Fever in children with urticaria
Young children can enjoy clean and firm skin around the clock. Ruddy cheeks, pink lips and a gentle, affectionate look that loving parents catch with such admiration. This is how we often describe the theme of their childhood to our now grown-up children. As soon as a small bubble appears on the body, parents immediately become wary and begin to immediately look for the reason that provoked the appearance of such a rash. Infants may develop heat rash simply because we wrap them up excessively in an attempt to protect them from colds. Poor quality diapers can sometimes cause heat rash. Although, here we are more likely talking about an allergic reaction. And even poor environmental conditions stimulate the development of more and more new diseases that our ancestors did not even suspect about. By the way, judging by historical references, allergies are considered one of them. Modern doctors have already learned not only to recognize this kind of ailment, but also to successfully treat it.
Diagnosis and preventive measures
This type of rash is quite easy to diagnose. To do this, take a glass of hot water (at 45 degrees) and apply it to your forearm.
If a reaction occurs within 5 minutes, you have failed the heat urticaria test. There is also another test: in it you need to immerse your shoulder or forearm in water at the same temperature as in the first option for several minutes.
After such testing, wait half an hour for a reaction to appear. If redness appears in the form of a rash or blisters, you have an allergic reaction that includes hives.
For a more accurate diagnosis, it is recommended to take tests to determine the level of acetylcholine. It is this substance that should be more than the usual norm.
Due to its increase, blisters and rashes form on the human body. Additionally, studies are carried out in which a person must work physically (sports exercises). The break between exercises is 5 minutes.
Only a doctor can tell you how to treat this disease by prescribing the appropriate treatment regimen. If you notice the slightest signs of heat urticaria, follow a number of rules that can help avoid relapses of the disease.
- Avoid exposure to heat-provoking agents on the skin.
- Take a bath or shower only at a water temperature of no more than 37 degrees.
- Use sedatives to be more resilient in stressful situations.
- Reduce physical activity to a minimum.
- Undergo a series of studies to identify additional allergic reactions and helminths.
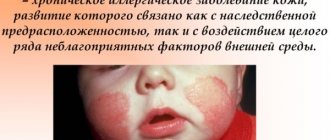
Urticaria - a general characteristic of the disease
A young mother came to see a dermatologist with a child in her arms and a complaint: a rash in the form of blisters of unknown origin had appeared on the baby’s body. No amount of powder helps get rid of them, and the child’s well-being clearly worsens. Why does a rash occur, what is the nature of such a rash?
It should be understood that the allergic reaction of the child’s body to any irritating factor can manifest itself in any form - sneezing, increased tearing, runny nose, cough, a rash in the form of spots, blisters, etc. may appear on the body.
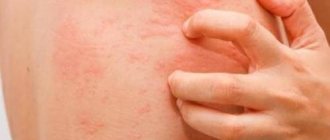
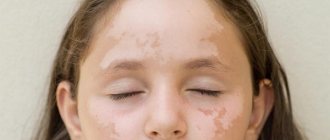
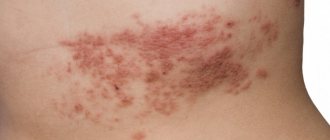
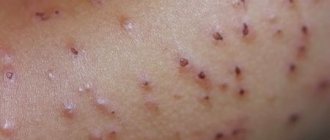
In medical practice, the term “urticaria” refers to a special type of allergic manifestation. This type of allergy is characterized by itchy blisters on the body, the size of which can reach from a millimeter to several centimeters. Such a rash can even appear on the mucous membranes.
Interesting fact! Externally, the rash strongly resembles a nettle burn. This is probably why doctors called this type of allergy urticaria.
But with hives, the rash is not the only symptom. The child may develop a fever, discomfort in the abdomen, nausea and even vomiting.
What is urticaria - types of disease
As mentioned above, urticaria is an allergic disease. It manifests itself in the form of a rash on the body, externally resembling a nettle burn.
Areas of skin with a rash become reddish and blistered. Children usually complain of severe itching and burning. Favorite places to localize the rash are the chin area, cheeks and mucous membranes. Depending on the form of the disease, urticaria can be: • acute, • chronic. The main symptoms of urticaria: • skin rash, • fever, • lethargy, • headache, • diarrhea, • vomiting.
Attention! Vomiting, diarrhea, headache and lethargy indicate swelling of the gastrointestinal tract.
The most dangerous symptom of urticaria is angioedema, which occurs in severe acute forms of the disease. Characteristic symptoms of Quincke are swelling of the mucous passages: swelling of the eyelids, cheeks, lips, tongue and an increase in the size of the larynx. Children with Quincke's edema cannot breathe freely, so at the first symptoms of its manifestation you should immediately call an ambulance.
Symptoms of the chronic form
If the rash on the body in children lasts more than a month, then doctors diagnose a chronic form of urticaria. This condition can last for years, periodically fading and progressing. As the condition progresses, children experience severe itching and an unbearable desire to scratch. If a secondary infection is added to the main disease, then the chronic form of urticaria turns into a chronic form of dermatitis. In the chronic form of urticaria, the rashes on the body are not so multiple, but can be localized on any part of the skin. Children become irritable, whiny, their sleep and appetite worsen.
Symptoms of urticaria at different stages of its development
Allergic disease manifests itself in mild, moderate and severe forms. 1. Mild stage - the child begins to rash, but he feels quite satisfactory. There is no swelling or weakness. 2. Middle stage - danger of developing Quincke's edema, rash on the body and weakness, fever and headache. 3. Severe stage - all of the above symptoms with more pronounced symptoms. Headaches, dizziness and confusion may be present.
Symptoms in childhood
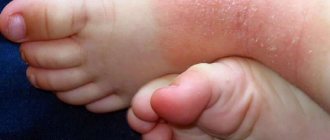
What are the symptoms of urticaria in children under one year of age? The disease begins suddenly , the child feels itching, and blisters appear on various parts of the skin. The localization of rashes can be not only on the skin surface of the body, but also in the lips, mucous membrane of the eye and gastrointestinal tract.
Signs of urticaria in children are accompanied by : swelling of the hands, lips, eyes, joints. Rash of varying sizes and swelling can last on the skin surface and mucous membranes from several minutes to hours. In some situations, symptoms persist for up to three days or longer.
You can learn more about urticaria in children under one year of age, what causes the disease and how to treat it by reading the article.
Temperature with urticaria
The acute stage of urticaria is always characterized by a high body temperature, which lasts throughout the entire period of the rash. Sometimes the body temperature of a child with urticaria can rise to 40°C. The combination of a severe rash and high fever requires immediate specialist intervention. Never self-medicate, because two such symptoms may indicate different diseases.
So, fever and hives in a child are a good reason to see a doctor.
In addition to the acute and chronic forms, there are other types of disease, which are characterized by the following symptoms:
1. Blisters from vibration. The child begins to rash after a massage, riding in public transport or after running. The rash may be accompanied by itching. 2. Pressure rashes. After applying pressure to the skin, blisters begin to appear. As a rule, the rash can appear from wearing tight clothes, pressure from straps, etc. Such rashes last up to half an hour and may be accompanied by itching. 3. Ambient temperature rash or cholinergic urticaria. Rashes on the body can appear from exposure to heat or cold, and sometimes from severe nervous strain. 4. Papular urticaria. The main places where papules are localized are the bends of the limbs. 5. Contact urticaria. The rash occurs as a result of contact with an allergen - animal hair, pollen, cosmetics. 6. Sun rashes. The rash appears as a result of direct exposure to ultraviolet radiation. It is extremely undesirable for children who suffer from this form of urticaria to be exposed to the sun for a long time. This can provoke disorders of the cardiovascular system and breathing.
Urticaria is a harmless disease, but some precautions should be taken. The most dangerous symptom of urticaria is Quincke's edema.
What it is?
When a child has hives, the symptoms manifest themselves in different ways. In childhood, rash elements are diagnosed; their localization on the surface of the skin can occur in any area. The causes of the disease are allergic in nature .
In children, rash elements most often appear on the torso, buttocks, and limbs in the bend area.
For effective treatment of this skin disease, it is necessary to know the signs of urticaria in a child and its causes.
Can there be a fever with urticaria in adults?
In an adult body, an allergic reaction rarely causes a fever. The indicator rises to a maximum of +37°C, which is due to the release of histamine and a change in metabolic rate.
Most often, fever with urticaria in adults is a negative consequence of infectious and inflammatory diseases. In the event of a relapse of the pathology after a recent recovery, a strong fever occurs +39...+40°C.
Often this temperature itself provokes the development of urticaria. And after the appearance of a nettle rash, people mistakenly believe that the cause of the fever is an allergy. In such a situation, allergic urticaria develops against the background of a viral or bacterial infection. This dermatitis is a type of urticaria and occurs as the body's response to a sudden release of alpha interferon.
- large blisters that can merge with each other;
- redness on the skin;
- Quincke's edema;
- itching;
- rashes.
Relief of the clinical picture occurs within 24 hours. In this case, the symptoms go away on their own (without taking antihistamines).
The development of a pathological process can be provoked by an increase in temperature against the background of:
- fungal diseases;
- violations of lymph outflow;
- bacterial pathologies;
- lesions of the gastrointestinal tract;
- endocrine system disorders;
- disorders of hormonal secretion of the thyroid gland.
In such a situation, urticaria becomes a symptom indicating the development of another pathology in the body.
Mechanisms of manifestation
Signs of urticaria can be recognized by blisters, the mechanism of manifestation of which is important to know. Small blisters appear due to swelling of a certain layer of skin (papillary). The swelling itself appears due to the release of various kinds of biological substances, for example histamines.
They, in turn, lead to the expansion of capillaries, which means that the permeability of its walls for various blood elements increases.
The mechanism of development of the disease is quite simple: as soon as an allergen enters the child’s body, the body (immune system) produces antibodies, as they are also called, protective proteins (igE). Such bodies accumulate and then attach to special cells - mast cells (cells of the immune system).
It is important to understand that it is in these cells that active biological substances are stored. It is logical that if a certain allergen enters the body again, it quickly combines with IgE antibodies, which, in turn, connect with mast cells. And this already leads to a certain number of disorders: dilation of the blood vessels themselves, the appearance of unpleasant itching, slight swelling and redness.
According to its mechanism, such a reaction is called immediate. The name is due to the fact that the disease develops too quickly, from a few seconds to several minutes (after the allergen enters the body).
As practice shows, most often the time of manifestation of the disease is 5-30 minutes.
It is by this mechanism that urticaria occurs, which was caused by food, or infection, sun or cold, as well as vibrational urticaria.
Does fever occur due to rashes in children?
Children under 12 years of age have an undeveloped immune system. She reacts sharply to external and internal irritants, so the risk of developing allergies until adolescence remains high. The child may develop nettle fever.
An increase in temperature is observed immediately after monomorphic blisters appear on the skin and inflammation subsides. In the absence of complications and the addition of a secondary infection, the indicators remain stably at the level of +37.5…+38°C. Fever may be higher in young children under 3 years of age.
Signs based on classification
The disease is classified depending on:
- duration of persistence of skin rashes;
- causes of rashes and blisters;
- time and speed of development;
- presence of long-term illness.
Most often, urticaria is divided into 2 forms: acute and chronic. The latter lasts more than 6 weeks. Acute symptoms appear within 1.5 months.
Acute form or angiodystonia
The development of this form of allergic reaction can be provoked by:
- pathogenic microorganisms and viruses;
- poisons that enter the bloodstream from insect bites;
- food products: strawberries, chocolate products, nuts, sea fish, flavor enhancers and flavorings;
- medications;
- fabric material: wool, latex.
In most cases, the cause of angiodystonia is raw fruits and vegetables. Ready-made meals rarely cause an inadequate immune response, because when exposed to high temperatures, up to 80% of the active compounds in the product are destroyed. Allergenic drugs include blood thinners, painkillers and decongestants.
The acute form of urticaria most often occurs in young children. The main symptom is a rash covering 40% of the skin area. Sometimes bright red blisters are present, ringed by an inflammatory process. Body temperature often rises to +40°C. Hyperthermia is accompanied by angioedema of the pharynx.
Chronic
Symptoms persist for 1.5 months or more.
The causes of chronic urticaria are:
- long-term severe infectious diseases;
- hormonal imbalance;
- pregnancy;
- the presence of malignant neoplasms;
- autoimmune pathologies.
With this form of allergy, the blisters are smaller in size, the skin around them does not swell and remains pale pink. There are few rashes, they are pinpoint and scattered over the upper part of the body.
When and how to reduce the fever?
Temperatures up to +38°C indicate the development of an inflammatory process. The hypothalamus specifically causes hyperthermia to facilitate the destruction of pathogens. In this case, you should not take medications. If the temperature rises to +38.5...+40°C, immediate use of antipyretics, application of cold compresses and ice baths are required.
In what cases is it necessary to reduce a child’s temperature?
When there is a fever against the background of urticaria, it is necessary to pay attention to the cause of the inadequate immune response. If hyperthermia was caused by an infectious agent, the fever should not be reduced to +38°C. When the reading is above +37°C with simple allergies, it is necessary to take antipyretic drugs.
In the latter case, indicators should not be allowed to increase above +38°C. Otherwise, interferon will begin to be produced, and the patient’s condition will worsen. The body cannot cope with the fever on its own, since the immune system is impaired.
What does official medicine offer?
If the cause of the development of high temperature was urticaria, antihistamines are prescribed:
If allergies occur as a result of infection, antipyretic medications such as Ibuprofen and Paracetamol are used. It is forbidden to give Aspirin to children to avoid the development of bleeding from blisters.
Traditional methods
At a temperature of +38°C, you can use traditional methods of treatment:
- Regularly ventilate the room where the patient is located to ensure access to fresh air.
- Give plenty of water. You need to drink 3-4 sips of liquid every half hour. It is not recommended to replace water with juices, compotes and tea. If desired, you can add 1 tbsp to the water. l. lemon or honey.
- A decoction of chamomile and linden helps reduce fever. 1 tsp. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over each ingredient and leave for 2 hours. Give the patient 3 times a day 150 ml.
- Do not force a person to eat.
- Avoid using warm blankets. They disrupt heat exchange.
The patient is provided with complete rest. He must remain in bed. Physical activity can lead to recurrent hyperthermia.
source
Diagnosis of temperature urticaria
The clinical diagnosis is made by a dermatologist based on the history and monomorphism of the rash, confirmed by provocative tests. For the cold version, the Duncan test is used: ice is placed on the elbow, if after 15 minutes the skin remains inert, there is no urticaria. For a more accurate test, immersion is used by immersing your hand in cold water (below 8 °C) for 5-10 minutes. The absence of itching and erythema during the test time is a negative result. You can place the patient naked for 10-30 minutes in a cold room with a temperature of 4 °C. In this case, care should be taken to avoid the development of colds or systemic reactions. An exercise test is also used at 4 °C for 15 minutes, after which the level of cryoglobulins in the blood is determined.
The local form of thermal urticaria is diagnosed using a test with a warm object: a glass of hot water (40–48 °C) is applied to the skin of the forearm for 1-5 minutes or a hand is immersed in water of the same temperature. Inert skin indicates the absence of urticaria. The common form is confirmed by blistering in a hot bath at a temperature of 40-48 °C or by walking for 30 minutes. Thermal urticaria of the cholinergic variant can also be diagnosed by a skin test with methacholine (blisters with intravenous or subcutaneous administration of the substance). To exclude other genesis of blisters, a blood test for allergens is performed.