Changes in the external genitalia are a reason to visit a doctor. There are a number of signs that you need to carefully study and contact a specialist. These include balls that appear on the labia.
By a ball on the labia majora or minora we mean a dense neoplasm of a round shape. It can be localized under the skin or deep in the tissue. The reasons for its appearance are very diverse. In any case, it is necessary to determine the provoking factor in order to select an effective treatment.
During the diagnostic process, parameters such as location, mobility, size, and pain of the lump are taken into account. To exclude malignancy, a histological examination of tissues taken from the patient is performed.
Why did a ball appear on the labia: possible reasons
There are several options for the appearance of compaction:
- Inflammation or cyst of the Bartholin gland. In this case, the lump is localized on the labia majora or two are formed at once, located symmetrically;
- Blockage and, as a result, inflammation of the sebaceous glands. In this case, small hard pimples form inside the labia minora;
- Inflammation of the hair follicle. Sometimes with inflammation it increases significantly;
- Infection. Neoplasms can appear when the body becomes infected, especially the urinary system. The disease can also appear in the presence of a sexually transmitted infection (eg chlamydia, gonococcus, human papillomavirus);
- Congenital pathologies of the development of the urethra or external genitalia. In this case, problems will appear in childhood;
- Benign or malignant tumor. A lump in the tissue may turn out to be a cancerous tumor, so it is very important to consult a specialist in a timely manner.
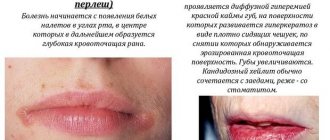
Herpes
Genital herpes is a recurrent viral disease that affects the mucous membranes of the vagina. White plaque on the labia is accompanied by the appearance of blisters, ulcers and erosions. The patient's inguinal lymph nodes are enlarged, symptoms of intoxication are observed, as well as swelling, a burning sensation and redness. In the vast majority of cases, herpes is transmitted from a carrier of infection to a healthy person through oral-genital, genital and anal-genital contact.
However, it is also possible to become infected by airborne droplets or rarely encountered in the household (through wet hygiene items), self-infection (transfer of pathogenic microorganisms from the face to the genitals) and transmission of the disease from mother to child during gestation.
Inflammation of the hair follicle and blockage of the glands
- Most often, this happens when the rules of intimate hygiene are not followed. As a result, the glands and follicles become dirty and inflamed. Inflammation very often develops due to ingrown hairs, for example, after depilation and epilation of the intimate area.
- Blocked sebaceous glands can also occur due to hormonal imbalance. For this reason, acne also forms on the face, forearms, and back. There may be a disruption in the endocrine system.
- If the ball appears for the reasons stated above, you need to start observing the rules of intimate hygiene, as well as treating the skin with antiseptic agents. You can use zinc ointment, and even baby powder will alleviate the condition. Underwear should be made from natural fabrics and be comfortable, as abrasions aggravate the situation.
- It is worth noting that in advanced cases surgical intervention is required. But in no case should you open/squeeze out the seal yourself - this can introduce an infection into the wound, thereby aggravating the course of the disease.
Forms and treatment of genital acne
Light-colored pimples can be large in size and cause discomfort or pain to a woman. The reasons for their origin lie in endocrine disruption, a decrease in the body’s immune strength, and hormonal surges.
Viral acne
A watery-looking body with an elongated apex and dense to the touch is a sign of human papillomavirus. Their appearance provokes reduced immunity and vitamin deficiency.
The labia minora or majora, strewn with small bubbles (1-2 mm), which burst and form erosions, is infected with another virus. The bubbles are crowded on a red base, and then their contents turn white. This rash is characteristic of the genital form of herpes, accompanied by itching and enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes. The disease is determined by analyzing a PCR smear. In case of a positive result, treatment is prescribed, including a set of measures:
- Therapy with antiherpes drugs
- Therapy with immune drugs.
- Prescription of antiherpetic vaccine.
- Auxiliary treatment with ointments.
Herpes is dangerous for both the woman and the partner, so timely consultation with a doctor guarantees the “catch” of the insidious virus and eliminates the possibility of relapse.
Molluscum contagiosum, a disease in which the labia is also affected by the virus. Most often, adults with weakened immune systems are affected by invasions in the genital area. The incubation period of such neoplasms is no more than 2 months. Their birth is characterized by the appearance of vesicles - 2-8 mm - flesh-colored with an indentation in the middle, slightly rising above the surface of the skin. When pressing on the element, a white substance is released. Sometimes adult patients experience symptoms of itching when a secondary infection is attached to the molluscum. Molluscum contagiosum should be distinguished from condylomas and papillomas. Nodules are also not a type of cancer. In healthy people, it disappears on its own without causing discomfort. A progressive disease is treated by destruction. For this purpose the following is used:
- chemical removal;
- cryodestruction;
- coagulation;
- removal with tweezers.
Read also: Pimple on the tongue: types and treatment
To establish a diagnosis, only an examination by a dermatologist is required; no studies are performed.
Hormonal nodes
Granular Fordyce cysts are frequent “guests” on the mucous membranes and genitals. A nodular defect is formed as a pimple of the sebaceous glands, small in size and light in color. A Fordyce nodule on the skin of the genital organs is not painful or dangerous. The reason for their appearance is considered to be the displacement of the sebaceous glands closer to the surface of the skin due to a surge in hormone levels. Sebum accumulates in the form of dense nodules and represents an aesthetic defect that is effectively removed using laser, liquid nitrogen and electrocoagulation. The surgical removal method is not used today because it leaves postoperative scars. There are also folk methods of dealing with cyst-shaped granules based on mumiyo. The product for external use "Retin-A" has a strong healing effect.
Tumors inside the labia
In the intimate area, benign neoplasms are more common. They appear due to excessively rapid proliferation of connective tissue cells.
What could a ball on the labia be like:
- Fibroma/fibromyoma are formations consisting of muscles. These most often grow on the labia majora. Treatment of fibroids/fibromyomas is only surgical;
- Lipoma is a formation consisting of adipose tissue. Lipoma can be felt as several small nodules or a large single ball. The danger is that the lipoma is prone to rapid growth, as a result of which complications develop. The tumor can provoke tissue necrosis. Like the previous ones, it can only be removed surgically;
- Hidradenoma is a tumor consisting of glandular tissue. Hydradenomas are rare, but very dangerous - there is a high risk of their degeneration into a malignant formation;
- Vulvar cancer. Malignant tumors differ from benign ones in that they can fester and bleed.
Purulent bumps on the pubis - photos and symptoms
cone
A lump under the skin on the pubis rarely occurs without symptoms. Usually this phenomenon is accompanied by certain clinical manifestations. The most pronounced of them is pain syndrome. Painful sensations vary depending on the reason for which disease the purulent lump appeared. The most painful lumps are those caused by folliculitis and lymphoma.
Another characteristic sign is hyperemia. It is characterized by redness of the skin in the affected area. Sometimes body temperature rises.
Lump with pus on the pubis in women
A pronounced clinical manifestation of this phenomenon is the release of the contents of the compaction. If we are talking about cysts, then it is transparent, with abscesses it is bloody with purulent impurities. If it is a syphilitic chancre, then the contents of the seal are bloody and have a pungent odor.
However, relying only on clinical manifestations, it is not possible to determine the nature of the neoplasm. You will need to undergo some examinations.
Bartholinitis and Bartholin gland cyst
Bartholin's glands are located at the entrance to the vagina. These are paired glands that are located in the subcutaneous fat layer, in the lower part of the labia majora. They produce a secretion that is released onto the inner surface of the labia minora, moisturizing them. This function is especially important during childbirth and sexual intercourse.
Bartholinitis is an inflammation of the Bartholin glands, which is provoked by pathogenic microorganisms.
The penetration of the latter is facilitated by the following factors:
- hormonal imbalance;
- decreased immune defense, for example, during pregnancy, after a cold, against the background of chronic diseases; immunodeficiency states;
- diseases of the gynecological sphere and urinary system;
- ignoring the rules of intimate hygiene, in particular during menstruation;
- damage to the perineum, for example, when rubbing underwear.
As inflammation progresses, symptoms become more pronounced.
- The ball, that is, the gland itself, increases and can reach an impressive size. This process is accompanied by pain and discomfort during sex, when moving and walking. Bartholinitis is often accompanied by a deterioration in general condition and an increase in body temperature. Sometimes purulent discharge appears.
- The excretory duct of this paired gland can become blocked due to infection, excessive secretion production, abnormal narrowing, etc. In such a situation, the secretion is not excreted, but accumulates in the excretory duct and the gland itself. As its volume increases, the walls of the capsule stretch, forming a cystic bladder filled with secretion.
Such cysts are benign and often resolve on their own. However, there is always a risk of complications. If bacteria enter the cyst, a purulent abscess will form on the labia.
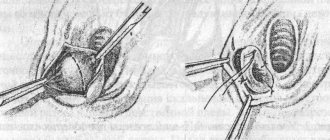
Treatment of bartholinitis always includes antibiotics (to destroy pathogenic microorganisms). Drug therapy is complemented by folk remedies to support and strengthen the body. Be sure to apply warm compresses and make baths, often with herbal decoctions. But sometimes surgical intervention is required, mainly in case of an abnormally narrow canal: the gland is opened, the accumulated secretion is removed, and plasty of the excretory duct is performed. If bartholinitis often recurs and is severe, doctors recommend completely removing the gland and its ducts.
Causes of infection
Gynecological specialists have identified the main causes of lumps on the labia minora and labia majora:
- An inflammatory process in the hair follicle is a fairly common cause, which is why a subcutaneous lump appears on the genitals. For the sake of beauty, girls struggle with hair in the intimate area. This leads to hair damage and inflammation. A small lump can be felt on the inside of the vagina. At the initial stage it is small in size. The lump then enlarges and fills with pus. It is necessary to get rid of inflammation as quickly as possible to avoid the spread of infection.
- Disturbance of local microflora. A large number of factors lead to irritation inside the vagina. These are synthetic underwear, poor personal hygiene, tight clothing and other reasons. The first signal of a microflora disturbance is redness and discomfort on the outer and inner labia. Sometimes these symptoms may go away on their own over time. However, an infection may occur, after which the patient discovers that a purulent lump has popped up on her lip.
- Infectious process. The Bartholinite gland is located next to the vagina. If the gland becomes infected, a small, soft lump appears on the outer and inner labia. The following microorganisms cause the disease: gonococci, E. coli and staphylococci. Recovery takes place under the supervision of a specialist and with the help of antibiotics.
Malignant neoplasms
Some of the changes in the area of the external female organs, especially if there is a compaction in the form of a ball, acquire threatening features due to the degeneration of connective tissue. The appearance of nodules is often combined with the development of cervical cancer if there is high oncogenic HPV in the body. With sarcoma of the vagina, there is always a large amount of secreted pus, blood, mucus, which has a pungent odor.
Hidradenoma is also dangerous - a fast-growing formation that reaches a compaction diameter of up to 1 centimeter. The dermis adjacent to the compaction dies off, eventually exposing muscle tissue.
Skin lesions increase the risk of secondary infection. Usually the changed tissue does not hurt or bleed. When diagnosing hidradenoma, there remains an increased likelihood of the spot becoming malignant.
A malignant formation between the labia refers to cancer of the vulva, which most often develops in patients with diabetes mellitus, infected with HPV or HIV. The first symptoms are the appearance of nodules, which then ulcerate, itch and grow. The deterioration of the condition is accompanied by a painful syndrome and serous-purulent exudate. Treatment is excision and radiation therapy.
How does infection penetrate the genital tract?
Infection in the labia can also penetrate through the urethra, as well as through the woman’s circulatory system.
When bartholinitis occurs in a woman, an inflammatory process occurs in only one of the glands. When the gland is blocked by an infectious process, pus begins to accumulate in it, or it is called purulent secretion.
Pus can accumulate inside the gland very quickly and eventually have no natural outlet. Therefore, in some women, on the labia it can reach the size of a chicken egg and even a large orange.
Against the background of a pathological increase in purulent lump, the patient notes such symptoms as:
- Chills;
- Fever;
- Increased temperature;
- Pain in an intimate place;
- Burning;
- Tingling;
- Unpleasant pain radiates to the vagina and anus.
If a purulent lump opens spontaneously, then a very foul-smelling, greenish-yellow liquid mixed with blood comes out of it.
After the lump on the labia opens on its own, the symptoms of the disease will subside a little, but, again, this is temporary. There is a huge risk of recurrence and formation of an infectious process.
Do not under any circumstances delay a visit to the gynecologist if you notice a lump on the labia. Otherwise, the condition may worsen. The sooner you see a doctor, the higher the chances of recovery.
There is a lump in the vagina
In most cases, a lump in the vagina or in the external genital area does not pose a threat to the life and health of a woman. Treatment depends on the causes of the pathology, the general clinical picture and the size of the tumor.
Lump in the vagina
The appearance of bulky lumps in the intimate area in women is a common gynecological problem.
Most often, such formations do not pose a serious danger and respond well to treatment.
Let's consider what diseases a lump in the vagina or on the external genitalia may be a sign of.
Causes of neoplasms
The concept of “lump in the vagina” includes any tumor-like formation located on the inner surface of the vagina, labia, or perineum. There are two groups of reasons leading to the development of the disorder.
Physiological reasons
In almost 70% of cases, the appearance of any irregularities in the genital area is associated with natural processes in the body and does not require mandatory medical or surgical treatment.
Most often, the cervix is mistaken for a tumor when the vaginal walls prolapse in young mothers.
The likelihood of developing the disorder increases with multiple pregnancies, repeated and traumatic births, and the birth of a large baby.
In most cases, the cervix returns to its natural position on its own within 6-8 weeks.
To prevent and eliminate the consequences of prolapse of the vaginal walls, Kegel gymnastics is used, which includes exercises for squeezing and relaxing the intimate muscles at different speeds and intensity.
Other factors that lead to cervical displacement include:
- Connective tissue diseases;
- Obesity;
- Endocrine disorders;
- Chronic severe cough;
- Excessive or insufficient physical activity.
In approximately 5-7% of cases, persistent weakness of the pelvic floor muscles can lead to regular prolapse and injury to the anterior or posterior vaginal vault, pathologies of the urinary system, and partial tissue necrosis due to circulatory disorders. Such patients are advised to undergo surgery to restore the shape and position of the internal genital organs.
Pathological causes
The main pathological causes leading to the formation of lumps in the intimate area include the following:
- Violation of hygiene rules;
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- Wearing tight or synthetic underwear;
- Microtraumas leading to disruption of the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes, followed by infection and inflammation;
- The presence of foci of chronic infection in the body;
- Regular hypothermia;
- Avitaminosis;
- Chronic stress;
- Some systemic diseases.
Symptoms and treatment of pathologies
Let's consider the manifestations of the main diseases, accompanied by the formation of seals and tumors in the vagina. If you suspect any violation, you should immediately contact a gynecologist.
Bartholinitis
A common gynecological pathology is inflammation of the large (Bartholin's) gland located near the entrance to the vagina. Bartholinitis is caused by pathogenic microorganisms (staphylococci, gonococci, trichomonas, E. coli) that penetrate the gland through its excretory duct with infected discharge from the vagina or urethra.
The disease is accompanied by significant swelling and redness of the skin around one of the labia minora. On palpation, a painful round or oblong compaction is felt.
Complex treatment consists of the following activities:
- Elimination of the underlying cause of the infection (most often antibiotic therapy is required as prescribed by a doctor);
- Cold compresses on the affected area (several times a day for 35-40 minutes);
- Application of tampons moistened with local anti-inflammatory drugs (Levomekol, ichthyol ointment);
- Physiotherapy on the 3-4th day from the onset of the disease (magnetic therapy, UHF).
When an abscess forms, immediate surgical treatment is required, which consists of opening it and removing the pus. In case of frequent relapses, it is recommended to completely remove the Bartholin gland.
Paraurethritis (skineitis)
Inflammation of the paraurethral glands and ducts is caused by the same pathogenic microorganisms as bartholinitis. The general clinical picture often corresponds to cystitis or urethritis. The main symptoms are discomfort during urination and sexual intercourse, pain in the perineum, the formation of lumps and abscesses near the urethra or vaginal opening.
Treatment consists of antibiotic therapy, anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating drugs. In severe cases, surgery is required.
Vaginal cyst
A painless round lump is most often located on the left or right side of the vaginal wall. A cyst is a sac of connective or muscle tissue filled with viscous serous or mucous contents. The pathology can be congenital or acquired as a result of injury to the internal surfaces of the organ.
The disease most often has an asymptomatic course and is detected during a routine gynecological examination.
Many patients are interested in the question of whether it is necessary to remove a cyst in the vagina. The main indication for surgical intervention is the large size of the formation, which causes discomfort to the woman or interferes with natural delivery.
Boils and abscesses
Purulent formations appear as a result of microtrauma during sexual intercourse or wearing uncomfortable underwear. In this case, a hard, painful lump often appears in the perineum between the anus and vagina.
For minor inflammation, patients are prescribed wound-healing creams or ointments for topical use. If the abscess hurts and continues to grow, it may need to be opened surgically.
Benign tumors
True benign neoplasms include fibroids, myomas, fibromyomas and lipomas that form in different layers of the vagina. Tumors are most often localized along the anterior wall of the vagina and do not cause any discomfort. Sometimes there are periodic pains, moderate discomfort and a sensation of a foreign body in the genital tract.
Despite the low risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor, it is recommended to remove all tumors surgically within the boundaries of unchanged tissue.
Oncological pathologies
Carcinoma poses the greatest threat to the life and health of the patient. In most cases, oncology is asymptomatic, but some women may be bothered by the following symptoms:
- Scanty intermenstrual bleeding;
- Discharge of a pathological nature (thick, foamy, with an unpleasant odor, inclusions of mucus and pus);
- Pain syndrome of different nature.
If any alarming signs appear, you should contact a specialist. Diagnostics includes an examination in a gynecological chair and an ultrasound, which makes it possible to detect dangerous pathologies at an early stage. If necessary, a biopsy and other clinical tests are performed.
Source: https://DrLady.ru/disease/shishka-vo-vlagalishhe.html
Features of tumor treatment
First of all, it is necessary to note the possibility of surgical removal of the seal due to enucleation (isolation of a tumor-like node from a healthy tissue cover). Next, the formed wound is sutured for benign formations on the external genitalia.
The next treatment option may be a vulvectomy. When we talk about this, we mean the surgical removal of everything connected to the external genitalia (for example, the labia, clitoris, and skin covering the perineal area). This is a fairly serious operation, which is performed for women only if such a stage of the oncological process has been proven at which any other intervention will not be sufficiently effective. In addition, experts point out that seals can be treated with some other methods:
- Radiation therapy, which consists of destroying malignant formations using special ionizing radiation (for example, X-rays).
- Chemotherapy is the destruction of cancer-dependent cells using cytostatics (components that create obstacles to division and renewal of cellular composition).
- The use of medications that promote the resorption of cysts.
- Carrying out a biopsy, which allows you to pump out fluid not only from cysts, but also, in some cases, from fatty tissues.
Is it possible to prevent tubercles on the labia?
Preventive consultations with a gynecologist are the key to health.
In order to prevent the formation of tubercles in the labia area in women in the future, it is strongly recommended to take certain preventive measures.
In particular, special attention is paid to the importance of giving up bad habits.
We should not forget about maintaining a healthy lifestyle. In this case, we are talking about constant physical activity, ensuring a healthy diet and avoiding fatty, smoked and canned foods. No less significant is the restriction on the use of salt.
For every woman, it would be best to undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist (it is advisable to do this at least twice a year). It is also important to attend to the treatment of so-called background and precancerous pathologies associated with the vulva area. We can talk about kraurosis (thinning, dryness and itching of the mucous membranes in the area of the external genitalia), leukoplakia (the formation of specific films or white plaques on the mucous surface of the external genitalia). Of course, special attention should be paid to genital warts (wart-like growths on the mucous surface of a woman’s genital organs, which can appear quite unexpectedly).
On women's forums you can often find a message with the following content: “Girls, what could this be? A small lump appeared on the labia. They are red and painful when pressed, but there is no pus yet. Help! Have you had this happen and, if so, how to remove this lump?”