The main reasons for the development of inflammation behind the ear
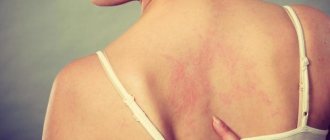
Sometimes redness appears along with inflammation. In infants and small children, the skin is very delicate, so it can often react with redness, and the immune system responds to any pathology by enlarging the lymph nodes behind the ear. In addition to the lymph nodes, the mastoid process of the temporal bone becomes inflamed, which leads to mastoiditis.
Enlarged lymph nodes behind the ear
When enlarged lymph nodes behind the ear are not accompanied by fever and other dangerous symptoms, most likely this is simply the body’s reaction to pathological changes, for example, a cold. Doctors call this condition lymphadenopathy: after recovery, the size of the lymph nodes returns to normal. In such cases, it is necessary to cure the underlying disease.
Eczema in children and adults
- allergic reaction of the body;
- hereditary predisposition;
- disruption of the sebaceous glands;
- changes at hormonal levels;
- nervous system disorders.
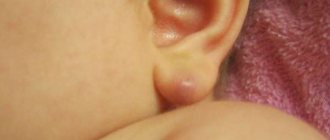
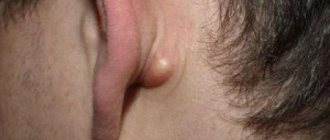
Atheroma formation
- hyperhidrosis;
- hormonal disorders;
- cosmetical tools;
- influence of the external environment.
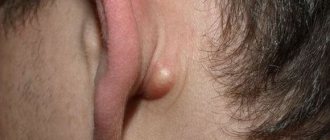
Lipoma and other formations
In addition to lymphadenopathy and other ailments, inflammation behind the ear can be a consequence of benign processes in the tissues. If a person is found to have a lump behind the ear, it may be a lipoma or a cyst on the bone.
Another cause is injuries in this area, as well as blood poisoning. Inflammation of the process of the temporal bone is a very dangerous condition, because the pus quickly moves to neighboring organs and, if it enters the brain, can be fatal.
Features of pathology in children
When to go to the doctor
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- heat;
- any tumors or lumps behind the ear;
- redness;
- severe itching.
If the formations are malignant in nature, surgery is often impossible.
Under no circumstances should you heat or rub the area where inflammation has developed, and you should also not pierce it, because this can only lead to a worsening of the condition. The best solution would be to seek help from specialists.
By
Inflammation of the lymph nodes behind the ears in children
Another common cause of redness behind the ears in babies is inflammation of the lymph nodes. There are quite a lot of them on the body - on the back of the head, in the area of the lower jaw, under the armpits, in the groin and near the ears. These points are responsible for the production of lymph, a substance that helps the body fight various infections. In the event of even the slightest health problem, the lymph nodes can make themselves known by enlargement, soreness, and redness. After recovery, they “hide” again and become almost invisible. But since the functioning of the lymphatic system in children is very imperfect, it can react very violently not only to serious diseases such as leukemia, lymphosarcoma, lymphogranulomatosis or tuberculosis, but also to the common cold and any infection.
The main reasons for the development of inflammation behind the ear
Sometimes redness appears along with inflammation. In infants and small children, the skin is very delicate, so it can often react with redness, and the immune system responds to any pathology by enlarging the lymph nodes behind the ear. In addition to the lymph nodes, the mastoid process of the temporal bone becomes inflamed, which leads to mastoiditis.
Enlarged lymph nodes behind the ear
When enlarged lymph nodes behind the ear are not accompanied by fever and other dangerous symptoms, most likely this is simply the body’s reaction to pathological changes, for example, a cold. Doctors call this condition lymphadenopathy: after recovery, the size of the lymph nodes returns to normal. In such cases, it is necessary to cure the underlying disease.
Eczema in children and adults
- allergic reaction of the body;
- hereditary predisposition;
- disruption of the sebaceous glands;
- changes at hormonal levels;
- nervous system disorders.
Atheroma formation
- hyperhidrosis;
- hormonal disorders;
- cosmetical tools;
- influence of the external environment.
Lipoma and other formations
In addition to lymphadenopathy and other ailments, inflammation behind the ear can be a consequence of benign processes in the tissues. If a person is found to have a lump behind the ear, it may be a lipoma or a cyst on the bone.
Another cause is injuries in this area, as well as blood poisoning. Inflammation of the process of the temporal bone is a very dangerous condition, because the pus quickly moves to neighboring organs and, if it enters the brain, can be fatal.
Features of pathology in children
When to go to the doctor
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- heat;
- any tumors or lumps behind the ear;
- redness;
- severe itching.
If the formations are malignant in nature, surgery is often impossible.
Under no circumstances should you heat or rub the area where inflammation has developed, and you should also not pierce it, because this can only lead to a worsening of the condition. The best solution would be to seek help from specialists.
By
Associated symptoms
Ear dermatitis can be identified by the appearance of characteristic signs that are similar to weeping dermatosis that occurs in various parts of the body.
At the initial stage of development of the pathological process, the patient may notice the appearance of:
- redness of the skin behind the ear in adults;
- constant itching;
- thickening of the skin in the ear canal area;
- swelling of the ear;
- the formation of rashes, inside which exudate accumulates.
The following symptoms may indicate that ear eczema has become chronic:
- frequent relapses of the disease, which are most often observed during the cold season;
- deformation and redness behind the ears, as well as the transition of the pathological process to the lobe;
- narrowing of the ear canal due to increased epidermis;
- localization of cracks near the external ear canal.
- A very itchy, profuse rash of small red spots may indicate lupus erythematosus and sexually transmitted diseases.
- A rash that is very painful when touched indicates damage to the body by amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, or severe viral infections.
- A colorless or translucent rash is a sign of keratosis; a whitish rash is observed with lichen and vitiligo.
- Watery, weeping rashes are characteristic of dermatitis, streptococcal and parasitic infections.
- Dense pimples and acne are observed during puberty, hormonal imbalance, and abuse of fatty foods.
- Small pink pimples in children indicate heat rash.
- A pustular rash can be the result of microbes getting under the skin.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Betadine for cervical erosion
Seborrhea is often the cause of a rash behind the ears in adults.
If a rash is detected on the ears, you must first consult a dermatologist who will make a diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. If metabolic disorders in the body are recognized as the cause of the rash, it is necessary to change the diet, introduce foods rich in protein into the diet, and eliminate sweets, salty foods and fatty foods. To determine the microorganism that caused the skin inflammation and the spread of the rash, swabs are taken from the earlobes.
After determining the origin of the pathogenic flora, a course of antimicrobial or antifungal therapy is prescribed. Autoimmune diseases are treated with hormones and immunosuppressants. Physiotherapy is used successfully in the treatment of rashes behind the ears of various etiologies.
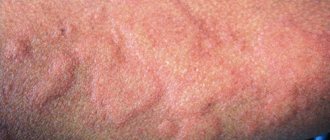
A rash behind the ear can be the result of many causes. Although different infections that cause it may present with different symptoms, there are some similar ones:
- Itchy bumps
- Bumpy rash
- Swollen lymph node behind the ear
- Headache
- Redness
- Peeling of the skin.
In many cases, the symptoms listed above go away on their own without treatment. If you do not experience relief from using any medications within one week, you should definitely consult a dermatologist to determine the cause of the problem. But it's better to do it even earlier. The rash itself may not be an infection, but it is certainly a sign of an underlying medical condition that should be treated promptly.
Weeping wounds behind the ear: what the symptom indicates, causes and treatment
Weeping skin behind the ears almost 100% indicates the presence of a certain skin disease. Such an unpleasant problem can affect both a baby or child and a completely adult person.
At first, the symptom may not be noticeable, but after several days, it worsens and is quite aggressive in nature. This affects a person's general condition, preventing him from concentrating and doing everyday activities.
Gets wet behind the ears
In most cases, this ailment is accompanied by the presence of a number of additional symptoms.
This may include redness behind the ears, itching, rashes, and much more. Depending on the existing symptoms, the patient is given an appropriate diagnosis.
Sometimes the manifestations of the disease can be quite vague, which requires additional diagnostics and tests. Treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, as there is a risk of progression of the disease.
This phenomenon is most likely to occur in infants and children. This is observed due to the fact that their immune system is not fully formed and is not able to protect itself from allergens and infections.
So, when collecting anamnesis, the doctor may encounter the following symptoms:
If the above symptoms are present, a person becomes quite irritable, he loses his ability to work, and the quality of sleep also deteriorates. The symptoms have a particularly detrimental effect on children.
Allergies and rashes behind the ears
Allergic rashes in children, as a rule, appear in places with the most vulnerable areas of the epidermis - in the folds, on the bends of the arms and legs, on the face, on the buttocks. The auricle also often becomes one of these areas. During an exacerbation of allergies or atopic dermatitis, the mother should pay special attention to the skin behind the ears - carefully and carefully remove dirt from it, treat it with special creams and ointments.
Sometimes an allergic reaction is accompanied by an infection. In this case, treatment is carried out not only with the help of antihistamines or corticosteroids, but also with local antibiotics, physical procedures (exposure to ultraviolet light) and probiotics to restore the microflora.
Peeling skin in the ears: causes, treatment methods and effective methods of prevention
The appearance of dryness in the auricle, accompanied by itching and flaking, is evidence of pathological changes in the body, against the background of which accompanying symptoms appear: pain, partial hearing loss, etc. Determining the source of the problem, making a final diagnosis and prescribing treatment should be carried out by a specialized specialist. With the first symptoms of peeling, you should contact an ENT specialist, who will conduct an initial examination. If the doctor cannot determine the cause of dryness and itching within his competence, he will refer you to another specialist - a dermatologist, endocrinologist or surgeon.
Inflammatory processes
Inflammatory processes of the internal and external auditory apparatus can stimulate tissue death. The inside of the ear begins to itch, and the skin begins to peel and itch.
The disease is infectious and inflammatory in nature against the background of pronounced symptoms: acute pain, hearing loss, accompanied by the discharge of pus. Due to the high probability of complications, therapy aimed at eliminating the source of the disease and its symptoms can be prescribed by a doctor only after a comprehensive diagnosis.
Infection in open wounds of the injured epidermis of the ear can cause the formation of a boil, indicating an acute stage of the inflammatory process. Swelling, hearing loss and redness of the skin accompanied by severe pain are the first symptoms of the disease. Elimination of a boil is possible only surgically with supportive antibiotic therapy as prescribed by a doctor.
Allergic reactions
Excessive dryness, itching and flaking of the skin both in and behind the ears are often the result of allergies. The most common sources of this reaction in the body are:
- shampoo, hair conditioner, shower gel or cleanser;
- dye or solution for biochemical hair perm;
- jewelry (earrings, chains, pendants);
- food products (eggs, citrus fruits, etc.).
Rash on ears itches
The rash that appears on the ears often itches. Typically, itching is observed with allergic rashes, poor hygiene and some infectious pathologies. However, in some cases, the cause of the rash lies deeper - in problems with internal organs. Thus, itchy rashes on the ears and neck may indicate a lack of oxygen due to pathology of the respiratory organs, in particular the lungs. Therefore, a rash on the ears, especially if it itches, is a reason to consult a specialist.
Poor hygiene can also cause itching and rashes on the ears and other parts of the body. In addition to regular washing, bedding should be changed periodically. If this is done too rarely, pathogenic microorganisms begin to actively multiply in the folds of the laundry. They, in turn, can cause the formation of rash elements.
In addition to reasons such as infections and allergies, a rash on the ears of a child in the first month of life may be associated with hormonal changes in his body after birth. Such rashes appear on the skin of the face, neck, and can also occur on the ears. This rash does not pose any danger and does not require special treatment. Attention should only be paid to maintaining hygiene and preventing secondary infection.
A rash on the ears and other parts of the body later in life indicates the presence of diseases or other problems in the child’s body. Therefore, when it appears, you should immediately call a doctor.
In adults, ear rashes appear for the same reasons as in children. In most cases, rashes are associated with an individual reaction to some factor, hygiene errors and allergies. A rash on the ears may appear in response to eating certain foods, wearing jewelry, or using cosmetics and detergents. In this case, firstly, you need to establish what exactly caused the reaction and remove this factor.
In addition to allergies, a rash on the ears in an adult can occur due to various diseases, such as measles, dermatitis, eczema and others. Only a qualified doctor can determine the correct diagnosis.
Possible complications
Untimely and incorrect treatment of dry and cracked skin in the ears can lead to a number of complications:
- Sepsis is when an infection enters the blood and spreads throughout the body.
- Deep mycosis is a fungal infection of body systems: the oral mucosa, lymph nodes, liver, etc. It is impossible to completely get rid of the disease; relapses can be observed throughout life, and if the immune system is severely weakened, it can lead to death.
- Otoanthritis or pathology of infants is the flow of inflammation from the middle ear to the mastoid process.
- Destruction of the auditory ossicles and due to severe and protracted inflammatory processes.
- Perforation of the eardrum as a result of inflammatory processes, improper hygiene or other manipulations.
When your ears are peeling, and the cause of what is happening is not known for certain, you should not self-medicate, since instead of healing, you can harm the entire body.
Depending on the primary source stimulating peeling in the ears, therapy may be prescribed, which includes:
- Medicines:
- Antibiotics in the form of ear drops ( Anauran, Otipax, etc.
) are used to fight bacterial infections. Their action is aimed at relieving itching, reducing pain and destroying pathogenic bacteria. If necessary, general antibiotics may be prescribed, for example, after opening a boil. - Antifungal agents for external use - against mold fungus Terbinafarin
, yeast -
Pimafucin
, etc., for oral administration -
Fluconazole
or its analogues. - Antihistamines ( Tavegil, Suprastin, Cetirizine
, etc.) are prescribed for allergies, eczema and dermatitis, depending on the source of the allergy and the form of the disease.
- Surgical intervention - to open the boils and clean the ear canal from pus.
Most drugs have a number of contraindications (for example, pregnancy) and side effects, which must be taken into account before starting therapy. The effectiveness of treatment directly depends on the correct diagnosis.
A separate group includes folk remedies that help in cases where the ears are peeling. The most effective are tampons soaked in sunflower or olive oil, which need to be inserted into the ear canal, held there for 20 minutes and removed. After this, the skin must be cleaned of residual oil and moisturizer applied. Some doctors advise repeating the procedure at least once within 7 days. The oil can be replaced with decoctions of string, chamomile and other herbs that have an anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effect.
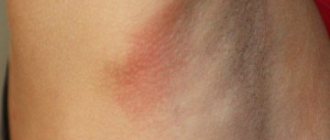
The earlobe has turned red/blue.
Somehow suddenly. The redness appeared at three o'clock and did not spread after a day's sleep. I am attaching a photo. I see a bluish color and suspect that the lobe was pinched while being carried in my arms, my husband sees a dot and suspects that he was bitten in the ear, that it is also likely that we are at the dacha and here whoever doesn’t fly. Please tell me, could this be something dangerous that needs to be shown to a doctor in person? The first photo is with flash, the color is bluer than it actually is.
The rest without flash, the color is more natural. It happened to my eldest son several times; it seemed to me that he was pinching it in a dream. I will not confirm anything, and in general I will end with personal experience.
We had this when we were 11 months old. One to one. Feel there is a seal inside? If there is, then it is a type of atheroma. I don’t know why it’s this color, but when the bruise was almost gone, I rubbed the lobe with my hands and it turned blue again. They cut it out under local anesthesia. Well, if it’s a bite, it will last for several days. If you pull a child's ears, the color will also change in a few days. Joint purchases Here people buy things at their real prices. Flea market New and used. My community. Create your own community of interests, publish materials and set your own rules of communication.
Create a community. Answers to BB. Ask a Question. Find girlfriends. Find girlfriends. My diary. Connect with other moms and make friends, get support and answers to questions. Keep a diary. To help mom. Photo contests Participate and win prizes! Test drives Apply and become a test drive participant. Horoscopes Mercury in the 3rd phase of the moon mysteriously affects the stars around you. Diseases of children. Evidence-based medicine, feeding issues, useful information about health and more.
Good evening everyone! My daughter's earlobe turned red. It doesn't itch, it doesn't hurt. Thank you in advance! Evgenia Seen on the site 59 minutes ago August 23, Ukraine, Alchevsk. Maybe during sleep the lobe curled up and pressed down? Katti Su Seen on the site 5 hours ago August 24, Russia, Moscow. Evgeniya Seen on the site 59 minutes ago August 24, Otkorney Dokonchikov Seen on the site 12 minutes ago August 23, Katti Su Seen on the site 5 hours ago August 23, Maybe a midge.
We have it here. The main thing for me is to know that this is not something dangerous. Alexandra Seen on the site 43 minutes ago Moderator August 23, Thank you, Alexandra, very much for your answer.
So it will go away on its own? I don't apply anything? How long do you think it will take for it to disappear? I'll guess with five notes! Search in the community Categories Uncategorized Photo albums Infectious disease corner Chat room Adult health Adult health Evidence-based medicine Help in finding information Children's health Child development Children's diseases Vaccinations Weight and height Breastfeeding Child behavior Organization of breastfeeding Compatibility of drugs Relactation.
Mobile version Search the site Agreement Copyright Holders. Babyblog is a site about pregnancy and motherhood. Pregnancy and child development diaries, pregnancy calendar, product reviews, maternity hospitals, as well as many other useful sections and services. Created with Sketch.
Scratching behind the ears may indicate the development of a fungal disease.
Prevention methods
The main methods that can prevent peeling of the skin in the ears are:
- Compliance with the rules for cleaning the ears - only the outer part of the ear canal is treated with a cotton swab, since wax comes out of the inner part on its own when chewing movements of the jaw are made.
- Regular treatment of hearing aids (if used) with special means, as well as the use of ear rinsing drops.
- Protecting ears from water, for example, in a swimming pool, which is important for adults and children. Infants (up to 1 year) must be bathed after closing the ear canals with special cotton swabs.
- Protect your ears from cold air and drafts.
- See a doctor and take prescribed medications for colds, acute respiratory viral infections, etc., which can stimulate the appearance of otitis media.
- To clean the ear canals, do not use improvised means that can injure the skin (hairpins, toothpicks, etc.).
Folk remedies
Most skin infections are harmless and not life-threatening. In addition to the treatment options described above, rashes in most cases can be effectively treated with traditional recipes. There are simple, affordable and natural treatment options that can be used to relieve some of the symptoms such as itching, inflammation and also speed up the healing process.
- Tea tree oil 2 is a natural antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agent. It is good for treating chickenpox, psoriasis, fungal infections and many other skin infections. To make it even more effective, you can mix the oil with honey and then apply it to the affected area of the skin.
- Turmeric, according to the Journal of the American Chemical Society, contains a wide range of antioxidant, antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties. It also contains a substance known as lipopolysaccharide, which helps stimulate the body's immune system.
- Aloe vera gel is another ideal remedy for skin rashes. The gel has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and antipruritic properties that are useful in preventing infections and soothing the skin. You need to apply the gel to the affected area and leave it for 20 minutes before rinsing it with water. Repeat the procedure twice a day for a week to achieve optimal results.
- Yogurt: Applying plain yogurt to the affected area can help soothe itchy skin and reduce inflammation.
- Baking soda: add a teaspoon of baking soda to a glass of warm water, apply the resulting paste to the skin and leave it for 20 minutes, then rinse. Repeat the manipulations twice a day for a week.
It is possible to alleviate the patient’s condition using both traditional methods of treating ear dermatitis in humans and traditional medicine. In order for the effect to be more pronounced for ear allergies, it is recommended to carry out complex therapy. Folk remedies can be used for allergies in infants on the face, head and ears.
Traditional medicine offers the following recipes for the treatment of pathologies such as ear rashes:
- For seborrheic dermatitis in the ears, it is recommended to wash the affected areas of the skin with raw potato juice, which must be prepared immediately before use. It is recommended to carry out this procedure several times during the day, which allows you to dry the inflamed areas of the epidermis and prevent them from getting wet.
- It is possible to speed up the process of regeneration of damaged skin with the help of herbal decoctions, which have a pronounced antiseptic effect. You can brew chamomile, string or calendula and wash the inflamed areas of the skin with the solution. In addition, a water tincture of oak bark has a powerful effect.
- At home, you can prepare a tincture from walnut shells. To do this, you need to take an unripe walnut, carefully crush its shell and pour vodka. The resulting mixture should be infused for 5-7 days, then strain and add the same amount of propolis.
You can cure a rash behind the ear using lotions made from a decoction of onion peels, an infusion of dried nettle leaves and castor oil with the addition of egg yolk.
Why does it itch behind the ear?
Itching is a signal from the body that forces you to pay attention to a particular organ. It is difficult to ignore this unpleasant sensation, especially if the scalp, for example, the parotid area, is itchy. Why does it itch behind the ears? This feeling is based on irritation of nerve endings under the influence of various mediators, primarily histamine.
The content of the article
Allergy sufferers are well aware of this phenomenon, since histamine plays an important role in the development of an allergic reaction. But not only allergies cause itching - it can occur as a result of infection, insect bites, contact with irritating chemicals, etc. Itching is characterized by an irresistible desire to rub or scratch the irritated area. Scratching can damage the outer layer of skin. Damage to the skin only increases itching and leads to secondary problems, such as infection, purulent inflammation, scarring, etc. This is why it is very important to treat itching behind the ears while the integrity of the epidermis is not compromised.
Possible reasons
Why do people itch behind their ears? The reasons for this phenomenon are very diverse. Thus, itching of the parotid area of the skin occurs under the following conditions:
- seborrheic dermatitis - inflammation of the skin associated with hyperactivity of opportunistic fungal microflora of the skin; accompanied by peeling, itching, and dandruff;
- allergic reaction to dust mites, jewelry, cosmetics (for example, if a woman itches behind her ears after dyeing her hair, the possibility of an allergy to the dye should be considered);
- psoriasis is a multifactorial disease; its main symptom is a rash covered with dense keratinized skin scales; in many cases, psoriasis primarily affects the area behind the ears and the scalp;
- with otomycosis - a fungal infection of the outer ear - itching behind the ears, in the auricles and in the ear canal is disturbing;
- with atopic dermatitis, the skin behind the ears itches, becomes wet, and turns red; At the same time, other areas of the body where the skin is thin and dry are usually affected.
It is not always easy to independently determine why your ears itch behind your ears - it all depends on the severity of the accompanying symptoms. To identify the true cause of the disease, an examination and consultation with a dermatologist will be required. In some cases, tests are necessary to clarify the diagnosis.
Therapy
- eliminate the irritant (jewelry, cosmetics, medicines),
- adhere to a hypoallergenic diet,
- Antihistamines are prescribed: Fenistil, Loratadine, Suprastin, Tavegil, Zyrtec.
- ointments, drops and solutions that can suppress the development of pathogenic microorganisms: Itraconazole, Terbinafine, Naftifine, Econazole, Clotrimazole, Fluconazole, Pimafucin,
- tablets: Flucostat, Pimafucin,
- medications to restore intestinal microflora: Bifiform, Acipol, Linex.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a fungal disease that affects areas of the skin rich in sebaceous glands. If a person suffers from itching specifically in the parotid area, the possibility of this disease should first be considered.
Seborrheic dermatitis develops as a result of an increase in the number of fungi of the genus Malassezia in the skin microflora. It is known that this disease affects people suffering from hypersecretion of the sebaceous glands (the fungus feeds on the lipids that make up the sebum). Malassezia is considered an opportunistic fungus, meaning it is present on the skin of most healthy people. When immune defense is reduced (for example, due to hormonal imbalance, sudden climate change, treatment with antibacterial drugs, etc.), the amount of fungal microflora increases significantly. As a result, the following violations develop:
- peeling skin behind the ears;
- dandruff;
- itching;
- oily skin and hair;
- the appearance of a rash (“irritation”) as a result of inflammation of the sebaceous glands;
- decreased skin resistance to infectious and chemical irritants.
Some symptoms are caused by the influence of fungal waste products on the skin, others by a decrease in the number of beneficial bacteria (since fungi and bacteria constantly compete for the surface of the epithelium as a habitat).
Seborrheic dermatitis primarily affects the scalp - the scalp, the upper part of the forehead and the area behind the ears. In rare cases, inflammation spreads to the groin and armpits.
The affected areas of the skin behind the ears often crack and bleed. The situation is aggravated by the patient scratching the skin (this increases the risk of secondary infection). The fungus that causes seborrheic dermatitis can also affect the ear canals, in which case otitis externa occurs.
If left untreated, seborrheic dermatitis develops into seborrheic eczema.
Provoking pathologies – scrofula, gneiss
Among numerous infectious diseases, scrofula can be called one of the most common in various age groups of patients.
In the vast majority of cases, children are susceptible to it due to incompletely formed immunity. But this problem does not bypass adults; scrofula can appear in young and elderly, relatively healthy people who are susceptible to various symptomatic diseases.
The causes of scrofula can be the following factors:
- excessive indulgence in sweets, overeating honey and sugar, sweets,
- immune system disorder
- genetic and hereditary changes,
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements, monotonous, poor menu,
- complications after viral diseases - influenza, ARVI, measles.
If some people look at the appearance of such an unpleasant phenomenon, when the skin behind the ears gets wet, as a harmless dermatological disorder, then in its essence the pathology is a very serious disease. It can simultaneously affect the circulatory system, joints, bone and cartilage tissue, which greatly complicates the course of the disease.
Traditionally, in mild cases, scrofula can be treated at home by following the recommendations of the attending physician; more complex cases of scrofula treatment require hospitalization in a medical institution.
No less often provokes the development of a condition where it gets wet behind the ears, a violation of metabolic functions of the hereditary type - gneiss. It usually appears as weeping patches on the head and skin behind the ears.
Today, experts determine the main set of reasons for the appearance of gneiss. These are the consequences of poor nutrition, inappropriate lifestyle, psycho-emotional stress, stress and nervous breakdown.