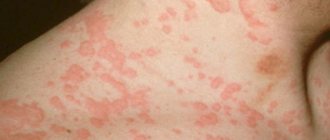
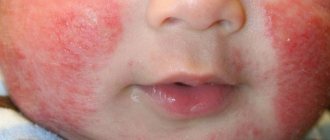
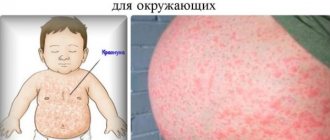
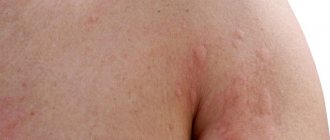
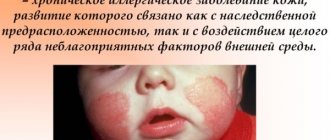
An appearance defect that causes psychological discomfort in people is a hemangioma on the face. It is most often diagnosed in young children, but it can also be present in adults.
The process in most cases is benign. Nevertheless, experts adhere to this point of view: if a tumor rapidly increases in size or causes mental suffering to a person, it is better to remove it. Various modern minimally invasive procedures have been developed for this purpose, each with advantages and disadvantages. The best option should be selected by a doctor.
Hemangioma on the face - what is it?
The main distinguishing feature of childhood and adult pathology is that it is congenital and cannot arise for the first time in a person who has crossed the threshold of adulthood.
This formation often remains under the skin surface for a long time. And due, for example, to a weakening of the body, it breaks out and grows at a rapid pace.
The tumor vascular structure comes in different sizes, starting with a small reddish mole and ending with a large formation on the floor of the face. Moreover, the outside of the spot becomes lumpy and rough.
Hemangioma on the face can appear in both children and adults. The formation is shown in the photo below:
In addition to being unaesthetic, it interferes with the normal functioning of the organs of vision, smell, and hearing.
A non-malignant formation does not threaten the baby’s health if it does not bother him. In frequent cases, the anomaly in children (particularly newborns) disappears on its own by the age of 5-7 years.
You should be afraid if it tends to grow, causes pain, itching, irritation of the skin, or threatens the health of the child. Then immediate treatment of the pathology will be required.
In order not to miss the dangerous manifestations of hemangioma on the face, you need to carefully monitor its condition and the baby’s behavior.
Signs of hemangioma and pathogenesis
Hemangioma is a red spot, in the center of which there is a point, and from it comes a network of small vessels. Usually the neoplasm is smooth and can protrude 1-2 cm above the skin. When pressed, it turns pale, but quickly returns to its normal appearance. A characteristic symptom is temperature unevenness: upon palpation, the hemangioma is noticeably warmer than the surrounding areas of the body. It may not manifest itself clinically and may be discovered by chance during examination.
The disease occurs in phases: growth, stabilization, and optionally spontaneous regression. Complications are possible during the growth and stabilization phases of hemangioma. If a neoplasm grows near a functional organ, its function may deteriorate - for example, in the periorbital zone it can contribute to decreased vision, and on the laryngeal mucosa - obstruction of breathing.
If the hemangioma is localized near the nerve ending, as it grows, weakness and numbness of the limbs, disruption of the bladder and gastrointestinal tract are possible. Large spinal hemangiomas can cause pain and increase the risk of compression fractures. New growths are easily injured, so they can cause bleeding.
What are the symptoms of the prevailing species (4 options)
To accurately determine the type of hemangioma, it is necessary to distinguish between the symptoms and distinctive features of the tumor.
- The simple form is endowed with a red or blue-purple tone, distinct outlines and location on the epidermal surface. Such formations damage mainly the epidermis and partially the subcutaneous fatty tissue. Their growth occurs laterally. The surface of tumors is mainly smooth. Uneven ones are rare; those protruding slightly above the epidermis are even rarer. Palpation is accompanied first by blanching of the formations, followed by restoration of the original tone.
- The cavernous appearance with a location under the skin surface looks like a limited nodular tumor formed by separate cavities (cavities) with internal filling with blood. Their structure is soft and elastic, which is revealed by palpation. Their initial tint is bluish with a gradual transformation into a blue-purple color, which is manifested in layered formations. When pressed, hemangiomas on the face fade due to blood outflow and grow when coughing or screaming due to tension and increased blood flow.
- The combined formation combines both simple and cavernous forms and appears as the dominant part of the vascular proliferation.
- The mixed form of hemangioma is a tumor cell containing a vascular base and tissues - connective, nervous, etc. Cells have an appearance, tone and structure, determined by the types of tissues in the formation.
The face is one of the places where such tumors are localized.
Types of cutaneous hemangiomas
The depth of location, process of formation and appearance of vascular hemangiomas allows them to be divided into three main types:
- Capillary - characterized by a superficial location, consists of endothelium, the cells from which capillaries are formed.
- Cavernous - formed in the subcutaneous tissue from venous and lymphatic abnormally dilated vessels, its size can reach 20 cm in diameter.
- Venous - consists of venous vessels, appears on the lower lip in old people.
Capillary
Other names: infantile, congenital, strawberry hemangioma. It is the most common type of neoplasm that appears above the surface of the skin in children at birth. Most often they can be observed on the skin in the head and neck area. Some congenital capillary hemangiomas disappear on their own before the age of 2 years, some are present on the body up to 5-9 years. In adults, acquired pathology looks like this:
Peculiarity. This hemangioma is soft to the touch. It may have a red or purple color, a smooth surface and clear boundaries. When pressed, the formation becomes lighter. Size from 1 to 10 cm in diameter.
Cavernous
They can occur almost anywhere on the body where there are blood vessels. They are often called raspberry-like because of their bubbly bumps. Unlike capillary types, cavernous ones are not prone to regression (disappearance, reduction).
Peculiarity. They almost always grow to the sides, so if left untreated they can grow, for example, on half of the face.
Rarely does such a neoplasm disappear on its own, and even then not without a trace. In most cases, in the future, cosmetic procedures will still be required to remove traces of its presence on the skin.
Venous
It is less common than the first two types. Most often in older people. The tumor is located on the skin of the face, often on the lower lip, for this reason it is also called a tumor of the senile lips. Ultraviolet radiation provokes the appearance of pathology.
Venous hemangioma can be flat or raised above the skin. The formation is soft to the touch. Its color is usually dark blue or purple. It does not cause any inconvenience to a person other than a cosmetic defect.
For reference: In adults, the most common cavernous-capillary form of formation is called combined hemangioma. The pathology is located in the subcutaneous layers. Formed from superficial and deep blood vessels.
How is hemangioma treated?
After examining the patient, the doctor will send him for tests to get a complete picture of the structure of the tumor.
Studies will indicate the depth of damaged tissues, the location of formations regarding connective tissues and nerve endings. Blood and urine tests and ultrasound examination of the hemangioma are also necessary.
If the affected area is large, an x-ray examination of the vessels will be required.
Usually, after reviewing the tests, the specialist recommends:
- systematic observation of the tumor, if it does not need to be removed;
- therapeutic treatment with hormonal drugs and compression bandages;
- tumor resection by a surgeon if there are indications for surgery;
- the use of other methods to eliminate hemangioma on the face.
The choice of correction method is carried out depending on the hypertrophy of the vascular formation and the degree of tissue damage.
Treatment of hemangioma in adults
Having noticed an area on their face with a vascular spot or even a tumor protruding outward, people are advised to immediately consult a dermatologist or surgeon. Self-medication is absolutely unacceptable - due to injury, hemangiomas cells can transform into cancer.
For small facial tumors and the absence of unpleasant, painful sensations, dermatologists prefer not to prescribe special therapeutic measures - they give recommendations on maintaining a healthy lifestyle, strengthening the immune system, and correcting nutrition.
But with the rapid growth of the hemangioma and the appearance of bleeding, trophic lesions of the spot, and severe pain, the therapy will be more massive and specific.
The main methods for eliminating tumors on the face:
- laser therapy – vascular cells are burned out with a directed beam of a laser beam, healthy tissue is not affected, so there is practically no scar left;
- cryodestruction - using liquid nitrogen, the tumor focus is frozen, then it is gradually rejected, the vascular tissue is replaced by healthy epithelial cells;
- electrocoagulation - the spot is carefully burned with a high-frequency electric current, the formed crust falls off on its own without scarring;
- sclerosing therapy - this method is more often used for cavernous hemangiomas; a special solution is injected into their cavity, which glues the walls of the lesion, after which it stops growth and development.
What therapeutic methods are used (3 methods)
Therapy for the treatment of hemangioma on the face in adults or children is used extremely rarely. If it is nevertheless used, then preference is given to compression.
The method applies to formations located in places where it is possible to apply a pressure bandage for a long period. After 2 months, the tumor apparently decreases in size or no trace remains of it.
Another way is to take hormonal drugs. However, the use of the method is strictly limited due to the manifestation of a number of serious associated effects, therefore it is used in rare cases strictly on the recommendation of a specialist.
The dosage of drugs is selected for a specific patient, especially a child.
Another method of treating vascular formations is to take the medications Propranolol and Timolol. The effectiveness of the treatment technique has been proven by experimental studies in Europe and the USA.
Therapy with such drugs is carried out under medical supervision with regular checking of blood pressure and blood glucose levels.
Propranolol or Timolol is prescribed in individual dosages.
Causes
In medicine, the causes of senile hemangiomas have not been fully studied. Some doctors claim that the reason lies in heredity, others highlight the effects of UV rays on human skin. The influence of infectious diseases that a woman suffered in the 1st trimester of pregnancy has been precisely established. At this time, the fetal circulatory system is formed, and the infectious factor contributes to the development of tumors. Perhaps doctors are in no hurry to study the provoking factors of the disease, since cherry hemangiomas do not pose a threat to humans. Treatment for this disease is cosmetic in nature. But sometimes there are exceptions that are alarming.
Senile hemangiomas, when injured, can bleed heavily and cause dangerous infection.
Traditional medicine to help
Despite the fact that folk recipes are not a panacea in the treatment of vascular formations on the face, many practice their use.
Celandine leads the list of plants for eliminating various formations from the facial epidermis. But often it does not remove the vascular tumor due to its rare structure.
Aloe juice has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects. But, still, scientific studies do not confirm its effectiveness in the fight against vascular tumors.
Why do hemangiomas appear?
The exact causes of hemangiomas have not yet been identified; It is generally accepted that their appearance can provoke disruption of intrauterine development of the fetus due to a viral illness of the mother or oxygen starvation. Additional risk factors for the formation of congenital hemangioma:
- multiple and/or late pregnancy;
- increased amount of estrogen in the mother;
- her sedentary lifestyle;
- unbalanced diet;
- alcohol or nicotine intoxication of the fetus;
- his low birth weight.
In adults, the cause of neoplasm can be a hereditary predisposition, diseases of the cardiovascular system, excessive ultraviolet radiation, and increased levels of the female hormones estrogen.
Indications for laser hemangioma removal
Removing the hemangioma is the only way to solve the problem.
One effective treatment option is the use of laser. With its help, it is possible to eliminate a simple or cavernous benign tumor, provided that it is located on the surface of the skin or does not involve deep soft tissues. If treatment for the disease is not started in a timely manner, the risk of complications increases significantly (especially if the tumor diameter is more than 3 cm):
- bleeding (including massive);
- thrombophlebitis (formation of blood clots in the veins);
- blood clotting disorder;
- rough scarring (with independent regression).
The main rule: do not touch, but observe and record
In the vast majority of cases, a hemangioma that has formed in the “right” place does not require any treatment, much less surgical intervention. And yet, it needs to be carefully and regularly monitored - with what dynamics it increases in size, where exactly does the growth extend, does it change color, etc. Once a week or two it is necessary to see a pediatrician.
And the best thing is not just to observe the hemangioma in your baby, but also to take photographs. So that at your next appointment with a specialist doctor, you can visually provide him with all the dynamics of the development of hemangioma in the “was - became” format from the moment of its appearance to the present day.
By the way, about doctors... It is very important that your child’s hemangioma is observed by not just anyone. And a really good, experienced specialist who encounters hemangiomas in newborns not just a couple of times a year, that is, from time to time, but every day.
Remember: this is not a dermatologist or a cosmetologist, but none other than a pediatric surgeon. You can always take a referral from your treating pediatrician.
Features of hemangioma removal
At the first visit, the doctor conducts an examination and collects anamnesis. He evaluates:
- education growth rate;
- dimensions (depth and extent of distribution on the skin).
The specialist then confirms the diagnosis.
If there are doubts about the benignity of the tumor, additional specialists or laboratory and instrumental studies may be involved. The doctor will also ask you in detail about allergic reactions to the administration of anesthetics in the past.
Then the procedure itself begins. Its progress can be represented as follows:
- Anesthesia. Local anesthesia allows you to completely eliminate any pain during laser exposure.
- Antiseptic treatment (to reduce the risk of infectious complications).
- Removal of the tumor. One by one, the laser eliminates all pathologically altered tissues. The technique does not require the capture of healthy skin, which also prevents the formation of scars or scars.
- Repeated treatment with antiseptic.
- Applying an aseptic dressing or plaster.
To get rid of the hemangioma completely, it is recommended to wear the bandage for several days. It eliminates the impact of environmental factors and accelerates the restoration of skin integrity. Rehabilitation can take from 5 to 14 days. In the first 1-3 days, discomfort may occur: itching or burning, slight tingling in the intervention area.
How is diagnosis carried out?
Consultation with a dermatologist is the beginning of diagnostic procedures. During the examination, the doctor’s diagnosis is based on such features as the development and location of the tumor, its growth into the epidermis and the extent of blood supply. Additionally, the parameters of the neoplasm are taken into account. Ultrasound is used to make the diagnosis accurately. If the hemangioma is located on internal organs, additional CT and MRI diagnostics are performed. Analysis of tissue samples during histological examination excludes or confirms the malignant nature of the pathology.
Diagnostic methods
A visually detectable tumor is diagnosed upon examination of the patient. In the process of interviewing the patient, the doctor determines the time of appearance of the formation, its tendency to grow, and the presence of signs of spontaneous resorption.
When neoplasms form in internal organs, ultrasound, computed thermography, angiography, radiography, rheovasography, and MRI are required. With the help of research, the exact localization of the pathology, the condition of the vessels and blood flow in them are determined.
With an asymptomatic course of the disease, formations can be detected randomly.