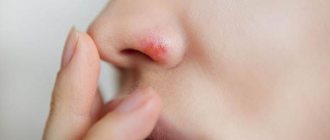
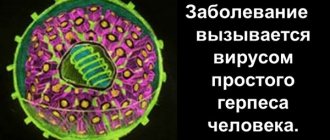
Herpes on the neck is a manifestation of the presence of a herpes infection in the patient’s body. This dermatological disease always develops acutely and has a characteristic clinical picture. Damage to the skin of the neck begins with the formation of a large amount of red rash on it, which is itchy and painful when you try to influence it tactilely. The origin of the disease is viral, it is considered incurable and can pose a threat to the vital functions of the entire body if adequate drug treatment of the pathology has not been carried out and the disease has acquired a complicated form.
What are the types of skin diseases in humans?
Skin diseases can have different origins. They all differ in their appearance, symptoms and cause of formation.
The most common of them:
- Fungi. Fungal diseases of the skin in humans are usually caused by parasitic fungi, whose origin is plant-based. Such diseases usually affect: the nail plate, hair, and skin. Fungal diseases are contagious, which means they can easily be transmitted from one organism to another.
- Ulcers. The causative agents of pustular skin diseases are staphylococci and streptococci. Also, the cause of the formation of ulcers can be infections as a consequence of cooling and mental trauma. Pustular skin diseases are divided into two main types: superficial pyoderma and deep pyoderma.
- Skin diseases that are caused by animal parasites. Such diseases include: lice and scabies. The first one is quite easy to cure. The causative agent of scabies is usually a scabies itch or mite. At the first symptoms of scabies, it is necessary to begin treatment, as otherwise it can lead to the formation of eczema.
- Ringworm. There are several types of lichens. The most common of them are: lichen rosea, lichen planus, herpes zoster, and lichen cauliflower. Each species has its own characteristics and reasons for formation.
- Diseases of the skin glands. The most common types of these diseases are: seborrhea and acne. If seborrhea affects the head, then hair loss begins. Acne most often appears at a young age, most often based on seborrhea.
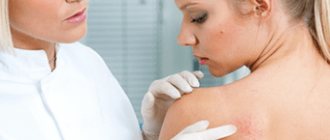
Dermatitis is a rash in the form of blisters, peeling, discomfort, itching, burning, etc. The reasons may be different, depending on which there are several types of dermatitis, for example, infectious, allergic, atopic, food, etc.
The cream contains exclusively natural ingredients, including beekeeping products and plant extracts. High efficiency, virtually no contraindications and minimal risks of side effects. Amazing results of treatment with this drug are evident in the first weeks of use. I recommend.
Photos and names of skin diseases in humans
Now it’s worth looking at photos of the main skin diseases, and below you can read their symptoms, causes and descriptions.
The most common skin diseases:
- Acne
- Dermatitis
- Lichen
- Herpes
- Eczema
- Acne vulgaris
- Bedsores
- Scabies
- Keratosis
- Carcinoma
- Hemangioma
- Melanoma
- Papilloma
- Dermatomycosis
Acne is a disease of the sebaceous glands, which is characterized by clogging and inflammation of the follicles. People often call this skin disease acne.
The main causes of acne:
- Hormonal imbalance, which causes the sebaceous glands to malfunction.
- Stress.
- Hereditary factor.
- Dysbacteriosis of the intestinal system.
- Contamination of the skin and poor cleansing.
Symptoms of acne formation:
- The formation of comedones in the form of black or white acne.
- Formation of deep acne: papules and pustules.
- Affects the chest, face, back and shoulders.
- Formation of redness and bumps.
- The appearance of purulent acne.
Dermatitis
Dermatitis is any inflammation of the skin. The disease dermatitis has several types. The most common types of dermatitis: contact, diaper, seborrheic, atopic.
Despite this, dermatitis has some main causes:
- Physical impact on the skin in the form of friction, pressure.
- Exposure to heat and sunlight on the skin.
- The use of chemicals and cosmetics used by humans.
- Impact of the external environment.
Symptoms of skin dermatitis:
- The appearance of burning and itching.
- Formation of blisters on the skin.
- Presence of swelling.
- Formation of redness at sites of inflammation.
- Formation of scales and dry crusts.
Here you can learn in detail about the characteristics and treatment of inflammation, as well as see photos of dermatitis.
Lichen
A skin disease such as lichen includes a number of several varieties. Each of these types differs in its pathogen, type of rash, localization and infectiousness.
Detailed information about the types of this disease and photos of lichen in humans can be found on the website.
The main causes of lichen on the human skin:
- Viral and fungal microflora.
- Weakened immunity.
- Stress.
- Heredity.
- Infectious diseases.
Symptoms of lichen disease:
- Formation of colored and flaky spots.
- Formation of spots on any part of the body, depending on the type of disease.
- Some types are accompanied by an increase in temperature.
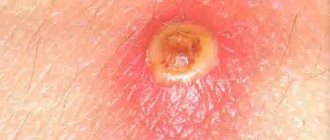
Herpes
You will find answers to the question about the treatment of herpes on the body here.
Herpes can also differ in its type and location, however, all types of herpes have common causes:
- Weak immunity (most often after suffering from a disease).
- Metabolic disorders in the body.
- Having bad habits (drinking large amounts of alcohol).
- Presence of acute respiratory diseases.
- Improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Main symptoms of herpes:
- The formation of bubbles that are filled with a clear liquid.
- Inflammation and redness at the site of formations.
- The bubbles burst after 3 days.
- Formation of a dry yellow crust on burst bubbles.
Eczema
Eczema is a recurrent inflammation of the upper layer of the skin, which can be caused by a variety of reasons, ranging from diseases to eating foods that cause an allergic reaction.
The main causes of the formation of eczema on the skin:
- Heredity and genetic predisposition.
- Improper functioning of the body's immune system.
- Hormonal imbalances in the body.
- The presence of mycosis.
- Presence of liver and stomach diseases.
Symptoms of eczema:
- Formation of weeping blisters on the skin.
- Formation of serous ulcers.
- Itching is rare.
- Severe erythema.
- Swelling of tissues.
Acne vulgaris
Acne vulgaris is a chronic skin disease that manifests itself as purulent-inflammatory changes in the sebaceous glands. Most often, acne vulgaris appears on the face, back and chest.
The main factors that provoke the appearance of acne vulgaris:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Heredity.
- Hyperandrogenism.
- Beginning of puberty.
- Impaired menstrual function.
- Diseases that were previously suffered.
- Factors associated with professional activity.
The main symptoms of acne vulgaris:
- Formation of comedones.
- Degeneration of comedones into papules or pustules.
- Localization on the back, face and neck.
- Scar formation after inflammation.
Bedsores
Bedsores are the development of a process characterized by necrosis, affecting soft tissues right up to the bone due to external irritants and tissue nutritional disturbances.
The main causes of bedsores:
- Any external mechanical irritants (plaster cast, denture).
- Violation of tissue nutrition.
- Urinary and fecal incontinence.
- Sedentary lifestyle of the patient.
- Protein deficiency.
- Dry skin.
- Poor patient care.
Symptoms of bedsores:
- Formation of redness.
- Swelling of the skin.
- Peeling of the upper layers of the skin.
- Bubble formation.
- Formation of deep ulcers after opening of blisters.
Scabies
The main reasons for the appearance of scabies in humans is the presence of scabies mites on the skin , which are almost impossible to notice with the naked eye.
Symptoms of scabies:
- Presence of itching on the affected areas of the skin.
- Formation of rashes due to severe scratching and skin infection. other infections.
- Bubble formation.
- Formation of stripes on the skin - scabies.
Here you can learn more about how to treat scabies.
Keratosis
This disease is accompanied by thickening and keratinization of human skin. With the development of keratosis, painful sensations and bleeding wounds may appear.
The main causes of keratosis:
- Genetic predisposition.
- External chemical irritants.
- Weak immune system of the body.
- Already suffered infectious diseases.
- Changes in age (most often the disease manifests itself in people over 50 years of age).
Symptoms of keratosis:
- Roughness and unevenness of the skin at the first stage of the disease.
- Formation of hard brown or red spots.
- Peeling of the skin around the formations.
- Presence of itching.
Carcinoma
The disease can form on any part of the skin. A sharp increase in the number of moles on the body should already be alarming.
Main symptoms of carcinoma:
- Formation of pearlescent or shiny bumps.
- Formation of ulcers.
- Formation of pink raised spots.
Hemangioma
Hemangioma is a benign formation on the skin due to a vascular defect, which most often occurs in children. Externally, the disease appears as bumpy red spots.
Causes of hemangioma:
- Taking medications during pregnancy.
- Hormonal imbalance in the body of a pregnant woman.
- Previous infectious diseases during pregnancy.
Symptoms of hemangioma:
- At the initial stage, the formation of a barely noticeable spot in the area of the child’s face or neck.
- Redness of the spot.
- The spot becomes burgundy.
Melanoma
Melanoma is another sign of skin cancer . At the first signs of melanoma, you should consult a doctor.
Main symptoms of melanoma:
- The mole has different shades.
- Roughness and unevenness of the neoplasm.
- The mole exceeds 5 mm in diameter.
- Swollen moles.
- Moles begin to hurt and itch.
- Lymph and blood are released from moles.
Papilloma
Papilloma is a benign tumor that appears on the surface of the skin in the form of a small growth.
Causes of papilloma:
- Weakened immunity.
- Stress.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Smoking.
- Drinking large amounts of alcohol.
- Presence of chronic diseases.
Main symptoms of papilloma:
- Formation of a pink or flesh-colored growth.
- The size of the formation can reach several centimeters.
- Formation of a common wart.
Dermatomycosis
Dermatomycosis is a group of fungal diseases of the skin. As a rule, this disease occurs in 20% of the world's inhabitants. The main cause of dermatomycosis in humans is the contact of fungi on the skin or mucous area of a person.
Symptoms of dermatomycosis:
- The formation of red spots that are covered with scales.
- Presence of itching.
- Hair loss and breakage.
- Peeling of nails.
Causes leading to the appearance of a rash
If a rash on the neck appears as a result of infection with the herpes virus, then the following options may be considered as the cause:
- Types 1 and 2 of the virus : most often manifest as a “cold” on the lips, but if self-infected they can spread to the neck area;
- Varicella-zoster virus (type 3) : causes both chickenpox and shingles. Most cases of herpes on the neck are manifestations of shingles;
- Epstein-Barr virus (type 4) and cytomegalovirus : skin rash is not a characteristic symptom of infection with these viruses and occurs only in patients with a very weakened immune system.
The main factors that “trigger” the virus include any conditions that undermine the immune system: hypothermia, colds (flu, ARVI), stress, the presence of concomitant infections, taking antibiotics
etc.
Risk subgroups
Most susceptible to the disease:
- people over 40 years old. At this age, weakening of the immune system is observed;
- presence of type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- patients suffering from obesity, cancer, fungal skin lesions;
- patients with chronic and HIV infectious diseases.
Infection in children: clinical features
The main features of the disease are:
- simultaneous damage to the skin of the cervical region and nerve endings;
- the appearance of ulcers on one side of the neck.
Infection is possible at birth and contact with a sick mother or breastfeeding. The manifestation of the disease in children under 2 years of age is extremely rare, since a newborn child has good immunity. The chances of getting sick increase at 3-4 years of age, and at this age the disease is more severe. The child’s body is weak and not yet strong, so the body’s protective properties cannot prevent the spread of the virus. The development of the disease process can affect the nervous system, internal organs of the baby and his vision.
Other possible causes of the rash
In addition to the herpes virus, skin rashes on the neck can be caused by:
- Fluctuations in hormonal levels;
- Poor personal hygiene;
- Allergic reaction to clothing made of synthetic fabric, perfumes, household chemicals;
- Gastrointestinal diseases;
- Other viral infections (measles, rubella).
One of the main features of herpes zoster, which distinguishes it from urticaria (an allergic reaction), is the unilateral primary localization of the rash - on the left or right side of the neck.
Another distinctive feature of this type of herpes is the ability to affect the nervous system and cause neuralgic pain. The pain can radiate to nearby parts of the body - head, arm, chest.
The causative agent of infection
The appearance of a characteristic rash on the neck can be caused by one of two types of viruses:
- Herpes simplex (HSV type 1). The infection usually appears on the lips, but sometimes spreads to other organs.
- Varicella-Zoster virus (HSV type 3). If the virus enters the body for the first time, chickenpox develops (usually in childhood). A severe weakening of the immune system in an adult who has had chickenpox in childhood leads to the appearance of herpes zoster.
The pathogen spreads along the affected nerves, causing rashes.
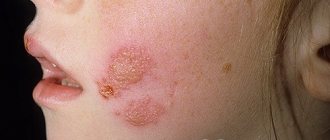
Symptoms of herpes on the neck
Rashes on the neck go through 4 stages of development:
- It all starts with skin itching, redness and tingling; when scratching, the skin becomes inflamed;
- A reddish rash appears on the affected area, consisting of small, painful blisters filled with clear liquid; over time, they increase in size, and the liquid contained in them becomes cloudy; itching and burning intensify;
- The bubbles burst, the liquid flows out; at this stage the person is contagious to others;
- The ulcers remaining in place of the vesicles dry out and become covered with a crust, which cannot be picked off to avoid relapse.
Scratching a herpetic rash on the neck is strictly prohibited - this can lead to the addition of a secondary fungal or bacterial infection, as well as to the formation of scars after the rash disappears.
In the general statistics of all cases of herpes zoster, rashes on the neck account for 12%.
Additionally, herpes zoster on the neck is accompanied by signs of general intoxication, which include:
- General weakness;
- Increased body temperature, fever, chills;
- Headaches and dizziness;
- Nausea;
- Appetite and sleep disorders;
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
Clinical picture
Herpes viruses types 1 and 3 have both common symptoms and differences. Timely recognition of the first signs of the disease will allow us to determine the specific type of infection and begin adequate therapy.
The first manifestations of the disease are not immediately noticeable. First, small areas of skin on the neck turn red, and a tingling and itching sensation appears.
One of the most common signs of herpes on the neck is enlarged lymph nodes, but this symptom does not appear in all cases.
Subsequent stages of the disease are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- A day after the first symptoms appear, blisters filled with clear liquid begin to appear on the reddened skin.
- Gradually, the bubbles enlarge and become larger, and the liquid inside them becomes cloudy.
- The bubbles burst and their contents come out.
- Bursted blisters become covered with a hard crust, which indicates the beginning of recovery. Treatment cannot be interrupted at this stage.
You should consult a doctor immediately after the appearance of severe and persistent itching in the neck area (bubbles will appear in 10-14 days). Treatment of the infection started in the first stages will allow you to quickly get rid of its manifestations.
There are several stages in the development of the disease:
- A severe headache appears. The patient feels unwell and chills. Symptoms may persist for 72 hours, and sometimes longer.
- In the area of future rashes, a feeling of itching and burning appears.
- Appetite is disrupted and temperature rises.
- The affected area on the neck begins to swell, spots with a diameter of about 3-4 mm appear.
- Within 24 hours, the spots turn into vesicles with serous contents.
- After a day, the swelling decreases slightly, the liquid in the blisters becomes cloudy.
- The rash begins to dry out and a crust forms in place of the burst blisters.
- The patient’s general well-being improves and the temperature normalizes.
Depending on the state of immunity, symptoms of the disease may manifest themselves differently.
If the disease proceeds normally, recovery occurs approximately 3 weeks after infection. When the rash on your neck goes away, the hyperpigmented areas will remain.
Treatment of herpes on the neck
At the first symptoms, such as a rash on the neck, itching, redness, you can lubricate the problem area with Acyclovir and take a Paracetamol tablet. For correct diagnosis and clarification of the diagnosis, it is better to consult a doctor: a virological study is carried out using the PCR method or the fluorescence method.
Effective treatment of the herpes virus should be comprehensive and include:
- The use of antiviral drugs (in the form of external use (ointments) and tablets);
- General restoratives and immunomodulatory drugs: interferon, nonspecific immunostimulants;
- Painkillers;
- Antipyretics (in case of high temperature).
One of the following antiviral drugs is prescribed:
- Valtrex – 2 tablets 3 times a day for a week;
- Famvir (has an anti-inflammatory effect) – 1 tablet 3 times a day for a week;
- Valaciclovir – 2 tablets 3 times a day for a week.
Antiviral drugs are used both to relieve the clinical symptoms of the disease and to prevent possible relapses in patients with reduced immunity.
It is impossible to completely get rid of the herpes virus, but you can extinguish its activity.
The following are used for external use:
- Zovirax – applied to the rash 4-5 times a day for 5-10 days;
- Acyclovir - applied 5 times a day for 5-10 days;
- Devirs - applied with massaging movements 5 times a day for 5-8 days;
- Panavir - applied 5 times a day for 4-10 days.
As a local treatment (ointments), antiviral agents are effective only at the stage of vesicular rashes. Once erosions have formed, their effectiveness is significantly reduced.
Manifestations of neuralgia are significantly reduced by painkillers such as Lidocaine and Acetaminophen
.
In order to strengthen the immune system, it is recommended to pay more attention to your diet, making sure that it is balanced and complete. When fighting the herpes virus, vitamins A, B and E are especially important, as well as ascorbic acid in combination with rutin . In addition to eating foods rich in these vitamins, it is recommended to take multivitamin complexes 2 times a year.
Vitamin A increases local immunity, the protective function of the skin and mucous membranes and prevents the virus from penetrating into the body;
Vitamin C increases the activity of white blood cells and the production of interferon, protecting body tissues from free radicals, and also helps preserve vitamin E, which is a powerful antioxidant;
Also, microelements such as zinc and selenium . Zinc protects cell membranes from the oxidative effects of other elements (iron and copper). An ointment containing zinc accelerates the healing of ulcers and reduces the intensity of blistering.
A healthy lifestyle and any measures aimed at strengthening the body's natural defenses are of great importance in the treatment of herpes. It is recommended to spend more time in the fresh air and carefully monitor personal hygiene.
There are also traditional medicine recipes for the treatment of herpes on the neck: you can treat rashes on the neck with camphor or fir oil, earwax 2-3 times a day.
You can make water compresses with interferon, which are applied to the areas affected by the rash. Additionally, natural herbal preparations are taken to improve immunity: echinacea extract, ginseng, cordyceps
.
The following also have good antivirus properties:
- Propolis extract is a natural bee product that is included in various ointments and is available in tablets;
- Garlic extract;
- Breast milk.
Diagnostic methods
To determine herpes on the neck, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Dermatological examination. Herpes manifests itself with characteristic symptoms, so in most cases this method makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis.
- Linked immunosorbent assay. When a herpes virus enters the body, it begins to produce specific antibodies that are easily detected using ELISA. Blood or cerebrospinal fluid is taken for testing.
- PCR. This method is used to determine the DNA of the virus in the sample being tested.
- Culture method. It is used for chronic and latent forms of the disease.
Possible complications of herpes on the neck
Complications in this case occur quite rarely, but it is necessary to be aware of them. In the absence of adequate treatment, the following consequences are possible:
- Postherpetic neuralgia, accompanied by severe and constant pain caused by nerve damage;
- Damage to the organs of vision;
- Brain damage;
- Attachment of a secondary bacterial skin infection.
As we see, an exacerbation of herpes is fraught with the development of a number of side effects . Taking antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs to treat complications of herpes is possible in conjunction with traditional medicine (herbal decoctions and tinctures) and hardening the body. If agreed with your doctor, regular exercise and visiting a sauna (bath) are also useful.
All information is provided for informational purposes. And it is not an instruction for self-treatment. If you feel unwell, consult a doctor.