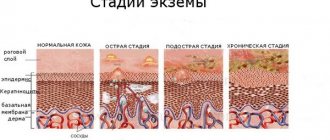
Infectious dermatitis is an inflammatory process caused by a microbial agent. This includes a virus, bacteria, fungus. They are concentrated both in the skin and can circulate in the body.
In the latter case, microbes release substances into the blood that have a toxic effect on the skin. In children, infectious dermatitis includes measles, rubella, chickenpox, scarlet fever and enterovirus infection. The article contains all the information about infectious dermatitis, including causes and treatments on the legs, arms and other parts of the body.
Reasons for appearance
The pathological process develops against the background of various infections. They can affect epithelial tissue or be transmitted sexually.
The risk of developing dermatitis increases with:
- the effect of high or low temperatures on the body;
- deep skin injuries and small cracks;
- long-term use of cytostatic and glucocorticosteroid drugs;
- varicose veins;
- immunodeficiency;
- long-term intoxication;
- chronic forms of diseases of the digestive system;
- disorders in the nervous system;
- kidney diseases;
- diabetes mellitus;
- lack of proper hygiene;
- individual intolerance of the body to bacteria that provoke decay.
Allergic dermatitis ICD code 10 – Dermatitis
Included: allergic contact eczema
Excluded:
- allergy NOS (T78.4)
- dermatitis: NOS (L30.9)
- contact control unit (L25.9)
- diaper (L22)
- caused by substances taken orally (L27.-)
- century (H01.1)
- simple irritable [irritant] contact (L24.-)
- perioral (L71.0)
If it is necessary to identify the drug, use an additional code for external causes (class XX).
Excluded:
- allergy NOS due to drugs (T88.7)
- drug-induced dermatitis (L27.0-L27.1)
Excludes: food-related dermatitis (L27.2)
Allergic contact eczema NOS
In Russia, the International Classification of Diseases
10th revision (
ICD-10
) was adopted as a single normative document for recording morbidity, reasons for the population’s visits to medical institutions of all departments, and causes of death.
ICD-10
introduced into healthcare practice throughout the Russian Federation in 1999 by order of the Russian Ministry of Health dated May 27, 1997. No. 170
The release of the new revision (ICD-11) is planned by WHO in 2022.
Sources used: mkb-10.com
Symptoms
Infectious dermatitis is the result of an infectious disease, so the rest of the clinical picture depends on the original cause.
Measles
The rash will spread throughout the body within 14 days:
- In the first day, the face, possibly the neck and part of the chest are affected.
- The rash then spreads to the rest of the body.
- On the third day, the rash completely stops and the disease develops. There is an increase in body temperature.
Scarlet fever
There is a rash with blisters containing a yellowish liquid. Such bubbles are observed for 5 days. After this, crusts form, which peel off greatly.
Typhus
Dermatitis does not appear immediately, but after 2-3 days. The rash can be localized to:
- breasts;
- stomach;
- hands.
After 2 days, the skin in some places becomes covered with pigment spots. The rash itself has clear boundaries.
Chicken pox
Chickenpox can occur on different parts of the body. The resulting rash leads to severe itching. It appears in a specific sequence:
- Initially, individual pink spots form.
- In place of the spots, bubbles form, inside of which there is a clear liquid.
- After 3-4 days, there is more fluid than initially.
- The blisters burst on their own, become covered with a crust and heal.
With infectious dermatitis that occurs against the background of chickenpox, it is possible:
- temperature increase;
- edema;
- itching
Types of pathologies
Allergic dermatitis with ICD-10 code L23 is divided into several types:
- Contact - occurs as a reverse reaction of the body to an external irritant, which develops immediately after the skin comes into contact with the allergen and manifests itself in the form of redness, rash, blisters at the site of contact.
- Toxic-allergic (toxidermia) - develops as the body’s response to an allergen entering the respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract or through injection, which manifests itself as a rash throughout the body.
- Atopic - is the cause of a combination of respiratory disease and chronic skin damage, which leads to the formation of a wet rash with symmetrical outlines of the rash areas.
- Fixed (erythema) is a local minor inflammation of the skin in the form of clearly shaped purple spots that appear in response to sulfonamide substances.
Most often, excessive sensitivity develops to a single irritant or to a group of similar substances.
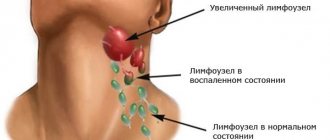
Diagnosis of infectious-allergic disease
The first step is to be examined by a dermatologist. He takes a sample of infected skin for bacteriological culture. This will allow us to determine what led to the development of the pathological allergic process.
Dermatologists use two diagnostic methods:
- virological;
- serological.
If it is difficult to determine the cause of the disease, then a biopsy specimen is used.
Diagnosis of contact dermatitis
The basis of diagnosis is a thorough study of the disease history, assessment of the prevalence and nature of morphological elements and the results of skin patch tests.
If indicated, a consultation with an allergist is scheduled.
Differential diagnosis
A number of skin diseases may have a clinical picture similar to contact dermatitis and require differential diagnosis. Among them are conditions in which the skin pathological process is the main manifestation of the disease (atopic dermatitis, dermatophytosis, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, scabies, lichen planus, etc.) and a number of systemic diseases (acrodermatitis enteropathica, porphyria cutanea tarda, phenylketonuria, etc.) .
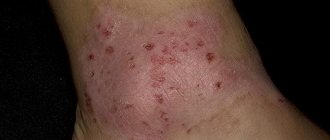
Locations with photos
Infectious dermatitis rashes can affect the following parts of the body:
- scalp;
- neck;
- forehead;
- wrist;
- extensor limb surfaces;
- groin area.
Below are photos of the disease on the legs and arms:
Treatment
Due to the complexity of the course of infectious dermatitis, its treatment must be comprehensive. In this case, it is necessary to take into account concomitant pathology. The main attention is paid to the treatment of infection.
Medication
For external treatment, the following groups of medications are used:
- Antibacterial agents. They eliminate colonies of microorganisms and stop their reproduction: Levomycetin, Erythromycin.
- Antiseptics with a disinfecting effect: Chlorhexidine.
- Glucocorticosteroids. They relieve itching and inflammation: Betadine, Advantan or Cortomycetin.
Oral medications are also included in the treatment regimen. Their action is aimed at eliminating fungi and bacteria. The following drugs have been developed:
- Lefoxcin.
- Leflobakt.
- Ciprobay.
- Ciprobid.
Folk remedies
You can treat infectious dermatitis at home using the following recipes:
- Take 20 g of St. John's wort herb and pour a glass of hot water. Place the mixture in a water bath and simmer for 15 minutes. Mix the filtered and cooled broth with 100 g of butter. Use the resulting ointment to treat affected areas 3 times a day. The course of therapy is 7-8 days.
- Dissolve 40 g of soda and salt in 3 liters of water. Treat the rash areas with the resulting mixture 3 times a day.
- Grind raw potatoes using a grater. Use the paste as a compress, which is applied for 15 minutes.
- Dilute celandine juice in boiled water in a ratio of 1:2. Use a lotion and apply for 15 minutes. As the inflamed areas decrease, you can add honey as a filler.
- Pour 20 g of chopped string and 100 ml of boiling water. Infuse the mixture until it turns dark brown. Soak a gauze bandage in the resulting solution and apply it to the affected area 3-4 times a day. The skin will recover within 2-3 days.
Important! Traditional methods of therapy will not cure the disease, since they do not act on the cause of the rash, but only relieve symptoms such as itching, swelling and discomfort.
Physiotherapy
This method of therapy is used as a simulating measure of influence on the human immune system in dermatitis. Physiotherapy can improve the patient’s condition after 2-3 sessions. The therapeutic method includes a set of specially selected procedures that help the body quickly adapt to the infectious processes that have affected it:
- magnetic therapy;
- ozone therapy;
- UHF;
- Ural Federal District;
- laser therapy.
Allergic dermatitis according to ICD-10 code
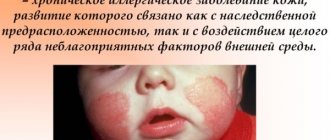
Allergic dermatitis according to ICD-10 code is a pathology affecting the epidermis. It occurs due to an inadequate immune response to an irritant and occurs with inflammation. Characterized by a rash on the skin.
Usually the disease is detected in childhood and is not eliminated until the end of life. With proper therapy and adherence to nutritional rules, it is only possible to avoid relapses.
To successfully prevent the recurrence of symptoms, it is worth familiarizing yourself with all the features of dermatitis.
Mkb 10 what is it
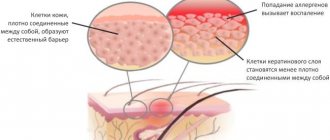
Allergic dermatitis, with ICD code 10, is one of the most common forms of allergies. Pathology is a phenomenon that occurs when the body’s protective properties do not function properly. The production of antibodies begins, aimed at destroying the irritant.
As a result of this process, an inflammatory response develops: immunoglobulin-sensitive IgE mast cells or mastocytes release histamine and heparin into the tissue. This causes redness and itching of the skin. Manifestations such as spasm of bronchial smooth muscles and severe swelling of the mucous membranes are fraught with death.
Diagnosis code – l23 9 allergic dermatitis.
There is a similar form of the disease – atopic dermatitis. The disease is often detected in children under 1 year of age and is genetically determined. It often goes away on its own after puberty.
Causes of allergic dermatitis
ICD code: allergic dermatitis appears in children and adults suffering from a hereditary or acquired tendency to allergies. Among the provoking circumstances are:
- skin or respiratory tract contact with chemicals;
- use of cosmetics;
- use of food additives;
- helminthic infestations;
- taking medications;
- stress, nervous shock;
- interaction with some plants.
With regular or one-time contact with an allergen, sensitization of the body occurs. Dermatitis develops after penetration of an irritant in one of the following ways:
- through the skin;
- Gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory organs;
- intramuscular or intravenous injections.
A small dose of the allergen is enough to develop an inadequate immune response. The period after the irritant enters the body and the onset of symptoms lasts from several minutes to days.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Allergic contact dermatitis is characterized by various symptoms. These include:
- eczema on the skin of the upper extremities;
- white spots on the epidermis of the facial area;
- rashes of various types - small pimples, blisters, papules;
- skin redness;
- swelling, itching of soft tissues.
With toxic-allergic dermatitis, hyperthermia, headaches, and spasms in joints and muscles occur. The disease is usually diagnosed in children and is accompanied by an urticarial, bullous rash.
The diagnosis is established by identifying a combination of 3 major and at least three minor criteria in the patient. Among the major diagnostic characteristics of allergic dermatitis are:
- repetitions of painful symptoms;
- hereditary predisposition;
- typical localization of rashes;
- pronounced itching of the skin.
Allergic dermatitis is classified as an inadequate reaction of the protective properties of the delayed type, in which the main role is played not by antibodies, but by immune cells, primarily lymphocytes. Symptoms differ in children and adults. In the first case, the clinical picture is more intense, due to the fragile protective functions of the body.
Additional and minor diagnostic criteria include:
- development of pathology in the first years of life;
- increased levels of IgE antibodies;
- hyperkeratosis of the follicular type, affecting the skin of the elbows, forearms, and shoulders;
- white spots on the shoulder girdle and face;
- folding of the soles, palms, neck;
- white dermographism;
- regular lesions of the skin by herpesvirus, fungi, staphylococcus;
- nonspecific dermatitis of the extremities;
- hyperhidrosis;
- ichthyosis, xerosis, peeling of the skin after bath procedures.
Using skin tests, the cause of dermatitis is determined. To determine the irritant, test strips impregnated with various allergens are used. They are fixed on the problem area of cleansed skin. After some time, they are removed and the changes are assessed. To find out about the presence of a concomitant disease, additional diagnostics are performed:
- urine test;
- biochemistry of blood plasma;
- blood sugar;
- general analysis of stool.
If the need arises, the patient is referred to a consultation with an endocrinologist or gastroenterologist.
Types of allergic dermatitis ICD 10
Unspecified dermatitis has the following classification.
| L23.0 | Metals provoked a negative reaction |
| L23.1 | Symptoms caused by adhesive elements |
| L23.2 | Intolerance to cosmetic products |
| L23.3 | Pathology caused by drug use |
| L23.4 | Symptoms of intolerance occurred after interaction with dyes |
| L23.5 | Allergy to chemicals |
| L23.6 | Immune rejection of certain foods |
| L23.7 | Plant intolerance (except food species) |
| L23.8 | Dermatitis is caused by other factors |
| L23.9 | Unexplained skin intolerance |
Since the disease does not have an infectious etiology, it is not transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person.
Treatment
The therapeutic regimen is selected individually and includes the use of tranquilizers, antiallergic, detoxification drugs, and anti-inflammatory drugs. They widely resort to specific hyposensitization, PUVA therapy, plasmapheresis, acupuncture, and a fasting-dietary course.
Standard drug regimen for eliminating allergic symptoms.
- Antihistamines are indicated to reduce skin itching, swelling, and in atopic syndrome - runny nose, asthma. Using first generation antiallergic drugs (Suprastin, Diazolin, Tavegil) daily, it is important to remember that they are quickly addictive. They need to be changed every week. Getting through the blood plasma into the brain tissue, first-generation drugs have a calming effect; they should not be taken by students, schoolchildren, drivers and other people whose activities require concentration. Second generation medications - Loratadine, Ebostin, Cetirizine, Astemizole - are less fraught with side effects and are practically non-addictive. They are prescribed in a course of 1 week.
- Hormones. They are used only for unbearable, severe itching, in a limited manner. Preference should be given to Metypred, Triacinolone. They are used for 3-5 days to eliminate attacks with a gradual reduction in dosage.
- If dermatitis is accompanied by intoxication, intensive therapy is prescribed using intravenous agents - Hemodez, Reopoliglyukin, polyline or saline solution. High results are achieved by hemosorption and plasmapheresis. These are special techniques for purifying blood plasma.
- In case of intense symptoms, they resort to light therapy. Ultraviolet radiation is carried out in 3-4 procedures per week, causing virtually no negative consequences.
- If an infection occurs, broad-spectrum antibacterial agents are required. Among the effective medications are Erythromycin, Vibramycin, Rondomycin for a course of 7 days.
- Hormonal drugs are used in external therapy, among them Celestoderm, Elokom, Triderm, Advantan in the form of ointment or cream.
Children over 9 years old are prescribed drugs of the tetracycline group - Doxycycline, Tetracycline. If a herpes infection occurs, Acyclovir and Famvir are indicated.
In the acute phase, when allergic dermatitis coded ICD-10 is supplemented by weeping ulcers and crusts, lotions soaked in Burov’s liquid, chamomile, and tea infusion are used.
After eliminating the acute stage, naftalan oil 2-10%, tar 1-2%, ichthyol 2-5% and sulfur are used.
For therapy to be effective, you should avoid interacting with the irritant: change cosmetics, use a more gentle powder, choose new clothes made from natural fabrics.
If the allergen is microscopic dust mites, choose pillows and blankets with synthetic down, and wash your laundry every week. It is recommended to do wet cleaning once every 2 days and wipe off dust daily.
Allergic dermatitis with code according to ICD-10, provoked by food products, requires adherence to a dietary menu. Food that causes an inadequate immune response is excluded from the diet. Dermatitis usually develops after consuming the following products:
- citrus fruits – grapefruit, orange, tangerine, lemon;
- nuts;
- coffee;
- chocolate;
- strawberry;
- any eggs;
- seafood;
- red meat;
- legumes.
Fried, smoked, salty foods should be avoided. They contain a lot of food coloring, aromatic additives, flavoring agents and preservatives. Before cooking, soak cereals for 10 hours, pour boiling water over fresh fruits and vegetables, and steam the meat. During therapy, it is better to refuse to eat in cafes, canteens, restaurants, and to eat at home.
Source: https://allergia.expert/allergicheskie-zabolevaniya/kozhnye-zabolevaniya/allergicheskiy-dermatit-po-kodu-mkb-10.html