Facial skin lesions are inflammations due to infections, allergies, heat and even medications. The outer covering is resistant to most influences, but is still vulnerable to invaders such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Staphylococcus is the name of a group of bacteria that can cause a number of diseases, including infectious ones - staphylococcus on the face. The structure of most of these microorganisms resembles a purple bunch of grapes (Staphylococcus is translated from ancient Greek as grape seed).
Features of infection with staphylococcus
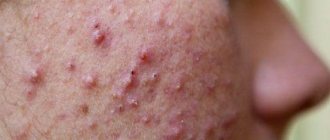
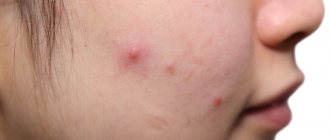
A rash is nothing more than a bacterial infection on the skin of the face caused by staphylococcus. Common symptoms of infection include swelling and redness in the eyes, cheeks and nose.
The cause of disturbances when rashes occur on the face is sought inside the body. The virus can settle both on the surface of the skin and take hold from the inside in human tissues.
Most people are only carriers of staphylococcus and do not develop an infection. However, if a person showed symptoms of the disease, it was due to bacteria that had been dormant in the body for years.
Staphylococcus can be transmitted from person to person. It is so hardy that it can live on inanimate objects (pillowcases or towels).
The infection waits for weeks to move on to the next person. The bacterium is resistant to the external environment and can be stored in a dried or frozen state for six months, is not afraid of sunlight, and can live in water and food products. The microbe easily tolerates stomach acid and increased salt levels.
In addition, a number of other causes and risk factors favorable for the development of the disease are known:
- Low immunity.
- Playing sports (risk of skin injury). Bacteria can easily spread through cuts, abrasions and skin-to-skin contact in the locker room through shared razors, towels, uniforms or equipment.
- Children (weak immunity, the protective function of the skin is not fully formed).
- Autoimmune (insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2) and oncological diseases (cancer). Medicines, chemotherapy, and radiation exposure can weaken the immune system and increase susceptibility to staph infections.
- Kidney failure requiring dialysis, HIV, AIDS, respiratory diseases.
- Foci of chronic infections, endocrine diseases, complications.
- Current or recent hospitalization. In hospitals, the infection attacks vulnerable and weakened people. The use of invasive devices (dialysis and breathing tubes, intravascular and urinary catheters) risks the virus entering the body from the external environment.
- Cooking food that does not meet sanitary requirements (transfer of infection from skin to prepared food).
- Increased level of sweating (violation of the bactericidal barrier, development of infection).
- Skin damage from eczema, burns, surgery, insect bites.
- Low quality cosmetics (irritation, inflammatory process).
- Ecology.
What it is
Staphylococcus aureus (lat. Staphylococcus aureus) is a bacterium that looks like a small ball. Approximately 2 out of 10 people are carriers of this infection. It can be in the nose, throat, genitals, or skin.
Enters the body by contact and airborne droplets. You can become infected in places where large numbers of people gather.
The main problem is that the bacterium produces a special toxin that poisons skin cells.
A completely healthy person has a powerful immune system that protects him from pathogenic bacteria. But when it weakens due to certain factors, a person can easily become infected with it.
Symptoms and signs of infection
Symptoms of infection in the face:
- Staphylococcus bacteria cause redness and swelling,
- increased temperature in the affected area,
- pores are enlarged and look larger, skin texture resembles orange peel (cellulite),
- areas of the face affected by staph infection are enlarged and painful to the touch,
- the patient experiences itching on the swollen skin,
- cervical lymph nodes are sensitive to touch,
- Some patients with staph infections on the face have a sensitive, swollen tongue,
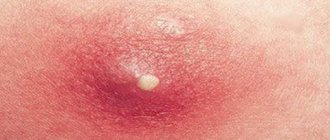
- A bulla (blister) often appears on the reddened area and red streaks are visible that extend from the affected area.
Of the 30 strains of staphylococcus, only three lead to disease. The most dangerous are considered golden, epidermal, saprophytic.
Each type of staphylococcal disease is distinguished by the presence of characteristic signs:
- folliculitis is an inflammation deep in the skin in the area of hair follicles, accompanied by reddening of ulcers and pustules with yellow-green discharge,
- boil is an inflammatory process that is accompanied by the appearance of pus in the cavities of the skin, sometimes multiple foci appear, which indicates the presence of furunculosis,
- carbuncle-funnel with pus inside, the skin becomes bluish, nausea and vomiting begins, weakness and loss of consciousness are possible, delay threatens with an abscess of the soft tissues of the face, the development of osteomyelitis,
- impetigo - yellow (red) rashes in the form of conflicts (bubbles), bumps, blisters leaking out,
- Hidradenitis is a disease accompanied by an inflammatory process in the area of the sweat glands on the face, suppuration in the form of pimples appears on the surface of the skin, swelling and pain appear.
Diagnostic methods
A dermatologist is able to determine the disease by appearance, based on clinical signs. More serious staph infections, such as bloodstream infections, pneumonia, and endocarditis, require culturing samples of blood or infected body fluids and tissues. Blood tests that show very high concentrations of white blood cells may indicate a staph infection, but the diagnosis is only confirmed after laboratory testing.
Microbiological examination of discharge is the main diagnostic method for detecting infection with staphylococcus; it allows one to identify the genus and type of pathogen. For this purpose, a smear is taken from patients. The material for the study is blood, pus, and nasal secretions. Feces, urine or vomit are also used. X-rays help doctors find internal abscesses and assess the severity of the infection. A needle biopsy (taking tissue and then examining it under a microscope) can be used to find out if the bones are affected.
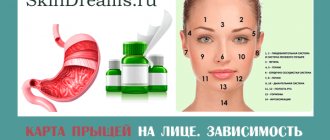
Characteristics of rashes on the face
Types of rashes:
- spot (skin color changes, degree of pigmentation, fuzzy edges, no irritation),
- tubercle (a compaction without a cavity in the deep layers of the dermis, tissue destruction, possible scars),
- blister (a cavityless element, the result of inflammatory edema of the upper layer of the dermis, disappears during the day, leaves no traces),
- node (red spots, provoke inflammation),
- pustule (a rash resulting from inflammation, filled with pus, appears in the face and back, forms scars and creates uneven pigmentation),
- papule (a pink nodule on the surface of the skin up to 3 cm in size).
First aid
It is necessary to have local first aid products in your first aid kit in case of infection. Any staphylococcal lesion is characterized by the appearance of suppuration. If a person discovers a boil, the first aid in getting rid of it will be to apply an antibacterial ointment. If the situation does not improve within 4 days, you need to make an appointment with a doctor.
Self-medication can be done only with minor inflammation of the skin and complete confidence in the diagnosis.
Treatment methods, local therapy
Staphylococcus on the face is always treated comprehensively. Initially, pathological bacteria are suppressed, then concomitant diseases are treated and the immune system is strengthened. In difficult cases, surgical methods are used.
Antibiotics are the main method in the treatment of staphylococcal infections on the face. If the disease is mild, then therapy is carried out using oral antibiotics; patients with a severe form (staphylococcal syndrome) are hospitalized and given intravenous injections. Antibiotics of the penicillin group are usually used. Oxacillin, cefotaxime, sulfa drugs, nafcillin and vancomycin are used to suppress bacteria. The choice of antibiotic is made by the doctor depending on the severity of the disease and whether the patient has an allergic reaction. After treatment, there is a possibility of recurrence of staph infection on the face. For this reason, patients are prescribed a longer course of antibiotics to ensure complete eradication of the bacteria.
Staphylococcus causes discomfort and pain in the patient, especially if the source of infection is located in the eye area (swollen tissue impairs visibility). Conservative treatment of symptoms includes washing with warm water and using an antibacterial agent to reduce inflammation. In addition, the patient is additionally prescribed painkillers Paracetamol and Acetaminophen, medications to relieve itching.
Bacteriophages, viruses that can identify and infect bacterial cells, help fight staphylococcal infections. Ointments with antibacterial properties help disinfect and restore the skin.
Surgery is performed if the patient suffers from a severe form of the disease. Sometimes a staphylococcal infection on the face provokes the development of an abscess, when pus accumulates under the skin of the face (furuncle, carbuncle). The operation allows you to remove pus from the affected areas, relieve swelling, and remove bacteria from the abscess. With a severe infection on the face, tissue necrosis cannot be ruled out. In such patients, dead areas are cut off, allowing the rest of the facial skin to recover.
General strengthening agents
A strong immune system helps resist microorganisms and bacteria. Taking multivitamin complexes, herbal preparations of adaptogens (ginseng, eleutherococcus), intramuscular transfusion of purified own venous blood (autohemotherapy) will help maintain the body’s defense at the proper level. Complex combinations of synthetic immunomodulators are also used when ready-made immune preparations (staphylococcal immunoglobulin) are administered.
Causes
The main reasons for how it is transmitted:
- deterioration of the body's protective properties due to frequent stressful situations, vitamin deficiency, use of antibiotics, side effects from certain medications;
- incorrect compliance with sanitary standards in the presence of open wounds on the body;
- eating vegetables and fruits that have been poorly processed;
- presence of chronic diseases.
The main problem with contracting this infection is that it is very difficult to treat.
Where can you get infected with Staphylococcus aureus?
Very often, this infection can be contracted from person to person in a hospital. Staphylococcus aureus enters the body both by eating food and by airborne droplets.
Infection occurs primarily through the skin, digestive tract, and respiratory tract. Bacteria spread throughout the body along with the bloodstream and affect other vital organs, such as the lungs, bones, heart, and brain.
Factors that provoke the disease
Unfortunately, not a single person has a chance to avoid the occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus. The problem also lies in the fact that microorganisms are capable of producing a special enzyme called coagulase. It is he who helps protect staphylococcus from the body's natural defenses.
There are several factors that significantly increase the chance of becoming infected with Staphylococcus aureus:
- drug use by injection;
- the presence of chronic diseases, including diabetes mellitus, circulatory disorders;
- weakened immunity in young children and older adults;
- use of medications that must be used intravenously;
- visiting places with large crowds of people (for example, a beauty salon, hospital, subway).
Ways to prevent diseases
Preventive measures and a number of precautions will help reduce the risk of developing staphylococcal infections:
- strengthen the immune system (diet and regular exercise),
- personal hygiene (wash hands thoroughly), personal care products and personal wardrobe (do not use other people’s toothbrushes, clothes, sports equipment),
- treat skin lesions, use sterile bandages and plasters for bandaging, the bandage will prevent the spread of microorganisms beyond the wound, will prevent the entry of new infections,
- wash clothes, children's toys, bedding in hot water,
- heat treatment of products and compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards during the cooking process.