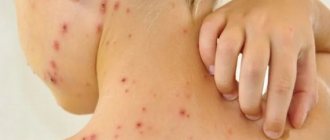
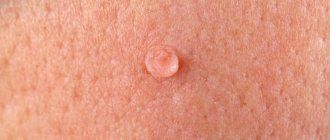
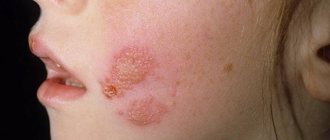
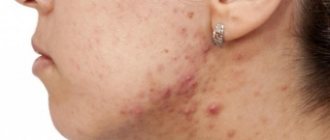
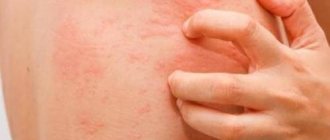
Skin ulcers are open wounds on the skin that take a long time or do not heal at all.
A person can get them as a result of injury, circulatory problems, or constant pressure on the affected area. The feet and legs are usually affected. However, defects can also form in other areas, such as on the hands or in folds of skin on the body. Ulcers may start small and grow larger over time. But a person may not notice them until they become the size of a coin, especially when it comes to diabetic foot ulcers.
Classification of skin diseases
In order to classify any skin disease, it is necessary to establish its localization, namely the place in which the disease process occurs.
Based on this, skin diseases can be divided into skin infections, infections of subcutaneous tissue and deeper tissues. It is important to determine whether the infection is systemic or local. The latter is characterized by the absence of intoxication and its signs, as well as the unchanged state of the body. If signs of a toxic state of the body are present, then we are talking about a systemic disease. As a rule, this characteristic affects the further treatment of the patient.
Any infection may have a different location on the patient’s body, but the symptoms remain the same. For this reason, experts classify skin infections according to the specifics of their pathogens. This includes fungi, viruses and parasites.
Human skin diseases photo and description
If you want to learn more about skin diseases, see photos and descriptions, read about treatment, then on this site you will find information about many skin diseases, you can also see photos of skin diseases, you will find above a detailed description of skin diseases, photos and descriptions him.
The skin protects the internal organs of a person, creating a boundary between the body and the environment. But in addition to its protective function, it is also a communication organ that helps exchange information with the outside world. Metabolism and the immune system are necessary for the skin because... they protect it from all kinds of skin diseases.
- poor nutrition;
- hormonal disorders;
- past viral diseases;
- weakened immune system;
- the presence of parasites in the body;
- heredity;
- Unhealthy Lifestyle;
- chronic stress;
- dysfunction of the nervous system;
- disorders of the blood, kidney or digestive system.
Separately, it is worth mentioning improper care or its complete absence - dear ladies, you should not use cosmetics that cause discomfort.
Select care products individually and approach this issue carefully, monitor the condition of your facial skin and stop using the cosmetic product at the first sign of unwanted reactions.
Bacterial infection: general characteristics
The most significant and most common bacteria that can cause skin diseases include:
- Borrelia.
- Plague bacteria.
- Anthrax stick.
- Streptococcus (this includes erysipelas).
- Staphylococcus.
- Rickettsia.
Each disease has its own clinical symptoms. However, in any case, the patient’s general condition changes, and symptoms appear more often on the skin and less often on internal tissues.
Causes of skin ulcers
Each pathological condition accompanied by ulcerative formations on the skin has an individual development mechanism and its own causes.
It is possible to identify a specific problem only separately for each disease.
In the overall picture, the following provoking factors are considered:
- Failure of the kidneys, liver, intestines, spleen, lymphatic system to neutralize and remove toxic substances from the body in full. They are produced during the life of the body, when taking medications, eating vegetables and fruits saturated with pesticides, etc. When the “natural filter” is dysfunctional, these substances begin to be excreted through the skin. As a result, dermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, etc. develop.
- Allergic reactions. Under the influence of chemicals, physical objects, the environment, etc., irritation may appear on the skin, causing the formation of ulcers.
- Infections. Infectious lesions can be not only external (ingress of fungi, viral infections, bacteria directly onto the skin), but also internal. Diseases such as hepatitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, etc. provoke ulcerative formations on the skin.
- Indoor allergens. These are protein substances produced by worms or opportunistic microorganisms (streptococcus, staphylococcus, fungus of the genus Candida, etc.). These substances live in the body constantly and serve as an ongoing source of irritation to the immune system.
- Stress. Against the background of strong experiences, severe processes develop, after which an allergic reaction appears, expressed as a rash on the body.
Skin diseases accompanied by ulceration
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD 10) includes many diseases that cause the appearance of ulcers on the upper layer of the epidermis. Here are a few of them:
- Acne. Blockage of the sebaceous glands leads to an inflammatory process. Ulcers appear on the face, back, shoulders, and décolleté. The disease is preceded by acne. Without timely treatment, severe acne develops. Reasons: hormonal imbalance, frequent stress, dysbacteriosis, heredity, non-compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- Dermatitis. Skin inflammation of any type (atopic, seborrheic, diaper, contact). Accompanied by severe itching, peeling, and redness. Occurs in a chronic form. Reasons: genetic predisposition, regular exposure to the skin (friction, pressure), thermal factor (exposure to temperature, sun rays), use of aggressive chemicals or low-quality cosmetics).
- Eczema. It may appear at an early age. The disease cannot be completely cured, it can only be controlled. People with allergies are at risk of developing eczema. Eczema covers the arms, legs, back, and neck.
- Lichen. A contagious disease that, without adequate treatment, develops into ulcers. At the initial stage, a red spot with brown edges appears. Over time, crusty ulcers form in place of the spots.
- Herpes. When the disease occurs, small blisters appear on any part of the body. In frequent cases, the affected area is the lip. On the first day, a crusty rash appears. On the third day, the crust is broken, and ulcers appear in this place. Causes: impaired immune function, disruption of metabolic processes, acute respiratory infections, gastrointestinal dysfunction.
- Skin invasion. This is a malignant formation in which red dense nodules appear. In their place, ulcers subsequently form.
- Melanoma. Oncological skin disease. The disease can be eliminated surgically. If you seek medical help in a timely manner, the skin defect can be successfully eliminated. The lack of qualified therapy leads to the formation of wounds. Melanoma is a pigmented spot of an asymmetrical nature.
- Psoriasis. Occurs in a chronic form. Medicine has not clearly established the cause of psoriasis, but it is known that it is not of an infectious nature. The disease causes red spots that spread throughout the body. The affected areas are covered with grayish or whitish scales. Without supportive care, ulcers form on the areas.
- Diabetes mellitus (DM). The initial stage of the disease is not accompanied by clear signs of ulceration. In this case, the skin becomes “lacquered”, swelling and hyperemia are noted. As diabetes progresses, tissue necrosis occurs, followed by the appearance of whitish spots. Further progression of the disease leads to the release of purulent mucous exudate with an unpleasant aroma. A trophic ulcer is diagnosed. The patient feels pain with moderate bleeding. Accompanied by severe itching, burning, and heaviness. With the addition of varicose veins, thrombosis or thrombophlebitis due to trophic changes, weeping wounds on the legs are diagnosed. This means the addition of an infection and an increase in the inflammatory process.
Article on the topic: Ladasten, a drug for the treatment of asthenic disorders: instructions, reviews
Streptococcus and staphylococcus
Infants are more susceptible to streptococcal and staphylococcal infections if they are not properly cared for. Also at risk are children who often get sick and even have weakened immune systems; adults can also be included in the latter group.
As a rule, the symptoms of these infections are variable, that is, the disease can affect any area of the skin or deep tissues. Most often, the following conditions are identified during diagnosis:
- The sebaceous gland and hair follicle are affected, and a boil occurs; it can be either one or many.
- Cellulitis occurs - a condition in which tissue begins to melt.
- The appearance of an abscess - a cavity with purulent contents.
Not only are diseases that carry an infection dangerous, but there is also a risk that the pathogen will spread, entering the blood and internal organs, starting inflammation in them. This is most critical for newborn babies and can be fatal.
During treatment, pathogens are destroyed and biochemical processes disrupted during the disease are restored.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics, salt and colloid therapy, and infusion therapy are used as drug treatment. Ointments that also contain antibiotics do not help. They will not be able to rid the patient of staphylococcus or streptococcus completely. Therefore, they should not be used separately. If the infection has spread quite widely and reaches the bones, then most often the best solution to this problem is surgical intervention: during the operation it is necessary to open the abscess and drain it.
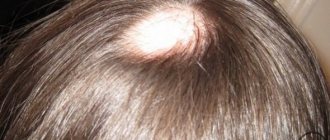
Seborrhea
Crusts on the head with seborrhea are not scabs, since there is no damage to the skin underneath. But because of their specific appearance, they are also called scabs.
Seborrhea is a disease in which the production of sweat and sebum is disrupted. In addition, its composition and consistency changes. The secretions of the glands become thicker and more viscous. Over time, they take on the appearance of light yellow layers and crusts, accompanied by an unpleasant odor and itching.
Seborrhea scabs do not disappear on their own; this pathology must be treated. Normalizing the diet and regimen, sometimes taking antihistamines, has a good effect. To eliminate crusts on the head, hair should be washed frequently with special shampoos.
In newborns, yellow crusts on the head are not uncommon. They usually peel off within the first three months. If this does not happen, you need to lubricate the baby’s scalp with cosmetic oil and after washing, carefully comb out the crusts with a fine-toothed comb.
Erysipelas
This inflammation is classified as streptococcal, as it is caused by one of its varieties. Children are rarely susceptible to this disease; elderly and middle-aged people suffering from diseases of the cardiovascular system or having unstable hormonal levels are at risk. Typically, symptoms of erysipelas are:
- Sudden onset of clinical symptoms.
- Increase in temperature and deterioration of the body.
- The formation of swollen, “hot”, “red” spots on the skin with a clear contour.
- The appearance of blisters with serous fluid or blood.
This skin infection is usually associated with a different microflora of microorganisms, which can affect the deep tissues of the skin.
To cure the patient, various antibiotics are prescribed and a wide range of infusion therapy is performed. However, even this cannot guarantee complete healing of the body. Most often, the disease appears again and again dozens of times. There is still no prevention against this disease.
anthrax
Bacillus anthracis spores are characterized by environmental resistance. They are the cause of infection of the patient's skin. These disputes typically remain active for decades.
People can become infected from infected farm animals directly through the skin. The infection can also be contained in milk, meat or hair from livestock. Adults are more susceptible to this disease than children due to more frequent contact with infected animals. Most often, it is the skin that suffers from anthrax, but there are cases where infection of the blood, intestines or lungs occurred.
Typically, anthrax is characterized by the following skin symptoms:
- The rash and its further change from a spot to an ulcer.
- Over time, the spots turn black and do not cause pain.
- Because of the blisters that form in the ulcer, it can grow.
This infection of the skin of the legs and arms is successfully diagnosed using specific tests. During diagnosis, it is important to distinguish a disease such as anthrax from a trophic ulcer and bedsores. Anthrax cannot be treated surgically. Also, ointments, lotions or any heating do not help. The main therapy is considered to be antibiotics for skin infections in children (photos can be seen in the article) and adults based on penicillin.
Features of facial skin infections
The blood supply to the organs of the head, face, and membranes of the brain is closely connected. Incorrect treatment and squeezing of pimples is dangerous due to the spread of bacteria through the blood and lymph. You can achieve an increase in the area of the affected area, such dangerous complications as meningitis, abscesses and phlegmon, and inflammation of the eyes.
Before deciding on cosmetic procedures - cleansing, peeling, mesotherapy - undergo an examination by a dermatologist to determine the cause of the pustular rash and receive treatment.
Plague (leather or bubonic)
Any form of plague is a fairly dangerous infection; it can easily be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person; as a rule, the disease is severe. If you ignore the symptoms and do not seek medical help, you can die. Yersinia pestis is the causative agent of plague. The sources are often various rodents, for example, harbor rats. Adults are at risk, but children rarely suffer from it.
Skin plague, as a rule, leads to necrosis of the skin and lymph nodes, plus the human body is depleted. The affected areas of the skin are painful, prone to redness and swelling, and it is impossible to control the affected limb.
If there is no specialized treatment, and it includes various antimicrobial drugs, such as streptomycin, then the person will die. The patient, no matter what form of plague he has, is dangerous to society, since someone else can become infected with the germs.
Symptoms of skin disease
The general clinical picture is manifested by the following signs:
- severe discomfort and sensitivity;
- itching;
- pigmentation in a focal area;
- thinning of the skin;
- an ulcer appears in the center of the affected area;
- bleeding;
- at the bottom of the wound there is grayish content (pus);
- With successful healing, a scar appears in the sore spot.
In addition to the general signs, there are symptoms characteristic of each type of ulceration:
- Venous. Location: ankle. Ulcerative skin lesions are small in size or occupy a large area. Without adequate therapy, almost the entire lower part of the lower leg is affected. The surrounding skin is dense and hyperemic. Purulent, serous or hemorrhagic discharge is noted. When pressure is applied to the focal area, severe pain appears.
- Diabetic. The fingers of the lower extremities are affected. They have an irregular shape, uneven outlines, and necrotic areas appear along the edges. Any impact causes pain.
- Arterial. Location: foot. Often this is the back of the sole, heel, big toe. The ulcers are small, round in shape, and the surrounding skin becomes dry and pale. With slight pressure, pain appears.
- Radiation. Appear as a result of irradiation. The lesions are deep, penetrating into muscle tissue and bones. They have a round shape, uneven edges. The surrounding skin is atrophied, with signs of pigmentation, telangiectasia is diagnosed.
- Neurotrophic. Location: heel tubercles, soles, lateral part of the feet. They have great depth and resemble a crater in appearance. Serous, purulent discharge with an unpleasant aroma is noted. The skin around the affected area is keratinized and dense. When pressing, the pain is practically not felt.
- Malignant tumors. Ulcers appear due to the breakdown of the tumor. Signs of skin damage are clearly expressed. The wound is located in the center of the dense infiltrate. The edges are lumpy, and necrotic areas are noted at the bottom. Putrid, crumbly discharge appears.
- Infectious. Multiple rashes appear, localized in groups. They can be located in any part of the body, often affecting the lower legs. They are characterized by shallow depth and have an oval shape. The bottom of the ulcers is covered with scab. The surrounding skin is inflamed and there is a purulent, thick discharge with an unpleasant odor.
Article on the topic: Tablets for dizziness and nausea - effective drugs with instructions and prices
Viral infections: general characteristics
Among the huge range of viruses regarding their distribution and significance, there are herpesvirus, papillomavirus, rubella and measles (children's droplet infections). It is also noted that measles, rubella and other childhood droplet infections are secondary to skin diseases. The main infection occurs in internal organs and deep tissues. These infections on the facial skin can occur not only in children, but also in adults.
Scabbers
Scabs are characteristic scabs on the head and body. They are formed due to bacterial infection of rashes and scratching. Scabs on human skin look like yellow scales, crusts, and layers. They are often accompanied by an unpleasant odor. Adults and children often experience painful itching.
Scabbing is a symptom of various dermatological diseases. Most often, the following pathologies manifest themselves:
- scabies,
- seborrhea,
- pyoderma.
The appearance of a scab indicates infection with scabies, purulent lesions of the integument, disruption of sebum production and metabolism in the body.
Herpes infection
Most often, viral skin infections are associated with the herpes virus. At the moment, there are 8 of them. As a rule, each type has its own symptoms. However, there are similar points, such as damage to the skin and sometimes soft tissues. A herpes infection is characterized by the following symptoms: if the soft tissue has also become infected, which is rare, then the number of blisters may increase; the affected area, as a rule, becomes wider, which brings with it unpleasant sensations.
It is difficult to completely get rid of such signs of herpes infection in acute form as blisters and redness - it is practically impossible to do this. Drugs that fight viruses, such as Acyclovir, are fast and effective, but they cannot stop the spread of the disease completely. As a rule, a herpes infection accompanies a person throughout his life, and people become infected even in childhood.
Principles of treatment
Therapy for infectious diseases is divided into three large groups:
- Etiotropic – involves the destruction of the causative agent of the problem.
- Pathogenetic – based on neutralizing the main points of the corresponding process.
- Symptomatic or supportive – involves minimizing the patient’s negative feelings without affecting the source of the problem.
When identifying a specific pathogen, specific medications must be used. If the cause of the pathology is bacteria, then doctors use antimicrobial agents (tetracycline ointment and others), viruses - antivirals and stimulants of the immune system (interferons, acyclovir), fungi - fungicides (fluconazole).
The speed of elimination of concomitant symptoms depends on correctly selected etiotropic therapy. The destruction of the pathogen automatically breaks the pathological process, which is accompanied by damage to the skin and other organs in the human body.
To speed up the process, auxiliary medications are used, which significantly increase the effectiveness of antibiotics and other groups of substances. The most popular remain glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone).
This group of hormonal drugs is used in moderate and severe cases to support the body and speed up recovery. Improper use of steroids is fraught with the progression of a number of complications and adverse reactions.
The following groups of medications are prescribed as symptomatic therapy:
- Antihistamines - Tavegil, Suprastin, Diazolin. The drugs help reduce the activity of itching and partially reduce the severity of the inflammatory process.
- Immunomodulators - Viferon, Arbidol and others. The drugs are used to enhance the activity of endogenous defense mechanisms.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – ibuprofen, paracetamol, acetylsalicylic acid. Prescribed to combat fever and pain.
To improve the condition of the skin, in rare cases, a variety of moisturizing creams are used. Their prescription should be carried out only after consultation with the attending physician due to the risk of worsening symptoms if used inappropriately.
HPV infection
Adults are more susceptible to it, but children rarely encounter it. Today this virus has dozens of species. Clinical symptoms vary. These may be skin manifestations, such as a papilloma or wart, and may even lead to a malignant formation in the reproductive organs. It is the localization that determines the future treatment of the virus; this can be either drug treatment or surgical intervention.
Skin fungus: general characteristics
Fungi are widespread and can be found in any country. A person leading an asocial lifestyle may not necessarily be susceptible to a fungal infection; children are often at risk due to contact with various objects surrounding them. As a rule, even minor damage is enough to become infected with fungus.
Signs of a fungal infection of the skin of the hands and feet:
- Changed skin color.
- Change in skin thickness, formation of peeling.
- There is no pain, but severe skin itching is observed.
The fungus cannot disappear without drug treatment; drugs that fight it are needed, both locally and systemically. Maintaining hygiene is also an important point.
So we can say that skin infections as well as soft tissue infections are observed in adults and children. They should not be treated on their own, as this can only aggravate the situation and lead to a disastrous result that no doctor can correct. That is why treatment can only take place under the supervision of specialists in a medical institution, who are fully familiar with the disease and all its symptoms, know the possible complications, using various drugs, such as antibiotics and antiviral and antibacterial agents.
Prevention
Observe the following rules:
- After visiting the gym, wipe the areas that came into contact with the equipment with an antiseptic.
- Treat cuts and wounds with antibacterial drugs (iodine, salicylic alcohol, hydrogen peroxide) immediately after they occur.
- Do not share hygiene items or cosmetics with other people.
- Places of abscesses and impetigo should not be washed with water, combed, or pressed.
- Avoid spicy fatty foods and sweets.
Make an appointment with a dermatologist on time.
The doctor will help you identify the cause of the inflammation, do the necessary tests, and select a treatment that suits the type and stage of pyoderma. December 5, 2020
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich