This disease got its name because its symptoms are identical to the skin irritation that occurs with a nettle burn. In middle-aged people, this pathology is diagnosed quite often . The consequences of its progression can be very serious due to the presence of serious complications. Why urticaria may appear in adults, symptoms and treatment, photos of this disease at its various stages - you can find out all this by reading the article.
general description
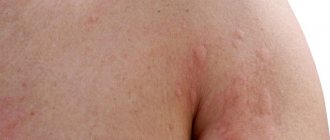
Nettle rash is a disease that combines several groups of diseases, but they all have the same symptom - blisters that look like a nettle burn . The rash can appear in isolated areas of the skin and then spread over most of the body.
Urticaria is accompanied by severe itching, and sometimes the temperature rises. Since urticaria can manifest itself in the form of an allergic reaction to any external irritant, it is necessary to exclude the allergen from contact.
In addition to its allergic nature, the disease in adults is a skin manifestation of an autoimmune disease, bronchial asthma. There are about five or more types of urticaria; the disease occurs in acute or chronic form. To prevent it from developing into the chronic phase, it is necessary to prescribe adequate treatment.
Traditional medicine recipes
Treatment with folk remedies can only be carried out in consultation with a doctor. The disease is dangerous due to angioedema, which can be fatal. Therefore, self-medication without consulting a doctor is strictly prohibited.
Related article:
Treatment of dermatitis during pregnancy
When fighting urticaria, the following recipes are most effective::
- Brew a tablespoon of chamomile with a glass of boiling water and leave the infusion for 20 minutes. Drink a glass, dividing the portion into 3 parts. You can also drink decoctions of string, calendula, oak bark and burdock root.
- Grate the celery root on a fine grater and squeeze the juice out of the pulp. Drink a teaspoon 3 times a day until the rash disappears. You can also pour boiling water over the root pulp and drink 70 grams before meals 3 times a day.
- Pour boiling water over a handful of cherry blossoms and leaves, leave the broth for 10 minutes, filter and drink 100 grams at least 5 times a day.
- The inflorescences and leaves of yarrow are poured with boiling water and infused. Take 3 times a day for 2 weeks. You can also prepare a tincture from the plant by taking 3 tablespoons of the herb and 100 grams of vodka. The mixture is infused in a dark place for 2 weeks and drunk every day, 30 drops in the morning.
- Pharmacy tinctures of motherwort, valerian or hawthorn will help relieve itching. They drink 25 drops 30 minutes before bedtime.
- It is necessary to mix a tablespoon of lemon balm herb, valerian root and hop cones. Pour a glass of boiling water over the raw material and take 70 grams before bed. The decoction can be stored in the refrigerator for 2 days.
- Baths are good for allergic reactions if decoctions of valerian, motherwort or cyanosis are added to warm water.
- A decoction of coriander seeds helps with illness. It is enough to pour boiling water over a bag of raw materials and take 50 grams at least 3 times a day.
Video
Causes of the disease
The causes of urticaria in adults are divided into two types:
- endogenous;
- exogenous.
Exogenous causes include temperature, chemical, and physical effects. The rash occurs due to medicinal influence, consumption of antibiotics.
These are also various food items that adults eat, insect bites. Endogenous causes are associated with the pathology of internal organs; in ancient times it was believed that any rash is only a reflection of some disease.
What causes urticaria in adults and children, according to research? Scientists have compiled the following list:
- Food allergies. Most often on eggs, nuts, citrus fruits and other foods;
- Metabolic disorders, bacterial infections;
- Inhalant allergens. These include dust, cat hair, flowering of various plants, etc.;
- Pharmacological drugs;
- Insect bites;
- Autoimmune diseases;
- Features of the body, increased sensitivity to the sun, cold, increased sweating;
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
How to prevent relapse
Prevention of recurrent urticaria is as follows:
- The diet prescribed by the doctor must be followed constantly, and not just during an exacerbation.
- Patients are advised to exclude exposure to the most common triggers - heat and cold.
- There is no need to neglect the treatment of concomitant diseases. It is important to prevent the development of bacterial and viral infections, which often become a trigger for the appearance of urticaria.
- It is advisable to constantly use hypoallergenic cosmetics and avoid contact with household chemicals.
Getting rid of idiopathic urticaria is not so easy, but if you follow your doctor’s recommendations, it can be done. It is necessary to take measures to combat rashes and treat other health problems that most often cause the disease.
Main symptoms
The main signs of urticaria:
- Itching;
- blisters;
- Rash.
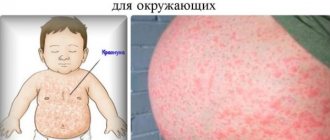
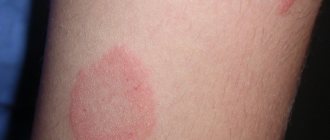
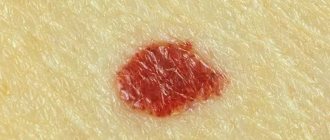
Itchy skin is the first symptom of urticaria in adults and children. If you start scratching the skin, redness begins, against which pale red blisters appear. They usually have a round appearance, but as the area of redness grows, a variety of large plaques form.
A hives rash can affect any area of the skin and usually appears suddenly. The bubbles are dense, pale pinkish in color. The nettle rash is very itchy, the blisters can be small or large in diameter.
The rash lasts for several hours, then the level of the rash decreases, sometimes blisters may appear in other places on the body. But usually nettle fever in adults disappears, leaving no noticeable traces.
Typically, urticaria lasts several hours or days. With chronic nettle fever, the rash lasts for months. Sometimes rashes and itching are accompanied by fever, lethargy, and upset stomach.
Types and forms
Each form of urticaria has its own course and type of symptoms. There are acute, chronic and chronic papular persistent varieties. In international practice, it is about form, that is, without external influence from outside, and physical - providing any effect on the skin. The physical form of urticaria in adults has several types:
- Dermographic. It appears after mechanical impact. Signs are detected after squeezing the skin for a long time. Often occurs after wearing a backpack, tight shoe straps in the summer, or adults sitting motionless.
- Cold. Skin manifestations occur against the background of external influences - cold wind, water, wind, temperature.
- Thermal. Symptoms appear due to thermal influence.
- Solar. Signs are related to exposure to light or UV radiation. You can learn about solar urticaria here.
Some types of urticaria occur due to emotional stress, overexertion, skin itching and rash due to the release of adrenaline. There is contact urticaria, which appears as a result of skin contact with an allergen, and aquagenic urticaria, which occurs when the epidermis is exposed to water.
It is noted that most often spontaneous urticaria is diagnosed in adults in the acute and chronic phase, dermographic (delayed) and contact.
Acute urticaria
An acute form of urticaria on the skin can occur at any age. Typically, people with a predisposition to allergies and a tendency to atopic dermatitis are at risk. The signs of the acute form are clearly expressed and can be easily diagnosed visually.
A dense rash with pink blisters covers a certain area of the body, accompanied by hard-to-quench itching. Blisters can merge into one spot, resulting in a large affected area.
In the complex version, nettle fever may be accompanied by swelling and headache. Rashes sometimes affect the mucous membranes, in particular the lips, nasopharynx, and larynx. In this case, there are complaints of difficulty breathing.
Urticaria rashes occur from a couple of hours to several days. The acute form of the rash is accompanied by a short period of time, usually as a reaction to some irritant.
Causes of the acute form:
- Drug and food allergies;
- Pollen, insect bites;
- Chemical cosmetics;
- Hepatitis B, dysbacteriosis, poisoning.
Classification of urticaria in the acute stage:
- Typical;
- Atypical.
With an atypical course in adults, there is no itching, and the blisters have a linear shape. An atypical type of rash usually occurs when the skin is exposed to mechanical irritants. This group sometimes includes contact urticaria. Read more about acute urticaria in this article.
Quincke's edema: acute limited form
Quincke's edema is described as a giant nettle fever that affects not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes, in particular the larynx, genitals, tonsils, lips, eyelids.
In some cases, swelling of the esophagus, intestines, and respiratory tract is observed. The patient suffers from swallowing problems, intestinal obstruction, vomiting, and barking cough. A dangerous outcome is asphyxia.
If with urticaria the rash is localized without swelling and with severe itching, then with Quincke's edema there is often no burning sensation. Usually the swelling subsides after a few hours, but relapses are possible. Sometimes Quincke's edema accompanies manifestations of typical urticaria.
Papular persistent form
Long-term rashes can develop into a papular form of the disease. The nature of the rash with papular urticaria looks like papular nodules. The papules have a burgundy hue, blisters of a dense structure and are very itchy.
Papules are accompanied by swelling, itching, and redness of the skin. They may be joined by a secondary infection - purulent blisters, pustules. When they heal, small scars remain in their place. Papular nodules are most often concentrated on the bends of the limbs, in the folds of the skin.
Chronic relapsing stage
The chronic form occurs when the body's sensitivity to the influence of irritants that cause an allergic reaction increases. Chronic foci of infections can aggravate the process. These include caries, tonsillitis, inflammation of the tonsils, cholecystitis.
In the chronic form of urticaria, the rashes do not have a wide girth. They can affect any area of the skin, but the blisters are not profuse.
Acne is sometimes accompanied by a headache, general malaise, and painful sensations in the joints. The cause of the chronic stage can be found out after a blood test and a general examination of the body.
Cold
After exposure to low temperatures, some adults develop blisters on the skin; the pathology occurs at any age, but is more often diagnosed in women. The cold form can be triggered by cold air, snow, draft or cold shower.
The main symptom is severe itching with a rash. Urticaria-type rashes occur in two variants:
- Immediate form. The rash begins immediately after exposure to the cold factor.
- Slow form. Rashes are detected after 8-9 hours of exposure to cold.
Elements of rashes mainly appear at the site of direct contact with the cold factor - neck, cheeks, arms, legs. Sometimes they occur under the knees and calves. If the impact of the irritant was strong, then nausea, swelling, pain in the back of the head, and chills are added to the symptoms.
Dermographic
The form of urticaria appears due to some mechanical influence. The main sign of dermographism is the sudden appearance of a rash and its rapid disappearance. Belts, clothing straps, tight collars, and narrow shoes usually act as irritants.
The skin rash is light in color, and the surrounding areas of the epidermis are reddish in color. The appearance of the blisters is usually linear. There is urticaria of a dermographic appearance with white lines on the epidermis without signs of redness.
The main symptom of this type is severe itching and burning. The appearance of dermographism is influenced by the state of the environment and skin sensitivity. When the mechanical factor is eliminated, nettle fever in adults goes away on its own within a few hours.
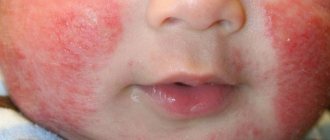
Solar
This type is considered one of the most popular; nettle fever occurs when exposed to direct sun or ultraviolet rays. Symptoms begin after 20-30 minutes of exposure to direct sunlight.
Prolonged sun exposure worsens symptoms. In adults, blisters are small in size, pink in color and accompanied by an itchy sensation. If an adult or child has been under the sun for a long time, then the blisters can be larger, reaching 2 centimeters.
The condition can be aggravated by other symptoms - nausea, lack of air, dizziness, fever. What causes the solar form of urticaria? Causes:
- Skin sensitivity to the sun;
- Use of perfumery products with essential oils;
- Disease of internal organs.
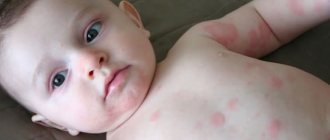
Urticaria in children
Rashes in the form of urticaria in children are easy to identify, as the child begins to complain of itching, areas of the body are covered with a rash. The disease is rare in children under six months of age.
Itching is difficult for children to endure; concentrated areas become scratched, and swelling may appear. Sometimes the rash is accompanied by fever, the temperature rises to 38 degrees. What can cause urticaria in children? The reasons are the same as in adults.
In children, the disease occurs in acute and chronic phases. The most dangerous development option is Quincke's edema. It leads to breathing difficulties, nervous system disorders, dizziness, and lethargy. At the first signs of edema, medical attention is needed.
Why does the temperature rise due to nervousness?
An increase in body temperature due to stress is a fairly common and common phenomenon. This usually happens in cases where negative emotions are suppressed, and there is no possibility of their splashing out, which should manifest itself in crying, crying or screaming.
As a result, not only can the temperature rise, but many other, more serious problems can arise. Most often, the following diseases develop against the background of regular negative emotional outbursts:
- respiratory tract lesions;
- peptic ulcer and other diseases of the digestive system;
- migraine;
- heart and blood vessel diseases;
- dermatological diseases, etc.
It has been established that self-confident, successful and sociable people experience almost no consequences of stress. But with an excess of negativity, aggression and hostility, there may be cases of diseases of the cardiovascular system, hypertension, skin lesions, as a result of which body temperature may rise. And calm and unsociable individuals are usually prone to the accumulation of emotions, which ultimately lead to serious damage to the digestive and respiratory organs.
To prevent the occurrence of dermatological problems, people prone to developing the skin lesions in question are advised to follow several rules:
- first of all, avoid stress and negative emotions as much as possible;
- strengthen the nervous system, do yoga;
- exercise;
- drink tea with the addition of healing soothing herbs such as chamomile, mint, etc.
- Avoid eating foods that can trigger allergies, such as citrus fruits or chocolate;
- provide the body with a full night’s sleep, which should last at least eight hours;
- strengthen the immune system, eat right and take vitamins;
- use natural cosmetics without fragrances and chemicals;
- do not neglect the rules of hygiene;
- Do not delay visiting a doctor if you experience symptoms of various dermatitis that appeared after suffering stress.
Following these recommendations will make life much easier and will allow you to maintain both psychological and physical health.
We recommend reading
Allergic rash in children and redness
Treatment of itching on the palms of the hands
Causes and treatment of dermographism
Causes and treatment of red cheeks in adults
Treatment
Treatment of urticaria is based on the general symptoms and severity of the manifestation. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate all severe factors that provoke urticaria in adults and children. In treating the disease, it is important to follow the following rules:
- Compliance with the regime, diet;
- Elimination of foci of chronic inflammation;
- Treatment of the gastrointestinal tract.
If the nettle fever does not go away for a long time, the rashes itch, then it is important to eliminate the influence of the external irritant. To completely exclude a recurrence of the disease, it is worth undergoing a test for helminths.
How to treat severe urticaria? In this case, it is necessary to include glucocorticoids and histaglobin in the drug regimen. Special ointments and other methods of external therapy are prescribed. For acute nettle fever in adults and a large area of coverage, the following medications are used:
- Antihistamines;
- Sedatives;
- B vitamins;
- Magnesium sulfate;
- Cleansing enemas.
Nettle fever is diagnosed by an allergist or dermatologist. You can also learn about treating urticaria in adults at home in this article.
Features of the flow
Urticaria as a disease occurs due to the accumulation in the body of substances identical to the type of histamine. Histamine comes into action when a foreign antigen penetrates. It dilates the capillaries, which causes the first symptoms of hives to appear: itchy blisters that itch and create discomfort.
Why does urticaria in an adult not go away? Why does it last more than two days and go into the chronic stage? This is due to the presence of a chronic infection in the body, it provokes the disease, so the nettle fever returns.
The causes of hives depend on many factors. One of them is a functional disorder of the nervous system. Stress also disrupts skin microcirculation, which leads to inflammation.
The appearance of rashes in general does not pose a danger to the body, but why is urticaria dangerous for adults and children? The main danger is angioedema and anaphylactic shock. They can be fatal without immediate medical intervention.
Diagnostics
If you notice symptoms of urticaria, you should immediately consult a dermatologist. He will conduct an examination and make a diagnosis.
The diagnosis process is divided into three stages:
- At the first stage, the doctor will examine the patient's skin.
- On the second, the doctor determines the severity of the disease based on the symptoms that have already appeared. Determines the time since which the patient became ill.
- At the third stage, the doctor determines the factors that caused the disease.
After the doctor has made a diagnosis, the patient is prescribed appropriate treatment, taking into account all the characteristics of his body.
It is worth taking into account that urticaria has one unique feature. It lies in the fact that quite often during a visit to the doctor, its symptoms disappear
To this feature of the manifestation of symptoms, and then their abrupt disappearance, the concept of ephemerality (illusory symptoms) is applicable:
- Medical research has proven that this phenomenon occurs due to the fact that when visiting a doctor, the patient in most cases experiences stress and fear. As a result, a fairly large dose of adrenaline is released into the blood, which plays the role of corticosteroid drugs.
- The ephemeral (ghost) effect is temporary, and most often symptoms return after 1-3 hours. In some cases, even with greater power of manifestation.
As a rule, if the patient has an ephemeral effect of symptoms, he is sent for an inpatient examination to the hospital. Usually the patient is under medical supervision for 3 to 7 days.
After the observation period has passed, the patient is discharged if the symptoms have completely disappeared and all tests are normal. Treatment is also prescribed if symptoms reappear.
If a person has chronic skin diseases, such as: Acne, Eczema, the disease can be a vicious circle. This complicates the process of diagnosing the disease.