Melanin and melanocytes
The natural pigment (dye) is melanin. In humans, it is present in hair, skin, retina and iris, and in the brain . The amount of melanin determines the intensity of skin color, eye color, and the ability to perceive a tan.
There are three types of melanin:
- Eumelanin is brown or black in color.
- Pheomelanin is yellow in color.
- Neuromelanin is a special type of pigment found in the brain.
In the skin, melanin is formed thanks to melanocytes - special cells that have many processes. The thyroid gland secretes thyroxine, which is captured by them and converted after oxidation into melanin. With the help of melanocyte processes, it enters skin cells and is deposited in them.
Melanin is not only a pigment, it has many functions. Among them:
- Antioxidant. Protects cells from the destructive effects of certain toxic substances and radioactive radiation.
- Increases the body's resistance to stress.
- Makes emotions stable, preventing excessive emotionality.
- Regulates the processes of sleep and wakefulness.
The human body is completely devoid of melanin due to a hereditary disease - albinism . It is known that albinos suffer from various diseases more often than others.
Why do moles appear?
An intradermal melanocytic nevus is a cluster of specially pigmented cells. Factors leading to the appearance of moles on the skin:
- ultraviolet radiation;
- phototherapy;
- severe skin damage;
- burns;
- some dermatological diseases;
- hormonal disorders;
- immunodeficiency.
Many people have probably noticed how new spots appear on the skin after severe sunburn. Exposure to sunlight can lead to disruption of pigment production and the formation of spots of any size.
In childhood, new moles often appear after a course of phototherapy. There is also an increase in the number of spots with atopic dermatitis in newborns.
Disturbances in skin pigmentation and the appearance of new age spots and moles are often observed after burns. Household, chemical and sunburns, accompanied by the formation of large blisters on the skin, are one of the common causes of the appearance of acquired melanocytic nevi.
Certain inflammatory processes and skin infections can also cause melanocytic spots to develop. The appearance of moles after treatment for lichen is often noted.
The formation of new moles is observed in women during periods of hormonal changes in the body. So, spots can appear on the body during puberty, pregnancy and at the onset of menopause.
The appearance of congenital melanocytic nevus is due to the peculiarities of intrauterine development of the fetus.
Causes of nevi
Most researchers are confident that all melanocytic nevi, including those that arise throughout a person’s life, have a congenital basis for their appearance . Skin developmental disorders leading to their formation occur in the embryonic period.
All the causes of dysplastic nevi have not yet been well studied. But the main sources include:
- Various fluctuations of hormones in the body of a pregnant woman: estrogens and progestins.
- A pregnant woman has a genitourinary tract infection.
- During pregnancy, adverse factors such as toxic substances and radiation influence.
- Presence of genetic disorders.
All these factors do not have the best effect on the development of special cells - melanoblasts , which should transform into melanocytes. Instead, it leads to the fact that melanoblasts are deposited in certain areas of the skin and turn into nevocytic cells.
Neocytes have two features that distinguish them from normal melanocytes:
- They do not have processes through which the pigment could spread to other cells.
- Dysplastic nevi are not able to obey the general systems of the body well, but have not completely lost this ability, unlike cancer cells.
It is believed that no new melanocytic nevi appear throughout life, but only those that were not visible but existed from birth.
New melanocytic nevi can occur for a number of reasons:
- Hormonal changes in the body. In adolescence, most nevi most often appear.
- Pigment spots occur under the influence of ultraviolet rays. Therefore, frequent sunbathing and solariums lead to the growth of melanocytic nevi.
- Pregnancy. As already mentioned, during this period fluctuations in the level of sex hormones occur.
- Menopause.
- Use of contraceptives.
- Skin diseases, inflammatory and allergic rashes, for example, acne, dermatitis.
What is a melanoform nevus?
Benign formation has code D22, according to the international classification of diseases, and is formed by three different types of cells - nevus, dermal and epidermal. The location of the spots can be any - neoplasms can appear on any part of the body, arms, legs, face. If a melanocytic nevus is formed after birth, then the melanoform type of formations is congenital, but moles appear only in adolescence. Throughout life, spots can appear, disappear, and change size.
Symptoms and types of melanocytic nevi
Nevi can come in a variety of shapes, colors and sizes. still no consensus among the professional community of doctors regarding the name of the formations that should be called “nevus.” Therefore, one can observe how precancerous formations on the skin in the form of a tumor that does not contain the pigment melanin are called nevi.
- Vascular tumors are hemangiomas . It is often red in color and occurs in many newborn babies, but disappears during the first year of life. Many doctors also call it vascular nevus.
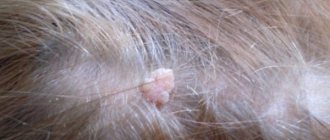
- Nevi of the sebaceous glands . Most of them are located on the head; they do not contain melanin. This neoplasm is more often called a sebaceous nevus.
- Teratomas (hamartomas) are congenital nevi, which are essentially congenital tumors. Consist of leather and other fabrics.
- Anemic nevus is a type of vascular mole. This is an area with underdeveloped vessels, hence its lighter color.
A true melanoform nevus is a formation consisting of altered cells - nevocytes.
Nevus melanocytic
There are a number of types of melanocytic nevi:
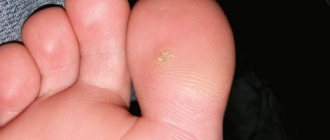
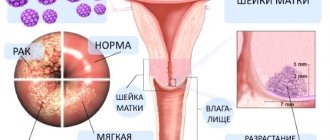
- Non-cellular borderline . This simple spot does not rise above the surface of the skin or protrudes slightly. It has clear contours and is brown in color. It can have different sizes and be located in different parts of the body. An accumulation of cells with pigment occurs between the epidermis and the dermis layer.
- Intradermal . It is a type of melanoform nevus. In this type, the accumulation of cells occurs in the thickness of the dermis.
- Pigment complex . It has the appearance of a mole: it rises above the surface of the skin, its color ranges from light brown to black. Often covered with coarse hair. It has a smooth surface and can be located throughout the body.
- Intradermal . It also protrudes above the surface, but feels lumpy and uneven to the touch. Almost always located on the neck or head. Often appears between 10 and 30 years. Over time, it separates from the skin; it seems to hang above the surface of the skin on a thin stalk. Almost always turns into a warty nevus. It forms irregularities, folds, and crevices in which dead cells are deposited. Microorganisms that can cause infectious processes can also accumulate.
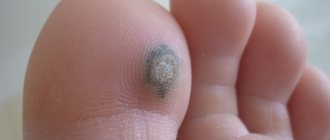
- Blue . So named because of its color. Melanin deposition occurs under the skin. It often occurs in people of Asian appearance. Dense and smooth to the touch, slightly raised above the surface of the skin, no hair. A blue mole is usually small, no more than 5 mm.
- Basal . Usually flesh-colored, therefore without pigment.
- Setton nevus is a special type of dermal nevus. An area of skin completely devoid of pigment is formed around the pigmented spot. Their origin has not yet been fully studied. A frequent companion is vitiligo (when there is no pigment on the skin) and melanoma. There is slight inflammation in the skin.
- Nevus Ota . Appears on the face in the form of “dirty spots”.
- Nevus Ita is similar to the previous type, but is located under the collarbone, in the area of the neck, shoulder blade, and chest. Most often found in people of Asian nationality.
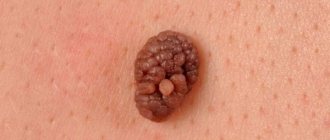
- Warty . It is similar to papilloma, is large in size, can often be found on the head and neck, but can also be present in other areas. It has an uneven surface, looks like a wart, and hair grows on it.
- Becker . It is most often found in boys aged 10–15 years. First, several small brown spots appear on the skin located nearby. Then they unite and form spots up to 20 cm with uneven contours. After which they become wart-like and covered with hair. It is believed that they grow due to the release of large amounts of androgens into the blood.
- Linear . This neoplasm appears from birth. On the skin there are many small nodules located in the form of a chain, the color of which ranges from light to black. The linear appearance can occupy 2 cm, or can stretch along the entire arm or leg. Sometimes hair grows.
- Eyes . Pigmented nevus is located on the iris. It is shaped like a spot and is clearly visible, and comes in different sizes and shapes. An ocular nevus may also be present on the retina. It is diagnosed by an ophthalmologist.
Treatment
Melanoma-dangerous moles must be removed surgically. The physician may make this decision based on three primary motivations, including:
- inconvenience caused by the mole rubbing against the skin or being cut off during shaving;
- the need to conduct a microscopic examination of the formation if there is doubt about the correctness of the diagnosis;
- aesthetic considerations.
Surgical removal
This method is indicated when neoplasms actively grow and occupy a large area, cause irritation, or are localized in hard-to-reach areas. During surgical excision, the nevus itself and part of the adjacent skin are removed. For children, the operation is performed under general anesthesia, for adults - under local anesthesia. The main disadvantage of removing a mole using a scalpel is the scarring that is left behind. This technique makes it possible to perform a biopsy of excised tissue. Possible dangerous complications of the procedure are:
- subcutaneous hemorrhage;
- wound infection;
- formation of a keloid scar at the site of the scar.
- Makeup for eyes with drooping eyelids
- Beaded keychains
- Quit smoking calendar
Cryodestruction
Using liquid nitrogen, carbonic acid or ice, the affected area is frozen, due to which a dense crust appears on the surface of the formation, and under it a new layer of dermis. As a result of cryodestruction, no defects in the form of scars remain. The advantage of the procedure is also the absence of pain or discomfort. However, cryodestruction is often effective, so it is usually performed several times. The method is applicable for removing small melanoma-dangerous moles.
Laser removal
As with cryodestruction, laser removal of melanoma tumors does not leave scars and is a painless procedure. However, the area of skin at the site of the nevus may become pale and noticeable due to a lack of pigment. During laser treatment, it is extremely important to completely remove the melanoma formation, otherwise there is a risk of complications or an increase in the size of the mole. This procedure is safe, so it is even used to remove vascular nevi on the face.
Radiosurgical removal
This technique began to be used recently; it involves exposing a melanoform nevus to a radioknife, which is a source of radiation. Radiosurgical removal is indicated both for unspecified moles and for the treatment of malignant tumors. The method is most effective for large nevi, and thanks to ultra-precise excision, only the mole is excised, and healthy tissue is not damaged. The wound is immediately cauterized and disinfected. When using radiosurgery, there is a risk of forming a small red scar.
Electrocoagulation
The impact on the nevus is carried out using high temperature. During cauterization of the medanoform formation, no blood is released, and there is no need to remove the skin adjacent to the mole. However, electrocoagulation brings significant pain to the patient; in addition, such an operation will not be able to remove a large melanoma tumor.
Complications of melanocytic nevi
The most dangerous to health is degeneration into a malignant form. A mole turns into a tumor (melanoma), which, if left untreated, becomes the most dangerous.
All of the types of nevi described above can develop into a malignant tumor, but the most dangerous are blue, borderline, and Ota.
Risk factors for developing melanoma are:
- Large moles from birth.
- They appear in middle and old age.
- Giant spots. The larger the size, the higher the likelihood of melanoma.
- A large number, more than 50, of non-waterermal nevi.
- Constant appearance of new moles
- Nevi that experience constant friction and impact from clothing.
- Frequent injury and inflammation of the skin in the mole area.
Symptoms of the beginning of the degeneration of a mole into melanoma can include:
- Rapid growth.
- The appearance of unpleasant sensations, for example, itching, pain, irritation, etc.
- Rapid color change and acquisition of black or blue color.
- Changes in the skin: bumpiness appeared, intensive hair growth began.
- Changing the shape of the spot with blurred contours.
- The mole is constantly wet or bleeds periodically.
- Peeling of unknown origin appeared.
If one of the listed symptoms appears, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Description
Melanoform nevi on the body are formed during intrauterine development of the fetus from cells that produce the pigment melanin. Its quantity determines the color of the formation. It does not appear immediately, but after a certain period after birth. With age, they may disappear or change on their own.
By its nature, a birthmark is benign, but sometimes it can degenerate into a malignant formation. This usually happens due to injury or hormonal imbalances in the body.
Congenital melanoform nevus is characterized by slow growth and changes with human development. It can be found not only on the surface of the skin, but also in the sclera and central nervous system, and even in the oral mucosa. There are many different types of it, which differ in shape. They can be barely noticeable points or occupy a fairly large area of the body.
The formations may be smooth, rough or warty. Hair also grows on them. Their location may be different:
- Face;
- Lips;
- Neck;
- Scalp;
- Hands;
- Legs.
It is imperative to constantly monitor birthmarks, as there is a significant risk of their degeneration into melanoma and do not forget that this is a rather serious problem that is difficult to cure.
Prevention of malignancy
At the moment, there are no specific ways to prevent the degeneration of nevi into melanoma. But those who are at risk still need to follow some rules:
- You should not stay outside for a long time between 11 a.m. and 5 p.m. During this period, the skin experiences strong exposure to solar radiation.
- Avoid strong tanning in areas where large nevi are located. Remember that in summer, even in cloudy weather, up to 85% of solar radiation is absorbed by the skin.
- Moles cannot be protected from the development of melanoma using special sunscreens.
- Tanning beds are also harmful to the skin as they have similar effects. This procedure is especially contraindicated for persons under 28 years of age, especially if there are age spots on the body.
- If existing moles behave suspiciously or new ones have appeared in large numbers, then you need to seek help from a doctor for examination and control.
Today, due to the unfavorable environmental situation, there is an increase in the frequency of transformation of moles into melanoma, especially in developed countries. In Russia, a malignant tumor occurs in 4 cases out of 100 thousand. Thus, in order to prevent the degeneration of a nevus, you need to carry out timely prevention of the disease and go to the doctor if you suspect melanoma.
Diagnostics
It is impossible to diagnose yourself. If suspicions arise, the doctor should examine the formation and, if necessary, take a smear. But this examination method carries a strong risk of causing microtrauma and the subsequent development of melanoma.
Therefore, more modern methods are often used for diagnosis, for example:
- Fluorescence microscopy. Oil is applied to the stain, and then using a demaskoscope this area is illuminated, and the cells that form the formation and the depth of their location are determined. This method of examination is absolutely painless and safe;
- Computer diagnostics. Using this method, you can obtain an image of a mole, after which its structure is studied, a diagnosis is established and treatment is prescribed;
- Laboratory diagnostics. The blood is analyzed for the presence of tumor markers in it, which indicate the development of melanoma.
The examination method is determined by the doctor, who then, based on the results, will select the type of treatment that will be most suitable.
Classification of the phenomenon
In addition to dividing into ordinary and cellular, nevus can be divided into several types according to other characteristics; first of all, it is divided into congenital and acquired. The first type is characterized by the fact that the baby is already born with skin tumors, the second involves the appearance of moles during life.
In the first case, the pigmented nevus can be small (less than 1.5 cm), medium (from 1.5 to 10 cm) and large (more than 10 cm). Medium and large neoplasms pose a particular danger to a child, since they more often than small ones lead to the appearance of a malignant tumor. For this reason, if moles or pigment spots more than 1.5 cm in diameter are found on certain areas of the skin of a newborn baby, he must be sent for examination.