Cetirizine) are used.
For advanced allergic dermatitis, hormonal creams and gels are prescribed, although more often it is treated in a hospital. A pregnant woman can use various ointments and infusions prepared from medicinal herbs, but again after consulting a doctor.
Is dermatitis contagious or not? This question often arises among expectant mothers suffering from skin allergies. Doctors give an unequivocal answer on this matter - the disease is not transmitted vertically, so mothers do not have to worry. It is impossible to become infected either during or after childbirth.
Childhood dermatitis
Photo: Children's dermatitis on a child's face
Allergic symptoms that manifest themselves on the skin of a child with the onset of dermatitis are a common occurrence for the sole reason that the immune system of children is not yet sufficiently adapted to the aggressiveness of the external environment. Children's dermatitis is also popularly called diathesis. Indeed, often manifestations can be one-time and harmless, quickly passing and disappearing altogether as the child grows older. However, if the child is not helped to cope with dermatitis in a timely manner, the disease can turn into a chronicle, and then will prevent the person from living a full life.
The symptoms of childhood dermatitis are the same as dermatitis in adults, but with one peculiarity - manifestations on the skin may disappear and then reappear. Inflammatory manifestations on the child’s skin are preceded by itching. Products that may show the first symptoms: eggs, milk, cereals, berries, fruits. Non-compliance with the diet by a mother who is feeding her baby with breast milk can also have an impact.
The causes of childhood dermatitis are primarily considered to be genetic predisposition.
Types of childhood dermatitis:
- infantile dermatitis . It can manifest itself before the age of two. The rash most often forms on the face, folds on the arms and legs, and in the groin. The skin is dry, may peel, have crusts and even crack;
- childhood dermatitis . Can manifest itself in the period from 2 to 12 years. Rashes appear on the folds of the arms and legs, as well as on the neck. Its characteristic feature is pronounced hyperemia. The skin acquires areas of swelling, redness and erosion appear, which are aggravated by the fact that the child constantly scratches the areas affected by dermatitis, up to serious wounds. This happens because the child experiences unbearable itching - the second feature of childhood dermatitis;
- teenage dermatitis . It may appear between the ages of 11-12 and 17-18 years. The most commonly affected areas are the neck, décolleté, hands and elbow pits. Boys are more likely than girls to experience teenage dermatitis.
Complications
Allergic dermatitis itself is not dangerous, but if left untreated, it can lead to unpleasant consequences. If the doctor's recommendations and hygiene rules are not followed, pathological conditions may be associated with the skin disease:
- deep dermal lesions and erosions;
- pyoderma;
- phlegmons and abscesses.
In addition to skin lesions, advanced dermatitis often leads to the development of bronchial asthma, autoimmune urticaria, and leukocytosis.