What is aquagenic urticaria?
While water is a harmless substance for most people, there are patients who suffer from side effects from its exposure. Aquagenic urticaria is sometimes called an allergy, but unlike other types of urticaria, the condition is not characterized by a true histamine-releasing reaction.
It is likely caused by an immune reaction to something inside the body rather than an overreaction to something foreign. The exact cause is unknown, data regarding the effectiveness of individual treatments is limited, and various medications and treatments have had varying success.
The pathogenesis of aquagenic urticaria is poorly understood and is mediated in both histamine-dependent and -independent ways. Diagnosis is based on a thorough clinical history combined with water testing. Some patients may need additional testing to rule out other types of hives.
Treatment of solar urticaria
Treatment for solar urticaria is carried out step by step:
- exclusion of possible allergens;
- protecting skin from sunlight;
- taking antihistamines;
- the use of creams and ointments that have a regenerating effect;
- taking steroids, antibiotics, or antifungals depending on complications;
- compliance with diet and preventive measures.
Photodermatitis cannot be completely eliminated with conventional treatment, but medications can help relieve symptoms.
What should you give up first?
When treating solar urticaria, it is necessary to follow not only the treatment rules, but also medical recommendations.
They consist of refusing:
- walking in direct sunlight;
- clothes in dark colors;
- cosmetic preparations (at least temporarily).
In addition, it is recommended to wear hats with brims when going outside and treat your skin with sunscreen.
What helps with photodermatitis?
The main drugs used in the treatment of photodermatitis are antihistamines:
- Kestin;
- Claritin;
- Zyrtec;
- Telfast.
All medications are selected only after consulting a doctor, since not all antihistamines are suitable for treating this particular type of urticaria. For severe pain, you can take Analgin or Ibuprofen.
Therapy is carried out with such drugs as:
- Diphenhydramine;
- Suprastin;
- Tavegil;
- Lomilan;
- Diazolin.
If the rash and skin itching are very severe, then you can use non-hormonal creams:
- Fenistil-gel;
- Bepanten;
- D-panthenol;
- Gistan.
Or hormonal:
- Elokom;
- Soderm;
- Flucinar;
- Advantan.
Severe peeling of the skin can be eliminated using any fatty creams, including regular baby cream.
Hormonal drugs are contraindicated for use in the presence of wounds on the skin, since their components can penetrate into the blood, causing hormonal imbalances.
Folk remedies
Like medicines, traditional methods only help to alleviate the symptoms of the disease or eliminate them in mild forms of urticaria. Products that can soften and soothe the skin are popular:
- lotions;
- baths;
- lotions.
A lotion made from strong black tea that has been cooled can be applied to the skin every 20 minutes to relieve itching. Burdock root infusion is also used as a lotion to relieve itching. They soak gauze and apply it to the skin.
Using cucumber or cabbage leaves helps cool the skin and relieve swelling and itching.
Baths help soften the skin well. They should not be hot, but warm. The following can be added as additional components:
- marjoram infusion (200 g, pour 2 liters of boiling water, leave, strain);
- oatmeal (600 g per bath);
- decoctions of fir, pine, spruce.
You can prepare a cream from rice starch mixed with glycerin in equal proportions. It is rubbed into the affected areas of the skin to relieve itching.
The use of folk remedies to combat the symptoms of urticaria should also be discussed with a doctor so as not to cause even more harm to the body.
Classification
According to the latest World Allergy Organization guidelines, aquagenic urticaria is classified as an inducible type of chronic urticaria (reclassified as a separate subtype of urticaria).
On this topic
- Hives
What are the dangers of mechanical urticaria?
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- August 17, 2021
Among the limited cases of AK (1 patient in 240 million people), there is a prevalence among women of reproductive age; Symptoms first appear during puberty, with genetic dysfunction being the most likely cause. It affects men less often. Extremely rare in children.
A few sporadic family histories have also been reported, particularly those associated with Bernard-Soulier syndrome, raising the possibility of an associated genetic locus for AK, but no specific gene has been identified to date.
Symptoms
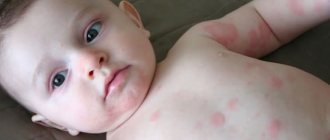
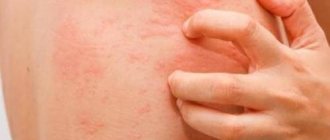
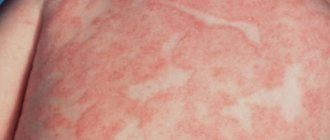
Patients develop characteristic folliculocentric wheals of 1-3 mm with surrounding erythematous patches of 1-3 cm within 20-30 minutes of skin contact with water. Damage is located mainly on the body (neck, back, shoulders, arms).
Patients experience itching, burning and tingling. Severe cases can lead to anaphylactic shock. Although systemic symptoms are extremely rare, the medical literature describes a case of a patient who presented with wheezing, difficulty swallowing, and subjective respiratory distress when drinking water.
Symptoms of aquagenic urticaria:
- itchy skin rash;
- burning after contact with water;
- blisters on the surface of the skin;
- pain and dryness in the eyes;
- labored breathing;
- swelling .
Uritary lesions usually resolve within 60 minutes of completion of skin contact with water. The affected areas are usually resistant to repeated stimulation for several hours.
AK appears when taking a bath or shower, while swimming in the sea or pool, or when exposed to rain. For some patients, sweat and tears are a potential hazard. Organic solvents (ethanol or acetone) applied to the skin do not cause aquagenic urticaria.
The condition has a significant impact on patients' quality of life, given that simple activities of daily living such as swimming or walking in the rain lead to distressing symptoms.
Due to its rarity, evidence-based treatments are lacking. Antihistamines are the cornerstone of therapy, although with varying degrees of effectiveness.
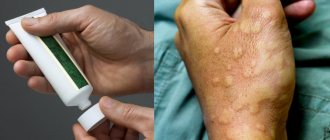
Aquagenic urticaria: photos, symptoms, causes, prevention and treatment methods
Aquagenic urticaria is a rare skin pathology that causes significant discomfort to sick people. The disease is an allergy to water and manifests itself during any human contact with liquid: bathing, drinking and inhaling fumes. Symptoms and treatment depend on the severity.
Causes
Water, or aquagenic, urticaria has common symptoms of this number of diseases, but in this case the irritant is water.
An allergic reaction is caused by substances dissolved in water that have a negative effect on the epidermis.
There are some factors that increase the likelihood of developing urticaria. These include:
- insufficient amount of antibodies in the body (immunoglobulins E),
- chronic disorders of the liver, kidneys and other internal organs,
- low level of immune defense,
- development of dysbacteriosis,
- helminth infection.
The presence of these factors is not one hundred percent proof of the occurrence of water urticaria, but they significantly increase the likelihood of developing the disease.
Therapy
Before prescribing a course of treatment, it is necessary to make a diagnosis based on the signs of pathology. However, this is quite difficult to do. Difficulties arise from the significant diversity of manifestations and rare occurrence of the disease.
Dermatologists suggest treating signs of urticaria using the following methods:
- reduce the amount of time in direct contact with water,
- use filters to reduce the chlorine content in water,
- use of hygiene products with hypoallergenic properties (without the addition of synthetic dyes, flavors and preservatives),
- before and after water procedures, it is recommended to use fat-based moisturizers,
- taking a course of antihistamine medications.
It is necessary to be careful about the food you consume and your lifestyle, since normalizing the body’s natural processes helps improve overall well-being.
Children's water urticaria deserves special attention. If the disease manifests itself in a child, it is recommended to use anti-allergy remedies and baths with the addition of soda or starch (the water should be warm, not irritating). This method is applied only to the pediatric form of pathology.
Medicines
Antiallergic drugs are used to treat urticaria:
- Suprastin,
- Tavegil,
- Terfenadine,
- Fenkarol,
- Astemizole,
- Pipolfen,
- Peritol.
The use of hormonal antihistamines of the corticosteroid series is permitted only after consultation with specialists, otherwise serious side effects may occur.
Folk recipes
Traditional medicine offers a wide range of remedies that reduce the symptoms of the disease in people of all ages.
- A medicine for water urticaria containing nettle is widely used to improve a person’s overall well-being. Pour 1 teaspoon of dried nettle into a glass of hot water. The infusion is kept for 1 hour, after which it is filtered. Use up to 4 times a day for 1 week.
- A product for the treatment of local skin irritations using baths. Pour 10 g of crushed wild rosemary leaves into a glass of boiling water. Infuse until rich in color and add to water during hygiene procedures, lasting up to 20 minutes.
- Apply fresh clover juice to a cotton pad. Wipe the affected areas or apply lotions for up to 10 minutes. After completing the procedure, the skin is thoroughly washed with filtered, boiled and cooled to room temperature water.
- You can use dill juice in the same way. The lotion helps relieve itching; it is recommended to leave it for half an hour.
Prevention
Basic preventive actions for water urticaria include:
- Use of artesian water.
- Timely replacement and use of cleaning filters.
- Quick implementation of water hygiene procedures.
- The use of natural cosmetics and detergents without the addition of preservatives and other allergens.
- Using micellar water to remove makeup.
- Compliance with the rules of a healthy lifestyle (proper nutrition, adequate sleep, elimination of toxins).
Urticaria is not transmitted from person to person, and the causes of its occurrence are associated with disorders of the internal systems of the body . That is why it is necessary to be attentive to your health and promptly seek advice from a dermatologist, since skin irritation may indicate the development of internal diseases.
Aquagenic urticaria is an unpleasant but rare disease, to reduce the manifestations of which it is necessary to use medications and follow the recommendations of your doctor. In addition, various traditional methods are used to treat the symptoms of pathology.
Attention!
The site administration advises you not to self-medicate, and in any controversial situations, consult a doctor.
Source: https://fr-dc.ru/kozhnye-zabolevaniya/opisanie-i-lechenie-akvagennoj-krapivniczy
Causes
The underlying cause of aquagenic urticaria is poorly understood. Some researchers and doctors theorize that the condition develops due to the skin's hypersensitive immune system reacting to one of several irritants.
Hypotheses include:
- Sensitivity to chemical additives in water (chlorine, fluorine, etc.); According to this theory, the cause of urticaria is most likely not water, but an allergen in the water, which, when it comes into contact with the skin, causes an immune response.
- Weakened skin mast cells react with water to release inflammatory histamine proteins.
On this topic
- Hives
How to prevent an allergic reaction like hives
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- July 28, 2021
Presumably, when the stratum corneum or sebaceous glands are exposed to water, a toxic substance is formed that stimulates mast cell degranulation and the subsequent release of histamine, which leads to the development of urinary lesions.
Perhaps the mechanism of aquagenic urticaria is associated with a change in osmotic pressure around the hair follicles, an increase in passive diffusion of water. Sudden pressure leads to indirect provocation of urticaria. Cases of localized aquagenic urticaria after epilation have been described, supporting the hypothesis.
Another explanation involves the presence of water-soluble antigens in the epidermis: they dissolve and diffuse through the dermis, releasing histamine (which activates “itch neurons” whose sole role is to experience itch).
However, there are studies of a mechanism completely independent of histamine release, where in some patients, exposure to water did not increase histamine levels sufficient to induce urticaria.
Common causes
Aquagenic urticaria is more common in women than in men. In addition, allergies to water occur in infants and adolescents.
Burning, redness and other associated symptoms are triggered by the release of histamine , which, in turn, comes into contact with nearby tissues and leads to this effect.
The reasons for the development of this aquatic form of dermatitis have not been fully studied. Experts have an assumption that the disease appears due to hypersensitivity of the immune system. There are several provoking factors:
chlorine in water;- weak skin mast cells that respond to fluids;
- genetic predisposition;
- lactose intolerance;
- HIV infections;
- cholinergic urticaria;
- atopic dermatitis;
- liver and kidney diseases.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of aquagenic urticaria is based on evaluation of the patient's clinical history (after exposure to water), analysis of potential signs that may cause relapse, combined with testing.
On this topic
- Hives
The best treatments for generalized urticaria
- Olga Aleksandrovna Kalinina
- July 18, 2021
The standard testing method involves applying a water compress to the patient's damp skin (arm or forearm) - a piece of cloth (or paper towel) soaked in water at 35 ° C - for 30 minutes. To check the difference in the reaction, distilled water, tap water, and saline are used over the next 10-15 minutes.
The main task of diagnosing AK is to differentiate the condition from other types of urticaria (cholinergic, cold, urticaria caused by physical factors). Water of any temperature can trigger aquagenic urticaria, but keeping compression at room temperature avoids confusion.
Thus, the symptoms of cholinergic urticaria are extremely similar to the symptoms of AK, but occur in response to appropriate stimuli: an increase in core body temperature due to exercise or emotional stress, eating spicy foods. In response to exposure to water at room temperature, this type will have a negative result.
When forming differential diagnoses, it is also necessary to take into account the clinical subtypes of AK. "Water" urticaria should be distinguished from aquatic urticaria, which is associated with polycythemia vera. With it, short-term contact with water causes intense itching, but without blisters and erythematous spots.
The physical examination also includes dermatography and a search for any systemic signs, such as rales. On laboratory evaluation, serum immunoglobulin E levels should be normal, which will help differentiate aquagenic urticaria from an immunoglobulin E-mediated allergic reaction.
In patients suffering from angioedema along with urticaria, it is useful to investigate its etiology by checking the level of C1-esterase inhibitor. It is important to note that serum histamine levels may or may not increase after exposure to water. Finally, the histopathology of aquagenic urticaria is consistent with a nonspecific form of urticaria and is therefore not important for diagnosis.
Treatment
Scientists have not sufficiently elucidated the causes of the body’s inadequate reaction to water. Therefore, today water urticaria is treated with antihistamines and immune-strengthening drugs.
Additionally, dermatologists provide recommendations regarding hygiene and nutrition.
General rules
If a person is prone to aquagenic urticaria, this does not mean that he is completely prohibited from contact with water. You just need to learn to do everything right. You can reduce the risk of itchy skin rashes by constantly observing the following points:
- If home water is of poor quality, then for hygiene procedures it should only be used boiled. But it is better to install an aquafilter to clean it.
- Reduce bathing time to 3-5 minutes.
- Do not use any bathing gels. They are based on the aqueous phase, so they create additional stress on the epidermis. The best option is baby soap.
- If a rash occurs after wet cleaning in an apartment, it is recommended to wear rubber gloves.
- If you are allergic to your own sweat, it is recommended to avoid overheating the body.
- Decorative cosmetics should be removed from the face using cosmetic milk or hypoallergenic micellar liquid.
Drug therapy
To ease the course of the aquagenic form of urticaria and relieve itching from the skin, antihistamines (Diazolin, Suprastin, Fenkarol) are prescribed.
In order to strengthen and normalize mast cells (they produce histamine), stabilizers are prescribed - Cromolyn or Ketotifen. The dosage and duration of taking the tablets should only be determined by a doctor.
The antipruritic agent Fenistil-gel and the anti-inflammatory drug Nezulin are recommended as local medications for aquagenic urticaria. To slow down the development of an allergic reaction, Gistan-N is prescribed.
How else can you help?
Water urticaria is usually treated by strengthening the immune system.
Dill juice also helps soothe inflamed skin and relieve itching due to water urticaria. It is squeezed out of a freshly picked plant onto a cotton pad, which is then applied to the sore skin for half an hour.
To do this, doctors recommend their patients:
- Eat a lot of vegetables and fruits every day.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Take a course of vitamins regularly.
To help the body quickly cope with the irritating manifestations of water urticaria, dermatologists prescribe an antihistamine diet to their patients. It helps normalize histamine levels in the body. This therapeutic diet is prescribed during the period of exacerbation of skin disease. Lasts about 7 days. Dietary table includes:
- dairy products;
- dietary meat;
- low-fat fish;
- cereal porridge;
- dried fruits;
- biscuits;
- yesterday's bread.
Fatty, smoked, sweet and too salty dishes, as well as fresh milk, coffee and various exotic fruits are excluded from the menu.
Traditional methods of treating water urticaria involve the use of steamed chamomile herbs as a compress. It is applied 2-3 times a day for 10-15 minutes to the allergy-affected areas of the skin.
Therapeutic options
Water is a causative factor in AK, but avoiding the causative agent appears to be an impractical and sometimes impossible task for patients. There is no absolute treatment that will relieve the symptoms of water urticaria. Most methods only help reduce the impact of the condition to maintain comfort when the body needs contact with water.
On this topic
- Hives
All about chronic urticaria
- Olga Aleksandrovna Kalinina
- July 12, 2021
Urticarial symptoms (blisters and itching) are thought to be mediated, at least in part, by the action of histamine on the H1 receptor. Thus, first-line therapy includes H1 antihistamines. To minimize the impact of aquagenic urticaria, the following are used orally:
- hydrochloride;
- hydroxyzine;
- terfenadine;
- Cyproheptadine.
The therapeutic response varies from patient to patient. First generation H1 blockers (hydroxyzine) have significant sedative and anticholinergic side effects that may last much longer than the therapeutic effect, which lasts only 4-6 hours.
Second generation H1-histamine receptor blockers - with less depression of the central nervous system, but a longer duration of action.
Other means:
- Parenteral corticosteroids (actual effect and benefits are not yet clear).
- Epinephrine: Used during acute attacks of urticarial symptoms to reduce the appearance of cutaneous vasodilation. Also helps inhibit mast cell degranulation.
- Ultraviolet light (used along with antihistamines): causes the epidermis to thicken and prevents water from penetrating into this layer and interacting with the cells underneath.
- PUVA therapy is used when oral and topical treatments are inadequate. Proposed mechanisms of phototherapy for the treatment of AK include a possible reduction in mast cell activity and reactive thickening of the epidermis.
- Stanazolol, which is an anabolic steroid without significant androgenic side effects, and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor drugs, which help achieve symptom control when combined with antihistamines and anticholinergic drugs.
- Capsaicin (used in the production of Zostrix cream) is often used to reduce the painful reaction of AK.
Symptoms and manifestations
A person often does not even assume that the cause of the disease was water. Aquagenic urticaria has symptoms similar to those of various allergies.
But this type of urticaria can be determined by the clinical picture of water intolerance.
The most common signs are:
- the disease is always accompanied by itching.
- The appearance of blisters similar to a burn after contact with nettles.
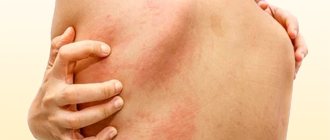
- The area of contact with water becomes covered with an extensive rash.
- A headache occurs.
- The skin dries out and begins to peel.
- A cough appears.
- Gastrointestinal disorder.
- Eyes turn red.
- Breathing becomes difficult and shortness of breath occurs.
These symptoms may appear immediately or within an hour after exposure to water. In some people, aquagenic urticaria can even appear from their own sweat or tears coming into contact with the skin.
The disease manifests itself with general symptoms at any age and does not pose a serious danger. But you shouldn’t relax, as recent studies have proven that there can be unpleasant complications.