What is the danger of the disease
The main representative of the pathogenic microorganism on the skin is Staphylococcus epidermidis. It can safely exist on absolutely any part of the body, and it feels especially comfortable on the mucous membranes and skin.
Staphylococcus epidermidis is not always capable of causing the development of pathology in humans. If the patient has a strong immune system, his body successfully copes with infections, and it is possible to avoid the appearance of purulent and inflammatory formations on the skin.
If the protective functions of the human body are reduced, then Staphylococcus aureus is activated, and skin rashes cover the entire body.
The insidiousness of Staphylococcus aureus lies in the fact that it can especially successfully resist various antibacterial drugs and antiseptics that are used to combat it.
In addition, such a microorganism can penetrate both the body of an adult and a small child . Staphylococcus aureus is able to penetrate absolutely any organ and provoke the development of, at a minimum, an inflammatory process.
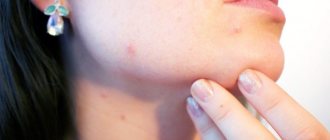
In the absence of effective therapy, Staphylococcus aureus continues to progress on the skin of the face (photo above).
Reference! Medical practice includes more than 100 types of pathologies, the development of which in the human body occurs under the influence of this pathogenic microorganism.
Staphylococcus aureus of the scalp produces harmful toxins that have a poisonous effect on the epidermis . The result is damage to skin cells and destruction of white blood cells.
The danger of Staphylococcus aureus on the skin is that the prognosis of such a disease is not entirely clear.
Bacteria can provoke the appearance of purulent formations on the skin, the development of an inflammatory process, or even blood poisoning.
When such a microorganism is activated on the skin, the development of general systemic pathologies is possible. The fact is that it is not difficult for such bacteria to penetrate from the epidermis into the vascular bed.
If correct and effective treatment is not prescribed, pathological conditions such as sepsis, streptococcal pneumonia and osteomyelitis develop.
Reasons for development
According to experts, staphylococcus of this type is a pathogen of nosocomial infection . You can become infected with a microorganism during manipulation procedures or during surgery. Infection occurs due to the introduction of foreign bodies into the body.
The surface of foreign bodies is a positive environment for the proliferation of staphylococcus. Once in the human blood, the infection migrates intensively throughout the body, causing damage to tissues, skin, and organs, becoming secondary foci of inflammatory processes .
A weakened immune system promotes the activation of one’s own microorganisms, and self-infection is possible.
Selected strains of epidermal staphylococcus are found and multiply in consumed food products; their accumulation in large quantities contributes to food poisoning (toxicoinfection).
A photo of staphylococcus on the skin of the face is presented below:
Babies often suffer from infections that affect the large intestine. A child can become infected from his mother during breastfeeding or in case of non-compliance with personal hygiene rules (pacifier, toys).
Once in the human body, staphylococcus does not pose a health hazard until a certain time . And only after the protective immune system has weakened, when the bacterium begins to actively function in human tissues and organs, should one begin to panic. Or it is better to seek help from a specialist.
There are widespread factors that awaken microorganisms:
- decreased protective function, weak immune system;
- skin surfaces are damaged;
- oncological pathologies;
- endocrine diseases;
- autoimmune diseases;
- chronic infections;
- poor environmental conditions.
Infants and young children are most often affected by the disease. The reason for this is a reduced level of immunity that is not 100% formed . In childhood, staphylococcus is often located on the scalp due to increased sweating or poor-quality personal hygiene products for children.
Causes of skin disease development
Staphylococcus aureus, like any other type of microorganism, can appear on the skin of absolutely any person. The fact is that the body is not able to cope with the threat, since such pathogenic microorganisms produce a special enzyme - coagulase .
The presence of such an enzyme in an organism with a compromised immune system leads to the creation of favorable conditions for the further spread of the microbe throughout all tissues and systems.
Experts identify some factors that increase the likelihood of infection:
- the appearance of problems with metabolic processes, including in elderly patients and those suffering from diabetes;
- artificial ventilation of the lungs causes the penetration of bacteria into the body if the rules of personal hygiene in a medical institution are not observed;
- performing tattoos on the skin and piercing various parts of the body;
- treatment of pathologies by introducing intravenous catheters;
- injection drug addiction;
- intravenous feeding of children born prematurely.
In addition, the following reasons can provoke active reproduction of Staphylococcus aureus on the epidermis :
- the patient has a viral infection;
- inflammatory process on the skin;
- disruption of the body's hormonal levels;
- frequent stressful situations and sleep problems;
- taking medications containing iodine and bromine;
- the patient has chronic intestinal diseases;
- consumption of synthetic vitamins.
It should be remembered that infection with Staphylococcus aureus is possible when visiting a regular beauty salon.
For this reason, you should ensure the sterility of the materials used and follow the rules of hygiene.
Staphylococcus aureus on the skin is an unpleasant pathology that poisons the patient’s life.
He begins to feel embarrassed about his appearance, which lowers his self-esteem and often becomes a cause of emotional distress.
Features of skin infection
Staphylococcus on the skin of the face forms acne in many patients; this is facilitated by pathogenic microorganisms, united under the concept of staphylococcus. They are different, and the location of the rash, symptoms, and consequences depend on this.
Staphylococcus epidermidis on the face is a type of pathogenic bacterium , which in many cases is found on the skin and mucous membranes of humans.
The peculiarity of the epidermal type of staphylococci is that in very rare cases it contributes to the formation of ulcers on skin areas; more often the bacterium affects the destruction of internal organs.
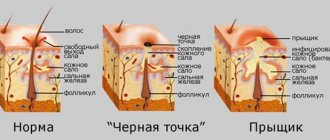
Modern medicine identifies several important features of epidermal infection. The infection grows rapidly, promoting the formation of white sticky colonies.
It is particularly resistant to a number of antimicrobial and antibacterial drugs . Among which the most common are:
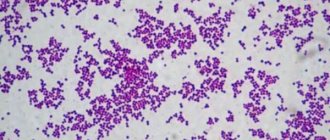
As a result of examining a smear, which is pre-stained with special means, the bacterium looks like a bunch of grapes, purple in color.
The pathogenic infection forms a mucous substance, attaches and grows on medical devices, thus penetrating the human bloodstream, migrating throughout the body to infect tissues and internal organs.
Fighting the infection is quite difficult due to the fact that it does not respond to many antibiotics and is resistant to the environment. If you do not seek help from a specialist in a timely manner, a number of unforeseen situations may arise that will lead to severe pathological processes.
A professional in his field will individually explain to each patient how to treat staphylococcus on the face, which drugs are more effective, and whether traditional medicine can be used in case of infection.
How does it appear on the scalp and face?
Usually Staphylococcus aureus on the skin causes the appearance of vivid symptoms that are difficult to miss. The main manifestation of this disease is the appearance of a rash, which can take on various forms . This or that form of the disease is determined by the location of the inflammatory process, the state of the patient’s immunity and the complexity of the disease.
What does Staphylococcus aureus look like on the skin and how not to confuse it with other pathologies? To do this, you need to study its signs:
- pustular rashes appear on the skin;
- the head becomes too oily and seborrhea bothers you;
- the whole body and face are covered with pimples, carbuncles and boils;
- deep internal pimples appear;
- subfebrile temperature persists all the time;
- Colds are often diagnosed.
One of the common manifestations of cutaneous staphylococcus is furunculosis, the development of which begins with the appearance of small redness on the epidermis with necrosis in the center. With further progression of the disease and tissue death, the appearance of purulent exudate from the resulting wound is observed.
Of particular danger are those boils that are localized on the neck and face in close proximity to the brain.
Another form of skin disease is phlegmon, which manifests itself in the form of severe swelling of the skin and its redness. If Staphylococcus aureus develops on the skin, symptoms in adults may include fever and bouts of nausea.
In the absence of timely diagnosis of the pathology and failure to carry out timely treatment, further penetration of staphylococcus into the tissue occurs and the result of this may be tissue death.
How does staphylococcus appear on the skin?
Infection with the described pathogenic microorganism has several similar manifestations. What staphylococcus looks like on the skin depends on the location of the bacterial inflammation, its intensity and the state of the person’s immune system. The introduction of microbes into the epidermal integument is always accompanied by:
- suppuration;
- swelling of nearby tissues;
- pain syndrome;
- hyperemia.
The main symptom that provokes staphylococcus is a rash on the skin. They can take several forms:
- blisters (vesicles with exudate);
- acne;
- boils;
- extensive red spots (erysipelas);
- carbuncles;
- felon;
- phlegmon;
- pustules;
- abscesses and others.
Staphylococcus aureus on the face
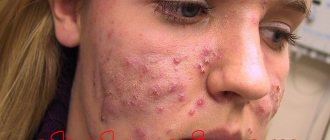
Infection with this microbe in the specified area is accompanied by a rapidly spreading rash. Staphylococcus aureus on the skin of the face causes a large number of acne. First, deep, painful inflammations form, which look like bright red bumps with severe swelling of the surrounding tissues. Signs of staphylococcus progress rapidly, and a white purulent “head” appears in the center of such pimples. Over time, it turns yellow and opens, leaving a pit-shaped scar at the site of inflammation.
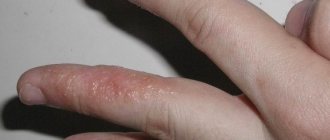
Staphylococcus on the skin of the hands
The main symptom of bacterial infection in this area is felon. Inflammation affects the fingers and periungual ridges and is often a consequence of a carelessly performed manicure. Staphylococcus aureus on the skin of the hands is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- accumulation of pus in the dermal layer;
- pronounced redness of the inflamed tissue;
- strong pain;
- twitching sensation in the affected area;
- swelling and swelling of the skin;
- change in nail color.
Staphylococcus on the body
The most common form of infection is a purulent rash. It can form on any part of the body, but is more common in the upper half of the body (chest, back, abdomen). Staphylococcus on the skin in this case looks like a cluster of deep red pimples with white “heads” in the center. When pressing on such elements, intense pain is felt.
Cutaneous staphylococcus on the body can have other forms. A more severe type of inflammatory process is a boil (boil). It represents severe suppuration of the sebaceous gland or hair follicle. In the center of the abscess there is a deep purulent core. If it is not completely removed, bacteria will penetrate and damage the surrounding tissue.
Another type of staphylococcal infection is erysipelas. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of a large red spot on the skin;
- swelling of inflamed tissues;
- local increase in body temperature;
- painful sensations;
- small pinpoint hemorrhages at the site of the lesion;
- sometimes – the presence of translucent blisters with a purulent mass on the epidermis.
conclusions
To eliminate a pathology such as Staphylococcus aureus on the skin, complex treatment will be required. The difficulty of drug therapy lies in the fact that such bacteria quite easily adapt to the effects of various environmental factors, which creates problems in choosing an effective antibiotic.
To prevent infection, it is necessary to observe the rules of personal hygiene and promptly treat wounds on the skin. If the epidermis is damaged by staphylococcus, treatment should be started as soon as possible, which will avoid the development of many complications.
What it is?
Staphylococcus aureus (lat. Staphylococcus aureus) is a bacterium that looks like a small ball. Approximately 2 out of 10 people are carriers of this infection. It can be in the nose, throat, genitals, or skin.
Enters the body by contact and airborne droplets. You can become infected in places where large numbers of people gather.
The main problem is that the bacterium produces a special toxin that poisons skin cells.
A completely healthy person has a powerful immune system that protects him from pathogenic bacteria. But when it weakens due to certain factors, a person can easily become infected with it.
Causes
The main reasons for how it is transmitted:
- deterioration of the body's protective properties due to frequent stressful situations, vitamin deficiency, use of antibiotics, side effects from certain medications;
- incorrect compliance with sanitary standards in the presence of open wounds on the body;
- eating vegetables and fruits that have been poorly processed;
- presence of chronic diseases.
The main problem with contracting this infection is that it is very difficult to treat.
Where can you get infected with Staphylococcus aureus?
Very often, this infection can be contracted from person to person in a hospital. Staphylococcus aureus enters the body both by eating food and by airborne droplets.
Infection occurs primarily through the skin, digestive tract, and respiratory tract. Bacteria spread throughout the body along with the bloodstream and affect other vital organs, such as the lungs, bones, heart, and brain.
Factors that provoke the disease
Unfortunately, not a single person has a chance to avoid the occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus. The problem also lies in the fact that microorganisms are capable of producing a special enzyme called coagulase. It is he who helps protect staphylococcus from the body's natural defenses.
There are several factors that significantly increase the chance of becoming infected with Staphylococcus aureus:
- drug use by injection;
- the presence of chronic diseases, including diabetes mellitus, circulatory disorders;
- weakened immunity in young children and older adults;
- use of medications that must be used intravenously;
- visiting places with large crowds of people (for example, a beauty salon, hospital, subway).
Features of staphylococcus
This is a microorganism that has the shape of a small ball and can cause inflammation in the respiratory tract, intestines, and body. When it develops, a toxin is released. When there is a large amount of the pathogen, especially in immunodeficient people, it breaks into the blood with spread throughout the body, forming secondary foci. Sepsis develops. A serious condition in which the entire body suffers. Complications lead to disruption of the blood coagulation system (DIC syndrome), failure of central and peripheral hemodynamics (infectious toxic shock), damage to the membranes and substance of the brain.
Symptoms
Staphylococcus aureus appears on the skin, depending on the location, stage of development and functioning of the human immune system (see photo below). In this regard, various diseases and disorders may occur in different parts of the skin.
Erysipelas is a very serious disease that occurs when infected with cutaneous staphylococcus. It develops in older people and affects the skin on the legs.
Swelling, redness, and itching appear on the skin. The body temperature begins to rise sharply to 39-40 degrees, and additionally nausea, vomiting, and a general unsatisfactory condition appear.
Phlegmon
This is a purulent skin lesion that spreads very quickly. With phlegmon, the body temperature rises sharply, the damaged area changes color, swelling and redness appear on it. But if it is not treated promptly, tissue necrosis may even occur.
Pyoderma
This lesion occurs in most cases in infants. The main problem is lack of hygiene. The child experiences damage to the upper layers. With pyoderma, blisters filled with pus appear on the skin.
Additionally, the temperature rises, general weakness and discomfort occur.
Felon
The lesion occurs around the nail. Redness of this area appears, local temperature rises, as well as mild pain. Gradually, panaritium on the finger spreads to all other fingers.
Furunculosis
This disease spreads most often. Furunculosis begins with small redness on the skin, with cell death in the center. Gradually, pus begins to come out of the wound.
For the human body, the most dangerous are boils that are located on the neck, near the lymph nodes.
Staphylococcal sepsis
The most dangerous staphylococcal infection. In this regard, microorganisms are damaged and spread along with the blood flow throughout the body. A very large number of lesions appear.
Skin lesions
Most often, changes are indicated on the skin. What reasons can enable the pathogen to progressively multiply, thereby causing damage to the dermis. These are the following conditions:
- Violation of the integrity of the skin due to injury. Microcracks, abrasions, maceration.
- Trophic disorders due to vascular pathology. Formed lymphostasis.
- Dryness and sagging in older people.
- The presence of hypovitaminosis, especially vitamins C, A, E, D.
- Hormonal changes leading to changes in the structure of the dermis.
- Anemia and other blood diseases.
- Kidney and liver failure.
- Gastrointestinal tract dysfunction. Intestinal dysbiosis.
- Various immunodeficiencies, congenital and acquired. HIV infection.
- Disorders of fat metabolism. Obesity.
- Chronic persistent viral infections (herpesvirus, chronic viral hepatitis).
Here are just a few of the possibilities for reducing local immunity.
What are the manifestations and symptoms of this pathology?
General manifestations in the form of fever and severe intoxication are rare. They appear either with extensive lesions or with generalization of the infection. The most commonly seen pathological conditions are:
Folliculitis
Festering follicles. Purulent folliculitis. Painful lumps and painful redness form around the hair follicles. The first symptoms will be pain on palpation, then infiltration and the appearance of a tubercle on which a white head will gradually form. The rashes can be abundant or sporadic. They occur most often on the face and back. Sometimes on the buttocks. During treatment they regress. However, in the areas of the rash, secondary changes persist in the form of a different skin tone, increased reaction to ultraviolet radiation, and changes in ambient temperature. And both cooling and overheating.
Suppuration of skin formations
Staphylococcus aureus can cause suppuration of atheromas and lipomas. Signs of inflammation will be redness and soreness of these formations. Possible suppuration, breakthrough. That is why a timely examination by a surgeon is necessary to provide prompt assistance. Individual purulent formations can form on the chest, thighs, and extremely rarely on the abdomen.
Panaritiums
This bacterium causes the formation of felons and paronychia. In which inflammation covers the areas around the nail. Gradually, the tissues melt and form a passage for the release of pus. This pathology requires the participation of a surgeon in the treatment.
Furuncle
The appearance of boils and carbuncles is also often caused by staphylococcus. A carbuncle is formed with the simultaneous inflammation of several hair follicles. The boil occurs alone, but unlike folliculitis, the damage is much more intense. A central purulent core is formed.
There is severe pain and swelling of nearby tissues. Partial melting and destruction of the layers of the dermis occurs. If the treatment is not correct, the process may progress with the formation of sepsis. Inflammatory foci of staphylococcal etiology can appear in the anus, on the mammary glands, and external genitalia. They will always have the character of ulcers.
Erysipelas?
Sometimes staphylococcus is attributed to participation in the development of erysipelas. This is an inflammation of a skin area of varying intensity with characteristic general toxic manifestations. However, the causative agent of this condition is different.
Erysipelas is a streptococcal infection!
Staphylococcus aureus in children
Infection of Staphylococcus aureus in young children can occur already in the maternity hospital. Signs in children are the same as symptoms in adults.
The child’s body can cope with this infection, even without the use of medications, this happens thanks to mother’s milk. Mother's milk enhances the body's protective properties.
If a child was born prematurely and has developmental pathologies, then his protective properties are weakened. In this case, the infection can lead to serious skin damage that is very similar to burns.
The child may also develop staphylococcal enterocolitis. It is necessary to urgently consult a doctor and undergo a course of treatment.
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium that can survive in many conditions. For example, the action of high temperature or, conversely, very low temperature does not affect this microorganism in any way.
The infection can remain in the body for a long time without manifesting itself in any way. Staphylococcus aureus appears on the skin only when the immune system is weakened. In this regard, treatment should be applied only after a diagnosis has been established and there are manifestations of the disease.
If staphylococcus is present in the body, it is necessary to take measures to strengthen the immune system.
How to treat? In order to cure the body of Staphylococcus aureus, it is necessary to use complex treatment:
- use of immunomodulators (Staphylococcal bacteriophage);
- vitamins, hormonal drugs and nutritional supplements;
- antibiotics (Clarithromycin, Vancomycin);
- antimicrobial drugs.
How to treat staphylococcus on the skin?
Bacterial infections can only be treated with antibiotics to which they are sensitive. Staphylococcus on the skin is eliminated mainly with local preparations in the form of ointments and creams. In case of extensive tissue damage and detection of microbes in the blood, systemic agents may be prescribed. Sometimes surgical intervention is required when Staphylococcus aureus is detected on the skin - surgical treatment is recommended in the case of boils, carbuncles and cellulitis.
In parallel with the basic therapy, immunostimulating, antifungal and symptomatic therapy is carried out:
- vitamins;
- lacto- and bifidobacteria;
- antimycotic;
- painkillers;
- anti-inflammatory.
Ointment for staphylococcus on the skin
Medicines with a wide spectrum of antibacterial activity are selected as local preparations. This helps prevent the development of a mixed infection. Staphylococcus on the skin of the face is best treated with creams; they are absorbed faster and are less comedogenic. Effective antimicrobial agents:
- Supirocin;
- Bactroban;
- Mupirocin;
- Bonderm;
- Fusidine;
- Baneocin;
- Altargo;
- Gentamicin and others.
Preparations for staphylococcus
Generalized lesions require complex therapy, including internal medication. A systemic antibiotic for staphylococcus on the skin should be selected only by a specialist in accordance with the results of analyzes of biological material. It is dangerous to purchase and use antimicrobial drugs on your own; this is fraught with the development of superinfection. In such situations, staphylococcus appears on healthy skin, spreading to large areas of the epidermis.
Effective systemic antibiotics:
- Vancomycin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Cefazolin;
- Cloxacillin;
- Cephalexin;
- Erythromycin;
- Oxacillin;
- Cefotaxime;
- Clarithromycin;
- Cephalothin;
- Clindamycin and others.
Treatment with drugs
Only the attending physician can prescribe the necessary method of rehabilitation therapy.
The following drugs are considered the most effective:
- Imudon . This drug promotes the production of large amounts of antibodies. They help “train” the immune system to fight this type of infection. This type of medication is considered the most effective for treatment;
- Staphylococcal bacteriophage . Immunoglobulin drug helps eliminate bacteria;
- Chlorophyllipt solution . Has an antibacterial effect;
- Ointments . This type of medication helps eliminate the external manifestations of the infection;
- Vaccine . It is used for prevention purposes.
Treatment methods
When staphylococcus enters the body, treatment on the face requires special attention. A specialist should prescribe medications after a complete diagnosis , based on the results of laboratory tests.
The use of traditional medicine is used very rarely, under the strict supervision of the attending doctor to avoid complications. Systemic antibiotics can be used in combination with other drugs:
- staphylococcal bacteriophage;
- immunostimulating drugs.
Traditional recipes for treating infection
How to treat? Staphylococcus aureus can be eliminated using traditional methods of treatment. You can cope with the infection with the help of juices, decoctions, and ointments. Treatment can act both to eliminate the cause of the disease and to strengthen the immune system.
To prevent the occurrence of this disease in young children, it is necessary to follow the rules of hygiene.
It is necessary to treat children's toys with antiseptic drugs. As soon as the mother begins to add some fruits to the child’s diet, the child’s body will be replenished with microelements and vitamins.
When staphylococcus appears on the skin, it is recommended to use herbs such as calendula, chamomile, St. John's wort, yarrow . They are used in the form of lotions and compresses. It helps to eliminate the infection in the initial stages of infection by treating manifestations with Fukortsin or Zelenka .
Nutrition
Fruits and berries are very beneficial for the body. They contain a large amount of vitamins necessary for the body. For example, black currant, apricot, rose hips.
Black currants contain a large amount of vitamins. It is recommended to use them to prevent the occurrence of disease and enhance the protective properties of the body.
Eating apricot promotes faster regeneration of skin cells. It helps increase vitality and strengthen the immune system.
Rosehip is a real Klondike of vitamins. It is recommended to be consumed as tea. It can even be used in autumn and winter as a prevention and treatment of colds.
Phytotherapy
You can eliminate general malaise and fever by taking decoctions and infusions.
- St. John's wort infusion . You need to take 1 tablespoon of the herb and add hot boiled water. Leave to infuse for an hour. You can take half a glass before eating.
- Infusion of burdock and comfrey leaves . You need to take 25 grams of burdock and comfrey leaves, pour a glass of hot boiled water. Take a glass before eating.
Preventive measures
Prevention and treatment of the occurrence of this disease consists of strengthening the immune system, observing hygiene rules, as well as using traditional or medicinal drugs.
You need to be as careful as possible when staying in a hospital or other crowded places.
Before eating food, it is necessary to thoroughly wash vegetables and fruits. To strengthen the immune system, it is necessary to take large amounts of vitamins and microelements, as well as other useful substances.
It is necessary to completely abandon bad habits.
If initial symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor. He will recommend what tests to take and what medications to take.
Preventive approach
The main preventive measure against staphylococcus on the face is hygiene. It is recommended to lead an active and healthy lifestyle, eat right and get plenty of rest. It is advisable to immediately treat all small wounds and cracks with disinfectants, and avoid situations where the skin on the face is very overheated or, conversely, overcooled.
If the infection does enter the body, it is recommended to take infusions and decoctions of medicinal berries and herbs, which help eliminate toxins, and also have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects and contribute to the speedy recovery of the body.
If there are diseases in the body that accompany staphylococcal infection, you should be more attentive to your facial skin and carefully care for it, avoiding microcracks and scratches. In particular, this applies to diabetes mellitus, when even a small wound on the skin can cause infection to enter the bloodstream.
It is necessary to carefully monitor the skin of young children and, at the slightest suspicion of infection, consult a doctor immediately. Under no circumstances should you visit a bathhouse or sauna if even the slightest inflammation occurs on your face, as the infection can spread throughout the body.
Videos on the topic
Facial skin lesions are inflammations due to infections, allergies, heat and even medications. The outer covering is resistant to most influences, but is still vulnerable to invaders such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Staphylococcus is the name of a group of bacteria that can cause a number of diseases, including infectious ones - staphylococcus on the face. The structure of most of these microorganisms resembles a purple bunch of grapes (Staphylococcus is translated from ancient Greek as grape seed).
Features of infection with staphylococcus
A rash is nothing more than a bacterial infection on the skin of the face caused by staphylococcus. Common symptoms of infection include swelling and redness in the eyes, cheeks and nose.
The cause of disturbances when rashes occur on the face is sought inside the body. The virus can settle both on the surface of the skin and take hold from the inside in human tissues.
Most people are only carriers of staphylococcus and do not develop an infection. However, if a person showed symptoms of the disease, it was due to bacteria that had been dormant in the body for years.
Staphylococcus can be transmitted from person to person. It is so hardy that it can live on inanimate objects (pillowcases or towels).
The infection waits for weeks to move on to the next person. The bacterium is resistant to the external environment and can be stored in a dried or frozen state for six months, is not afraid of sunlight, and can live in water and food products. The microbe easily tolerates stomach acid and increased salt levels.
In addition, a number of other causes and risk factors favorable for the development of the disease are known:
- Low immunity.
- Playing sports (risk of skin injury). Bacteria can easily spread through cuts, abrasions and skin-to-skin contact in the locker room through shared razors, towels, uniforms or equipment.
- Children (weak immunity, the protective function of the skin is not fully formed).
- Autoimmune (insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2) and oncological diseases (cancer). Medicines, chemotherapy, and radiation exposure can weaken the immune system and increase susceptibility to staph infections.
- Kidney failure requiring dialysis, HIV, AIDS, respiratory diseases.
- Foci of chronic infections, endocrine diseases, complications.
- Current or recent hospitalization. In hospitals, the infection attacks vulnerable and weakened people. The use of invasive devices (dialysis and breathing tubes, intravascular and urinary catheters) risks the virus entering the body from the external environment.
- Cooking food that does not meet sanitary requirements (transfer of infection from skin to prepared food).
- Increased level of sweating (violation of the bactericidal barrier, development of infection).
- Skin damage from eczema, burns, surgery, insect bites.
- Low quality cosmetics (irritation, inflammatory process).
- Ecology.
Causes of staphylococcus on the face
The main reason for the appearance of staphylococcal inflammation on the face is the manifestation of the pathological activity of the bacterium.
Favorable factors for the development of staphylococcus are:
- Reduced protective functions of the skin and immune forces of the body.
- Traumatization of areas of the dermis of the face.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Oncological diseases.
- The age of the person. Doctors note that children, especially younger ones, often suffer from staphylococcus on the face. This is due not only to unformed immunity, but also to the weak protective function of the skin.
- Diseases of the endocrine gland, the presence of foci of chronic infections.
- Hypothermia and overheating of the facial skin, which significantly reduces its protective properties.
- Increased sweating, which leads to a change in the bactericidal properties of the skin and becomes a fertile environment for the development of bacteria.
- Using low-quality facial care products that cause skin inflammation.
- Ecological state of the external environment.
Symptoms and signs of infection
Symptoms of infection in the face:
- Staphylococcus bacteria cause redness and swelling;
- increased temperature in the affected area;
- pores are enlarged and look larger, the skin texture resembles an orange peel (cellulite);
- areas of the face affected by staph infection are enlarged and painful to the touch;
- the patient experiences itching on the swollen skin;
- cervical lymph nodes are sensitive to touch;
- Some patients with staph infections on the face have a sensitive, swollen tongue;
- A bulla (blister) often appears on the reddened area and red streaks are visible that extend from the affected area.
Of the 30 strains of staphylococcus, only three lead to disease. The most dangerous are considered golden, epidermal, saprophytic.
Each type of staphylococcal disease is distinguished by the presence of characteristic signs:
- folliculitis - inflammation deep in the skin in the area of hair follicles, accompanied by redness of ulcers and pustules with yellow-green discharge;
- boil - an inflammatory process that is accompanied by the appearance of pus in the cavities of the skin; sometimes multiple foci appear, which indicates the presence of furunculosis;
- carbuncle-funnel with pus inside, the skin becomes bluish, nausea and vomiting begin, weakness and loss of consciousness are possible; delay threatens with abscess of the soft tissues of the face and the development of osteomyelitis;
- impetigo - yellow (red) rashes in the form of conflicts (bubbles), lumps and blisters leak out;
- hidradenitis – a disease accompanied by an inflammatory process in the area of the sweat glands on the face; suppuration in the form of pimples appears on the surface of the skin, swelling and pain appear.
Symptomatic manifestations
In newborn children, staphylococcus resembles scalded skin, with all the signs associated with such a syndrome. Basically, the symptoms of the pathology depend on the severity and nature of the infection:
- Folliculitis – affects most of the face and head. The skin around the formed follicle is always red, and pus with a serous tint collects inside it.
- A boil is a pathogenic formation with a large amount of pus inside. Formed mainly by Staphylococcus aureus.
- Carbuncle - with this development of the disease, the affected area of the skin generally always turns blue, and small holes appear in the form of funnels, from which pus periodically oozes. When a carbuncle occurs, the patient's body temperature rises, weakness and malaise appear.
- Hidradenitis is very rare, but still affects the skin of the face; basically, this type of infection predominates in the sweat glands.
Diagnostic methods
A dermatologist is able to determine the disease by appearance, based on clinical signs. More serious staph infections, such as bloodstream infections, pneumonia, and endocarditis, require culturing samples of blood or infected body fluids and tissues. Blood tests that show very high concentrations of white blood cells may indicate a staph infection, but the diagnosis is only confirmed after laboratory testing.
Microbiological examination of discharge is the main diagnostic method for detecting infection with staphylococcus; it allows one to identify the genus and type of pathogen. For this purpose, a smear is taken from patients. The material for the study is blood, pus, and nasal secretions. Feces, urine or vomit are also used. X-rays help doctors find internal abscesses and assess the severity of the infection. A needle biopsy (taking tissue and then examining it under a microscope) can be used to find out if the bones are affected.
Characteristics of rashes on the face
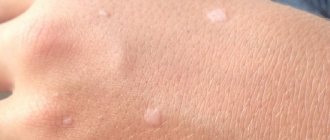
- spot (skin color changes, degree of pigmentation, fuzzy edges, no irritation);
- tubercle (compaction without a cavity in the deep layers of the dermis, tissue destruction, possible scars);
- blister (a cavityless element, the result of inflammatory edema of the upper layer of the dermis, disappears during the day, leaves no traces);
- node (red spots, provoke inflammation);
- pustule (a rash resulting from inflammation, filled with pus, appears in the face and back, forms scars and creates uneven pigmentation);
- papule (a pink nodule on the surface of the skin up to 3 cm in size).
Treatment methods, local therapy
Staphylococcus on the face is always treated comprehensively. Initially, pathological bacteria are suppressed, then concomitant diseases are treated and the immune system is strengthened. In difficult cases, surgical methods are used.
Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for staph infections on the face. If the disease is mild, then therapy is carried out using oral antibiotics; patients with a severe form (staphylococcal syndrome) are hospitalized and given intravenous injections. Antibiotics of the penicillin group are usually used. Oxacillin, cefotaxime, sulfa drugs, nafcillin and vancomycin are used to suppress bacteria. The choice of antibiotic is made by the doctor depending on the severity of the disease and whether the patient has an allergic reaction. After treatment, there is a possibility of recurrence of staph infection on the face. For this reason, patients are prescribed a longer course of antibiotics to ensure complete eradication of the bacteria.
Staphylococcus causes discomfort and pain in the patient, especially if the source of infection is located in the eye area (swollen tissue impairs visibility). Conservative treatment of symptoms includes washing with warm water and using an antibacterial agent to reduce inflammation. In addition, the patient is additionally prescribed painkillers Paracetamol and Acetaminophen, medications to relieve itching.
Bacteriophages, viruses that can identify and infect bacterial cells, help fight staphylococcal infections. Ointments with antibacterial properties help disinfect and restore the skin.
Surgery is performed if the patient suffers from a severe form of the disease. Sometimes a staphylococcal infection on the face provokes the development of an abscess, when pus accumulates under the skin of the face (furuncle, carbuncle). The operation allows you to remove pus from the affected areas, relieve swelling, and remove bacteria from the abscess. With a severe infection on the face, tissue necrosis cannot be ruled out. In such patients, dead areas are cut off, allowing the rest of the facial skin to recover.
General strengthening agents
A strong immune system helps resist microorganisms and bacteria. Taking multivitamin complexes, herbal preparations - adaptogens (ginseng, Eleutherococcus), intramuscular transfusion of purified own venous blood (autohemotherapy) will help maintain the body's defense at the proper level. Complex combinations of synthetic immunomodulators are also used when ready-made immune preparations (staphylococcal immunoglobulin) are administered.
Principles of therapy
An infection such as staphylococcus takes a very long time to be treated, as it is highly resistant to external and internal factors. Bacteria have toxic properties that can affect not only the upper layers of the skin, but also the lower ones. Staphylococcus is resistant to antibiotics, ultraviolet rays and freezing, so getting rid of it is quite difficult. In this regard, if there are unpleasant signs of staphylococcus, treatment should only be carried out by a doctor; under no circumstances should you do anything on your own.
Despite the fact that the treatment of staphylococcal infection in the body takes quite a long time, it is necessary to get rid of it completely, since the bacterium can spread throughout the body, and due to the pus accumulated under the skin, infection of the blood or bones can occur, and this is fraught with very serious consequences.
Therapy for staphylococcal infection lasts a long time and it is advisable to carry it out comprehensively, trying to simultaneously influence the cause of the disease and strengthen the body:
- Antibiotic therapy. The doctor should treat such an issue as prescribing antibiotics very carefully, since only a few types of antibiotics have an effect on Staphylococcus aureus. The drug is usually administered intramuscularly or intravenously. For staphylococcal infections, antibiotics such as Gentamicin, Oxacillin, Ampicillin are considered effective - these drugs stop the growth of the infection and prevent it from spreading further.
- Vitamins. Vitamin therapy increases and strengthens the immune system, and also prevents the spread of infection throughout the body. Vitamins are usually prescribed intramuscularly, but the patient is advised to eat more vegetables, fruits and greens. As an additional drug, tincture of ginseng or eleutherococcus may be prescribed.
- To increase immunity, you can take a course of Imudon or Irs-19.
- Ointments, gels and creams. All external agents used to treat staphylococcus must be based on antibiotics. These drugs include Gentamicin, Methyluracil ointments and Levomekol. They should be applied in a thin layer to the affected area of the skin 2 times a day, morning and evening.
- Blood transfusion. During this procedure, blood is taken from the patient’s vein and injected back, but intramuscularly.
Often, in order to get rid of a staphylococcal infection, bacteriophages are prescribed, which are able to absorb bacteria that have spread throughout the body and promote a speedy recovery.
In particularly severe cases, surgery may be required. This procedure is carried out when there is a need to open the abscess and remove all its contents. The edges of the resulting wound are treated with brilliant green, Altargo or Bactroban ointments, over time the wound begins to dry out and gradually disappears.
In addition, the facial skin should be wiped with a solution of Chlorophyllipt, vitamin A, Fukortsin, potassium permanganate or other disinfectant. It is important to remember that with a staphylococcal infection, any water procedures are contraindicated for the patient until complete recovery from the disease.
Ways to prevent diseases
Preventive measures and a number of precautions will help reduce the risk of developing staphylococcal infections:
- strengthen the immune system (diet and regular exercise);
- personal hygiene (wash hands thoroughly), personal care products and personal wardrobe (do not use other people’s toothbrushes, clothes, sports equipment);
- treat skin injuries, use sterile bandages and plasters for dressing; the bandage will prevent the spread of microorganisms beyond the wound and prevent new infections;
- wash clothes, children's toys, bedding in hot water;
- heat treatment of products and compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards during the cooking process.
Causes of pathology
The main factor influencing the occurrence of facial rashes associated with staphylococcal infection is the pathological activity of staphylococcal bacteria. The most provoking factors contributing to the development of staphylococcal infection are:
- Decreased immunity, diseases of the endocrine system (in this case, diabetes), various injuries to the skin, cancer, age (mostly young children with weak immune systems are exposed to staphylococcus), frequent overheating or, conversely, hypothermia can also cause the development of infection .
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards, use of low-quality cosmetics, excessive sweating, poor ecology.