Last update: 01/14/2020
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin disease. Microbial eczema is a type of eczema that is secondary in nature. It is localized in areas of long-term skin damage: non-healing wounds, abrasions, ulcers, varicose veins, fungal infections. With a decrease in immunity and the susceptibility of a given area of skin to microbes, inflammation begins, and symptoms characteristic of eczema are added to the already existing manifestations of the background disease.
According to various sources, microbial eczema is diagnosed in almost 30% of all cases of eczema.
Causes of microbial eczema
The origin of this disease is different - eczema can develop as a result of allergies, with a hereditary predisposition, under the influence of various external factors and diseases of internal organs.
Microbial eczema is divided according to the reasons for its appearance:
- Varicose eczema - develops on the lower extremities with an advanced case of varicose veins.
- Numular eczema - the lesions are round in shape and localized on the extremities.
- Paratraumatic eczema - develops at the site of wounds that have not healed for a long time.
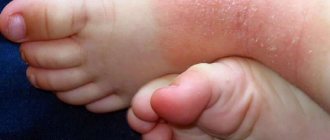
In children, microbial eczema can appear without serious skin lesions. Its cause is the weakening of the child’s immunity and the sensitivity of his body to various infections.
Very often, eczema develops as a result of internal diseases - problems with the gastrointestinal tract, kidney disease, endocrine system disorders.
Chronic microbial eczema
With constant exposure to infections and allergens on the human body, the disease can become chronic. Such microbial eczema is very difficult to treat - periods of remission are followed by regular relapses. Exacerbation of eczema can be caused by a cold or a small wound on the skin.
Therefore, it is very important to diagnose microbial eczema in time and treat it before it becomes chronic.
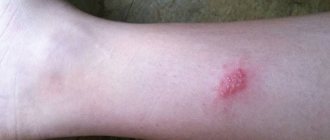
What is coin eczema
Coin-shaped (or nummular, discoid, plaque) eczema is a skin lesion characterized by the formation of multiple round-shaped lesions in the form of coin-shaped plaques (“nummus” in Latin means “coin”). This disease is often chronic, relapsing and difficult to treat.
Coin eczema
The occurrence of the rash is observed mainly in older males. The disease belongs to the microbial variety of eczema, that is, the triggering factor for its formation is pathogenic microorganisms.
Recently, there has been an increase in incidence against the background of increasing resistance of the pathology to traditional methods of treatment. This disease is rare in children; the average age from the onset of the first rash is 5 years. In many patients it is accompanied by atopic dermatitis. Deterioration of the condition occurs most often in the winter season.
Symptoms of microbial eczema
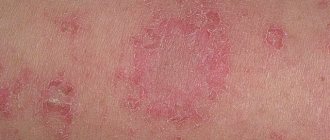
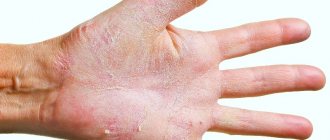
The general clinical picture of eczematic skin lesions is as follows: eczema is located around the main wound, at the site of postoperative scars or varicose veins (microbial eczema on the legs). Inflamed, clearly defined spots with uneven edges appear. The spots begin to shed the stratum corneum, which leads to the formation of layered accumulations of purulent crusts. Weeping and itching begins, seropapules and papulovesicles appear. There may be small, dry, scaly patches around the affected area.
Depending on the place of occurrence and external signs, the following types of microbial eczema are distinguished:
- Nummular eczema (also called coin-shaped or plaque eczema) is most often localized on the hands. The lesions look like coins with a diameter of 1-3 cm with clearly visible edges. Damaged skin swells slightly and becomes covered with purulent gray crusts.
- Varicose eczema develops in areas of varicose veins. Mainly affects the lower extremities at the sites of trophic ulcers or when the skin is injured at the sites of varicose veins. Microbial eczema of the legs is characterized by a large number of lesions with clear boundaries; the disease is accompanied by itching.
- Post-traumatic eczema can appear anywhere where the skin has been injured, and due to reduced immunity or illness, it does not heal for a long time.
- Sycozyform eczema - appears in areas where the skin is affected by sycosis (inflammation of the hair follicles, which is more common in men). Typical locations are the beard, upper lip, armpits and groin area. Weeping and itchy lesions are red in color; often the inflammation affects not only the hairy area, but also spreads beyond the boundaries of the hair growth.
- Nipple eczema occurs in women during breastfeeding when infection gets into microcracks. In the area of the areola, red lesions are formed, covered with dry crusts, there is severe itching, and painful sensations due to constant irritation of the nipples during feeding.
Lack of timely treatment for microbial eczema can lead to the appearance of secondary allergic rashes. The further course of the disease leads to the fact that areas of the affected skin grow, the rashes merge into one large plaque, and erosion spreads to healthy skin.
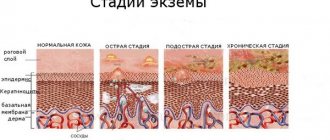
Stages and degrees of coin-shaped eczema
Nummular eczema develops as follows:
- Erythematous stage. Individual pockets of redness appear, most often on the legs and arms, which then spread to the torso.
- Papular stage. Cavityless nodules appear on inflamed and swollen skin.
- Vesicular stage. Gradually, point erosions and bubbles filled with liquid form.
- Wet stage. The bubbles burst and the affected areas become wet.
- Cortical stage. After the skin lesions resolve, crusts form.
These changes can occur either gradually or simultaneously. The presence of several types of rashes at once is a characteristic sign of this type of eczema.
The severity of the disease is assessed according to several parameters:
- erythema (redness);
- getting wet;
- formation of compactions in the skin;
- the presence of vesicular-pustular rashes associated with infection with staphylococci or streptococci;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- area of skin affected.
The total score for these parameters can range from 3 to 36, and the degrees of severity are distributed as follows:
- mild – <15 points;
- average – 16-25 points;
- severe >25 points.
Diagnosis of microbial eczema
If you notice any symptoms similar to those described above, contact your dermatologist to confirm or refute the diagnosis.
The secondary nature of the development of the disease will allow the doctor to assume microbial eczema. However, for an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to take a scraping or conduct a bacteriological culture to identify the infectious nature of eczema and find out its exact causative agent.
A histological examination is also carried out to exclude other skin diseases: dermatitis, psoriasis, pemphigus, etc.
Types of coin-shaped eczema
Coin-shaped eczema, the causes and treatment of which are described above, can occur in 3 main forms:
- Spicy. Various elements of the rash (nodules, blisters) are observed on the reddened skin.
- Subacute. Characteristic signs of this form are redness, thickening of the skin, crusting, and peeling.
- Chronic, in which there is weeping, increased skin pattern, change in skin color (pallor or, conversely, darkening), pain.
Microbial eczema: how to treat it
When treating microbial eczema, the main emphasis is on combating the primary disease, as well as relieving the unpleasant symptoms of eczema itself (itching, skin irritation, weeping).
- Depending on the primary disease, drug therapy for infections, ulcers, and treatment of varicose veins and microbial eczema on the legs is prescribed.
- In parallel, local treatment is necessary to heal the skin and prevent the spread of infection. For this purpose, hormonal ointments, creams with an antimicrobial component, compresses, and antiseptics are used.
- If necessary, systemic antibiotics are prescribed.
- When treating microbial eczema, antihistamines are prescribed, which can eliminate itching and other allergy symptoms.
- In the absence of contraindications, the patient is prescribed physiotherapy: ultraviolet irradiation. UHF, ozone therapy, laser therapy.
- To improve the patient’s condition, it is necessary to maintain a healthy lifestyle: get enough sleep, reduce stress levels, switch to a hypoallergenic diet, take vitamins./li>
- It is important to avoid injury to the affected area of the skin and pay special attention to its hygiene.
Ointments for microbial eczema
In severe cases of the disease, local therapy using hormonal ointment is prescribed.
In some cases, your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic ointment to “kill” the infection.
Once the main symptoms have subsided and the eczema is no longer active, you can use skin healing products. La-Cri medicinal cosmetics are perfect for this. All products have a non-hormonal composition with natural ingredients.
- Seed extract has an anti-inflammatory effect, relieves itching and redness.
- Violet extract soothes irritation.
- Panthenol and avocado oil promote rapid regeneration, soften and moisturize the skin.
- Walnut extract has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and healing effects.
What are the symptoms of eczema in intimate places?
Eczema in the groin in women and men usually occurs polymorphically, i.e. At the same time, the patient can notice papules, weeping areas, peeling, and serous cortical surfaces. The aesthetic defect of the disease is not the only problem that the disease causes the patient.
Foci of eczema in the groin at any stage are accompanied by the following sensations:
- severe constant itching;
- swelling;
- pain when touching, walking and physical activity;
- burning sensation and swelling;
- thickening and pigmentation of the skin during healing.
Eczema in the groin (especially common in men) causes a decrease in performance, prevents proper rest, which entails neurotic disorders. The patient suffers from insomnia, becomes irritable and weakened. Constant scratching often leads to bacterial or fungal infections.
Microbial eczema: treatment with folk remedies
If you are diagnosed with microbial eczema, you should not indulge in self-medication. Traditional medicine can be used as an auxiliary measure in combination with drug treatment and after consultation with a doctor.
There are a large number of “grandmother’s” recipes to relieve symptoms of the disease.
- It is effective to use fish oil in liquid form. Use it as a lotion: moisten gauze and apply to the area affected by eczema.
- Take 1 chicken egg white, 1 tbsp. spoon of fresh cream, 1 tbsp. a fly in the ointment. Mix thoroughly until smooth and apply as an ointment to the affected area of skin.
- Take equal parts of pure tar, yellow sulfur powder, and copper sulfate, burn over a fire until a white powder forms. Pour water over the powder and boil for 5 minutes, stirring constantly. Use the resulting mixture to lubricate microbial eczema until it is completely cured.
- Take a bunch of grapes with seeds, mash them and apply the resulting pulp to the affected skin. Cover the top with parchment paper and let sit all day. After the procedure, try not to wet the eczema for 4 hours.
- Pour 6 tbsp. spoons of viburnum with 3 cups of boiling water, leave for 4 hours. Take half a glass of infusion orally 4 times a day.
- Pour 8 g of crushed marshmallow root with cold water, soak for 1 hour, strain the resulting solution through cheesecloth. You can add honey or sugar to improve the taste. Take 2-3 tbsp orally. spoons every 2 hours.
Sources:
- Skin diseases of newborns and infants. Guide for doctors / Gorlanov I. A., Leina L. M., Milyavskaya I. R., Zaslavsky D. V. St. Petersburg: Folio. 2021.-208 p.
- Fokina R.A., Atopic dermatitis: stages of development of classification forms, Siberian Medical Journal, 2007 https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/atopicheskiy-dermatit-etapy-razvitiya-klassifikatsionnyh-form
- A.N. Pampura, A.A. Chuslyaeva, Modern approaches to the treatment of atopic dermatitis in children https:/cyberleninka.ru/article/v/sovremennye-podhody-k-terapii-atopicheskogo-dermatita-u-detey
Photos of eczema
Photo album on the diseasePrevention of coin-shaped eczema
Coin-shaped eczema, the causes of which can be different, requires an integrated approach. After drug treatment, it is necessary to adhere to preventive measures that help avoid relapses.
These include:
- dietary nutrition, exclusion of foods that are allergens or lead to deterioration of the gastrointestinal tract (citrus fruits, eggs, chocolate and cocoa, hot seasonings, tomatoes, legumes, mushrooms, caffeine-containing, alcoholic and carbonated drinks; concentrated broths and fatty foods, nuts, whole milk );
- eliminating stress;
- using skin moisturizers;
- avoiding contact with allergens;
- wearing clothes made of hypoallergenic materials;
- use of neutral detergents;
- regular cleaning of the living space and humidification of the air.
Medications for the treatment of eczema in the groin area
To overcome the external manifestations of dermatosis, you will have to resort to a whole range of drugs and medicines. These include:
- Antimycotic drugs (Flucinar, Mycoseptin, Terbinafine, Lamisil, Ungusan, Clotrimazole). These agents have antifungal, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Antimycotic ointment for eczema in the groin is a mandatory medication, without which treatment will not bring the expected effect.
The external manifestation of eczema (dermatosis) can be overcome with the help of special medications, one of which is Flucinar ointment
- Hormonal ointments (Triderm, Soderm, Dermovate, Elokom). The drug must be prescribed by a doctor; the specialist also determines the method of use and duration of the course. They help eliminate itching, swelling and hasten the onset of healing, however, such medications cannot be used for more than 7-10 days - they are fraught with side effects.
- Non-hormonal ointments for eczema on the pubis and groin (zinc, ichthyol, naphthalan). Absolutely safe products without corticosteroids are usually prescribed to continue anti-inflammatory therapy after the end of the hormonal course.
- Antihistamines (Tavegil, Zyrtec, Loratadine, Claritin). You can suppress an allergic reaction that occurs due to poor diet or wearing synthetic underwear with the help of antihistamine tablets and drops. Often, the doctor recommends long-term use of such medications.
- External lotions (silver nitrate, furatsilin solution, Fukortsin, Resorcinol, iodine solution). These drugs are used as local antiseptics, they also help relieve inflammation. Treatment of painful eczematous spots is carried out before applying medicinal ointments.
Eczema in the groin in women and men, complicated by the spread of symptoms to the genitals, requires regular washing and wiping the skin folds dry. For complete adsorption of exudate from erosions in order to prevent microbial infection after bathing, you can use pharmaceutical talc and baby powder.
What causes skin pathology in the groin?
Considering the causes of eczema in the groin, it is worth noting that the disease occurs against the backdrop of a weakening of the body’s defenses. As a rule, it is the mycotic lesion of the epidermis in the intimate area that plays a predetermining role in the development of the disease.
Several main factors can provoke the appearance of fungal microorganisms in the groin area:
- excessive sweating;
- lack of hygiene;
- wearing low-quality synthetic underwear;
- high temperature and high air humidity;
- overweight, obesity;
- allergic reaction;
- skin damage;
- poor blood circulation.
Unlike manifestations of dermatosis in the stronger sex, eczema in the groin in women, as a rule, also affects the external genitalia. If left untreated, the disease affects the areas under the mammary glands, and foci of inflammation gradually appear on the extremities.
The fungal pathogen Epidermophiton floccosum, whose name served as the name for epidermophytosis, gets on the skin in the groin area when:
- disturbances in the functioning of internal organs;
- change of climate zone;
- deterioration of working conditions;
- deviations in normal metabolic processes;
- nervous disorders;
- injury to the upper epidermal layer.
Treatment
This pathology in men and women is treated according to the same principles. In order to prevent the expansion of the affected area, it is necessary to eliminate the factors that contributed to the introduction and parasitism of the fungus on the patient’s epidermis. That is, it is required:
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- Replacing synthetic underwear with underwear made from natural fabric (for example, cotton).
- Treatment of endocrine diseases.
- Loss of body weight.
- Controlling excessive sweating and other measures that prevent the creation of favorable conditions for fungal colonies to thrive.
Medicines
This pathology will need to be treated with the help of antifungal agents, which are designed to inhibit pathogenic microflora and suppress its growth. In severe cases, complex drugs are used, the active ingredients of which are hormones and antifungal components (Travocort).
As additional therapy use:
- Antihistamines (Claritin, Fexadin, Loratadine, Zyrtec, Suprastin), which reduce burning and itching.
- Drying agents in the form of lotions and pastes for weeping (this can be decoctions of chamomile, string, oak bark, Resorcinol or zinc paste, salicylic-sulfur, sulfur-tar).
- Antiseptic drugs (fucorcin, iodine and silver in the form of solutions).
- Mild sedatives.
The last group is used if the patient complains of sleep disturbances and increased irritability associated with constant discomfort. Such complaints appear especially often in typical localization of lesions (that is, in the intimate area).
This disease, especially in its advanced form, should be treated comprehensively. That is, using local agents (external antibiotics) and general ones (tablets). A popular means of combating fungus today is Triderm. Clotrimazole, Lamisil and other proven drugs are also used.