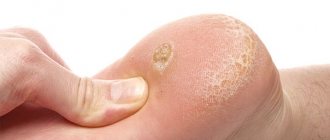
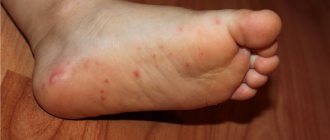
Friction of the skin on hard surfaces causes detachment of the epidermis from the underlying layers of the dermis, followed by the formation of a cavity filled with clear intercellular fluid. The formation caused by mechanical damage to the skin is nothing more than a wet or soft callus, colloquially called dropsy. The phenomenon is so common that no one can be protected from wet calluses. And although this kind of damage in most cases is minor and does not pose any serious danger to health, when walking they cause considerable discomfort.
If you ignore the problem, the bubble may burst. And in its place there will be an inflamed, wet wound of bright pink color, open to any infection. Infection of the wound area is fraught with problems much more serious than discomfort and pain when walking. Therefore, treatment of wet calluses should not be taken lightly. You need to start doing something as soon as dropsy appears on the foot, and not wait for complications. How to treat a wet callus on the foot is described in detail below.
Appearance mechanism
Wet calluses occur in areas of greatest friction. A sharp mechanical impact provokes peeling of the epithelium and inflammation. The injured area swells slightly. The bladder begins to grow, gradually filling with intercellular fluid. If there are particles of blood in it, it means that small vessels are damaged. In both cases, painful sensations are disturbing. When pressing on the blister, the walls become tense, the burning sensation and discomfort intensify.
If the negative impact on the affected area continues, the bubble ruptures. Fluid saturated with leukocytes flows out. Through the wound, infection easily enters the body, leading to suppuration.
The mechanism for the appearance of water calluses differs from the usual roughening of the skin. Corns and dry patches are the result of regular minor irritation. From it, the top layer of cells slowly dies. The keratinization protects the deep layers of the dermis from destruction, but it looks unsightly and can interfere with walking.
Causes of pathology, symptoms and consequences
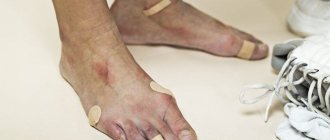
Wet calli appear on the feet or hands.
They are caused by friction or pressure on an area of skin over a long period of time. When uncomfortable shoes rub, dropsy appears on the heels or toes. They can appear on your hands if you work without gloves, from playing musical instruments or when playing sports.
Some diseases also lead to their occurrence:
- arthritis;
- lack of vitamins;
- excess weight;
- sweaty feet;
- flat feet.
During excessive pressure or friction, the top layer of the dermis peels off. The space that has formed is filled with a clear liquid. Water callus protects against infection entering the blood.
Improper exposure of the epidermis causes redness and swelling. The rubbed area will begin to hurt. These are the first symptoms of a wet callus.
If the cause is eliminated at this moment, there will be no dropsy. The affected area should be covered with a plaster. If you don’t get rid of the cause, education will definitely arise.
Reasons for education
Most often, wet calluses form on the feet and hands. The most vulnerable places are the thin skin between the toes, little toes, and heels. The main causes of foot rubbing are:
- tight shoes;
- thin, low-quality sole;
- excessive sweating;
- high heels;
- systematic sports activities that overload the legs.
Calluses on the hands are caused by physical labor, rubbing the skin with sharp items of clothing. The tendency to develop wet calluses increases if a person suffers from endocrine diseases, has an unbalanced diet, and neglects hygiene procedures.
Plaster for soft calluses
If you need a remedy for a wet callus, the first thing you think of is a patch. It is clear and easy to use, reliably protects the skin from friction, promotes rapid healing of calluses on the foot, sole of the foot, heel, and ankle.
But! A regular medical adhesive plaster is not suitable for treating calluses. The adhesive ability of this product is high, but the structure of the tape is too dense, completely blocking the access of air to the skin. If you seal a wet callus with a regular adhesive plaster, a greenhouse effect occurs, as a result of which the walls of the blister soften. When the patch is removed, the bubble bursts, opening direct access to the wound to all kinds of bacteria, viruses, and pathogens.
When buying a patch at a pharmacy, you need to clarify that the product is required for the treatment of water calluses. These are special bactericidal self-adhesive tapes with a perforated, highly breathable surface, such as the well-known Compeed callus plaster. They are easy to use and not only protect damaged skin from friction and infection, but also create an optimal environment for the speedy healing of soft calluses.
What to do if the callus bursts
The bubble often bursts when careless pressure is applied to the walls. A rupture is fraught with serious danger, as dirt gets into the wound. It is urgent to wash the sore area with Chlorhexidine to remove sweat and dust. Apply generously with antibiotic ointment and apply a bactericidal patch.
The wound should be opened several times a day to expose it to air. Thanks to this, the damage dries out and a crust begins to form, under which tissue regeneration occurs.
Preventive measures
For prevention purposes, you should follow simple rules:
- buy comfortable shoes with a soft back. Too hard leather on the back of dress shoes causes the skin to rub until it bleeds;
- for recreation and sports, use comfortable shoes designed for the chosen sport;
- for long trips or hikes, it is better to avoid socks with rough seams or stripes;
- use gloves to protect your hands during autumn field work;
- Make sure the skin on your feet remains dry. Damp skin is more susceptible to the formation of calloused blisters.
In any circumstances, a bactericidal patch comes to the rescue. Despite the variety of recommendations and advice, remember - in case of a complex and chronic course of a cosmetic defect, you need to consult a doctor.
Treatment
It is important to treat a wet callus quickly. Even small blisters can cause inflammation, suppuration and other complications.
Large calluses on the heel and toes are at high risk. They are easy to damage. Staphylococcus and streptococcus bacteria can penetrate into the burst bubble, and therapy will take a long time.
Treatment tactics depend on the size of the damage. Doctors usually recommend combining traditional and folk methods.
Is it necessary to pierce
If a small watery callus occurs, the bladder should be protected from damage. The liquid inside promotes tissue healing and prevents infection. Large blisters that are very painful and can burst on their own are best pierced under sterile conditions. The procedure must be done in the first 2 days after injury.
If it is not possible to see a surgeon, the procedure can be performed at home. To do this you need:
- Treat the affected area with hydrogen peroxide and iodine solution.
- Disinfect the needle with alcohol or heat it over a fire.
- You can use a sterile needle from a disposable syringe.
- Make 2-3 punctures parallel to the surface of the bubble. You need to act carefully so as not to damage the wound or tear the walls of the blister.
- Press the callus with a sterile bandage and squeeze out the liquid.
- Apply a healing antibacterial ointment, for example, Levomekol, and apply a breathable bandage.
Dressings are required twice a day. It is advisable to leave the wound open at night so that the cells receive sufficient oxygen.
There is no need to trim dead skin. Its presence on the wound speeds up the healing process. If you exclude the penetration of bacteria into the punctured callus, recovery occurs within a week.
Medications
By storing the liquid in the callus bladder, it is possible to get rid of the damage faster. Pharmaceutical preparations are used for processing. Before application, the skin should be cleaned with warm water and soap and disinfected with peroxide, Chlorhexidine or Miramistin.
To heal the damage and reduce pain, ointments are prescribed. The following drugs have proven themselves to be effective:
- Levomekol. The ointment contains chloramphenicol and methyluracil. The product has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, eliminates gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, and accelerates regeneration. The ointment is applied under a sterile bandage 2-3 times a day.
- Baneocin. The product contains neomycin sulfate and zinc bacitracin. The substances destroy pathogenic bacteria, prevent the development of infection, and promote healing of wounds. The injured area is treated with ointment several times a day, and a bandage is applied on top .
It is easy to cure wet calluses using the effective Compid patch, made on the basis of hydrocolloid technology. Its mechanism of action prevents the wound from drying out and prevents repeated irritation and the penetration of dirt and dust. The medicinal components of the patch relieve pain and accelerate healing. It needs to be glued to the entire surface of the callus and changed once a day.
Folk recipes
In combination with drug treatment, it is useful to use traditional methods. They help relieve pain and speed up the recovery of damaged tissue.
- Aloe juice relieves discomfort in the rubbed area. It is necessary to cut off the bottom leaf of the plant, wash and dry. Cut a piece to the size of the callus, extract the pulp and apply to the skin. Cover with adhesive tape and leave for 6 hours. Repeat applying the compress twice a day until the damage heals.
- You can take advantage of the properties of plantain. Fresh leaves should be finely chopped. Wrap in gauze, place on the wound and bandage.
- Herbal lotions are useful for treating calluses. You need to take a spoonful of calendula and chamomile flowers. Pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. Strain the liquid. Moisten a sterile bandage, squeeze lightly and place on the sore spot. Do not remove for 15 minutes. Apply lotions 3-4 times a day.
- An ancient folk remedy that dries out the bladder is chicken egg film . The product must be cooked and cleaned. Separate the thin film on the inside from the shell. Carefully glue to the callus. Wait until the film dries and remove.
- It is easy to remove calluses on your toes and heels using baths. You need to pour boiling water (0.5-0.6 l) into a spoonful of oak bark and place it in a water bath. After 15 minutes, remove and cool. Dilute by half with warm water and place the sore leg in the solution for 20 minutes. Then dry the skin and lubricate the damage with tea tree oil mixed with olive oil in a 1:3 ratio.
How fluid collects in calluses
During friction, separation occurs under the surface of the skin. The interlayer space is occupied by liquid in the callus - transudate. This phenomenon occurs when blood serum fogs, water-salt balance and blood circulation are disrupted. A characteristic feature of transudate is the absence of an inflammatory nature. For this reason, the accumulated liquid has a transparent structure. With prolonged exposure of the skin to an external irritant, an accumulation of bloody substance is observed in the cavity of the bladder, which can be released.
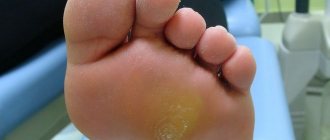
If an infection occurs when a watery callus is damaged, an inflammatory process begins. Then exudate accumulates in the bladder - this indicates infection and the beginning of the inflammatory process. In this case, the exudate can be serous (clear liquid) or purulent (cloudy green contents).
The longer the affected area is rubbed, the more fluid accumulates under the surface of the blister. An overfilled blister can burst from a slight touch, creating a risk of introducing pathogenic bacteria. When the liquid comes out, after a certain period of time the bubble begins to refill.
We recommend reading
- Features of silicone toe pads for calluses
- What can replace callus plaster?
- The effectiveness of using wound-healing ointments for calluses
Complications
If an infection has entered the wound, obvious symptoms of the inflammatory process appear:
- pain increases;
- large swelling forms;
- the skin around becomes purple;
- intercellular fluid becomes cloudy;
- pus oozes from the burst bladder;
- Body temperature may rise.
You cannot self-medicate in such a situation. You need to urgently contact a surgeon.
The doctor will provide qualified assistance by opening the suppuration and cleaning the wound. After the procedure, you must maintain sterility and regularly go to the clinic for dressing changes.
Structure and appearance
When soft skin is rubbed with hard elements, the upper layer of the epidermis dies and peels off from the healthy tissues that lie deeper. As a result, a bubble is inflated. Between the thin wall of the resulting blister and the entire skin tissue, fluid accumulates, which is lymph from damaged tissue. If a blood vessel is affected, the contents of the blister may contain blood. When the bladder is opened and the film is removed, a small wound surface is exposed. If a microorganism gets into it, inflammation and suppuration may develop. The skin around the callus becomes swollen, hyperemic, and severe pain appears. If the inflammation is not treated, an abscess may form, which only a dermatologist or surgeon can help get rid of.
In the absence of proper treatment for watery calluses, the film from the bladder can thicken and harden. A dry callus forms in the problem area, which is more difficult and takes longer to treat.
Prevention
Preventative measures reduce the risk of developing calluses and help maintain healthy skin. It is important to follow simple rules:
- purchase shoes made to size from natural materials;
- Avoid wearing high heels for long periods of time;
- To reduce sweating, treat feet with talcum powder;
- buy cotton socks with elastic that doesn’t squeeze your feet;
- wear shoes according to the season and always dry them thoroughly after getting wet.
It is advisable to stick special silicone pads on the backdrops, which reduce friction of the epidermis. When working in the garden, protect your hands with gloves, and avoid excessive strain during sports activities .
For prevention, it is useful to carry out healing baths. They make the skin soft and eliminate pathogenic flora. The solution is prepared at the rate of 1 tablespoon of baking soda and sea salt per liter of water. The procedures are carried out three times a week. Softened feet should be rubbed with pumice and lubricated with castor oil.
Baths for wet calluses
Fresh soft calluses respond well to treatment at home using accessible folk methods. First of all, these are therapeutic foot baths.
Foot baths when treating water calluses should not be hot. The optimal water temperature is 36C.
A simple remedy such as table or sea salt will help to disinfect the surface of the skin, dry the callus and stimulate rapid healing of the wound. To prepare a therapeutic foot bath, you need to dissolve a tablespoon of salt in a liter of lukewarm water. Immerse the painful area of the foot in this solution for 2-5 minutes. If you don’t have time to take a bath, you can simply wipe the callus with cotton wool soaked in a saline solution.
A bath with potassium permanganate helps quickly get rid of soft calluses. A weak, pale pink solution is prepared from potassium permanganate powder. Immerse your feet in it for 5 minutes. Potassium permanganate has a pronounced disinfectant property, dries the wound well, and relieves inflammation.
Causes of watery calluses
In most cases, the factor that causes water blisters to appear on the skin is friction against the surface of the shoe. Wearing features will cause problems:
- new shoes;
- rough backs with a seam in the middle;
- absence of socks or violation of their integrity;
- long walking during the day;
- poor quality shoe material.
To prevent damage, you need to carefully select shoes and take your time when trying them on.
What is dropsy?
Dropsy is a subcutaneous blister filled with translucent liquid. Its occurrence is a natural reaction of the body to prolonged friction. In this way, the human body is protected from damage and wounds on the skin.
If you notice discomfort in time and remove your shoes, dropsy will not form. Otherwise, rubbing will cause the surface layer of the skin to separate from the lower layer and fill the space with intercellular fluid.
Such a blister is quite painful; a strong burning sensation is felt in its place, which increases when touched. In general, this is a fairly harmless phenomenon if the skin is treated correctly. The danger arises if the dropsy is torn off and an infection develops.
When infected, the skin around the blister turns red, the internal fluid becomes cloudy, and pus may ooze. This situation should be avoided in every possible way, preventive measures should be taken, and if dropsy appears, things should not be left to chance.