Characteristics and features
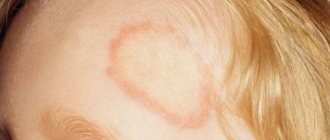
Keratosis of the skin in a child - photo:
Follicular keratosis is a violation of the process of death of dead skin cells, when they do not exfoliate, as they should normally, but clog the lumen of the hair follicle .
As a result, the normal production and secretion of sebum is disrupted, and an inflammatory process develops. Characteristic nodules and growths appear on the skin in the affected areas , which cause not only aesthetic, but also physical discomfort.
The disease has a wave-like nature, that is, at certain periods of time the situation can worsen, the number of nodules on the skin increases.
These periods are followed by periods of remission , when the condition of the skin normalizes and the growths become less noticeable.
Preventive measures
To avoid exacerbations of keratosis, it is necessary to adhere to certain prevention methods.
Namely:
- In winter, lubricate your skin with a rich cream every day.
- Eat foods containing sufficient amounts of vitamins and fat, and take courses of multivitamins.
- Try to wear clothes made from natural materials.
- When swimming, use gentle detergents.
- It is necessary to normalize the daily routine.
- Try to strengthen the condition of your nervous system.
Now, we think, the issue of treating keratosis pilaris will be clear to you. Share this article with your friends and give it 5 stars!
Causes
The main reason for the development of the disease is a disruption in the process of separation of keratinized skin cells, resulting in clogging of the sebaceous ducts and inflammation of the hair follicles.
The pathology has a chronic course, and negative factors contributing to the development of exacerbations:
- Exposure to low temperatures on the skin (many children suffering from keratosis experience exacerbations during the cold season).
- Hypovitaminosis, in particular, a lack of vitamins A, C, E, necessary to maintain the skin in a healthy condition.
- Poor nutrition.
- Prolonged contact with synthetic fabrics (for example, when wearing synthetic clothing that impedes the access of oxygen to the skin).
- Using inappropriate personal care products (such as soap), which dry out the skin and promote irritation.
- Chronic diseases of the digestive system and disruption of the processes of digestion and absorption of food.
- Frequent stressful situations (for example, unfavorable family conditions, changes in the child’s usual living conditions).
You will find recommendations from specialists for the treatment of seborrhea in children on our website.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you don't like the quality of your child's skin, don't self-medicate. Many mothers change their diet, bathe their baby daily in string and chamomile, smear Antoshka cream from head to toe... Take your child to a dermatologist! Jokes with the skin can end sadly, and the grown-up child is unlikely to thank you for the scars and marks left after home treatment.
The dermatologist may take a scraping of the skin to rule out a bacterial infection. Will issue a referral for a blood test, which will show the general condition of the body and the path to search for pathology. In addition, along with keratosis, the child may develop concomitant dermatological problems that the mother does not see.
Contact your pediatrician, but if you have the opportunity to take your child to a skin specialist, take it.
Localization of the lesion
Characteristic manifestations of keratosis pilaris can occur on almost any part of the body where there is hair (hair follicles).
Thus, nodular formations can affect the area of the face and arms (this happens most often), as well as the hips, buttocks and legs, the area between the shoulder blades and the chest.
On the inside of the palm and on the skin of the feet, these changes practically do not occur (with the exception of some forms of the disease), since there are no hair follicles in these areas.
Types of disease
There are two types of follicular hyperkeratosis of the skin.
- Type I develops with a lack of vitamin A. It is characterized by increased dryness of the skin on the elbows, knees, extensor surfaces of the limbs and buttocks and the appearance of spiny nodules at the mouths of the hair follicles.
- Type II develops with a lack of vitamin C. Its difference is the dark color of the nodules that clog the mouths of the follicles, since they consist of blood or pigment. The outer thighs and abdominal area are most often affected.
The disease can be congenital or acquired.
Classification of the disease
Depending on the causes, manifestations and other characteristic factors, it is customary to distinguish the following types of keratosis pilaris:
- Pityriasis pilaris. Despite the scary name, this form of lichen is considered safe. Nodules and growths on the skin are painless and do not cause any discomfort to the child (with the exception of psychological if the affected areas are, for example, on the face).
- Lenticular hyperkeratosis. In children, this form is extremely rare; representatives of the older generation are most susceptible to developing the disease. The disease is localized in the area of the feet and palms, the skin of which becomes covered with specific crusts. If these crusts are removed, a bleeding funnel-shaped wound will form under them, which is very painful.
- Devergie's disease. Pathology develops gradually, over many months and sometimes years. Initially, the first signs of the disease appear in the area of the scalp, which in some places becomes covered with characteristic crusts (as happens, for example, with seborrhea). Gradually, the lesion covers new areas of the skin, and symptoms of the disease can be seen on the shoulders, arms and other parts of the body. If left untreated, spots and crusts cover the child's entire body over time.
- Ulerythema supercilii. It occurs as a result of hereditary predisposition, but a bacterial nature of the lesion cannot be excluded. It appears in the form of characteristic nodules that appear in the area of the brow ridges and forehead. Over time, hair loss occurs in these areas.
- Morrow-brook keratosis. The disease has a hereditary type of transmission, initially manifests itself in the form of changes in the skin on the palms and soles (dryness and flaking of the skin), after which these areas become covered with growths. The affected area covers not only the skin, but also the child’s nails.
- Darier-White keratosis. This form of keratosis pilaris is characterized by the formation of yellowish crusts on the skin. These areas have an unpleasant odor. The affected area becomes more extensive over time. The pathology is inherited.
As a rule, the disease goes away on its own when the child reaches puberty.
How to treat acne in newborns? Read about it here.
Keratosis of the skin
Skin diseases are a common occurrence these days. This is due to unfavorable ecology, poor diet, stress and chronic diseases. One of these ailments is keratosis.
What is keratosis
Keratosis is a concept that includes a whole group of skin diseases that are non-inflammatory in nature, and it is associated primarily with keratinization of the skin. To put it simply, this is a dermatosis in which there is a strong compaction in the epidermis of the stratum corneum.
If we divide this group of diseases according to the degree and features of localization, then we can divide keratosis into the following types:
- diffuse;
- localized.
According to the nature of origin, it is also divided into types:
- hereditary or congenital;
- acquired or essential;
- symptomatic.
Classification
The clinical picture of the disease is first expressed in slight peeling of the skin, then horny layers begin to form, followed by thickening. Among the main types of classification of keratosis, there are three:
- follicular keratosis,
- seborrheic,
- actinic.
Now we will dwell on each of the species separately, since both in their appearance and in the nature of the etiology, they differ quite sharply from each other.
Keratosis follicularis
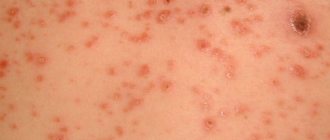
Follicular or hairy appearance is a violation of the process in which the stratum corneum of the epidermis is desquamated. In the upper layer, the keratinization of skin scales accelerates, their timely separation does not occur, and the hair follicle begins to become clogged.
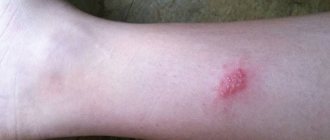
Normal sebum secretion is disrupted, and a local inflammatory process occurs. This type can lead to the occurrence of folliculitis. The result is small red and grayish nodules. This phenomenon is popularly called “goose bumps”.
The causes of keratosis pilaris are not fully understood. There is a tendency as a result of heredity. It begins to appear at a very early age. Causal factors of exacerbation include:
- cold weather;
- deficiency in the body of vitamins A, C, D;
- use of hormonal and contraceptive drugs;
- nervous tension and stressful situations.
Actinic keratosis
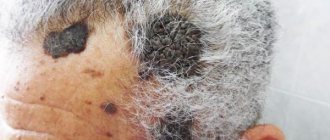
Actinic or solar keratosis. This type of disease forms in those areas of the skin where there were areas previously damaged by exposure to sunlight. This is a precancerous skin disease and is most often caused by people who spend a lot of time outdoors. The risk group for this type of keratosis is mainly elderly people.
This type is benign in nature, but can sometimes develop into squamous cell carcinoma.
This is especially risky when a person has many areas of their skin with actinic keratoses.
The prognosis of the disease is quite difficult to predict; there are cases of the disease disappearing on its own, but the risk of cancer cannot be excluded. For whom is this species most dangerous?
- for people with fair skin,
- with sunburn,
- those who have reduced immunity, those infected with HIV,
- with pigmentation disorders,
- rarely genetic predisposition.
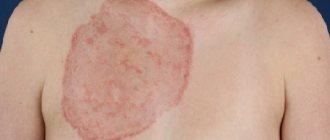
Seborrheic keratosis
This type is the most common phenomenon. These are small tumors in the form of neoplasms, they are not contagious and develop most often in older people, regardless of gender. With age-related changes, seborrheic keratoses may gradually increase in size. This species does not require any special treatment. Possible reasons for its appearance may be:
- solar exposure,
- papillomavirus,
- factor of hereditary predisposition,
- gradual aging of the skin.
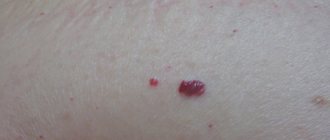
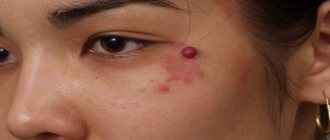
The tumor is a hyperpigmented spot with clearly defined boundaries, resembling in its appearance a brown plaque or a wart with crusts of keratinized skin.
Neoplasms are observed both in the singular and in the plural. They can occur in any part of the body.
The shade can vary and can be from light to almost black, and may bleed if pressed or rubbed hard.
Palmar and plantar keratoderma
Palmoplantar keratosis can manifest itself in different ways. These include painful deep heel cracks, neoplasms, blisters and keratinization.
There may be several reasons why this illness arose: infectious diseases, severe influenza, sore throat, tuberculosis, sexually transmitted diseases, leprosy and many others.
If a person has cured the disease, then this type of keratosis may disappear.
If the reason lies in mechanical or traumatic damage, then you should think about comfortable shoes, or other external irritants. It is also worth contacting a pedicure office so that they can help you get rid of dense keratinized areas of your feet.
Actinic keratosis
This phenomenon is associated with skin degeneration due to age. It manifests itself in the form of warts and spots that can be localized on the face, shoulders, back, arms and other places, mainly in the upper part of the body. Such manifestations do not pose a threat to life and health and never degenerate into malignant tumors.
Treatment of keratosis
In order to begin proper and effective treatment of this disease, it is necessary, first of all, to consult a specialist. A dermatologist deals with these problems. After examination and tests, the cause of the disease is determined and an accurate diagnosis is made. In case of severe symptoms, external manifestations, inconvenience and discomfort, therapeutic therapy is prescribed.
Diet. This is a very important point in the process of treating keratosis. It should be compiled taking into account the inclusion of products with a high content of vitamin and mineral components.
These are vegetable dishes, herbs, a variety of cereals, side dishes, seafood and fish, and vegetable oils.
Exceptions from the usual diet should include fried foods, spicy foods, marinades and pickles, cakes and baked goods, foods with a lot of fat, smoked foods and carbonated drinks.
As for drug therapy, in most cases it is not necessary. The doctor may prescribe a complex of vitamins, such as Aevit or ascorbic acid.
The use of local medications in the form of ointments, creams, sprays is prescribed taking into account the type of disease and the degree of skin damage. Mild products that have a moisturizing effect, based on sodium chlorite and vitamin A, are appropriate here. Salicylic and sulfur-salicylic ointments are a good medicine in this case.
When keratosis occurs, increased care and attention to the affected areas is required.
- Direct sunlight should be avoided.
- You should not scratch, rub or resort to other mechanical methods of influence, and you should also remove rough fabrics and uncomfortable shoes from clothing and household items in order to protect sore spots from contact with them in every possible way.
- Maintaining personal hygiene is an important condition for keratosis. Taking a shower or bath should become a daily ritual.
The attending physician has the right to resort to prescribing other methods of treatment, such as ultraviolet irradiation, mud, soda or salt and phytotherapy. But such programs are selected strictly individually.
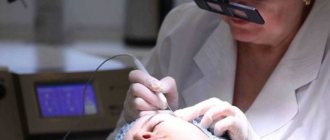
Methods for removing keratoses
There are several ways to remove foci of the disease:
- dermabrasion, grinding of the stratum corneum with a special apparatus.
- Cryotherapy, freezing, in which dead epidermal cells are exposed to liquid nitrogen.
- Chemical removal occurs by exposing the stratum corneum to acids and other chemical compounds.
- Laser removal.
- Using a radio knife.
Treatment at home
Various compresses, lotions and decoctions are used as folk methods of getting rid of the disease. Herbs and herbs with a healing effect are suitable for preparing medicinal products. Among them, chamomile, burdock, aloe, onion peel, raw potatoes and others are especially popular. Soda compresses help well, and the use of tar soap also contributes to successful recovery.
Treatment of keratosis should have a comprehensive approach, taking into account all possible methods of treatment. Sometimes the healing process takes a long time.
- The main and main task in eliminating the disease is softening and dissolving the thickness of tumors and neoplasms.
- The use of a pedicure, especially for palmoplantar keratosis, is simply irreplaceable. For children, when the disease manifests itself, you need to strictly adhere to the diet, monitor the cleanliness of the body and replenish the body with vitamin reserves.
- All age groups should strengthen their immunity and avoid hypothermia and overheating of the skin.
With the right lifestyle, giving up bad habits, keeping the epidermis clean, and a positive outlook on life, keratosis will not have a chance of success, and your skin will always be healthy.
about keratosis and methods of its treatment
Source: https://pokozhe.ru/novoobrazovaniya/dobrokachestvennye/keratoz.html
Symptoms and signs
The clinical picture includes a whole group of characteristic signs, such as:
- the formation of numerous growths on the skin in the form of nodules;
- clogging of the lumen of the hair follicle;
- rashes are localized on any part of the body, in most cases affecting large areas of the skin;
- the nodules have a diameter of about 3 mm, however, during periods of inflammation they can increase almost 2 times;
- the rash may be translucent or reddish. Sometimes their color does not differ from the natural color of healthy skin;
- skin itching (occurs rarely);
- swelling and redness of the skin (rare);
- exacerbations and inflammations develop suddenly and also disappear suddenly.
Folk remedies
Home recipes are aimed at reducing inflammation and cleansing the epidermis. Most components for the treatment of pilaris are easy to find in every home. Be sure to get the go-ahead from your dermatologist to use traditional medicine recipes.
Starch baths Dissolve 0.5 kg of starch in cold water. Take warm water and pour in the solution. Take a bath for 30 minutes. After the procedure, rinse your body, wipe dry, and apply moisturizer.
Treatment of aloe Select a plant. Which is at least five years old. Trim off the thick, fleshy leaves. Immerse in boiling water for 10 seconds, wipe, wrap in dry gauze, and put in the freezer for three days.
Take out the aloe leaves, defrost, cut as thin as possible. Apply the plates to the affected areas and cover with plastic wrap. Keep it until the morning. Remove the leaves and wipe the skin with salicylic alcohol.
The frequency of procedures is 3 times a week. Be sure to let your skin breathe, otherwise diaper rash will appear.
Potato compress Simple, accessible, cheap! Grate the potatoes on a fine grater and apply the mixture onto clean gauze. Apply the compress to the rash. After an hour, remove and apply a fresh compress. After the end of the same period, another one is needed.
Carry out the procedure every day. The skin becomes fresher and the number of rashes is reduced.
Beetroot compresses Take richly colored root vegetables, chop in a blender or grate. Leave the mixture in the bowl for 2 hours. There is no need to clean it in the cold.
The difference from potato compresses is that the beet mass is applied once. The duration of the procedure is 5–6 hours. Wash your skin with warm water, apply a light moisturizer.
Masks with propolis This healing product is widely used in cosmetology and dermatology. Apply the valuable substance to the rash areas. After a while, the body will be covered with a film. Do not wash it off for two or three days.
Wash your face and give your skin a rest. Repeat the procedure with a break of 3-4 days.
Treatment
Treatment of the disease is carried out at home, but in compliance with all the instructions of the attending physician. Treatment is aimed at moisturizing the skin, eliminating the inflammatory process, and restoring normal skin renewal.
Read about the symptoms and treatment of furunculosis in children here.
Drug therapy
To eliminate the manifestations of the disease, topical agents , such as:
- salicylic acid to normalize the process of exfoliation of dead cells;
- retinol (part of vitamin A) is necessary to normalize cell division and the skin regeneration process;
- Hormonal ointments are prescribed only for severe cases of the disease and for teenage children.
Traditional medicine
Traditional recipes will help speed up the process of skin restoration and healing:
- Aloe leaves. It is necessary to take a leaf of an adult plant, wash it thoroughly and freeze it in the refrigerator for several hours. After this, the sheet is cut into plates, which are applied to the affected areas of the skin. Apply polyethylene and a gauze bandage on top. The compress is left for 12 hours. It is recommended to repeat the procedure once every 2 days.
- Propolis . The product is applied in a thin layer to the skin, covered with a film on top and tied with a gauze bandage. It is recommended to wear such a compress for several days, and after 1-2 days the procedure is repeated.
Follicular keratosis in children: treatment, symptoms, causes, ointment, photo, video
Follicular (pilar) keratosis in children is the most common form, often combined with atopic dermatitis. In most cases, it goes away spontaneously after puberty.
Keratoses are a group of diseases caused by an imbalance between the processes of keratinization and desquamation of the epithelium. These are chronic diseases that occur with exacerbations and remissions. The disease occurs in 30-50% of the child population.
Causes
The reason why keratosis develops is excessive keratinization of the skin. Follicular (pilar) means that the disorder is localized in the area of the hair follicles of the child’s skin. That is, the epithelium surrounding the mouth of the bulb divides excessively and does not have time to slough off.
As a result, it clogs the hair exit. A small dense tubercle of white, white-gray, sometimes pink or red color forms on the surface of the skin. The tip of the hair may be visible in the middle of the tubercle. The rash becomes red when inflammation occurs.
In children, the disease worsens due to the following reasons:
- cold season;
- deficiency of vitamins A, E, C;
- diet violation;
- wearing synthetic clothing;
- use of drying cleansers for the skin (hard soap);
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- stress in the child (divorce of parents, adaptation to a new school).
In case of exacerbations, treatment is prescribed.
Symptoms
In children, keratosis pilaris looks like a nodular rash or goose bumps. Numerous dense nodules, several mm in diameter, are visible on the surface of the skin. They are dense and rough to the touch when you run your hand.
During the period of remission they do not cause any discomfort other than appearance. When the rash worsens, the rash becomes red and itching may occur. There is a general tendency to dry skin. If the rashes are combined with increased dryness of the palms and feet, then keratosis is hereditary.
Favorite localizations are the legs, thighs, buttocks, shoulders, face and scalp, but can occur on any part of the skin.
Usually nodules appear symmetrically on both limbs and parts of the head. The disease is most pronounced during puberty, and treatment may be required at this time.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a dermatologist based on an examination of a small patient. In rare cases, an additional skin biopsy is performed to confirm the disease. This need arises when the course is atypical.
Treatment
The disease is treated on an outpatient basis, although in most cases treatment is not required at all. The problem is more of a cosmetic nature. Treatment aims to moisturize the skin, exfoliate and relieve itching if necessary. Use topical products - ointments, creams, rubs.
Creams, ointments, rubs
Before applying the ointment, it is recommended to take a bath with soda for 10-15 minutes to loosen the stratum corneum of the epidermis. Creams and ointments are made from petroleum jelly with the addition of salicylic acid or retinol.
- Salicylic acid has a good keratolytic effect; it can be wiped over the affected skin several times a day.
- Retinol is a precursor to vitamin A, which has a regulating effect on the processes of skin cell division.
Only a doctor can prescribe ointments, since if the skin is traumatized by too high a concentration of medicinal substances, the disease will worsen.
Products with added acids are not prescribed to young children; their use is possible during puberty. If the keratosis has seriously worsened and causes severe discomfort, glucocorticoids in the form of an ointment are added to the treatment.
Folk remedies
Follicular keratosis is treated with the following folk remedies:
- Compress with aloe. To make the product, you need the leaves of a plant that is at least five years old. They are washed, frozen for several days, then cut into thin slices and applied to the affected skin. A film is applied to the aloe leaves, secured with a bandage on top and left in this form overnight. The procedure is repeated every other day.
- Compress with propolis. A thin layer of it is applied to the skin, a film and a bandage are placed on top. It is advisable to leave the compress for several days - this way the treatment will be more effective. Repeat at intervals of one or two days.
- Potato compress. Grate the raw potatoes with their skins, wrap the resulting pulp in gauze and apply for 1-2 hours.
Prevention
There is no way to effectively prevent keratosis pilaris, but it is quite possible to prevent its exacerbations. To do this you should:
- in the cold season, lubricate the child’s skin with a rich cream every day;
- stick to a diet with sufficient fat and vitamins, take a course of multivitamins in spring and autumn;
- buy clothes for your child only from natural fabrics;
- avoid contact with allergens (food dyes, animal hair);
- Use mild detergents when bathing your baby.
In order for the disease to proceed favorably and not cause discomfort to the child, you just need to follow simple rules and treat exacerbations in a timely manner.
Source: https://LechenieDetej.ru/kozha-volosy-nogti/follikulyarnyj-keratoz.html
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Before you begin to treat the disease, you need to find out why it appeared , and only then take any action.
In some cases, the disease goes away on its own , however, sometimes the child still requires adequate therapy.
You should not self-medicate, since children's skin is very sensitive to the effects of many medications that can cause serious irritation. Therefore, only a doctor should prescribe therapy.