Neurodermatitis (atopic dermatitis) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease of a neurogenic-allergic nature. The key symptom of the pathology is a rash, which consists of itchy papules. Manifestations can appear on different parts of the body, but neurodermatitis is most often diagnosed on the hands. The disease begins in early childhood and can recur throughout life. It is observed in patients with a hereditary predisposition in combination with pathologies of allergenic etiology.
Etiological factors
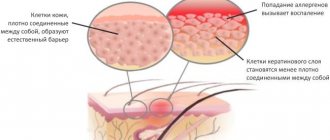
The impetus for the occurrence of neurodermatitis (atopic dermatitis) in childhood is given by the immature immune system and the inability of the fragile body to withstand adverse environmental factors. Hereditary predisposition plays an important role in the occurrence of dermatological problems. There is evidence that the presence of skin pathologies in close relatives significantly increases the likelihood of developing chronic dermatosis in a child.
Another reason that triggers a chain of pathological reactions in many dermatological diseases, including neurodermatitis, is an allergy to certain foods. Allergens that cause redness on the skin also include fluff, pollen, dust, and pet hair. The appearance of this condition in a baby is facilitated by improper eating habits in a pregnant woman, long-term drug therapy, smoking and alcohol consumption. Among other unfavorable circumstances that provoke the development of neurodermatitis, the following should be highlighted:
- Stressful situations. In childhood, the psyche is characterized by extreme lability, so even minor psycho-emotional shocks can provoke skin pathology.
- Frequent infectious diseases. Children who are susceptible to bacterial and viral infections, according to statistics, are more likely than others to experience neurodermatitis.
- Deviations from the gastrointestinal tract. One of the main culprits of skin rashes are pathologies that are accompanied by impaired absorption and assimilation of vital elements and vitamins. Nutrient deficiency results in the functioning of the immune and nervous systems suffering.
- Helminthic infestations. During their life, parasitic worms release huge amounts of toxins. Gradually poisoning the body, helminths undermine the child’s immune system, resulting in ideal conditions for the appearance of neurodermatitis.
- Living in an unstable climate zone (cold, damp climate).
Reasons for appearance
The following reasons can serve as an impetus for the development of dermatological diseases:
- Genetic predisposition when there were cases of the disease in the family.
- Neurological disorders - emotional instability, tendency to worry.
- Weakened immunity, which can be caused by frequent viral diseases and chronic somatic pathologies.
In addition to the immediate causes, there are provoking factors that create a favorable background for the emergence of a pathological process in adulthood:
- unbalanced diet;
- frequent stressful situations;
- intense physical activity;
- intoxication of the body due to poisoning, illness;
- parasitic infestations;
- diseases of the digestive tract;
- disturbance of intestinal microflora;
- bad ecology;
- harmful working conditions;
- failure of the hormonal system;
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
During medical practice, it was noted that neurodermatitis on the hands is often combined with allergic diseases: bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, food allergies, as well as chronic recurrent dermatological diseases. The allergenic counterparty acts as an irritant, which further reduces the body's protective properties. Not only food, but also household chemicals, cosmetics, plant pollen, and animal hair can become an allergen.
Main types of pathology
Depending on the location of the inflammatory foci and the nature of the clinical manifestations, doctors distinguish several types of neurodermatitis. These include:
- Limited. It is characterized by the appearance of pathological rashes in a single anatomical area.
- Diffuse. In this case, skin rashes are observed on several parts of the body at once.
- Linear. Dermatological changes affect mainly the upper and lower extremities of the baby.
- Follicular. The rash is localized in areas where hair grows.
- Hypertrophic. Typical signs of neurodermatitis are observed in the groin area.
- Psoriasimorphic. The rashes, which can be found on the skin of the face and scalp, resemble psoriatic plaques in appearance.
Symptoms of neurodermatitis
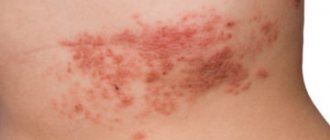
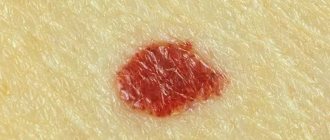
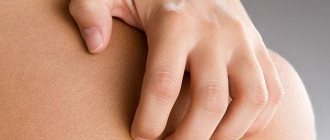
The most typical signs of the disease include itching, rash, peeling, redness of the skin and neurotic disorders. The most characteristic symptom of neurodermatitis is the occurrence of severe skin itching even before the appearance of rashes. Next, small skin nodules with a shiny surface gradually form on the skin. At first, they do not differ in color from normal skin, and then acquire a brownish-pink color. After some time, the nodular formations begin to merge, forming a solid lesion covered with scales or hemorrhagic crusts with blurred boundaries. The affected area of the skin becomes bluish or purple in color. At the same time, depigmented areas are often observed in old lesions.
It should be emphasized that with neurodermatitis, the area of distribution of the pathological process can be varied and depends on its type. Most often, the lesions are localized in the groin area, the fold between the buttocks, in the scrotum, on the labia majora, in the popliteal and elbow folds, as well as on the neck. As the disease develops, there is a significant decrease in adrenal function, causing the patient’s skin to darken. At the same time, patients often lose body weight, which has a very negative impact on the general condition of their body. There is also a decrease in blood pressure, and there are complaints of fatigue, weakness, apathy and increased nervous excitability. When conducting a diagnostic laboratory test, a decrease in blood glucose levels and a decrease in the secretion of gastric juice are noted.
In some cases, neurodermatitis in adults can cause the development of lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes), and this, in turn, leads to deterioration in the functioning of many organs.
As a rule, relapses of the disease occur in the cold season, and in the summer, patients, on the contrary, experience significant improvements in their health.
It should be noted that persons whose lesions are localized on their hands are subject to the greatest suffering. This is due to the fact that the hands are most susceptible to moisture and mechanical stress, which aggravate the course of the pathological process.
Clinical picture
The first signs of neurodermatitis, usually appearing already in the first months of a baby’s life, are difficult to miss. As a rule, the older the child, the more pronounced the symptoms of the disease become. You can suspect something is wrong based on the following characteristic manifestations:
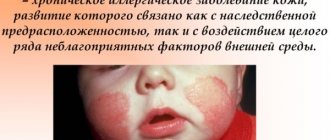
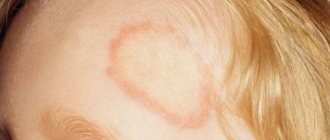
- Red spots. Noticeably different in color from healthy skin, they can take different shapes. In some cases, numerous small blisters filled with serous fluid form on the skin.
- Severe itching. The child constantly scratches the itchy skin, which leads to the formation of wounds into which any infectious agent can easily penetrate and cause suppuration.
- Dryness and flaking of the skin. During examination, longitudinal and transverse grooves are found on the inflamed epidermis. Disruption of the sebaceous glands on the scalp leads to the appearance of dry seborrhea.
Due to the incessant itching, the child’s behavior changes significantly. Favorite activities do not bring pleasure, appetite disappears, and insomnia appears. A patient with neurodermatitis becomes irritable, quickly gets tired, and experiences difficulties in learning and adapting to a team.
Diagnostic procedures
Diagnosis of neurodermatitis is the responsibility of a dermatologist and allergist-immunologist. There are no specific laboratory and instrumental markers of the disease. The criteria that allow you to confirm or refute the diagnosis are signs of the disease such as dry skin, severe itching and constant relapses . An important role is played by the presence of bronchial asthma or rhinitis of an allergic nature in the child.
The result of a blood test usually shows a high concentration of allergen-specific immunoglobulins and an increased level of eosinophils. Histological examination of the biopsy specimen reveals a picture characteristic of neurodermatitis.
If a specialist doubts the accuracy of the diagnosis, he is obliged to conduct a differential diagnosis, which allows one to exclude diseases with similar symptoms - scabies, psoriasis, lichen, seborrheic dermatitis and eczema.
Diagnostic methods
When visiting a doctor, the first step is to examine the skin. The specialist assesses the size of the spots, the area affected, and studies the symptoms that are bothering the little patient. After this, a laboratory blood test is prescribed and a scraping is taken from the surface of the rash.
How to distinguish it from psoriasis?
During the diagnostic process, it is important to distinguish neurodermatitis from psoriasis. Their manifestations are similar, but in fact the diseases have different characters and are treated differently. The differences between the pathologies are as follows.
With psoriasis, spots form more often on those parts of the body that are most exposed to friction by clothing, as well as on the skin over the joints. If the rash is scraped, an “oil stain effect” occurs, and after removing the scales, a thin film of a pinkish tint is formed, which is easily damaged and bleeds.
With the development of neurodermatitis, there are no such manifestations.
Principles of treatment
Treatment of neurodermatitis in children has two main goals: to eliminate existing functional disorders and to reduce the frequency and duration of exacerbations. Complex therapy is based not only on the use of various medications, but also on improving sanitary and living conditions. Before choosing a particular therapeutic strategy, regardless of whether it involves taking potent drugs or is based solely on unconventional methods, you should definitely consult a doctor .
Using Local Remedies
Local treatment of neurodermatitis in children, the symptoms of which can easily be confused with allergic diathesis, involves the use of all kinds of ointments, gels, emulsions, and mash. For weeping areas, it is advisable to use drying preparations, for example, zinc ointment. To soften the skin, Gistan cosmetic cream is suitable.
Ointments based on birch tar, ichthyol, and sulfur are designed to quickly remove inflammation. You can reduce itching with Glutamol and Elidel. The preparations Bepanten and Panthenol have excellent regenerating properties that allow healing and restoring the delicate skin of a child. If the disease has acquired an extremely advanced form, you cannot do without the use of ointments containing hormones.
Oral medication
To relieve the child from painful itching and stop inflammation, new generation antihistamines (Levocetirizine, Claritin, Fexofenadine), which are famous for the minimal number of side effects, are used.
In advanced cases, with a large area of damage and complications in the form of an acute allergic reaction, glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone) are prescribed with caution. To avoid unwanted side effects, they should be used in short courses. Treatment of dermatological pathology complicated by a secondary infection is carried out in parallel with the use of antibacterial or antifungal agents.
During periods of exacerbation, doctors recommend using enterosorbents to help remove toxins from the body. It would be useful to take medications that support the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract.
Physiotherapeutic activities
The most important component of complex therapy for chronic neurodermatitis in children is physiotherapy. Inflamed areas of the skin are exposed to magnets, oxygen, ozone, electric current, heat, and ultraviolet radiation. Phonophoresis and injection of localized neurodermatitis with corticosteroids have a good effect. Reflexology and thalassotherapy also have potential benefits for the entire body, including the central and autonomic nervous systems.
Each method has its own indications and contraindications. To achieve a visible effect, a minimum of 15-20 sessions are required. Sanatorium-resort treatment on the southern seas has a positive effect on the overall course of the disease, prolonging remission for a long time.
Traditional medicine recipes
A good addition to the main treatment can be the use of recipes from traditional healers. Lotions or water treatments with decoctions of medicinal herbs will help speed up the process of skin restoration, reduce itching and relieve irritation. For these purposes, chamomile, string, celandine, oak bark, and sage are suitable. To prepare a herbal decoction, you need to pour 3 tablespoons of dry raw materials with a glass of water and put on low heat for 10 minutes, then strain and cool. Use the product twice a day.
To soften dry and irritated skin, you can use oatmeal compresses. They need to be poured with boiled milk and left to swell. The resulting mass applied to the affected areas must be covered with a clean gauze cloth on top. The compress is kept on the skin for 15 minutes.
A mask made from crushed mint leaves has an anti-inflammatory effect. The main ingredient must be poured with boiling water. The resulting pasty substance is applied to the areas of inflammation for 20-30 minutes.
Prognosis and possible complications
The prognosis largely depends on the age at which the disease was diagnosed and how successful the measures taken to eliminate it were. Neurodermatitis in infants, which arose due to the immaturity of the body, is easily treatable - you just need to provide the child with a balanced diet and hypoallergenic living conditions. Systemic therapy is rarely required. Once immunity is fully developed, the response to the allergen will most likely disappear.
If the problem manifests itself at a later age or is not treated, the chances that the disease will become chronic are repeatedly increased. Treatment measures will have to be taken for the rest of your life.
Of the most common complications of atopic dermatitis, special attention should be paid to inflammatory diseases of the epidermis. Penetrating into the affected area, pathogenic microorganisms form ulcers that are fraught with sepsis. If neurodermatitis is not treated, the child may develop chronic furunculosis.
When and how does neurodermatitis develop in children?
Cases when neurodermatitis makes itself felt in very young children are extremely rare. As a rule, the disease occurs and “takes root” in children aged 2 to 5 years. 8 out of 10 children who develop neurodermatitis develop a diffuse form of this “scourge”. Which almost always comes “in company” with hay fever or allergic rhinitis.
At first, individual pale pink nodules, which over time grow to large areas of redness with elements of a rash, appear in strictly defined places:
- On the neck
- On the face
- In the bends of the arms and legs
Preventive measures
It is unlikely that it will be possible to protect a child one hundred percent from the occurrence of neurodermatitis. However, by adhering to the following recommendations, you can minimize the likelihood of skin problems:
- A child with a tendency to allergies should not be given foods that can trigger them.
- Monitor compliance with the daily routine - certain hours should be allocated for eating, playing and resting.
- Protect the baby from stressful situations as much as possible; in case of increased nervous excitability, it is necessary to give him light sedatives.
- Give preference to clothing and bedding made from natural fabrics.
- Carry out wet cleaning of living areas on a regular basis.
- Make it a habit to carry out hardening procedures.
Chronicity of neurodermatitis is the main danger of the disease. Parents of a sick child need to constantly keep their finger on the pulse, promptly responding to the first signs of exacerbation of the disease.
Prevention
The goal of preventing neurodermatitis is to eliminate or minimize the effects of factors that can trigger the onset or relapse of the disease. To do this, it is recommended to do the following:
- provide proper nutrition without allergens, but with sufficient vitamins;
- keep the child’s clothes and room clean;
- dress the child according to the weather;
- limit contact with allergens if the child has a tendency to allergies.