Causes
Despite more than 150 years of clinical history, the causes of dyshidrotic eczema are still unclear. The disease is most often considered as one of the symptoms of an allergic reaction provoked by food or drug hypersensitivity.
In addition, it has been noted that this form of eczema often appears after immediate stress or prolonged nervous tension, which may be associated with genetic inheritance.
Excessively dry or sensitive dermis of the hands and feet, as well as working in damp conditions or frequent contact of the skin with cement, nickel, asbestos, chromium and other aggressive substances can also increase susceptibility to dyshidrotic eczema.
In many patients, dyshidrotic eczema of the hands and feet occurs against the background of previous or existing diseases:
- endocrine system disorders;
- metabolic deterioration;
- decreased immunity;
- avitaminosis;
- improper intake and use of medications;
- various minor injuries to the skin of the hands and feet;
- hyperhidrosis;
- severe infectious diseases;
- violation of hormonal status.
An exacerbation of dyshidrotic eczema can also be caused by poor nutrition, addiction to all kinds of diets, frequent fasting, nervous or physical exhaustion.
Classification and forms
Skin disease is divided into several forms, depending on the cause and symptoms. Classification of the disease:
- True
The disease begins to appear on the face and later spreads to the limbs. The vesicles quickly burst, which distinguishes the true (idiopathic) form from other types of the disease. The peak development of the pathology occurs between the ages of 30 and 40 years, but can also be observed in young people. The clinical picture of the disease is manifested by specific symptoms (typical localization, rashes appear for no apparent reason on unchanged skin), simplifying diagnosis.
- Microbial
Microbial eczema is a type of dermatitis, characterized by the development of the disease against the background of disease or as a result of microbial and fungal infections of the skin. Unlike other forms, microbial eczema is manifested by the appearance of ulcers. A similar phenomenon for the true and contact forms is a complication. Often the appearance of microbial eczema is associated with the presence of damage to the skin in the form of wounds, cuts, burns, and trophic ulcers. This form accounts for about 1/3 of all cases of eczema.
- Contact
The cause is a pathological allergic reaction to a certain irritant (food, cosmetics, fabric, household chemicals, medicines, jewelry, plants). People with a genetic predisposition to allergies are often affected. The acute form of contact eczema is characterized as contact dermatitis.
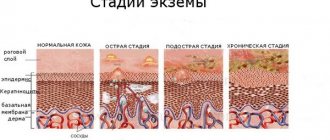
It is classified according to the nature of its flow. There are 3 stages of the disease:
- Spicy.
It is characterized by a sudden appearance of vesicles, a pronounced change in phases, and intense symptoms (swelling, redness, itching). Wetting of the lesion with copious discharge of fluid is observed. Vesicles are replaced by erosions, then crusts of yellow, brown or gray color. The duration of the course is 3-6 weeks.
- Subacute.
The development of the disease is not as rapid as in the acute form. Symptoms and exudate are moderate. The affected area is distinguished by the acquisition of a bluish tint. The duration of the disease can last up to 24 weeks.
- Chronic.
There is coarsening, thickening of the stratum corneum, increased infiltration, itching and hyperemia. Exacerbation of the chronic form is characterized by the appearance of exudate.
Symptoms
The first sign of eczema is at first mild, and then increasingly intensifying itching of the affected areas of the skin. Symptoms gradually increase, the dermis at the site of inflammation becomes irritated, reddens and thickens.
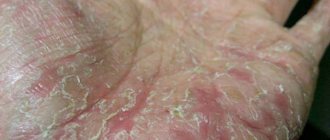
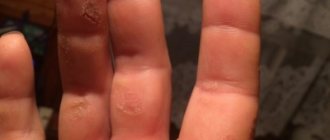
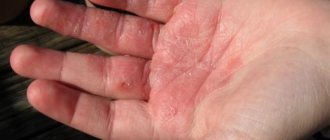
Bright pink, disturbing blisters with serous contents appear on the fingers, palms or soles. A feature of dyshidrotic eczema is the deep occurrence of vesicles - at the level of the epidermal layer of the skin.
As dyshidrotic eczema develops, the rashes burst and dry out or form weeping erosions. The process of opening the bubbles is accompanied by changes in the structure of the dermis - it begins to actively peel off, turns red and cracks. If pathogenic microflora penetrates into the wounds, purulent inflammation joins dyshidrotic eczema and pyoderma begins.
This development of the disease leads to the formation of pustules, a deterioration in the patient’s general well-being - the temperature rises, the inflamed palms and feet begin to swell and begin to hurt, and nearby lymph nodes increase in size.
The dyshidrotic form of eczema quickly becomes chronic, occurring in several stages simultaneously, i.e., the skin has a primary rash, ruptured vesicles, erosions, purulent pustules and drying crusts. It is difficult to cope with such a pathology - inflammation constantly worsens from the slightest environmental influence.
How to deal with eczema?
Eczema is one of the common skin pathologies. What are its reasons? Is it transmitted from person to person? How is it treated?
These and other questions are answered by the dermatologist at Clinic Expert Tula, Candidate of Medical Sciences Vladislav Leonidovich Sheinkman.
– Vladislav Leonidovich, let’s start with a definition: what is eczema?
– This is a chronic recurrent skin disease with acute inflammatory symptoms caused by serous inflammation of the epidermis and dermis.
– What are the causes of eczema?
– There is a hereditary predisposition, a relationship with the nervous system - stress can also lead to disease. Post-traumatic microbial eczema occurs around the wound surface.
Is there a stress vaccine? Read our article
– What types of eczema are there?
– True (or, otherwise, idiopathic) eczema most often turns into chronic. Patients are bothered by severe itching, blisters appear on the skin, then they burst, and the weeping stage begins. There are many foci of inflammation on the body, they involve more and more new areas of the skin.
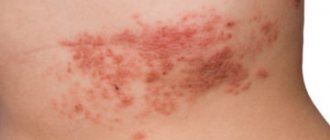
I have seborrheic eczema. It is localized on the scalp, face, arms, and neck. There is no weeping stage, but itching is present.
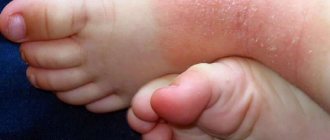
Dyshidrotic eczema affects the arms and legs; In this case, bubbles appear; they, of course, bother the patient, but may not open. There are painful sensations when moving the hands and feet.
Microbial eczema occurs at the site of fractures, injuries, or some microbial foci. Not only characteristic blisters appear, but also pustules.
There is also occupational eczema, which affects people who are forced to constantly come into contact with harmful substances at work.
“A doctor of this specialty is engaged in establishing the connection between existing pathologies or disabilities and the characteristics of work activity.” Quote from the material “Educational program on medical specialties. Let’s go to an appointment with an occupational pathologist.”
Horny, or tylotic, eczema affects the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
Childhood eczema - it begins around 3-6 months of a child’s life, often has a hereditary nature, and is preceded by diathesis. Locations are the cheeks, forehead, then lesions can appear on the shoulders, hips, and legs. Eczema can spread to the head and ears.
– Is eczema contagious?
- No.
– Can eczema go away on its own without treatment?
– Since this is a chronic skin disease, it may seem to subside for a while, but sooner or later a period of exacerbation will return. Unfortunately, many people self-medicate - they use some kind of ointments, tinctures. This is something that you absolutely cannot do if you have eczema. You need to be treated by a dermatologist - only he can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. And self-medication often leads to serious complications.
– How is eczema treated?
– A patient of any age must follow a hypoallergenic diet - that is, foods that can serve as disease-provoking factors should be excluded from the diet. For adults, these are alcoholic drinks, compotes, juices, lemonade, products with dyes, preservatives, sweets, chocolate, honey, jam, berries, imported fruits.
Patients should try to avoid stress. They are recommended to examine the gastrointestinal tract - problems with the liver and stomach are often detected. Do not come into contact with chemically active substances (including synthetic and chlorine-containing detergents).
Treatment consists of prescribing desensitizing, antihistamine drugs; antibiotics can be used for microbial eczema.
You can read more about antibiotics in our articles here and here
Various lotions are used in treatment - for example, with a solution of Miramistin or Rivanol, pastes, creams. Hormone-containing drugs are used exclusively under the supervision of a doctor.
– Is it possible to swim in the sea if you have eczema?
– There is such a myth: if a patient with eczema swims in the sea - especially in the Dead Sea - he will be cured immediately. Nothing like this! During an exacerbation, it is generally not advisable to swim in the sea: exposed inflammatory foci react to the salt in sea water, and the itching and rashes intensify. If you go to the sea in the remission stage - when there are no rashes, this has a beneficial effect on the prevention of all skin diseases in general.
– Is it possible to prevent the development of eczema? And if so, how?
– Prevention is possible. It is necessary to normalize the daily routine, eat rationally, and, if possible, control the functioning of the nervous system.
You can make an appointment with a dermatovenerologist here
ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
Interviewed by Igor Chichinov
The editors recommend:
When the sun is your enemy. What is solar dermatitis?
What is demodicosis and how to cure it forever?
Nerves under control! How to maintain mental health?
For reference:
Sheinkman Vladislav Leonidovich
Graduate of the pediatric faculty of the Smolensk State Medical Institute in 1994.
From 1994 to 1995, he completed an internship, and from 1996 to 1998, a clinical residency in the specialty “Dermatovenereology”.
Has an academic degree of Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Currently working at Clinic Expert in Tula as a dermatovenerologist. Provides reception at the address: st. Boldina, 74.
Diagnostics
There are no special methods for diagnosing dyshidrotic eczema. Characteristic signs and clear localization of the rash help to quickly suspect this pathological process, and the recurrent course of the disease once again confirms the guess.
To make a diagnosis, the patient is prescribed the following tests:
- scraping the skin for fungus (allows us to exclude the mycotic onset of eczema);
- culture of the contents of the vesicles (confirms the non-infectious nature of the disease).
If dyshidrotic eczema is suspected of being allergic, the patient will be advised to do an allergen test.
Is eczema contagious or not and can it be transmitted to another person?
Some skin diseases spread to others through contact, such as scabies.
Almost all dermatological diseases are accompanied by redness. Redness, peeling, scratches and tears in the skin on the hands rarely inspire confidence on the part of the interlocutor. Doubts are raised at first in the patient: is it possible to infect others? Eczema is very common in people. The list of reasons for its appearance is also quite large: from ordinary contact with chemicals to emotional changes or hormonal imbalances. The risk of infection is higher in people with low immunity.
It is localized in various parts of the body, most often the arms, legs, and face. People of any age are equally at risk of contracting eczema. Accompanied by severe peeling and redness of the skin. Is eczema contagious or not? Is eczema transmitted from person to person, through sex, transfusion or other conditions?
Treatment of eczema
Medical care for dyshidrotic eczema should be comprehensive. The first step is to localize the probable cause of the Pompholyx outbreak and create a favorable psychological climate for recovery. Then symptomatic therapy should be carried out and signs of malaise should be eliminated.
Antihistamines
Systemic treatment for dyshidrotic eczema necessarily includes the use of antiallergic drugs. It is better if these are antihistamines of 2 and 3 generations. They have fewer adverse reactions, do not cause drowsiness and allow you to drive vehicles.
The following medications will help eliminate itching and inflammation of the skin with dyshidrotic eczema:
- Zyrtec.
- Claritin.
- Erius.
- Citrine.
If unpleasant symptoms prevent you from falling asleep, it is better to use 1st generation antihistamines. They will relieve insomnia, relieve tension and calm the nervous system.
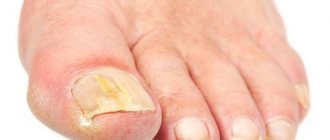
Dyshidrotic eczema on the legs is often accompanied by the addition of mycosis. In this case, the complex of therapeutic measures must be supplemented with antifungal drugs.
Local remedies
For dyshidrotic eczema, a variety of medications are used for external use. Moreover, for superficial lesions, creams are often prescribed, and for deeper lesions, ointments and lotions are prescribed.
Non-hormonal drugs for eczema:
- D-Panthenol.
- We see.
- Solcoseryl.
- Destin.
- Thymogen.
- Fenistil.
- Naftaderm.
- Giistan.
- Radevit.
Antimicrobial ointments for dyshidrotic eczema are used in case of secondary infection. These medications include:
- Bactobran.
- Fucidin.
- Levosin.
- Erythromycin, Gentamicin and Lincomycin ointments.
External hormone-based remedies to combat eczema are used only in the presence of weeping ulcers or long-term non-healing cracks and erosions. Such medications should be prescribed by the attending physician and used under his supervision, since incorrect application of corticosteroids will only worsen the condition and cause a severe relapse.
For antiseptic dressings and washings, you can use a solution of Furacilin or Tannin, 1-2% boric acid, silver nitrate, resorcinol.
Physiotherapy
One of the best ways to treat dyshidrotic eczema. The influence of physiotherapeutic factors increases the body's resistance, relieves itching and irritation, and reduces the amount of medications taken.
Patients with eczema are most often prescribed:
- electrosleep;
- laser;
- cryotherapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultraphonophoresis;
- darsonvalization;
- General Ural Federal District.
For dyshidrotic eczema, local hydrogen sulfide, radon or mineral baths and mud therapy provide an excellent healing effect.
You can receive such treatment at a city dispensary or by going to any suitable sanatorium. The resorts of Pyatigorsk, Ust-Kut, Belokurikha, and Molokovka are especially good for patients with eczema.
Vitamin therapy
To improve immunity and overall health of the body, as well as to prevent relapses, vitamin therapy is used with great success.
Patients with dyshidrotic eczema are recommended to take ascorbic acid, tocopherol, carotenoids, and B vitamins. Multivitamin complexes with minerals and seaweed have a good strengthening effect. It’s great if the drugs contain sulfur and
Protecting the skin from external influences
For dyshidrotic hand eczema, treatment requires mandatory protection of the skin with rubber and cotton gloves. The former protect the dermis from exposure to harmful substances, the latter help to avoid moisture and loosening of tissues.
For personal hygiene, it is recommended to take baby soap or gel with a minimum content of fragrances and dyes, intended for hypoallergenic skin care. After cleansing, hands should be thoroughly dried and lubricated with a soft cream, thereby moisturizing and protecting the dermis.
No less care is required for dyshidrotic eczema of the feet. If a rash and itching appears on the feet, you should avoid wearing synthetic socks and tights. It is recommended to select shoes from natural materials, comfortable and in size.
Diet
Dyshidrotic eczema can also be treated with proper nutrition. It is recommended to remove alcohol, chocolate, hot herbs and spices, citrus fruits, eggs, sugar, delicacies and baked goods from the diet. It is necessary to limit the consumption of salt, canned food and semi-finished products - these products contribute to the accumulation of water in the body and increase swelling.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies helps quite well against dyshidrotic eczema. To eliminate painful symptoms, it is recommended to use anti-inflammatory and soothing herbs:
- sequence;
- coltsfoot;
- chamomile;
- calendula flowers;
- oak bark;
- peppermint;
- yarrow;
- celandine;
- elderberry sprigs.
For dyshidrotic eczema, local baths are made from medicinal plants by brewing 5 tbsp. l. dry raw materials in three liters of water. The solution is infused for 20–25 minutes, poured into a convenient container and the limbs are lowered into it. Keep until the liquid cools.
Fresh and juicy coltsfoot leaves passed through a meat grinder are used for compresses. A gauze napkin is moistened in a liquid paste of greens and applied to the areas of the dermis affected by eczema. Cover the top with cellophane and keep for 2–2.5 hours.
Sea buckthorn or almond oil may be recommended to soften rough and flaky skin. The products have a good wound-healing and soothing effect, prevent scarring and tissue hardening.
Another home remedy for dyshidrotic eczema is oatmeal. Apply steamed flakes to the inflamed areas or make a bath of warm broth. The crushed grain can be used instead of soap to cleanse the skin, and the powder can be sprinkled on cracks and ulcers.
Help from a psychologist
Dyshidrotic eczema on the fingers brings not only physical, but also moral suffering. Patients are very hurt by the excessive attention of others to the affected areas of the body, the need to constantly hide their hands and answer questions about health.
In such cases, if the patient cannot cope with the psychological problem on his own, the help of a specialist is recommended.
Predisposition to disease
Currently, the reasons why dyshidrotic eczema may occur are unknown. Only those factors that can cause the appearance of symptoms of the disease have been identified. In 22% of cases of hand eczema, it is impossible to determine the cause of its occurrence. Risk factors for eczema on the fingers include:
- The occurrence of an allergic reaction;
- Disruption of the normal functioning of the body's immune system;
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- Impaired metabolism;
- Hereditary predisposition to the disease;
- Impaired functioning of the nervous system;
- Digestive problems;
- Disturbed functioning of the endocrine system;
- Prolonged experience of stress;
- Hypothermia;
- Occupational hazards (cleaners, washers, plasterers, painters, etc.);
- The influence of detergents and cosmetics.
- Gastrointestinal tract dysfunction
In 50% of cases, a hereditary predisposition to the manifestation of symptoms of the disease is determined. Therefore, for signs of deviation to appear and become more active, it is enough for a person to experience severe stress or the appearance of disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
Hand eczema can be caused by an allergy to a specific substance with which the body has interacted.
Often such a reaction is observed from the influence of household chemicals, as well as when using cosmetics. In some cases, the cause of eczema is hyperhidrosis, in which increased sweating is observed.
Source: allrg.ru
Prevention
Prevention of dyshidrosis cannot be called difficult. It consists of maintaining personal hygiene and constantly caring for the skin of your hands and feet.
It is necessary to use mild detergents, moisturize and protect the dermis with creams, and avoid hypothermia and injury to the extremities. In addition, you should increase your immunity, learn to cope with stress and eat right.
With proper and timely treatment, the symptoms of dyshidrotic eczema disappear after 3-4 weeks without visible complications. Unfortunately, this does not mean a complete cure. Once it begins, the disease can return again and again under the influence of various unfavorable factors.
Author: Elena Medvedeva, doctor, especially for Dermatologiya.pro
How to prevent the disease
In order not to encounter unpleasant symptoms of eczema in the future or to weaken the course of an existing disease, you must follow certain recommendations:
Features of eczema prevention
- Maintain hygiene of your body and facial skin. Wash your face every day and take a warm shower, use special products (choose a product specifically for your skin type), wipe dry with a clean towel;
- promptly treat all dermatological diseases that may cause eczema. The same can be said for varicose veins;
- pay special attention to swelling or scabies - these are warning signs;
- Before each meal, as well as after visiting hospitals, shops and other public places, be sure to wash your hands with soap;
- if even minor ulcers or scratches appear, use iodine to treat the affected skin;
- Women are not recommended to wear nylon tights or stockings frequently. This material does not allow air to pass through, so the skin cannot breathe and function normally;
- Change your wash brush and washcloth regularly, as various bacteria can accumulate on them. It is recommended to replace it at least once a month.
Prevention of eczema
To prevent eczema during pregnancy, experts recommend following a special drinking regime. This is due to the fact that allergens can enter the placenta along with blood, which poses a threat to the health of the unborn child. You also need to monitor your diet and take vitamin complexes containing vitamins A and B. The combination of all these measures will prevent the occurrence of eczema and other skin pathologies.