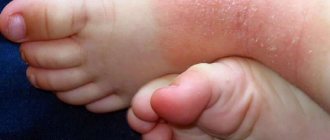
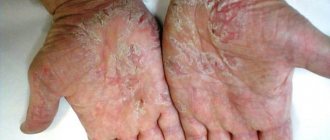
Eczema on the fingers is a dermatological disease, and one of the most common places for its localization is the fingers. In addition to the unflattering appearance, the formation of lesions in these places brings severe discomfort, because A person does any work with the help of his hands, thus this disease has difficulties in treatment, due to the inability to ensure safety and complete isolation of the hands from external influences.
The peculiarity of this disease is a long course, which can subside and then reappear, sometimes even after complete recovery.
Causes of eczema on fingers
The exact etiology of the disease has not been identified, but a number of trigger factors have been identified that can contribute to the development of the disease, and the same factors may or may not cause the disease in different people. Eczema can occur in people of different ages, and regardless of gender.
External:
- Chemistry is the most common cause of the development of eczema on the fingers, constant contact with chemicals or aggressive components, for example, due to duty.
- Thermal effects - severe frost or dry air can trigger the development of the disease; hyperhidrosis of the palms is also a fairly common cause.
- Mechanical damage - wounds or abrasions on the hands, constant contact with metals to which allergic reactions can occur is also a fairly common factor.
- Food, which is considered a source of possible allergies, often provokes the development of the disease.
- Constant violation or non-compliance with hygiene rules.
Internal:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Diseases of the nervous system, prolonged stress.
- Helminth infestation.
- Chronic or latent infectious infestations.
- Fungal diseases.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Malfunctions of the endocrine system.
- Reduced level of immunity.
- Avitaminosis.
The above factors can provoke the occurrence of the disease, both individually and in combination, but are not required. For example, a reduced level of immunity will not necessarily cause eczema, but it may contribute to it.
Find out more
External causes of cracks and itching of the skin of the hands
Negative environmental influences and the use of household products cause irritation. It can be expressed by slight redness of the tissues, and with serious damage, the skin on the hands cracks and itches severely, and sores appear. In some cases, even protective gloves can provoke an allergic reaction.
Let's consider the main external causes of itching and dry hands:
- Chemical reagents. This factor affects people whose activities are associated with hazardous production, the service sector, when contact with aggressive cleaning agents, paint, and solvents is necessary. In everyday life, these are common means of putting things in order. Palms are more likely to itch and crack after using budget powders and gels. If a person has thin and sensitive skin, then it can react sharply to gentle components of household chemicals.
- Weather. The epidermis dries from ultraviolet radiation, frost, and wind. If prevention is not carried out and moisturizers are not used daily, cracks will appear and open the way for germs.
- Dirt. Gardening and picnics lift your spirits and provide pleasant fatigue, but have a negative impact on beauty. The epidermis dries, peels, cracks appear on the palms of the hands, and the fingers itch.
- High humidity. Protecting yourself from chemicals or dirt by wearing rubber gloves can also cause irritation. Obstruction of air circulation, sweating of palms and accumulation of moisture have a detrimental effect on the condition of the skin of the hands. In most cases, the palm of a person who wears gloves throughout the working day becomes red, itchy and peeling.
- Hot water. The habit of taking a bath or washing your hands with very hot water ultimately leads to accelerated death of epidermal cells. The normal regeneration process takes place quickly, peeling becomes noticeable, palms itch, and cracks may appear.
- Antiseptics and soap. The need to frequently treat your hands with antiseptics leads to dry skin and subsequent peeling and cracking. Soap, especially antibacterial soap, is no less harmful. With increased sensitivity, cracks in the bends of the fingers and near the nails are possible.
Types of eczema on fingers
Depending on the cause of eczema on the fingers, the following types are distinguished:
- True or idiopathic eczema - occurs against the background of stress, diseases of the nervous system, genetic predisposition, malfunction of the endocrine system, diseases of the digestive system.
- Atopic eczema - occurs due to frequent allergic reactions; people with bronchial asthma are also at risk.
- Occupational eczema is caused by frequent contact with allergens on duty. Often these are health workers, builders, metallurgists and people who work with printing.
- Microbial eczema - as the name of this type implies, occurs due to the entry of pathogenic bacteria through wounds, abrasions, and burns.
- Mycotic - occurs in people who have nail fungus.
- Dyshidrotic eczema - occurs against the background of hyperhidrosis of the palms.
In addition, eczema on the fingers is divided into:
- Dry eczema - as the disease progresses, the papules begin to disappear, and dryness and peeling are noted at the former sites of lesions.
- Weeping - papules and vesicles open on their own, forming weeping areas.
Depending on the course of the disease.
In the photo section you can see what each individual type of eczema looks like.
Internal causes of skin diseases
Endogenous (internal) causes often influence changes in the epidermal layer. The following can lead to an inflammatory process of the dermis localized on the hands:
- hormonal changes (most often in adolescence);
- nervous tension;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- metabolic disorders;
- intestinal dysbiosis.
The individual characteristics of the body, previous diseases, a tendency to allergic manifestations, and heredity are of great importance.
Each skin type needs special care; any wounds should be immediately disinfected
Symptoms of eczema on fingers
Since eczema is divided into several types, each of them may differ in its course and symptoms:
- True – symmetrical rashes (papules) appear, the rash tends to merge, and as the disease progresses, eroded areas of the skin form. This type is accompanied by severe itching, which may appear even before the formation of rashes. This type can become chronic.
- Atopic - before the appearance of a rash, there is hyperemia and swelling of the tissues on the skin. A rash in the form of papules or vesicles with cloudy contents opens up on its own as the disease progresses, forming weeping areas. Then these areas dry out and in their place there is dryness and the formation of crusts, which are covered with scales, the skin itches and flakes.
- Professional - has similar symptoms to the idiopathic form. The rashes are localized in places where there is constant contact with the irritant, most often on the fingertips.
- Microbial - localized in the area of a previously acquired wound, abrasion, etc., in the absence of treatment, the symmetrical formation of a rash is noticeable, and the transition to healthy segments of the skin. The vesicles burst open, forming weeping areas. Accompanied by slight itching.
- Mycotic - rashes in the form of papules, localized in the area of nails affected by fungus. This species is characterized by severe itching.
- Dyshidrotic - a rash occurs, the blisters are filled with fluid. There is swelling and hyperemia of the skin. As the disease progresses, weeping areas are formed that are prone to simultaneous peeling. This species is characterized by severe itching. Localized on the edges of the palms and on the sides of the fingers.
Despite the fact that eczema that is localized on the fingers has several types, general symptoms and course can be identified:
- in some species, before the formation of a rash, there is hyperemia, swelling of the skin, accompanied by itching;
- formation of a rash in the form of papules or vesicles with cloudy contents;
- opening of papules, formation of weeping areas;
- drying out of wet areas, formation of crusts, dryness and peeling of the skin in areas of lesions.
Each type may differ in its course (sluggish or rapid progression), the development of weeping areas, some types are prone to becoming chronic, but what each type has in common is a favorable outcome if the disease is not ignored.
Possible complications
Even a harmless pimple can become infected and become complicated, not to mention more serious skin problems and diseases that cause an obvious pathological process. There are many complications from such diseases. It all depends on the type and degree of their development. They can be mild or very severe.
For example, dermatitis, in which sores appear not only on the hands, but throughout the body, causes:
- skin pigmentation;
- tissue scarring;
- dyschromia;
- atrophy.
Therefore, if a sore appears on your body, you should definitely consult a doctor and not self-medicate. The specialist will definitely tell you how to treat a dermatological disease and give appropriate recommendations.
Treatment of eczema on fingers
Before starting treatment, it is very important to confirm the diagnosis and establish the cause that contributed to the development of eczema. To do this, the doctor prescribes:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- stool analysis;
- scraping of separated particles of dermis;
- histological analysis;
- allergy tests;
- in some cases, consultation with highly specialized doctors may be necessary.
After receiving the results, the dermatologist prescribes complex therapy, which is primarily aimed at eliminating the cause.
Treatment of eczema on the fingers with folk remedies
Traditional medicine has many recipes that, in addition to the main treatment, can alleviate the condition and help a speedy recovery. Often these are decoctions or tinctures based on herbs that have a soothing, wound-healing and antiseptic effect, including:
- chamomile;
- calendula;
- plantain;
- Oak bark;
- nettle;
- Birch buds.
It is best to purchase all components for preparing decoctions and tinctures at a pharmacy, and you should consult with your doctor about the possibility of using any method.
It is important to remember that traditional methods can only be used as a supplement to the main treatment; herbal medicine cannot have a detrimental effect on infections or fungi, and it cannot reduce the influence of allergens.
Treatment of eczema on the fingers with medications
For the effectiveness of therapy, a complex of medications is prescribed that are aimed at internal and external effects. Most types of eczema occur against the background of allergic reactions, so in addition to medications, dermatologists advise adjusting the diet by excluding foods that are considered allergenic, and the main diet should be based on proper nutrition.
For the treatment of eczema the following is prescribed:
- Antihistamine tablets or ointments - to relieve itching and reduce the effect of allergens on the body.
- Anti-inflammatory ointments/creams or tablets - to relieve pain, eliminate redness and swelling of the skin.
- Vitamin complexes - to maintain immunity, for patients with reduced immune status.
- Calcium injections.
- Antibiotic therapy - in cases of fungal or infectious invasions.
- Enterosorbents – to reduce intoxication and remove harmful substances from the body.
- Enzyme preparations – for diseases of the digestive system.
- Antibacterial drugs - in cases of secondary infections or microbial eczema.
- Antiseptic solutions - for treating affected areas before applying ointments.
It is very important not to interrupt treatment, even if the symptoms begin to subside, this is fraught with the development of repeated relapses and the disease becoming chronic, which can subsequently cause complications.
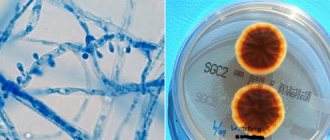
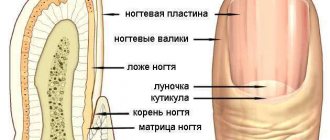
Fungal diseases and their consequences
One of the vulnerable places of the human body is the nails. Pathogenic microorganisms, affecting the upper extremities, also affect the nails, changing their natural shape, and the skin around them itches and turns red. The nail plates also reflect various problems in the functioning of organs. Symptoms of mycosis include thickening or brittleness of the nails and a change in their shade. Because nails peel and crumble, they do not grow back. Even after healing, the skin continues to peel for a long time.
Mycosis provokes the appearance of erysipelas, and also delays the treatment process for the latter
A person who sweats excessively, does not observe good hygiene, or has reduced protective functions is more likely, in addition to mycosis on the hands, to become a victim of a disease of the toenails or the skin around the nail plates.
Remember. Treatment of fungus takes a long time, the effectiveness of therapy depends on the correctly identified type of microorganism.
Fungus on the upper extremities is much less common than on the lower extremities. The disease may begin to develop in the legs and then move to the arms.
Prevention of eczema on fingers
To prevent the development of the disease or prevent the development of repeated relapses, it is necessary:
- maintain immunity levels.
- exclude allergens.
- adhere to the rules of personal hygiene.
- use protective equipment when in contact with chemicals and other substances that contain aggressive components.
- lead a healthy lifestyle - avoid hypothermia, give up bad habits.
- use hypoallergenic cosmetics and detergents.
- follow the doctor's instructions.
- treat concomitant diseases.
- avoid hypothermia.
- exclude allergens.
- pay increased attention to personal hygiene.
By following these simple preventative tips, you can avoid illness or speed up your recovery.
Toxidermy
- a disease of an allergic nature. As a rule, it manifests itself in the form of damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Often localized on the skin of the hands. This is usually a reaction to drug allergens. Manifestations of the disease occur after the allergen enters the body through injections or the digestive tract, sometimes through inhalation.
There are two forms of toxicoderma: fixed and widespread. The first is characterized by the appearance of red spots on the hands (usually raised above the surface of the skin), which are subsequently covered with a brown crust, or a watery bubble forms in the center, which bursts under mechanical stress. Symptoms disappear after stopping the drug that causes the allergy.
Loading…
Common toxicoderma manifests itself more pronouncedly: not only the skin, but the entire body suffers. There may be an increase in temperature, irritability, nervousness, problems with the digestive and respiratory systems. This is a more severe form of the disease: skin lesions can develop into Lyell's syndrome - the appearance of blisters with serous contents on the skin, which burst and leave behind extensive bright red ulcers. It is important to ensure the sterility of the area of skin lesions and hospitalize the patient, because with this form of dermatitis there is a high probability of blood poisoning.
Please note : if symptoms of this disease appear, you should immediately consult a doctor!
Prevention of skin diseases
To prevent dermatitis, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Avoid contact with allergens.
- Do not be nervous.
- Take care of dry skin.
- Avoid hand sanitizers.
- Use hypoallergenic powders and rinse clothes thoroughly after washing.
Following these simple rules is not difficult at all. They will help not only prevent unpleasant skin diseases on the hands, but will also help preserve their youth and health for a long time.
www.syl.ru
Since the human skin protects the body from external influences, it performs many functions and is subject to many influences. Dermatological diseases are the most common. The skin can be affected by both mild ailments and more serious ones that require professional treatment. Skin diseases on the hands require timely diagnosis and treatment. How do hand ailments manifest themselves?
The epidermis serves as a kind of barrier that protects internal tissues. He may be susceptible to various diseases. Skin defects can be associated with exposure to both external and internal factors.
Since the skin serves as protection for the entire body, one of the important preventive tasks is to protect it from the occurrence of pathologies.
It is skin diseases on the hands that are the most common cases of dermatological problems, since this part of the body is almost impossible to protect from provoking factors.
Types of skin rashes
The rash that appears on the body comes in various forms. For example, the patient may find:
- small rash;
- bubbles;
- papules (pustules);
- blisters;
- plaques.
Important. Identifying symptoms early increases the effectiveness of treatment.
Knowing the cause of the skin disease on the arms and legs, you can prevent it from becoming chronic and other complications.
Unlike internal diseases, skin ailments have unaesthetic external manifestations, which causes not only unpleasant sensations, but also emotional suffering.
Diagnosis of illnesses
Based on the patient’s complaints, symptoms, location of sores and examination, a preliminary diagnosis is established. Further examination confirms a certain disease of the skin of the hands or refutes it.
To determine the nature of some pathologies, skin scrapings are taken with a special glass or the blunt end of a scalpel. Some research methods include palpation of the skin.
Laboratory diagnostics includes a complex of various tests. To identify the pathogen, a general blood test, urine test, and biochemical blood test are prescribed. To determine the presence of helminthic infestation, a stool test is prescribed.
Types of skin diseases
The most common hand skin diseases:
- Dermatitis. Redness accompanied by swelling, itching and peeling.
- Scabies. Itchy, paired pimples and profuse redness.
- Mycoses (fungal pathologies). Reproduction of fungal microorganisms in the layers of the dermis.
- Eczema. There is compaction, itching and peeling of the integument.
- Acne. There is no itching, but it causes discomfort. It is a consequence of dysfunction of internal organs.
- Hives. The blisters merge to form a large spot. When they burst, they cause discomfort and pain.
- Scleroderma. It is expressed by tense skin, changes in the shape of nails and fingers.
- Psoriasis. Has several varieties.
- Toxicoderma (toxic-allergic dermatitis). It is characterized by a rash of various types (spots, nodes, blisters, ulcers) and a protruding vascular network as a result of toxic damage to blood vessels and tissues.
The location of the skin rash is one of the criteria for diagnosing the disease, but not the main one
Symptoms of rashes
Depending on the lesions of the skin, the symptoms appear brightly or covertly. There are several groups of manifestations:
- skin color changes from natural to red or pale;
- sensation of pain, itching, burning;
- the normal condition of the skin is replaced by excessive dryness, tightness - these manifestations are typical for the palms or feet;
- formation of skin elements (tubercles, rash).
Any formations can be triggered by various diseases or allergic reactions.
Important. It is very difficult to independently diagnose skin diseases on the hands. Although it is possible to establish the correct diagnosis, experts recommend immediately contacting a medical facility to determine an accurate diagnosis and begin proper treatment.
Fungal diseases and their consequences
One of the vulnerable places of the human body is the nails. Pathogenic microorganisms, affecting the upper extremities, also affect the nails, changing their natural shape, and the skin around them itches and turns red. The nail plates also reflect various problems in the functioning of organs. Symptoms of mycosis include thickening or brittleness of the nails and a change in their shade. Because nails peel and crumble, they do not grow back. Even after healing, the skin continues to peel for a long time.
Mycosis provokes the appearance of erysipelas, and also delays the treatment process for the latter
A person who sweats excessively, does not observe good hygiene, or has reduced protective functions is more likely, in addition to mycosis on the hands, to become a victim of a disease of the toenails or the skin around the nail plates.
Remember. Treatment of fungus takes a long time, the effectiveness of therapy depends on the correctly identified type of microorganism.
Fungus on the upper extremities is much less common than on the lower extremities. The disease may begin to develop in the legs and then move to the arms.
Symptoms of erysipelas
Erysipelas is one of the ailments that occurs on both the upper and lower extremities. Erysipelas of the skin of the legs is more common than the hands, face or other parts of the body.
Signs of inflammation vary depending on the form of the disease:
- The mild form has muted manifestations. The patient feels weak and has an elevated body temperature.
- Moderate form. It has more acute symptoms and a longer duration.
- Severe form. The acute course is complemented by a violation of the mental state.
- Recurrent. In case of unfinished primary treatment, as well as in a weakened body, inflammation may appear in the same place.
Important. To avoid complications, you must carefully follow all doctor's instructions.
Lack of treatment threatens complications from the cardiovascular system and kidneys
External causes of hand skin diseases
The wide distribution of skin diseases of the hands in humans is explained by the fact that, in addition to the protective function, the covering of the upper extremities performs a receptive function. When coming into contact with surrounding objects, it is difficult not to become infected.
Exogenous (external) factors affecting the epidermis:
- contact with a chemical (alkali, acid, paint);
- irradiation (x-ray, ultraviolet);
- contact with pathogenic microbes (anthrax, leprosy);
- sudden temperature changes (hypothermia, frostbite, burns);
- parasitic effects (fleas, mosquitoes, bedbugs).
Adverse external influences irritate the epidermis, causing the appearance of pigment spots, burning, and itching. Careless handling of dangerous objects may result in personal injury. And with age, the regeneration of epidermal cells is disrupted.
Important. The patient can independently diagnose the disease, but in case of an erroneous diagnosis, the situation will be aggravated by incorrect treatment. If primary symptoms are detected, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist.
Even the smallest members of the population suffer from skin defects. Allergic dermatitis is especially common. A skin reaction to an allergen manifests itself in the form of inflammation, peeling, rashes, and spots. The skin becomes dry and itchy.
Many dermatological diseases are caused by dysfunction of internal organs.
The main symptoms indicating damage to the skin include:
- irritation, burning;
- skin redness;
- rash;
- painful sensations.
Internal causes of skin diseases
Endogenous (internal) causes often influence changes in the epidermal layer. The following can lead to an inflammatory process of the dermis localized on the hands:
- hormonal changes (most often in adolescence);
- nervous tension;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- metabolic disorders;
- intestinal dysbiosis.
The individual characteristics of the body, previous diseases, a tendency to allergic manifestations, and heredity are of great importance.
Each skin type needs special care; any wounds should be immediately disinfected
Preventive actions
To avoid allergic reactions and infectious diseases, you must adhere to certain rules. There are only two main methods of prevention:
- The most important point is hygiene . Since hands are exposed to constant contact with external factors, it is important to carefully monitor their cleanliness. A large number of microorganisms are concentrated on the dermis. Sweat secretions and dirt accumulated in the skin folds lead to inflammatory processes.
- Skin care. This includes cleansing of dead layers of the dermis, moisturizing and nutrition with the help of pharmaceutical and cosmetic preparations.
To prevent skin diseases of the lower extremities, it is also necessary to follow certain rules. Shoes must be of high quality and well ventilated. There should be no debris or dust inside. The skin of your feet should always be dry. After taking water procedures, you should wipe the skin between your fingers especially carefully. If sweating is increased, you need to take special medicinal baths. All hygiene items must be strictly individual.
All skin diseases are conventionally divided into contagious and non-contagious. Prevention is hygienic in nature. By following the rules of hygiene, you can protect yourself as much as possible from various types of skin diseases.
zkozha.ru
Skin diseases on the hands are a fairly common pathology. Occurs everywhere in all age groups. Pathologies have a variety of origins. The clinical presentation of skin diseases also varies widely.
Some diseases are contagious, that is, they can be transmitted from person to person. Each pathology requires diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Skin diseases are treated not only with local, but also with systemic means.
What is prevention – 5 general rules?
In order to prevent the occurrence of such a disease, without looking for some effective remedy, you just need to remember a few important rules. Avoiding dry eczema on the hands is possible by following the following five preventive rules:
- You cannot use household cleaning products, detergents, paints, varnishes, or repair putty without gloves.
- Regularly lubricate your hands with a softening cream suitable for your healthy skin type after contact with water.
- If someone works in an industry that is hazardous to health, they should not ignore the protective attributes of workwear, shoes, and headgear.
- A diseased liver, stomach, and intestines should be actively treated and their chronic disease state should be prevented.
- Avoid infecting the body with viruses, fungi and other pathogens that can infect humans.
When monitoring a patient, diagnosticians take a bacterial culture of the flora and do a biopsy of a piece of skin that has peeled off. This allows them to decide at what stage the disease is, as well as what nature of its occurrence. Thanks to this knowledge, it will be easier for the skin doctor to establish the correct treatment, as well as prescribe the necessary pills, ointments, creams and prescribe the appropriate diet. Any violation in the treatment plan can lead to low effectiveness, and therefore it is better to strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease that is accompanied by the appearance of pink plaques, spots and peeling. Itching is also a characteristic symptom of psoriasis. The reason for the appearance of scaly plaques is that the cells of the epidermis begin to divide several times faster, which leads to the fact that most of them do not have time to develop and die, subsequently peeling off, which is accompanied by itching. The immune system begins to control the process: it begins to act against its own cells, which leads to the formation of inflammation in the affected area.
There are several types of psoriasis, each of which differs in the nature and intensity of the disease. Plaque, guttate or pustular psoriasis most often develops on the skin of the hands. Sometimes seasonality is observed: the disease worsens in the spring and autumn.
The main causes of psoriasis are not known for certain. There are many assumptions: hereditary factor, stress, genetics, disorders in the endocrine system. However, it is impossible to say exactly what can trigger the disease.
Treatment consists of complex therapy: relief of itching, elimination of external manifestations of the disease in order to alleviate the patient’s condition. Along with treatment with external agents, it is necessary to periodically undergo a course of general therapy.
Contrary to popular belief, psoriasis is not a contagious disease. It is not transmitted through contact with the skin of a patient or through household appliances.
IMPORTANT TO KNOW: even if all plaques disappear and there are no symptoms, preventive therapy and periodic visits to a dermatologist should not be neglected!