Every person during his life faces some kind of skin problems that develop for completely different reasons. Hives are one of the most common types of allergic reactions. It manifests itself by the development of a characteristic urticarial rash on the skin and mucous membranes. Its Latin name is urticaria. This name hides a whole group of skin pathologies with symptoms similar in description. Different types of urticaria according to ICD-10 have their own code - from L50.0 to L50.9.
Description of the pathology
Urticaria has a number of characteristic features that distinguish it from other skin diseases:
- The elements of the rash are blisters of varying sizes.
- The localization of rashes can be completely different. They can even move: on different days they are found in different parts of the skin.
- Blisters (in the absence of complications) usually disappear completely without a trace: without the formation of scars on the skin or areas of hyperpigmentation.
- Clinical manifestations become more pronounced in the afternoon and at night . At this time, the body's cells produce more histamine, which is responsible for the development and severity of allergy symptoms.
Diagnostics
The appearance of hives on the face is a reason to consult a dermatologist or allergist. The basis for successful treatment of a disease is eliminating the cause, which can only be determined after a detailed examination of the body.
Diagnosis of pathology begins with a physical examination and medical history. The doctor evaluates the nature, frequency and duration of rashes, the time of appearance and disappearance of blisters. At the same time, the presence of current pathologies, allergic dermatoses in the hereditary line, features of lifestyle and diet are clarified.
Mandatory laboratory tests:
- clinical and biochemical blood tests;
- general urine analysis;
- testing for hepatitis B, C and RW;
- allergy examinations (skin tests).
Studies for selected indications:
- rheumatic tests;
- coproocystoscopy;
- bacteriological studies (stool, material from mucous membranes);
- identification of infectious agents;
- tests for the presence of parasites.
Instrumental methods:
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- ECG;
- EGDS;
- X-ray of the chest cavity and nasopharynx.
If physical urticaria is suspected, the method of provocative tests is used:
- mechanical irritation of the skin;
- exposure to cold;
- water compresses;
- physical activity, immersion in a hot bath;
- photoirradiation.
Further examination of the patient is carried out based on the results of the initial diagnosis. In this case, provocative tests are used for different types of allergens, screening studies for hormone levels, differentiation is carried out from other types of dermatitis with a possible urticarial rash.
Varieties
A clear typology of the disease used by all specialists has not been developed. Wikipedia provides a classification based on various characteristics of the disease.
There are several types of urticaria, depending on the severity and nature of clinical manifestations:
- Acute urticaria is a disease manifested by severe general and local symptoms. There is increased body temperature, weakness, dizziness, and headache. The rash appears quickly and consists of itchy blisters, localized exclusively to one area or spread throughout the body. The skin looks swollen and inflamed. Urticarial elements often merge with each other, forming flat, extensive plaques with jagged edges. This pathological condition lasts up to several days. Most often, symptoms disappear within 2-3 hours.
- Subacute urticaria: the clinical picture is no longer so pronounced. The duration of this form of the disease is several weeks.
- Chronic urticaria has an even longer duration (more than 5 weeks). The clinical picture is blurred.
- Chronic recurrent urticaria can last a long time - for many years. The etiological factor of the disease often remains unknown. This type of urticaria is characterized by a wave-like course with alternating stages of exacerbations and remissions. The incubation period (without symptoms) is usually long. During a relapse, the patient is bothered by painful itching of the skin.
4. Treatment of urticaria
Since the causes of idiopathic urticaria are not identified, its treatment, as a rule, is symptomatic (rather than etiopathogenetic) in nature:
- antihistamines;
- prednisolone;
- sedatives;
- soda baths;
- herbal tinctures for rubbing and oral decoctions.
Taking some medications is fraught with quite severe side effects, so you should not prescribe them yourself without consulting a doctor.
Treatment with folk remedies is also always very individual - what helps one may harm others - therefore, “traditional medicine” should be treated very carefully
It is recommended to wear clothes made from natural fabrics, use only hypoallergenic children's cosmetics and hygiene products, and exclude spicy, fried foods, as well as foods with known allergenic effects from the diet. At the same time, the diet should be varied, rich in vitamins, proteins and fats.
It is advisable to continue keeping a diary, since in many cases it helps to sooner or later identify the dependence of exacerbations on certain factors. In this case, the diagnosis “idiopathic” changes to a clearer one and treatment is aimed at correcting certain factors.
Immunological treatment and detoxification bring one or another positive effect in idiopathic urticaria
, and this type of medical care can begin already at the examination stage. Digestive enzymes and sorbents can also be auxiliary agents.
Physiotherapy is also widely used for relief during exacerbations of urticaria.
: electrophoresis, UV irradiation, UHF irradiation.
Stages
In the pathogenesis of urticaria, it is customary to distinguish 3 successive stages:
- Immunological stage: characterized by contact of the body with an allergen or any physical, chemical or mechanical irritant. This antigen disseminates in the bloodstream throughout the body and provokes the production of antibodies in the blood.
- Pathochemical stage: primary formation or release of histamine and other biologically active substances that provoke allergic manifestations.
- The pathophysiological stage is characterized by the launch of a response of body tissues to the release of allergy mediators. At this stage, characteristic complaints and objective symptoms appear.
Etiology
Modern medicine cannot name the exact cause of this disease. It is believed that the development of this pathology can be provoked by the simultaneous impact of several unfavorable factors. However, chronic idiopathic urticaria can also occur as an independent disease. It can also act as an element of clinical manifestations during the development of other pathologies.
Symptoms that manifest themselves according to the type of this disease can develop against the background of:
diabetes mellitus; oncological, less often benign neoplasms, and it does not matter in which area the undesirable process occurs; infections; systemic collagenosis; autoimmune diseases; rheumatoid arthritis; endocrinological disorders; kidney disease or pathologies of the digestive system; manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus; Sjögren's syndrome; lymphogranulomatosis or Hodgkin's disease; parasitic infestations; hormonal imbalances; dental diseases. External provoking factors most often include: various dust and pollen, insect bites and exposure to household chemicals, cold and exposure to sunlight, occupational hazards and stress.
External provoking factors most often include: various dust and pollen, insect bites and exposure to household chemicals, cold and exposure to sunlight, occupational hazards and stress.
It has been noted that in some cases, treatment of symptoms of idiopathic urticaria occurs against the background of food allergies, which manifest themselves as a result of the consumption of certain foods, as well as food additives and flavor enhancers included in their composition.
The culprit in the development of this disease can be certain pharmacological agents and medications if they are taken inadequately.
In addition, idiopathic urticaria (photos are presented below) can appear due to a genetic predisposition.
Reasons for appearance
The etiology of urticaria varies. Risk factors for the development of this pathology are usually divided into 2 groups - external and internal.
External (exogenous) causes
This is a very large group of reasons that cause allergic manifestations on the skin in the form of urticaria. It, in turn, is divided into several subgroups:
- Physical: exposure to ultraviolet radiation when tanning in the open sun or in a solarium, the influence of high or low air or water temperature, vibration, mechanical impact (rubbing the skin with clothing).
- Chemical: medications (antibiotics, vitamins and others), food allergens (seafood, fish, citrus fruits, chocolate, nuts, honey), flavors, preservatives, dyes or other harmful chemical compounds in products. This group of causes also includes cosmetics, perfumes, and household chemicals.
- Biological: allergies to plant pollen, insect bites (bees, wasps), fur and secretions of domestic animals.
Internal (endogenous) factors
Internal factors are various diseases or conditions of the body in which autoregulation processes are disrupted and defects in the immune system appear. They are expressed in the form of hypersensitivity (inadequate reaction of the body to various substances).
The main endogenous causes of urticaria:
- endocrine diseases (pathologies of the thyroid, parathyroid, gonads);
- hormonal changes during pregnancy, lactation, in the premenstrual period, at the stage of puberty;
- diseases of the digestive organs (stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas) are one of the most common causes of non-allergic urticaria, judging by the reviews of specialists;
- autoimmune pathologies with damage to connective tissue;
- hereditary predisposition to allergic reactions;
- immunodeficiencies of any etiology;
- helminthiases, mycoses, chronic bacterial infections;
- blood diseases, pathologies of the lymphatic system;
- oncological diseases;
- neuropsychic disorders (increased anxiety, asthenia), stressful situations.
It is often difficult to reliably identify the allergen. This type of urticaria is called idiopathic.
Features of aquagenic urticaria
An allergic rash appears after skin contact with any water - running drinking water or natural rain and snow. It is not the liquid itself that provokes this phenomenon: it does not pose a serious health hazard if the chemical composition is absolutely pure.
Various compounds and salts that dissolve in water lead to a rash. According to medical statistics, representatives of the fair sex suffer from the disease more often than men.
Similar symptoms also often appear in adolescents during adolescence, when puberty begins. It is not always possible to accurately determine the causes of aquagenic urticaria.
According to some options, the pathology appears due to a hypersensitive immune system, which gives “its own” reaction to certain stimuli. These include:
- lactose intolerance;
- chlorine;
- chemical additives in water;
- liver or kidney disease;
- weakening of skin mast cells;
- heredity;
- HIV;
- atopic type dermatitis.
When the first symptoms appear, you should contact your physician (pediatrician), allergy specialist or dermatologist. This type of disease is an incurable disease.
Any therapy is aimed only at stopping the signs of urticaria and temporarily eliminating them. The specialist needs to be told about the symptoms that have appeared and possible cases of the disease in blood relatives.
The patient must undergo a general blood test. As a basic test, a water compress is placed on the skin. If a rash appears within a few minutes, the diagnosis is confirmed.
Main symptoms
Symptoms of aquagenic urticaria appear within a quarter of an hour after contact of water and the patient’s skin occurs. Over the course of another two hours, the lesions gradually “spread”, covering increasingly larger areas of the body, and pain appears.
At the site of contact with water, the skin becomes covered with small pink-red spots, gradually merging into large papules. The rash is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- burning;
- itching;
- headache;
- tightness and dryness of the skin;
- cracks;
- wheezing;
- cough;
- difficulty swallowing.
If too much water gets on the skin, shortness of breath and hyperemia of the mucous membranes of the eyes may occur.
Signs of the disease appear after bathing, swimming, or after being exposed to rain or snow. In the most severe cases, the risk of angioedema, anaphylactic shock and a sharp increase in temperature increases.
This video will tell you what aquagenic urticaria is:
Necessary therapy
It is quite difficult to completely eliminate all contact with water. The main goal of therapy is to quickly relieve the symptoms that bring the patient significant discomfort. First aid for an attack consists of the following:
- quickly eliminate contact with water;
- treat the affected area with an anti-itch remedy;
- take an antihistamine.
The patient will have to monitor water quality throughout his life. You can only use boiled, spring or mineral liquid, free of harmful impurities. To take a normal shower, you will have to install filters that purify the water.
Suitable medications
Antihistamines are practically the basis of therapy for aquagenic urticaria. In particularly difficult cases, experts advise taking large doses of medications or combining different drugs.
It is not recommended to select medications on your own; you should consult an allergist for this.
Can be appointed:
- Zyrtec;
- Suprastin;
- Tavegil;
- Erius;
- Claritin.
The average duration of treatment is 14 days, but the drug must be taken with each attack. Additionally, mast cell stabilizers are prescribed to enhance the body's resistance.
Cromolyn or Ketotifen are used for these purposes. Less commonly, the patient is recommended F-therapy - treatment with ultraviolet radiation. The method is effective, but expensive. In addition, excess UV rays can lead to the development of skin cancer.
For local treatment of affected skin areas, the following are used:
- Gistan-N;
- Fenistil Gel;
- Nezulin.
The products are applied in a thin layer to the rash during an attack. Before use, be sure to study the instructions, special attention is paid to contraindications.
ethnoscience
It is impossible to cope with aquagenic urticaria only with folk remedies; they are used as an auxiliary therapy. To eliminate the rash, homemade ointments made from natural herbal juice, infusions, decoctions, baths and lotions are suitable.
You can use one of the following recipes:
- A teaspoon of dry nettle leaves is poured into a glass (200-250 ml) of boiling water. Leave for one hour, cool and strain. Drink 3-4 times a day for a week. After a month's break, the course is repeated.
- If you are not allergic to bee products, use natural honey. It is simply applied in a thin layer to the rash that appears.
- Fresh dill juice is applied to a cotton pad or bandage and applied to the damaged area of skin. Keep for about 20-30 minutes to reduce itching. If possible, dill is replaced with fresh meadow clover.
- For 10 gr. small wild rosemary leaves need 200 ml of hot boiled water. Leave for 10 minutes, strain and dilute with 0.2 l. cool boiled water. The resulting liquid is added to the baths.
- A tablespoon of dry chamomile is scalded with a glass of boiling water.
The liquid is drained, the resulting wet slurry is wrapped in gauze and applied to the skin. You need to be careful with the temperature to avoid burns.
When choosing a recipe, you should take into account the individual characteristics of the body: any of the components may be an allergen. If the clinical picture only worsens, the product should not be used.
Symptoms in adults
The clinical picture is characterized by redness of the skin in the initial stages, development of itching of the affected areas.
At the next stage, rashes appear. From the moment of contact with the allergen to the appearance of characteristic manifestations of the pathology, it takes from several minutes to many hours.
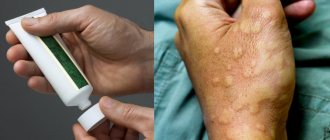
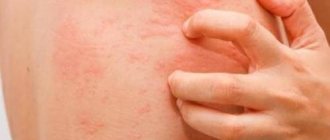
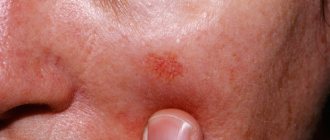
Elements of the rash - blisters - are found on different parts of the body: on the stomach, back, buttocks, arms (especially on the inner bends of the elbows), legs, face. The affected skin swells and becomes inflamed. The patient may develop fever and intoxication. The photo below shows the external symptoms of urticaria.
Rarely, the blisters are located on the palms, fingers, and feet. This is how allergies manifest themselves after contact with chemical allergens or animals. The itching at the stage of the appearance of the rash intensifies even more. A constant itchy sensation provokes the development of depressive, asthenic conditions, and sleep disturbances.
The rash lasts for varying amounts of time, depending on the form of the disease . Symptoms of the disease in adults and children are generally similar.
Idiopathic
Go to Medicines Catalog
Return to Catalog of medical terms
A B C D E F G H I
K L M N O P R S T U V H C CH W SCH E Y
Idiopathic - The term is used in relation to a disease or condition in a person that is caused by an unknown cause or occurs spontaneously. — Idiopathy (idiopalhy).;
Found in 210 questions:
traumatologist-orthopedist September 3, 2021 / Anastasia…
Hello! Daughter is 13 years old. First doctor's diagnosis: idiopathic
S-shaped juvenile thoracolumbar scolisis, 2nd degree.
Diagnosis of the second doctor: Idiopathic
scoliosis Lenke5B. Severe degree according to James. Surgical treatment is recommended. ... open
hematologist July 19, 2021 / Maria
Hello! I am 29 years old. Two months ago I was diagnosed with idiopathic
myelofibrosis. Blood tests are normal. the spleen was significantly enlarged 22.5x10.5. There were many more tests. the V617F mutation of the jak-2 gene was identified. A bone marrow trepanobiopsy was performed ( ... open
oncologist April 20, 2021 / Svetlana... / Lugansk
Good evening ! My husband had a CT scan and was questioned about the idiopathic
fibrosing alveolitis, to clarify the diagnosis they are sent to do an open biopsy by opening the lung and cutting off the tissue, the question is, is it possible to take another method ... open
hematologist April 15, 2021 / Ekaterina...
... time of day. Several years ago I was diagnosed with idiopathic
myelofibrosis, this diagnosis is indicated everywhere in the extracts.
In ... myelosis. This is the first time I've heard such a name. idiopathic
myelofibrosis and subleukemic myelosis the same thing? Just... open
hematologist April 13, 2021 / Elizaveta...
… day! Please advise and evaluate the treatment. My mother (58 years old) was diagnosed a couple of days ago: Idiopathic
myelofibrosis in the stage of pronounced clinical manifestations. Thrombosis of the splenic vein. Portal hypertension. Hydronephrosis. No complaints and... open
03-Ambulance December 7, 2015 / Elena
... no nose, no cough. The stool is normal. I tried to palpate the abdomen myself; the abdomen was soft and painless. History of idiopathic
myelofibrosis, condition after splenectomy, cirrhosis of the liver (as I was told as a consequence of myelofibrosis). These were all delivered… open
homeopath October 31, 2015 / Anonymous
... becomes, reading stories), and the majority is inclined to believe that I am healthy, I don’t need to take medications and I have idiopathic
hirsutism.
And only a cosmetologist can supposedly help me. I have already reached the point of weekly cosmetic procedures and this is not... open (1 more message)Last 5:
proctologist August 22, 2015 / Marina / Voronezh
Hello! tell me, I don’t know what to do. 2 years ago I had a laparoscopy and discovered idiopathic
megacolon. They then told me to do an MRI or CT scan in the future. and now I went to the therapist about the mucus discharge from the anus. and more bloating... open
arts methods August 19, 2015 / Anna
... left 1 st. Testicular calcification on both sides. Chronic epididymitis on the left. Chronic bacterial prostatitis, latent course. Idiopathic
OAT syndrome. Testicular calculi. Cyst of the left epididymis. The urologist prescribed stimulation for 2 months ... open
pediatric orthopedist March 24, 2015 / Olga / Omsk
Hello. Please tell me, based on your practice as an orthopedic doctor, what type of postural disorders is more common in children 7–9 years old? open
March 24, 2015 / Miloserdov Alexander
Olga, most often idiopathic
option.
pediatric orthopedist January 12, 2015 / Oksana
Good afternoon. We have such a problem - our son has juvenile idiopathic
arthritis of the knee joint, also in the same knee there is a discoid meniscus. We've been injecting Methodject for a year now. Doctors said that due to arthritis, it was impossible to go into the knee to perform meniscus surgery. So... open
disabled people November 24, 2014 / Anonymous / Volgograd region. r.p. Erzovka
...does she have a disability with such diagnoses: type 2 diabetes. diabetic polyneuropathy of the lower extremities initial manifestations. idiopathic
granulomatous hepatitis. hypertension 2nd degree, risk 3. diffuse euthyroid goiter 1st degree. anemia 1st degree. ... open
AIDS July 30, 2013 / Alexander... / Kyiv
Hello Eric. This is not the first time I’m writing to you. After sex with a hiv+ girl, I started having health problems: diarrhea, stomatitis, urticaria, hair loss, lymph nodes... open (3027 more messages)Last 5:
October 15, 2014 / Anonymous
... features of cases with AIDS-associated complex.
Results: A qualitative systematic analysis suggested that idiopathic
CD4+T lymphocytopenia (ICL) and non-tuberculous mycobacterium (NTM) infection had similar characteristics to AIDS-...
Clinical manifestations in children
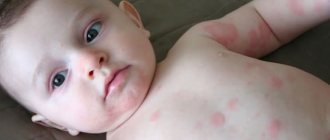
Signs of urticaria can appear even in a small child who is breastfed, as a result of errors in the mother’s diet. Urticaria in children usually develops acutely. First, severe itching of the skin appears in different parts of the body (limbs, back, butt, stomach). Then characteristic rashes are found on the skin, sometimes on the mucous membranes.
The most dangerous is considered to be swelling in the mucous membranes of the mouth, nasopharynx, and upper respiratory tract, as this can impair breathing.
This health and life-threatening condition is called Quincke's edema, is accompanied by cough, hoarseness, blueness of the skin, impaired consciousness and requires immediate hospitalization in the intensive care unit.
Another feature of urticaria in children is that it is difficult for them not to scratch the itchy elements of the rash. Constant scratching leads to the formation of crusts, microtraumas, and weeping rashes. When a secondary infection occurs, ulcers and abscesses develop, especially with sharply reduced immunity .
In children, urticarial elements in urticaria often have to be differentiated from symptoms of infectious diseases with skin manifestations (measles, rubella, chickenpox), especially when rashes are detected in uncharacteristic places (palms, feet). Typical symptoms of urticaria in a child can be seen in the photo below.
Treatment of angioedema
Treatment of this pathology must be carried out in a very short time in order to relieve an attack of an allergic reaction. It is almost always necessary to admit the patient to a hospital department. This is due to the fact that even if it was possible to quickly relieve inflammation, this does not mean that it cannot arise again after some time, especially in cases of an undetected reagent.
Urticaria and angioedema require the following treatment:
- Mandatory exclusion of the suspected provoking factor.
- Antihistamines help relieve the first signs of edema.
- If necessary, treatment with hormonal drugs (Prednisolone) is prescribed.
- Treatment with Enterosorbents is also necessary, which helps remove the allergen from the body faster.
- It is advisable to carry out detoxification therapy in combination with diuretics.
- A good effect is achieved by prescribing hyposensitizing drugs (Sodium Thiosulfate)
Treatment of this pathology is simply impossible without following a hypoallergenic diet, since cross-reactions can quite often occur. It is also important to drink plenty of fluids to remove all irritants as quickly as possible and thereby relieve swelling.
Angioedema can often be very severe, requiring its treatment in intensive care units.
Is the disease contagious?
Urticaria, like any allergy, is a non-contagious skin pathology and is in no way transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person, despite the presence of a rash that frightens many.
Contagious dermatological diseases are caused by a variety of microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, viruses). But urticaria is not infectious, but allergic in nature, so it cannot be acquired either by airborne droplets or through direct tactile or even sexual contact with a sick person. Contact with the blood of a person with hives is also safe.
What tests will you need to take for urticaria?
If hives appear, you should consult either a dermatologist or an allergist.
As we have already said: a symptom such as urticaria can be caused by a huge number of reasons. In this regard, a patient with urticaria is always offered to undergo a fairly large number of tests. This, of course, can be scary, but there is no other way! If the exact cause is not established, treatment may be ineffective.
So: the recommended examination plan for a patient with urticaria:
1) clinical blood test; 2) general urine test; 3) biochemical blood test (CRP, AST, ALT, total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, creatinine, urea, alkaline phosphatase, glucose); 4) antibodies to viral hepatitis B and C ( HbsAg + HCV antigen), blood for HIV; 5) blood test for syphilis; 6) to exclude autoimmune diseases, a blood test for antinuclear factor, antibodies to double-stranded DNA; 7) for physical urticaria (urticaria caused by physical influences), a dermagrophic test is performed ( carry out a spatula in the interscapular area with a moderate load and evaluate the skin reaction for 5-10 minutes); for cholinergic urticaria, perform a physical stress test; for cold urticaria, the Duncan test (apply an ice cube to the skin of the forearm for 2-3 minutes and evaluate the skin reaction within 15 minutes); to exclude pathology of the endocrine system, consultation with an endocrinologist is necessary with a mandatory blood test for thyroid hormones (T3, T4 free), a blood test for antibodies to thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin;9) to exclude foci of chronic infection, swabs from the throat and nose are taken for microflora and mushrooms, stool analysis for dysbacteriosis. Women – consultation with a gynecologist. Everyone - consultation with a dentist. 10) stool analysis for coprogram; 10) blood test for antibodies (immunoglobulins of classes G and M) to the antigens of the parasites Giardia, Toxocara, Toxoplasma, Ascaris, Opisthorchis, Trichinella, etc.; 11) Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is mandatory abdominal organs and thyroid gland;12) according to indications - esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGDS);13) ECG, and in the presence of deviations from the norm: ultrasound of the heart; 14) radiography of the chest and paranasal sinuses; 15) an allergy examination is mandatory. In this case, preference is given to taking a blood test for specific immunoglobulins E (IgE to certain antigens). They start with a blood test for food allergens and household allergens.
to exclude pathology of the endocrine system, consultation with an endocrinologist is necessary with a mandatory blood test for thyroid hormones (T3, T4 free), a blood test for antibodies to thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin;9) to exclude foci of chronic infection, swabs from the throat and nose are taken for microflora and mushrooms, stool analysis for dysbacteriosis. Women – consultation with a gynecologist. Everyone - consultation with a dentist. 10) stool analysis for coprogram; 10) blood test for antibodies (immunoglobulins of classes G and M) to the antigens of the parasites Giardia, Toxocara, Toxoplasma, Ascaris, Opisthorchis, Trichinella, etc.; 11) Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is mandatory abdominal organs and thyroid gland;12) according to indications - esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGDS);13) ECG, and in the presence of deviations from the norm: ultrasound of the heart; 14) radiography of the chest and paranasal sinuses; 15) an allergy examination is mandatory. In this case, preference is given to taking a blood test for specific immunoglobulins E (IgE to certain antigens). They start with a blood test for food allergens and household allergens.
If there are indications, it is possible to consult other specialists or expand the list of tests.
Symptoms and manifestations
This form of the disease manifests itself only against the background of contact with water .
The skin begins to itch and turn red, usually the rash and redness appear within 1-15 minutes after the area of skin is exposed to water. Within 20-120 minutes, the lesions can begin to actively develop and become quite painful. Areas of contact with water become covered with small burgundy spots, which accumulate into large papules.
In addition to itching, burning and inflammation, patients note the following manifestations of aquagenic urticaria:
- difficulty swallowing, wheezing, coughing, or respiratory distress (such as after drinking);
- Development of blisters in areas in contact with water;
- Dry skin, feeling of tightness, appearance of cracks;
- Headache;
- Hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- Dyspnea.
Symptoms of aquagenic urticaria can occur after taking a bath, taking a shower, swimming in a pool, river, sea, lake, and even while walking in the rain.
Attention! This form of the disease is not accompanied by angioedema, fever and anaphylactic reactions.