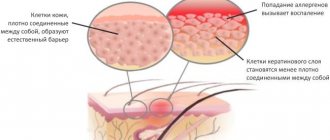
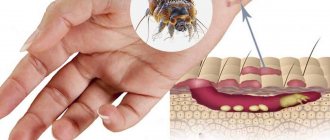
Fungus on the hands is a dangerous disease that affects the skin and nails. It is easy to become infected with mycosis, because spores of pathogenic fungi can be found anywhere. Peeling off along with the scales of the epidermis from the surface of the hands of an infected person, they settle on household items and are often found in public places. If there are wounds on the hands, microscopic spores penetrate through them into the epidermis and begin to develop. Another common route of infection is when a person suffers from foot fungus and self-infection of the hands occurs while caring for the feet. Since no one is immune from mycosis, it is important to know the signs of this disease, as well as effective treatment methods.
What is foot fungus
Recently, mycotic infection of the feet has spread to such a scale that almost every fourth inhabitant of the planet can become infected with it. Such sad statistics are largely due to a decrease in the quality of shoe products, which directly affects the condition of the feet. Thus, increased sweating of the feet, coupled with poorly breathable materials of your favorite shoes, boots and other fashionable items, create all the conditions for active growth of the fungus. The disease is transmitted from person to person. The risk of infection is especially high among family members of an infected person.
It is important to note that the disease often occurs after visiting public places: saunas, swimming pools, solariums. In addition, about 30% of diabetic patients suffer from mycotic foot infections. The initial signs of toenail fungus in such patients appear as the underlying pathology develops. Sugar surges, as a rule, provoke an exacerbation of mycosis. The causative agent of the disease feels at ease in the body with reduced immunity, so it is very important to monitor your own condition and correct any deviations in a timely manner.
What does foot fungus look like?
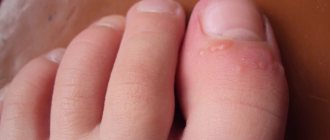
Symptoms of the disease vary depending on the location of the lesion. Therefore, by clearly understanding what foot fungus looks like, you will be able to take all measures to destroy the pathogenic agent even in the initial stages of the disease. So, if the feet are affected, deep cracks are found on the heels. When nails are infected (onychomycosis), yellow spots of different sizes are visible in the thickness of the plates, and hyperkeratosis of the subungual bed is observed. A crack with detached particles forms between the fingers. Severe itching occurs in this area and throughout the foot as a whole.
Symptoms of squamous foot fungus
With such damage to the feet, the infectious focus is usually localized on the outer layers of the skin; in some patients, there is an overgrowth of the nail plates. In addition, pronounced symptoms of squamous foot fungus are manifested by keratinization of the sole. The latter eventually turns into areas of rough callus with a further tendency to the appearance of deep heel cracks. The initial symptoms of foot fungus in the form of peeling skin and slight redness appear on one leg, but over time the infection spreads to the other limb.
Dyshidrotic form of fungus on the legs
This diagnosis implies that blisters appear on the surface of the patient’s foot. After these peculiar blisters burst, erosions form in their place. The situation is complicated by the fact that bacteria and viruses penetrate the wound surface, which subsequently cause inflammation of the skin. Judging by the photos of the legs of patients suffering from this form of mycosis, it can be understood that the disease has a long course. In addition to the main signs of the disease, lymphadenitis often occurs against the background of a secondary infection, and the temperature rises.
Intertriginous form
This type of mycosis affects the space between the fingers. With the intertriginous form of the disease, cracks appear surrounded by skin scales. Symptoms of fungus on the legs develop, as a rule, as a result of squamous mycosis. Thus, existing cracks are replaced by superficial skin lesions in the form of erosions. This form of infection in most cases takes on a long-term chronic course. In advanced stages of the disease, a streptococcal infection occurs. At the same time, the appearance of the feet leaves much to be desired:
- swelling occurs;
- areas of hyperemia (redness of the skin) are observed;
- purulent vesicles appear;
- an unpleasant odor appears.
Onychomycosis of the feet
This disease is characterized by negative changes in the nail plates. The pathological process begins with the appearance of yellow spots and stripes. Subsequently, the affected nail thickens and crumbles. The feet look very depressing. Changes in the color of the nail plate and its hyperkeratosis contribute to the fact that the patient develops many complexes, which can only be dealt with if the fungus is cured. In this regard, it is important to note that the duration and nature of the course of therapy depends on the form of onychomycosis, which can be:
- hypertrophic – involves a change in the color of the nail, its deformation and thickening;
- mold non-dermatophyte - does not develop independently, but only in the presence of symptoms of concomitant nail diseases;
- atrophic – characterized by complete destruction of the nail plate.
Candidiasis fungal infection of the feet
This form of the disease occurs latently. For this reason, only a specialist can help you answer the question of how to recognize foot fungus caused by yeast-like organisms. If you have the first signs of infection, you should immediately consult a doctor. A dermatologist will help determine the extent of the damage and tell you how to effectively prevent the fungus from spreading to healthy nails. It is important to know that the candidal form of mycosis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- hyperemia of the skin;
- the presence of swelling at the site of the lesion;
- the formation of small ulcers and blisters;
- the presence of severe itching.
- Greek surnames for women and men
- Flat warts: treatment and reviews
- Blastocysts in the stool of an adult - treatment of blastocystosis. What to do if blastocysts are found in stool
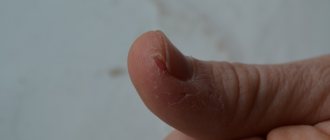
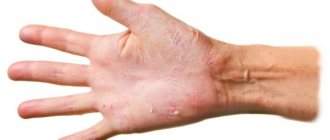
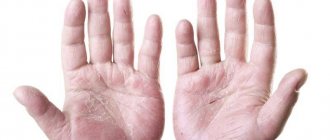
Candidiasis of the fingers
Candidiasis accounts for about 25% of all infections. In traditional societies, it is mainly women who suffer from it - they do the “lioness’ share” of caring for children, washing surfaces, dishes, laundry, cooking, etc. Sometimes yeast fungus on the fingers is called “housewives’ disease.”
The second large group of potential victims are people in “wet professions”, whose hands are constantly exposed to liquids - cements and solutions, soapy water, detergents, alkaline and acidic environments, etc.
Let's name food workers (canners of vegetables and fruits, confectioners, cooks, dishwashers), milkmaids, builders, cleaners and car washers, employees of bathhouses, spas, swimming pools, manicure and pedicure salons. Fungus on the fingers likes to settle on swollen and then dry skin.
They are the ones who can “miss” the first stage of development of fungus on the finger, because from constant exposure to water and an acid-base environment, the skin of their hands dries out, becomes rough, cracks and becomes horny (the so-called maceration phenomenon). Candidiasis has the same primary signs.
If the skin on your hands is fine, but disturbing symptoms appear on your fingers, you may have become infected with candidiasis like this:
- Through contact with a patient during a handshake, and the skin on your fingers was damaged and did not fulfill its protective functions;
- Through contaminated gloves;
- In a poorly sanitized nail salon;
- On our own behalf. Candida lives in the human body and is not always activated. They can affect smooth skin in large and small folds of the body, mucous membranes, genitals and mouth, nails and hair.
The first signs of nail fungus
The initial symptoms of infection are manifested by a slight change in the shade of the nails. In this case, the patient develops dull or slightly yellowish plates. Primary signs of fungus on the feet often do not cause concern and are attributed to insufficient treatment, which allows the pathological process to spread unhindered to healthy areas. In most cases, the infection affects the big toes, but it is not uncommon for onychomycosis to affect all of the patient's toes.
White plaque on legs
This symptom is evidence that a person has candidal mycosis. The clinical picture of the disease begins with peeling of the skin. Subsequently, the dermis peels off and turns from scales into white flakes, which, falling off, create a “dust effect” on the legs. Something similar can be observed in older people, whose immunity is not able to resist the spread of infection.
Types of disease
The causative agents of fungal diseases are 3 types of fungi:
- yeast;
- dermatophytes;
- moldy.
Each species can develop in conditions of high humidity and temperature, affecting not only the areas between the fingers, but also the nail plate. Most often, mycosis is caused by dermatophytes - they affect the interdigital areas, starting with the area under the little finger and thumb.
Diagnostics
External symptoms of foot fungus are nonspecific. Experts classify pathological changes in the nail plate or skin of the foot only as the occurrence of a painful condition, the cause of which must be established. So, to confirm the preliminary diagnosis, the doctor gives the patient a referral for the following laboratory tests:
- microsporia;
- cultural research;
- DNA diagnostics.
Prevention methods
It is easier to prevent pathology than to treat it.
To do this, there are several rules that must be followed:
- in case of prolonged contact with liquid, it is necessary to wear personal protective equipment - gloves;
- if the lesion worsens, it is recommended to avoid interaction with water;
- normalization of diet is a source of good health;
- abstaining from bad habits will help avoid any defeats;
- compliance with personal hygiene standards and the use of individual underwear, clothing, shoes - a guarantee of the absence of fungus;
- special attention should be paid to the prevention of stress, depression, and relaxation.
At the first suspicion of interdigital mycosis, you must contact a specialist who will establish an accurate diagnosis and select the correct treatment.
Treatment
In the early stages of fungal infection, the use of external antimycotics is justified. It is important to note that more than 70 clinical studies conducted in the Russian Federation have confirmed the high effectiveness of terbinafine-based drugs. In addition, for obvious symptoms of mycosis, it is recommended to use fungicidal foams, ointments and gels. In the case of extensive lesions, systemic therapy is carried out, which involves oral administration of antifungals.
Recently, it has become much easier to get rid of mycosis with the help of a medical pedicure. This procedure is carried out using modern equipment under conditions of absolute sterility. Photos of patients' feet before and after a hardware pedicure session are very impressive. With all this, there is often a need for surgical removal of the infected area, which in most cases is fraught with the dyshidrotic form of leg lesions. Meanwhile, for systemic therapy of less advanced cases of the disease, the following treatment regimens are used:
- Classic - tablets must be taken daily throughout the course.
- Short – the medication ends before the new nail grows.
- Pulse therapy - the use of antimycotics is carried out at long intervals, significantly exceeding the time of the treatment course.
- Intermittent - taking medications is combined with short periods of rest from them.
Remember that therapeutic measures help to completely get rid of the annoying fungus only if you follow all the recommendations of specialists for the prevention of mycotic lesions. Particular attention must be paid to proper disinfection of shoes and socks. In addition, it is recommended from time to time to carry out preventive courses against foot fungus using special means for topical use:
- Miconazole;
- Levorin;
- Ketoconazole;
- Nystatin.