Description of the disease
Urticaria, or, as doctors also call it, nettle fever, is a dermatological disease of an allergic nature. The disease, which many also know as urticaria, is accompanied by the appearance of a vesicular rash on the skin, which occurs along with other unpleasant symptoms. It may be a full-fledged disease or a symptom of some other disease.
What is urticaria
Why does it occur
Since urticaria is allergic in nature, the main causative factor contributing to its development is an allergic reaction. The role of an allergen can be played by various irritants, including:
- Food;
- medications;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- severe stress;
- synthetic fibers;
- pet hair;
- pollen or road dust;
- chemicals.
Reasons for the development of urticaria
Sometimes urticaria develops against the background of other diseases or pathological conditions:
- chronic infection, such as infectious gastritis;
- dental caries or chronic tonsillitis;
- liver failure;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
Etiology of urticaria
Note! If urticaria manifests itself as a concomitant symptom, it usually has a chronic course. The symptoms of the pathology are less pronounced, and periods of exacerbation practically do not occur.
Characteristic symptoms
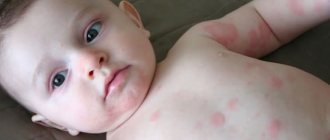
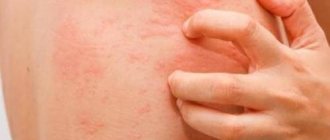
Urticaria is usually accompanied by pronounced symptoms. A pink or red rash suddenly appears on the skin. The blisters have a round shape, and in some cases they merge into one large blurry formation. The affected areas of the skin are very itchy, but after a certain time the rash goes away and appears in another place.
Signs of hives
The transition of nettle fever to a chronic form leads to the fact that the patient’s condition can alternate between exacerbation and improvement. The duration of such periods is always different. When urticaria worsens, additional symptoms appear:
- Strong headache;
- general weakness;
- diarrhea;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- increase in body temperature.
On a note! The most complex form of the disease is Quincke's edema or giant urticaria. This is an acute allergic reaction, accompanied by massive swelling of the mucous membranes or skin. This condition requires immediate medical intervention.
Dangerous symptoms of urticaria
All of the above signs refer to the external manifestations of urticaria, but there are changes that occur inside the patient’s body. Upon contact with an allergen, the cells of the body are gradually destroyed, resulting in the release of histamine (tissue hormone). It affects the body in such a way that liquid enters the cavity between the cells from small blood vessels. This leads to redness and swelling of the tissue.
Urticaria: contagious disease or not?
This disease poses a significant problem for humans. It not only creates considerable physical discomfort due to constant itching, but also spoils a person’s appearance. A particular nuisance is that rashes often appear in areas that are not covered by clothing.
Therefore, this illness can complicate a person’s relationship with his environment. This is especially acute for a child in a children's group.
Seeing such redness, rashes and blisters on the skin, as shown in the photo below, both the patient himself and the people around him wonder whether urticaria is contagious or not.
Really: is hives contagious? How dangerous is a person suffering from this disease to others? Is this disease a personal problem for the patient himself, or is there a possibility of infection spreading? How much precautions should be taken to prevent infecting other people? And how is urticaria transmitted if it is contagious?
So, is hives transmitted from person to person?
What is hives and is it contagious?
Among the various skin lesions, there are those that can be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one.
Various types of lichen, infectious dermatitis and other skin diseases caused by viruses, bacteria and parasitic fungi can indeed be transmitted from an infected person to others. For this, sometimes direct contact between people is not even necessary.
For example, when shaking hands, infection can also occur through various objects that come into contact with the patient’s skin. Is urticaria transmitted in this case?
To begin with, urticaria is not an independent disease caused by any specific single factor. It may be an element of the overall clinical picture of any disease. This disease is a combination of the following symptoms (see photo):
- severe skin itching;
- lumpy rashes on different parts of the skin;
- blistering.
What is the reason for this clinical picture?
What causes hives and is it contagious or not?
As research by scientists has shown, the cause of rashes is an allergic reaction of the body. Allergies in this case can be caused by the following factors:
- side effects of antibiotics and other drugs;
- toxic effects of certain chemicals;
- intoxication of the body with waste products of parasites;
- the effect of allergens contained in a number of food products;
- exposure of the skin to sunlight, water, ambient temperature;
- mechanical effect on the skin;
- some infectious diseases;
- nervous tension, stress.
When the skin is directly exposed to factors that provoke pathology, allergy sufferers experience contact urticaria (see photo). The appearance of this type of disease can be caused by:
- skin contact with chemicals;
- contact with certain plants;
- wearing rubber gloves;
- contact with animals;
- use of cosmetics.
The cause of the skin reaction is an increase in the content of histamine in the blood, which makes blood vessels more permeable.
As a result, the skin turns red, becomes swollen, and blisters appear.
An increase in the amount of histamine occurs under certain external influences on the body or during internal intoxication caused by infectious diseases or parasitic infestations.
Different people have different susceptibility to certain agents that can cause allergies. This is determined by the state of the immune system, the presence of certain internal pathologies, hereditary predisposition, and so on. Therefore, it is impossible to say in advance what exactly can cause a corresponding skin reaction in a particular person.
Thus, urticaria itself is not transmitted either through direct contact of a sick person with a healthy person, or through objects.
How dangerous is hives?
This disease in itself does not lead to death or disability. However, the lack of timely treatment can lead to very unpleasant consequences.
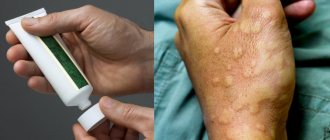
Usually, the disease, even without taking any therapeutic measures, ends a few weeks after the first symptoms appear. However, chronic urticaria sometimes develops (see photo), which can last for years.
As a rule, the causes of this form of the disease are internal pathologies of the body, such as:
- internal secretion problems;
- oncological diseases;
- foci of various infections;
- helminthiases;
- chronic diseases of the nose and throat;
- cholecystitis;
- disorders of the digestive system.
Therefore, although the skin rashes themselves do not pose a serious danger, they can signal the presence of a serious illness, including a cancerous tumor. And if long-lasting rashes appear on the body, it is necessary to undergo a full examination of the body.
Despite the fact that skin problems do not pose a threat to life, if no measures are taken when itching and blisters appear, severe complications of the disease may develop. Thus, pathological processes in the skin can spread to the subcutaneous tissue, resulting in Quincke's edema, shown in the photo below.
The process can also spread to the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract and digestive organs. When the stomach and intestines are affected, vomiting and diarrhea appear. Damage to the upper respiratory tract is especially dangerous: the development of laryngeal edema in the absence of urgent measures leads to death from suffocation.
The appearance of rashes and papules on the skin indicates exposure to an allergen. If this effect is not eliminated in time, the result can be anaphylactic shock, which sometimes ends in death.
Therefore, the appearance of skin problems requires urgent elimination of the cause of the allergic reaction. So, if a skin rash occurs after taking any medication, then it is urgent to replace the drug used.
Is infectious urticaria transmitted?
Rashes with the formation of blisters can appear with some infectious diseases, such as:
- rubella and measles;
- herpes;
- diphtheria;
- cytomegalovirus infection;
- typhoid and typhus.
All of these infections can pass from person to person. But here it makes sense to talk not about the contagiousness of urticaria, but about the contagiousness of the corresponding diseases.
In addition, a skin reaction with a clinical picture in the form of blistering rashes does not always occur with these diseases.
This or that form of allergic reaction depends on the individual characteristics of the body, such as general health and hereditary predisposition.
Therefore, if one person has become infected from another person with a disease that can cause urticaria, this does not mean that he will necessarily develop the corresponding symptoms.
For example, the cause of a skin allergic reaction may be intoxication of the body due to helminthic infestation.
Some worms can pass directly from person to person, but the same helminthiasis can cause severe allergies in one person and be asymptomatic in another.
In some cases, it may seem that the skin rash may be transferable. For example, when a rash appears at the same time in several family members.
This can happen if these people have been exposed to the same thing, and not necessarily of an infectious nature.
If there is a genetic connection between people, then it is possible that they have the same predisposition to allergies.
That is why, if a nursing woman develops a rash, she should temporarily stop breastfeeding her baby. After all, the allergen that caused a skin reaction in the mother may be contained in her milk and enter the baby’s body with it. Due to heredity, a child may also be allergic to this type of irritant.
So, is hives contagious in adults and in children? It all depends on what caused it. If the causes of this disease are infectious, then one person can infect another. However, infection itself does not mean that the clinical picture of the developed disease will include urticaria.
In any case, the appearance of rashes and blisters requires urgent consultation with a doctor so that he can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Source: https://derms.ru/krapivnitsa/yavlyaetsya-zaraznoi-krapivnitsa-ili-net.html
Etiology and diagnosis
Another factor that raises doubts about whether urticaria is contagious or not is the lack of a general theory about the etiology of this disease. Unfortunately, even experts cannot name the exact cause of the development of urticaria and its origin. It is believed that some forms of nettle fever can be transmitted genetically. Therefore, within the family of the infected person there is a fear that the disease will spread to other members.
Differential diagnosis of urticaria
Despite the level of modern medicine, doctors cannot always find a connection with the patient’s pathology and the resulting skin rash. To clarify the etiology, it is necessary to carry out various diagnostic measures. But even this does not give a 100% result, so the origin of urticaria in some infected people cannot be determined.
Features of diagnosing urticaria
When can you get hives?
Is urticaria contagious to others and is it transmitted by airborne droplets? These questions worry many people who have had to deal with itchy skin and rashes. As noted earlier, the disease can be triggered not only by infectious pathologies, but also by allergies to medications and various allergens, hormonal disorders and other disruptions in the body. But to encounter signs of urticaria, infection with an infectious pathology alone will not be enough.
Is hives contagious?
The causative factor against which the infectious form of urticaria develops is predominantly a viral disease. Such clinical cases are dangerous in terms of infection. But even here the key role is played by the state of immunity with the individual characteristics of the body.
Note! The process of producing special antibodies to allergens is not always activated in the body suffering from an infectious disease. Therefore, typical symptoms of urticaria in the form of a skin reaction will not develop.
Is it possible to get infected with urticaria?
The appearance of urticaria and, therefore, its contagiousness is influenced not by the infection itself, which can be contracted, but by the characteristics of the human body. The weaker its protective functions, the greater the chance of developing nettle fever.
Is hives contagious to others?
Red blisters on the skin all over the body, unbearable itching and general malaise are all symptoms of urticaria. Whenever you see a skin rash, anyone will wonder if hives are contagious and if you can catch it from someone who is sick.
Urticaria is an allergic reaction of the human body to unfavorable factors. These factors are infections, poisoning, chronic diseases and even stress.
An acute intolerance reaction occurs against the background of excessive production of histamine and other inflammatory mediators in the body, which increase vascular permeability, which causes rashes and blisters.
What causes hives
A tendency to allergies is an individual characteristic of the human body, which not everyone has. It is inherited from parents to children. It also occurs due to some serious problems:
- hormonal imbalances;
- endocrine disorders;
- chronic weakness of the immune system;
- intolerance to other irritants.
An attack of urticaria can only occur in a person with a predisposition to this disease after the influence of unfavorable factors causing intolerance. Such irritant factors include:
- stress and nervous disorders;
- acute viral and bacterial infections;
- hypothermia and overheating;
- contact with some plants, six animals, dust;
- contact with household and other chemicals;
- use of cosmetics;
- poisoning (food and others);
- infection with worms;
- injuries.
Is hives contagious? No. The manifestation of the rash depends on the characteristics of the human body at risk. Main symptoms:
- blisters and redness on the skin;
- itching;
- swelling;
- general malaise.
The appearance of rashes and blisters should be a reason to go to the hospital and see a therapist or dermatologist. Doctors will be able to determine the cause, which will determine whether it is contagious.
A predisposition to urticaria, which is not contagious in itself, is inherited from parents to children, but not the disease itself.
The answer to the question of whether urticaria is contagious or not is this: intolerance to something cannot be transmitted from person to person, so it cannot be considered dangerous.
But infectious diseases that can provoke this reaction are dangerous for the people around the patient.
How dangerous is the disease?
The danger of urticaria (another name is urticaria) is not that it can be “contagious.” Without treatment, the disease can develop into a generalized form and affect not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes. A severe attack of acute allergies can provoke Quincke's edema - severe swelling of the skin, mucous membranes and subcutaneous tissue, which is also not contagious, but can be fatal.
Is hives contagious in adults?
So, we found out whether urticaria in adults is contagious or not. In adults and children, urticaria is not contagious.
But if the rash is provoked by viral, bacterial infections or helminthiasis, these diseases are contagious.
The allergic reaction itself does not spread from person to person and is not dangerous to others. But diseases that provoke it in an adult can be dangerous.
Urticaria can be conditionally called contagious only if it is transmitted from parents to child (propensity to it). In other cases, urticaria cannot be considered contagious. It will not be transmitted to a person who is not prone to it, even through close contact with a sick person who has obvious signs of an acute allergic reaction.
If the rash is caused by an infection
If an acute allergy is provoked by bacterial or viral infections, then it is not the urticaria that is transmitted from a person to other people, but the infection itself. It is not 100% likely to manifest itself in an infected person.
It depends on the presence of a predisposition. But infections will definitely appear, but their symptoms have nothing to do with urticaria.
Diseases that are possible triggers of urticaria and are contagious include:
- viral infections (ARVI, HIV, herpes, chickenpox, etc.);
- bacterial infections (tonsillitis, diphtheria, scarlet fever, whooping cough, salmonellosis, tetanus);
- helminthiasis (infection with worms and other parasites).
Sometimes urticaria is confused with other diseases that are very contagious and dangerous, due to the fact that they have similar symptoms. Such diseases include:
- tuberculosis (transmitted to another person by airborne droplets);
- fungus (contagious through household items and personal belongings);
- chlamydia (infection possible through sexual contact);
- mycoplasmosis (similar to chlamydia, and also transmitted by airborne droplets and household);
- herpes (contagious and spread in a variety of ways).
These diseases can be contracted very easily. They are transmitted in the following ways: airborne, household, sexual, through personal belongings (clothes, shoes, combs, toothbrushes, cosmetics, underwear, etc.). If an infection has occurred, you can distinguish them by their symptoms.
With urticaria, the rash is randomly scattered throughout the body or concentrated at the site of contact with the irritant; it resembles red or pink dense blisters or swellings of various shapes and sizes (up to 10 cm). The spots itch and become even more inflamed due to mechanical trauma.
With tuberculosis there may be ulcers, the fungus causes severe peeling, chlamydia can cause small spots on the body, herpes can cause a small blistering rash in the area of the lips or genitals.
Is urticaria genetically transmitted from person to person?
Let's consider how allergies are transmitted at the genetic level and whether this is possible. The child will not always have a rash with blisters all over the body. Instead, an allergy to any irritant with other symptoms may appear, for example, nasal congestion and tearfulness or cough.
Only a predisposition to urticaria is transmitted at the genetic level from parents to children. The presence of the disease in parents does not guarantee its manifestation in the offspring, but it increases the likelihood.
The presence of intolerance symptoms in a pregnant woman does not affect the condition of the fetus. The baby is reliably protected from irritants and inflammatory mediators by the placenta.
But if urticaria has become a chronic disease, then certain complications for the child are possible, for example, developmental delay due to hypotension.
How to behave if you see characteristic rashes on a person
Knowing whether the disease is contagious or not, we can conclude: contact with a person with obvious signs of urticaria is allowed and it is absolutely safe. But only if these are symptoms of allergies, and not infections. It is difficult for the average person to distinguish the symptoms of infections from allergies. When in contact with a sick person, it is advisable to always keep your distance and be careful:
- try not to touch the rash with your hands or other parts of your naked body (especially if there are wounds);
- do not give away your personal belongings;
- wash your hands after touching a rash (for example, when a mother treats a child’s rash);
- do not communicate too closely;
- do not use the patient’s belongings (towels, clothes, dishes);
- do not have sexual intercourse.
Manifestations of allergies are similar to many contagious skin pathologies (herpes and others), so they are often confused. If a relative or loved one has a skin rash, you should persuade him to go to the hospital and get tested. Only in a hospital can you find out exactly what caused it and how to treat it. After successful treatment, to prevent relapses it is recommended:
- avoid contact with the irritant;
- change your lifestyle;
- maintain proper nutrition;
- treat infectious diseases (flu, acute respiratory viral infections and others) in a timely manner.
Not all pathologies are contagious. This should be remembered when contacting patients. Expressing your disgust can greatly offend. You need to react appropriately and calmly to a person with allergy symptoms.
Source: https://tden.ru/health/zarazna-li
In what cases is infection impossible?
Some internal factors that contribute to the development of urticaria provoke a non-contagious pathology. These factors include:
- formation of malignant tumors;
- hormonal imbalance;
- increased sensitivity of the patient's body to acetylcholine;
- consumption of certain foods;
- exposure to water, sunlight or cold;
- entry of various toxins into the body;
- consequences of taking certain medications.
When it is impossible to catch hives
If the causative factor is severe stress, then the blisters that appear on the skin will not be contagious. In such cases, the optimal method of therapy would be to maintain a calm lifestyle, avoid stressful situations and maintain a healthy diet. The appearance of skin symptoms under the influence of all of the above factors is nothing more than the reaction of the body, or rather the human dermis, to various negative processes.
Pathogenesis of urticaria
Urticaria and children
If we talk about preschool children, they rarely encounter signs of nettle fever. If the causative factor for the appearance of a red rash is an allergy, then the likelihood of infecting other people is minimal. But if parents identify blisters on their child’s skin, then they need to consult a doctor to determine the cause of such an allergic reaction.
Urticaria in children
Children are most often exposed to infectious diseases, including rubella, chickenpox, scarlet fever and others. All these pathologies do not pose any danger to adults, but for children whose bodies have not yet fully formed, they can lead to serious consequences.
Features of the development of urticaria in children
Pediatric urticaria
If the expectant mother has a rash before contractions, then the newborn will not become infected with hives while passing through the birth canal.
The disease is not transmitted through breastfeeding. The only thing a mother can do is find out the type of rash from a dermatologist. This will allow you to determine the danger of rashes for the newborn.
In a situation where the disease is caused by an allergen - an endogenous irritant, there is a possibility of it entering the blood. Substances are excreted in milk and enter the child’s body.
This causes childhood pathology of a more severe nature than that of the mother.
Rashes in children can be the result of diseases: chickenpox, rubella , scarlet fever, measles and others. These pathologists are not dangerous for adults. The likelihood of healthy children contracting infectious diseases through contact with sick people is very high.
It is important to find out the nature of the rash in order to confidently answer the question of whether urticaria in children is contagious. Having established the cause, the pathology that caused it is expected to appear.
Can a child get infected from his mother?
During the process of passing through the birth canal, the child can become infected with certain types of pathologies from the mother. But if a pregnant woman suffers from allergic rashes, then infection cannot occur. During breastfeeding, the disease can pass to a small child through breast milk. If an endogenous irritant acts as an allergen, then it, being present in the circulatory system, can enter the mother’s breast milk.
Is urticaria transmitted from mother to child?
To determine the degree of danger of urticaria, you need to monitor how the disease manifests itself. In itself, it does not pose any threat to the patient’s life, but under certain factors anaphylactic shock or Quincke’s edema may occur. Such complications require emergency medical attention.
Quincke's edema is a dangerous complication of urticaria
General recommendations
Regardless of the type of urticaria that occurs, experts recommend following the following recommendations:
Diet for urticaria
- carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene, especially if you suspect the development of an infectious disease. This is an excellent preventive method;
- subject all products to thorough heat treatment during cooking;
- Monitor the general condition of your body. If even the slightest violations are detected, you need to contact a specialist for examination. You also need to follow all the doctor’s recommendations, since incompletely cured urticaria can lead to complications;
- take vitamin complexes to protect the body from the possibility of developing an allergic reaction. A properly selected course of vitamin therapy will improve immune barriers;
- try to avoid stressful situations, since along with an existing rash that has arisen as a reaction of the body to an external irritant, a rash may appear due to severe stress.
Principles of treating urticaria
Try to explain to people around you that a skin rash that appears is not a sign that they are contagious.
What is urticaria?
The similarity of skin rashes with traces of nettle burns determined the generally accepted name of the disease. Doctors often use the term “urticaria”, since in Latin “urtica” means nettle.
According to statistical data, every fifth inhabitant of the earth has encountered manifestations of urticaria at least once in his life. In most cases, it is diagnosed in women between 20 and 50 years old and young children.
Urticaria may appear against the background of a chronic disease of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine system, or autoimmune disease (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus, myasthenia gravis, multiple sclerosis). But, most often, urticaria is of an allergic nature and occurs as a response of the body to an irritant.
What can trigger hives?
There are many factors that can cause signs of urticaria to appear on the human body. The most common ones include:
- food products (milk, honey, nuts, fish, citrus fruits, sweets and others);
- medications;
- plant pollen;
- animal hair and excretions;
- household dust;
- synthetic clothing;
- chemical substances.
In addition, urticaria can be triggered by prolonged exposure to the sun (thermal urticaria), exposure to frost (cold), mechanical impact on the skin (dermatographic), working with certain tools (vibration), physical activity (cholinergic), and water procedures (aquagenic).
Skin rashes can appear as a result of stress, nervous or emotional overload, hormonal changes in the body, poor environmental living conditions and other reasons.
The risk group includes people with a genetic predisposition whose parents or immediate relatives have allergies.
How to get rid of hives
The key to successful treatment and quick recovery is a timely visit to a doctor and a correctly prescribed therapeutic course. Complex therapy for urticaria must include:
Preparations for urticaria
- correct diagnosis to identify and eliminate the causative factor;
- take antihistamines;
- the use of external agents that eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of nettle fever;
- desensitizing treatment;
- use of hormonal drugs (prescribed for severe disease);
- compliance with a therapeutic diet. A combination of drug treatment and diet therapy will speed up the recovery process.
Features of the treatment of nettle fever
On a note! Provided that all measures are taken in a timely manner, the symptoms of urticaria disappear literally after 1-2 days of treatment. But if adequate assistance is not provided to the patient, the pathology may accompany him for several weeks.
Treatment of urticaria in children
Statistics show that children suffer from urticaria quite often. The disease is accompanied by white or red skin rashes, as well as severe itching. The rash can appear on different parts of the body; it often appears on the child’s face. But how to fight a disease when you can’t use potent drugs? To do this, you need to follow the instructions below.
Step 1. Use antihistamines at the first onset of hives symptoms, without waiting for the symptoms to go away on their own. But medications can only be given to a child as prescribed by a doctor.
Give antihistamines
Step 2. Relieve the unpleasant symptoms of hives with oat lotion. This will help relieve burning and itching. Parents should also ensure that their child does not scratch the affected area of skin.
Make lotions from oats
Step 3. Treat the rash with a special herbal-based ointment. Local products containing aloe vera cope well with skin irritation. You can also relieve swelling and itching with a cold compress. Just wrap a few ice cubes in a handkerchief and apply to the sore spot.
Use external remedies
Step 4. Dress a child infected with hives in clothes made from cotton fabric. This will help the body to breathe, which will prevent the disease from spreading. Tight clothing should be avoided.
Use clothes made from natural fabrics
Step 5. If swelling occurs on the child's face during therapy, stop taking the medications and take the child to the doctor. Often, bloating leads to swelling of the throat, which is very dangerous for the child’s health.
Contact your doctor if complications develop
If an allergic reaction occurs after taking a medicine prescribed by a doctor, parents should contact the doctor immediately. Similar reactions can also occur after eating.
Summing up
Urticaria is not a contagious disease, but this does not make it any less dangerous to the patient’s health. In addition, urticaria in some cases is inherited. But if the cause is an infectious disease, then healthy people may well become infected by airborne droplets. Therefore, when diagnosing urticaria, it is important to determine the causative factor.
Difficulties in treating urticaria
Skin rashes, which appear depending on the state of immunity, can lead to serious complications in the absence of timely medical care. The most dangerous of them is Quincke's edema. But to summarize, we can say with confidence that urticaria is not transmitted to healthy people, so there is no need to be afraid of a skin rash on your loved ones or friends, knowing that it is urticaria fever.
Preventing the development of urticaria
Is an allergic skin rash transmitted from person to person, is hives contagious or not?
Urticaria (urticaria) is the body’s reaction to any substances perceived as foreign. A characteristic symptom of the disease is a rash all over the body. This symptom often occurs with other diseases.
Is the disease contagious to others? Experts clearly answer this question in the negative. The disease is the body's response to an irritant.
However, the factors that triggered the onset of the disease are varied. If an allergy occurs in the presence of infectious diseases, then you can become infected with them. The appearance of urticaria in this case depends on the condition of the person and his immune system. Often, skin rashes appear in the presence of harmful viruses; they can also be transmitted from one person to another.
The appearance of nettle rash is due to the reaction of the body, not to infection.
Reasons for appearance
The main reasons for the appearance of such a disease are external factors. Most often this is direct contact with an allergic irritant; in some cases, such an irritant is fungal or bacterial in nature.
In addition, there are cases when hives were caused by an insect bite to which the person was allergic to enzymes and acid.
Some other reasons that trigger the appearance of a rash on the body:
- hypothermia for a long time;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- prolonged exposure to heat;
- previous viral infection;
- prolonged use of antibiotic drugs;
- liver dysfunction;
- nervous tension;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys.
Important: the severity and form of the disease depends on the provoking factor.
You can't get infected
Is urticaria always dangerous for people? There are certain factors that cause rashes, but do not pose a danger to humans.
Factors:
- Medicines,
- Toxic substances,
- Natural phenomena (frost, sun),
- Food,
- Hormonal imbalances
- Malignant tumors.
Such factors are not contagious and cannot be transmitted from one to another. If hives arose as a result of a reaction to such irritants, then there is nothing to be afraid of - you cannot become infected with it.
The disease can occur during severe stress and depression. In such a situation, it is also not contagious to others.
Diagnostic methods
It is impossible to determine the cause of the blisters by visual inspection. Allergic rashes have many varieties, so in order to accurately make a diagnosis, you need to take a number of measures:
- laboratory test of blood composition - with urticaria, the number of eosinophils is increased;
- checking the concentration of immunoglobulins - the presence of allergies is indicated by high IgE;
- search for specific antibodies that the body produces in case of a negative reaction to certain foods.
Based on the test results, therapy is prescribed. If it turns out to be ineffective, the patient is referred for an examination of the lymph nodes, a biochemical blood test, and a urine test.
Contagiousness of urticaria in children
Is nettle rash in children dangerous for others? In preschool children, this disease is diagnosed quite often. The reason for this is that the immune system has not yet strengthened. Children often suffer from airborne infections.
Infections:
- Rubella,
- Piggy,
- Measles,
- Chickenpox,
- Diphtheria,
- Typhoid fever,
- Flu.
A child can become infected with viral diseases that can cause urticaria.
Virus:
- Cytomegalovirus,
- Herpes,
- ARVI.
Children are often diagnosed with helminthic infestations. Worms can be transmitted from person to person and cause the development of hives.
However, when infected with any disease, urticaria does not necessarily appear immediately. The disease occurs when the immune system is rather weakened. The disease can be inherited. Often the rash occurs in children whose parents are allergic.
If suspicious signs are detected in your baby, you must contact a medical facility to identify the exact allergy factors.
In what cases is the disease not dangerous?
The following forms of urticaria are considered non-contagious:
- medicinal – after using various medications (anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics), characteristic rashes occur;
- toxic - a rash develops as a result of the influence of toxic substances that enter the skin or inside the body;
- food - characteristic rashes occur after eating various foods;
- cholinergic – the development of blisters occurs under the influence of emotional overstrain and stress;
- demographic - the rash is localized at the site of mechanical irritation of the skin;
- rashes that appear under the influence of water, sun, heat, cold.
Contagiousness of urticaria in adults
What danger does urticaria in adults pose to people around them? An allergic reaction can occur for various reasons.
If there are viral diseases in adults, you can become infected not with urticaria, but with viruses. Whether an allergic response will manifest itself in such a situation depends on the state of the human body.
Transmission of rash from mother to child
During childbirth, the baby can become infected with various diseases from the mother. However, urticaria is not one of them. In a child under the age of six months, this phenomenon is diagnosed quite rarely. The reasons may be cosmetics, products consumed by the mother and ingested by the baby with milk.
One type of urticaria is miliaria. It appears as a result of irritation on the skin from sweat and mechanical damage.
Thus, a child cannot catch hives from the mother, but there may be other factors that influence this.
Stages of rash treatment
Is this disease dangerous? The disease does not pose a particular danger to humans. However, it requires care and adherence to the rules of therapy. In severe cases, it can cause Quincke's edema, which can be fatal. Treatment of urticaria includes certain stages.
Stages:
- Making a diagnosis, identifying the cause of the allergic reaction.
- The use of various medications - antihistamines, sedatives. External agents are used - creams, ointments, gels, solutions.
- The use of traditional medicine is allowed.
- In certain cases, it is advisable to use physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Be sure to prescribe a suitable diet during the treatment process, excluding foods that can cause allergies.
Treatment is carried out until complete recovery; the prescribed diet is followed for at least six months.
Prevention and conclusions
To avoid the appearance and recurrence of allergic urticaria, it is necessary to observe certain prevention.
Measures:
- Review your diet and eliminate allergy-causing foods.
- For prevention, you should periodically take antihistamines.
- When prescribing medications, you should carefully study the instructions for use, and if necessary, you should inform your healthcare professional about possible allergic reactions.
- Nervous shocks and stress should be avoided.
- It is worth treating all illnesses on time.
- It is necessary to give preference to natural cosmetics and hypoallergenic household chemicals.
- It is better to choose clothes from natural fabric.
- Contact with the allergenic substance should be avoided.
- When the first signs of allergic urticaria appear in a child, you should go to the hospital.
- It is necessary to adhere to hygiene rules.
If you follow simple rules, urticaria can be completely avoided.
conclusions
Is hives contagious? No, this disease cannot pass from one person to another. But by inheritance such a transition is possible.
Result:
- A nettle rash occurs in the presence of certain factors. With a good immune system, symptoms of the disease may not occur at all.
- It is impossible to contract the disease, but it is quite possible to catch viruses that can cause it.
- Nettle fever is not transmitted by airborne droplets; in this way, you can become infected with infections that cause it.
Thus, there is no need to be afraid of infection. If suspicious signs appear, you need to determine the reasons that caused it. Treatment is selected based on diagnostic results. Proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle are very important.
Symptoms
To understand the issue of the contagiousness of urticaria, it is important to know the symptoms of this disease. The main difference of the disease is the sudden appearance of numerous bright pink blisters. The majority of rashes occur in the first hour and a very small number appear later.
After a few hours, the blisters may disappear completely, or the disease will make itself felt with a second wave of rash. But as for other infectious skin pathologies, the opposite is true: the rash appears, starting with several formations, then gradually increasing.
Chronic urticaria lasts for months, or even years. Depending on how affected the skin is, the patient’s general condition may remain within normal limits (except for itching). But in some cases, headaches, fever, and general malaise are possible.
Is this type of urticaria contagious? The answer to this question is, of course, negative. Chronic forms of this pathology are associated with autointoxication and are mainly characteristic of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver, inflammatory foci in the tonsils and gall bladder, dental ailments and helminthic infestations.
Allergic skin lesions include childhood urticaria. It affects babies who are bottle-fed and those who are often fed foods that are inappropriate for their age.
The most complex form of the disease is Quincke's edema. It seems especially dangerous when it occurs in the larynx area. If timely assistance is not provided, the person or child may die.
The factors that provoke urticaria are different. Thus, those who do not tolerate cold well may experience cold urticaria. Failure to perceive ultraviolet radiation can cause solar urticaria.
For older people, this manifestation is possible through a sharp change in temperature. Toxic urticaria can occur as a result of contact with certain plants, animal insects, and fish.
Even the presence of a cat in the apartment can cause a sluggish chronic form of this pathology.
It is quite clear that in all of these cases, urticaria cannot be transmitted either by sneezing or shaking hands.
Source: https://gidroz.ru/kozha/zarazna-li-krapivnica.html