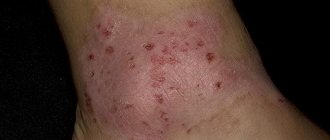
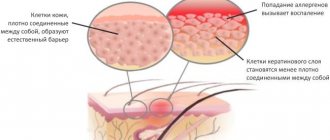
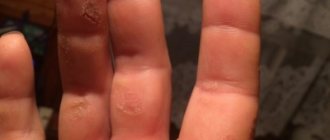
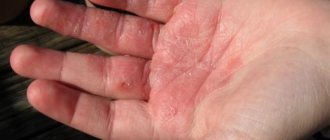
Allergic dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin resulting from exposure to certain substances. The inflammatory process causes blood vessels to dilate, which leads to increased blood flow. The liquid seeps into the tissue. Therefore, the skin becomes red, swollen and accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. Allergic dermatitis in children (see photo below) in 20% of cases occurs against the background of asthma and rhinitis. Let's look at what this disease causes and what symptoms are characteristic of it.
What is it - atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis in a child is a specific reaction of the immune system, genetically determined , to substances that enter the body, called allergens. The disease manifests itself as a rash that turns into an inflammatory process in various areas of the skin. This manifestation is often called diathesis.
In a child, the manifestation of atopic dermatitis is a sign of internal tolerance of various substances by the body. The disease makes itself felt after the allergen accumulates in sufficient quantities, which leads to the rapid development of the disease.
Other manifestations of allergic dermatitis are also possible, these include:
- runny nose;
- food allergies;
- conjunctivitis.
At the first signs of illness, contacting a doctor is mandatory.
Causes of allergic dermatitis
Allergic dermatitis , treatment of which should begin as early as possible, occurs for various reasons. Most often, the hereditary factor is combined with unfavorable environmental factors, and a total imbalance occurs in the body.
Allergic dermatitis in the form of spots
If the mother and father of the baby have hypersensitivity to various irritants, then the probability that a child will be born with atopic dermatitis exceeds 85%.
| Causes | Formation mechanism |
| Food allergies | Allergic dermatitis, food-type dermatitis, typically manifests itself in the first months of a baby’s life. Atopic dermatitis due to the incorrect diet of a pregnant woman, as well as if the mother consumed highly allergenic foods during breastfeeding. Another significant reason is previous viral diseases of the esophagus in infants 1–6 months of age. |
| Difficult pregnancy | The causes of predisposition to atopic dermatitis at the time of bearing a child are very diverse: the threat of miscarriage, exacerbation of serious chronic diseases, the apathetic state of a woman, past infectious diseases, fetal hypoxia, which greatly affects all aspects of infant health. |
| Diseases suffered by the child himself | Intestinal dysbiosis (long and debilitating), atonic colitis or gastritis, enterocolitis, helminthic infestations. Such ailments have a particularly negative effect on the body if parents ignored the problem for a long time or engaged in dubious self-medication with folk remedies. |
| Constant contact with dangerous allergens | So-called chronic atopic dermatitis can be caused not only by food allergens, but also by irritants migrating through the air (pollen, house mites, household chemicals, aerosols, cosmetics). Incorrect medicinal effects on a child can also lead to the development of dermatitis: abuse of children's cosmetics, incorrectly selected medications, incorrect use of certain medications. |
| Stress experienced by the child | Often, atopic dermatitis develops against the background of an unstable psycho-emotional state of the child. An exacerbation of the pathological process can be caused not only by an encounter with an allergen, but also by nervous overexcitation. |
| Passive smoking | If an allergic person is constantly surrounded by smokers and is not protected in any way from cigarette smoke, the risk that atopic diseases will appear is extremely high. |
| Unfavorable environmental situation in the region where the child lives | “Dirty air” is extremely dangerous for children. Transport and industrial facilities can pollute the environment. If background radiation is increased or intense magnetic radiation is present, this can also have a detrimental effect on the general condition of the child (both an infant or one-year-old child, and relatively adult adolescents). |
| Seasonal weather changes | A sharp change in weather entails the risk of seasonal illnesses, infectious and viral diseases. Because of them, other problems arise - the immune system suffers, which leads to the development of atypical allergic reactions. |
Causes of development of atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis in a child mostly occurs due to hereditary predisposition. Dermatitis and allergies are not the same concept.
If in the first case the probability of overcoming the disease as you grow older is high, then the allergy occurs once and accompanies the person throughout his life. In addition, atopic dermatitis can be caused not by one specific allergen, but by a whole spectrum of them.
Modern medicine identifies several factors that are the impetus for the development of the disease:
- Food allergies in a child can be caused by both breastfeeding and bottle feeding. In the first case, atopic dermatitis can be observed when the mother consumes a product that provokes the pathology. With artificial feeding, rashes occur due to the composition of the mixture or failure to comply with hygiene standards when washing dishes. The problem may also arise during the period of introducing complementary foods. Quite often there are reactions from the child’s body to citrus fruits and confectionery products, especially chocolate.
- A predisposition to this kind of dermatitis in a child can contribute to a difficult pregnancy, namely the exacerbation of chronic diseases, the development of intrauterine infections and any other pathologies leading to the threat of miscarriage.
- There are often cases when atopy in a child occurs in combination with other problems of the digestive system: dysbiosis, enterocolitis, gastritis, helminthic infestations. This list can be expanded with diseases that negatively affect the immune system, especially bacterial infections.
Atopic dermatitis is provoked by household allergens. Accumulating in a child’s body, they provoke damage to various areas of the skin.
Such provocateurs include:
- particles of household and industrial dust;
- pollen during the flowering period of allergenic plants;
- domestic parasitic beetles;
- home cleaning products;
- chlorine-containing preparations;
- air odor improvers;
- child care products;
- diapers;
- medications.
It is impossible to talk about one single factor that is the source of dermatitis in a child. In addition, once atopy occurs, it can make itself felt in the future.
This may be affected by:
- Psycho-emotional and neurological overexcitation. Stress and overexertion provoke the appearance of atopic rash.
- Smoking in the presence of a small child, especially an infant, causes skin problems, including dermatitis.
- Unfavorable environment and external factors that weaken the body's defenses.
- Climate changes and changes.
- Excessive physical activity.
Atopic dermatitis in a child must be treated at the first signs of the disease. Treatment of an advanced form of the disease will be longer and more expensive, and all this time the dermatitis will cause discomfort in the child.
Types of dermatitis in infants and their manifestations
In infancy, the following types of this disease occur in children:
- contact dermatitis;
- allergic dermatitis;
- atopic dermatitis;
- seborrheic dermatitis;
- diaper dermatitis.
All of these options have different symptoms and causes, and therefore they are treated differently.
Contact dermatitis
This type of dermatitis develops immediately after contact with obligate irritants, which include high and low temperatures, strong wind, friction, alkalis, acids, some plants, etc. In children, this form of the disease is most often provoked by friction due to rough seams on clothing, incorrectly selected diaper size, etc.
Contact dermatitis in newborns appears as red spots or stripes clearly at the point of contact. By the shape of these spots, you can determine what exactly caused their appearance, since they follow the contours of the irritating factor. After eliminating the damaging agent, all symptoms resolve on their own.
Allergic dermatitis
Allergic dermatitis in infants is quite common. Its development can be triggered by food products (in the mother’s diet or as part of the baby’s complementary foods), cosmetics, washing powders, etc. Therefore, their choice must be approached responsibly, cosmetics and detergents should only be purchased with the appropriate marking, especially if there is a hereditary predisposition to this disease.
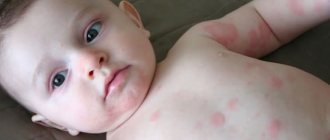
Dermatitis in an infant of allergic etiology is manifested by red itchy spots. Often, against their background, small bubbles appear, filled with serous fluid, which can burst, forming a crust after drying. Allergy rashes are most often localized on the baby's face (on the cheeks and chin), on the buttocks and in the groin area, but can appear on any other part of the body.
Atopic dermatitis
This is one of the types of allergic dermatitis. With it, most often it is not possible to identify a specific allergic factor. Sick children have an atopic reaction to several stimuli, and it is never possible to accurately predict what will trigger atopy and what will not.
For the first time, atopic dermatitis in an infant appears during the first half of life, reaching the peak of the disease by the age of one year. Rashes with it are similar to manifestations of allergies. On red, inflamed, swollen skin, small vesicles with serous contents appear, which open and form a moist surface with cracks and crusts. The baby is restless, cries a lot and scratches the lesions. Because of this, the skin is injured even deeper. Such scratching can lead to the addition of a secondary bacterial or fungal infection, which always aggravates the course of the underlying disease.
Over time, the weeping dries up, the crusts gradually fall off, and the skin heals. But if the process becomes chronic, dry skin, itching and frequent exacerbations will bother the baby for a long time.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis in infants is provoked by two main factors - the restructuring of the hormonal system after birth and the activity of the yeast-like fungus Malassezia furfur.
When the baby is in the mother's belly, he receives her hormones through the blood. After birth, the child’s body begins to produce them itself. But until this process is fully adjusted, hormonal fluctuations in the blood are possible within varying limits. This leads to excessive secretion of the sebaceous glands, which, in turn, provokes an increase in the activity of yeast-like fungus. Therefore, many children develop seborrheic dermatitis during the first few weeks of life.
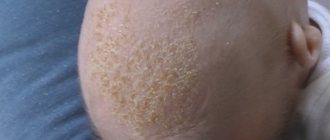
The rashes associated with this disease appear as gray or yellow greasy scales. Most often they are localized in the scalp, less often - behind the ears, on the face, in the gluteal folds and inguinal folds.
The scales of seborrheic dermatitis have a rather characteristic appearance, which is why this variant of the disease cannot be confused with any other. You can view photos of this pathology in specialized reference books.
Inflammation and itching are not observed with seborrheic dermatitis, so children tolerate it calmly. Within a year, all crusts usually peel off. The chronic course of this form of the disease is not typical.
Diaper dermatitis
Almost all parents encounter this type of dermatitis in children. It develops when changing diapers infrequently, being in wet diapers, excessively wrapping and overheating the baby, etc. That is, it is a consequence of improper care of the child.
Diaper dermatitis manifests itself in infants as inflammation of the skin in the area of the inguinal folds, buttocks, and lower abdomen. Prolonged contact with urine (due to late changing of diapers or diapers), increased sweating from overheating cause skin irritation and itching. The baby in such a situation is restless, cries a lot, and bends over.
The disease may be complicated by the addition of a bacterial or fungal infection.
How does atopic dermatitis manifest?
Atopic dermatitis, recognized in time, is the key to successful treatment. The disease has distinctive features, which are most often localized in certain areas of the skin.
The main signs or clinical manifestations of atopic dermatitis in a child are:
- severe itching, worse at night;
- redness in areas of scratching;
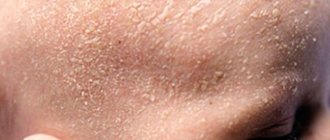
- dryness, peeling and rashes on the skin;
- wetting of lesions;
- formation of crusts and damage in areas of rashes;
- formation of cracks and strengthening of the skin pattern on the lesions;
- the appearance of rough areas and pityriasis scales;
- formation of pustular rashes on the skin;
- the appearance of diathesis.
The appearance of pathologies on the skin is accompanied by internal discomfort.
Itching deprives the child of proper sleep, as a result he becomes whiny and restless. Constant nervous tension suppresses appetite, which can lead to weight loss. But atopic dermatitis manifests itself differently at every age, and the course of the disease and its manifestations differs depending on the type of disease.
Types of atopic dermatitis
To select adequate treatment for atopic dermatitis in a child, a comprehensive analysis of the pathology is necessary.
It is important to correctly determine:
- phase of the disease;
- degree of skin damage;
- age, since the disease manifests itself differently at different age levels;
- severity of the pathology.
Each of the listed characteristics is equally important. When diagnosing, doctors identify phases of the disease, which determine the extent of damage to the surface of the child’s skin.
The degree of skin damage is distinguished according to the following categories:
- A limited area of the lesion is characterized by 5% of the total area of the entire skin.
- When localized in an area of up to 25%, it is customary to diagnose widespread lesions.
- Diffuse changes are characterized by numerous skin lesions.
Depending on the age of the child, there are:
- infantile atopic dermatitis, observed in children under 2 years of age;
- childhood atopy, which occurs until adolescence;
- teenage dermatitis, which can be troublesome until adulthood.
The severity of the disease is determined based on the general condition of the child:
- A mild course is characterized by moderate itching, slight swelling and dry skin. The disease is easily controlled. The periods of remission are long.
- The average severity of the disease is characterized by the appearance of a rash over a large area of skin, itching and the presence of a cracking crust that forms when the rash blisters open. The child's general condition worsens, and the likelihood of additional bacterial skin lesions increases.
- Severe degree is the most painful for the child. Itching, sores, crusts and other clinical manifestations are observed over the entire surface of the skin, and nervous overstrain makes the child especially capricious.
Atopic dermatitis in a child is a disease that is mostly observed in children, which forces doctors to pay especially close attention to the age of the child. In the future, when choosing a drug for treatment, this indicator is decisive.
Types of allergic dermatitis in children
To select the most effective medicine for the treatment of allergic dermatitis in children of different ages, it is necessary to take into account a lot of nuances: the course of the disease, features of manifestation, the presence of secondary pathologies, the degree of tissue damage. Allergic dermatitis is characterized by a typical localization associated with the age of the baby.
Let's look at the details in the table.
| Age of the child with allergic dermatitis | How does allergic dermatitis manifest? | Typical localization of rashes in a child with allergic dermatitis |
| From birth to 6 – 10 months | Erythema on the skin of the cheeks and forehead, resembling a milky scab, serous papules, and erosive surfaces after opening. Total peeling of the skin with intensification around the rash. | The scalp, ears, cheeks, forehead skin, lower segment of the chin, elbow and knee bends. |
| From 10 months to 1.5 years | Redness of the skin with swelling and the appearance of exudate, a typical allergic syndrome | Mucous membranes of the mouth, larynx, nasopharynx, digestive tract, urinary tract. |
| From 1.5 to 3 years | Dryness and thickening of the epidermal tissue against the background of an intensification of the pattern. | Feet, neck, flexion areas, wrists. |
| Over 3 years old | Ichthyosis and neurodermatitis. | Folds of the surfaces of the upper and lower extremities. |
In children 1–2 years of age, allergic dermatitis can occur as a seborrheic or nummular type. In the first case, scales appear on the head from the first days of life. Young mothers do not know what it is and may apply inappropriate products to it, further exacerbating the problem. The nummular type is manifested by skin rashes with crusts.
The nature of the symptoms of the disease depending on age
When identifying and diagnosing a child with suspected atopic dermatitis, doctors focus on the child’s age, which most often determines the location of manifestations on the skin.
| Child's age | Localization | Clinical manifestation |
| Infancy includes the period of life up to two years | The lesions occur on the face, the bends of the limbs, sometimes the scalp, buttocks, and the entire torso. | The inflammatory process is observed in the form of redness and weeping of the affected areas |
| The childhood period includes the age range from 2 years to 12 | Rashes are observed mainly on the skin in the neck, hands and bends of the limbs | The rash looks like nodules or blisters. Cracks, crusts, and scales form on the surface. There is dryness of the skin and its unevenness, areas of compaction. The rash is accompanied by severe itching |
| Adolescent atopic dermatitis occurs during puberty, i.e. from 12 years to 18 | The rash affects a large area of the body and is observed in the décolleté, elbow fossa, and wrist. Particularly strong manifestations are observed on the surface of the skin of the face and neck. | The skin on the affected areas thickens, and unbearable itching leads to loss of sleep and increased nervousness. |
Atopic dermatitis in a child most often manifests itself as a response of the body to a product with a high allergic potential, regardless of the age at which it appeared.
In children in the early stages of life, this is explained by an insufficiently well-formed gastrointestinal tract. In other cases, atopic dermatitis transforms into an allergy that will accompany the person throughout his life.
Treatment of food dermatitis
Diagnosis proceeds as follows: the doctor performs an external examination of the patient. When symptoms of food dermatitis are confirmed, the allergen that caused them is determined. A certain product, when eaten, causes rashes and redness. The doctor determines which product it is using special tests. The patient is injected with allergens using a syringe, then injected with sterile water and the skin reaction is observed. If redness appears, this indicates an allergic reaction. The patient undergoes all tests, skin biopsy, and various other procedures necessary to draw up a clinical picture.
The doctor will tell the patient in detail how to treat food dermatitis.
Treatment of food dermatitis with folk remedies
Folk remedies are used only as part of complex treatment of food dermatitis. If they are used independently, they will not have sufficient effect.
The most commonly used plants are chamomile, nettle and primrose.
Treatment of food dermatitis with medications
The attending physician prescribes medications for treatment in accordance with the patient’s tests.
Treatment of food dermatitis proceeds as follows. To begin with, a product with an allergen is completely excluded from the diet. Antihistamines are used to cope with allergies. These may be Suprastin, Loratadine, Claritin. The duration of the course is usually a couple of weeks. If necessary, sedatives are used to relieve inflammation, itching, and redness.
To remove the allergen from the body, agents are taken that adsorb.
Probiotics restore the intestinal microflora, and with the help of creams they relieve the symptoms of food dermatitis - redness and itching. Hormonal drugs are prescribed by the attending physician; they must be used very carefully in case of severe inflammation.
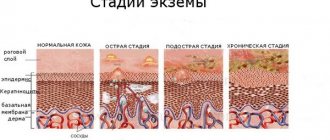
Stages of development of atopic dermatitis
The development of atopic dermatitis in a child occurs gradually. First of all, the allergen enters the baby’s body. Only after its concentration reaches a certain level can visual manifestations of the disease be observed.
Stages of atopic dermatitis in a child.
Doctors distinguish the stages of atopic dermatitis:
- The initial stage is characterized by minor manifestations of the disease. They are often confused with other diseases, as there is a slight increase in temperature.
- The acute stage of atopy is characterized by the development of the main and accompanying manifestations of the disease.
- During the transition to the chronic phase, the following are observed: redness and puffiness of the foot, peeling and cracks in the skin, deep wrinkles in large numbers on the lower eyelids in children and thinning hair on the back of the head.
- The period of subsidence or remission of the disease is characterized by a partial or complete absence of atopic symptoms and an improvement in the child’s general condition.
- The disease is clinically considered defeated if its symptoms do not appear in the period from 3 to 7 years.
If you seek help for diagnosis in a timely manner, it increases the likelihood that the course of the disease will be brought under control.
Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis in a child is diagnosed comprehensively.
When a diagnosis is made, the following measures are taken:
- A visual examination of the child allows you to determine the presence of obvious clinical manifestations of the disease.
- Questioning and conversation with parents will reveal the period of onset of the first symptoms, predisposition and causes of the disease.
- After carrying out the initial measures, the doctor will prescribe the necessary set of laboratory tests.
Laboratory tests are necessary to make a final diagnosis and identify the causes of atopic dermatitis.
Such studies include:
- blood test for immunoglobulin E;
- general blood test - will determine the increased reaction of the immune system to the allergen;
- The immunogram is designed to determine the state of immunity, in particular, why a reaction in the form of atopic dermatitis occurs;
- A biochemical blood test, a general urine test and a stool test will help determine the general condition of the body and exclude or confirm other pathologies;
- A blood test for HIV is necessary because dermatitis and AIDS rashes are often similar.
Additionally, scraping from the surface of the skin may be prescribed. If after treatment of dermatitis there is no clinical recovery after 4 years, additional tests for allergens are recommended.
Such a comprehensive approach to the treatment of atopy in a child guarantees the selection of an adequate treatment regimen.
Prevention measures
- You should not bathe your baby too often, as this helps wash away the protective fat layer from the surface of the skin and dries it out, creating excellent conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
- You can add decoctions of string or chamomile to the bathing water. These herbs have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects.
- The child's living conditions must comply with established standards. It is better if the baby has a separate room from birth.
- Cleaning, ventilation and air humidification should be mandatory procedures.
- Cosmetics and household chemicals intended for everyday child care must be of high quality and free of fragrances, parabens and other toxic substances.
- The atmosphere in the apartment should be calm and friendly, since stress is one of the main factors provoking the development of allergic dermatitis and other skin diseases.
- Ban smoking in the apartment if there are smokers in the family.
If a child is diagnosed with atopic dermatitis, it is important to start treatment on time, since the chronic stage of the disease is fraught with serious complications.
Compliance with hygiene rules, a hypoallergenic diet and timely therapy will help to avoid unpleasant consequences and maintain the baby’s health, regardless of his age.
Treatment with medications
The selection of medications, regardless of the conditions for their administration, should be carried out by a highly qualified specialist. It is not recommended to make an independent decision and risk the baby’s health under any circumstances. Treatment is most often complex.
Depending on the severity and stage of the disease, oral medications included in the table below are prescribed:
| Atopic dermatitis phase | Purpose of the drug | Representatives |
| Acute phase | Drugs that have antiallergic effects |
|
| Drugs that neutralize inflammation |
| |
| Decay phase | Drugs that support the immune system |
|
| Drugs that strengthen cell walls |
| |
| Remission | Specific immunotherapy | Cyclosporine A. |
Special creams and ointments for external use:
| Name | Release form | Mode of application |
| Skin cap | aerosol; cream, | The product is distributed in a thin layer over the surface of the skin in a certain way, depending on the form of release. Treatment duration is up to 3 weeks, recommended age is from 12 months. |
| Advantan | ointment; cream; emulsion | It is recommended to combine the product with baby cream and rub into the affected area. The drug is used from an early age, the duration of treatment is no more than 4 weeks. |
| Triderm | ointment; cream | The product is rubbed into and around the affected area 2 times a day, but not more than 4 weeks. |
| Fenistil | gel; emulsion; | The drug is distributed on the affected area until completely absorbed up to 3 times a day. |
| Lokoid | cream; ointment | Apply a thin layer to the affected area until complete recovery. |
How to cure dermatitis on legs
Treatment of dermatitis on the legs should be comprehensive. Only this guarantees a positive result of the therapy. Only a doctor knows how to cure your dermatitis. For this reason, you should begin therapeutic measures only after consulting a specialist.
Avoiding contact with the allergen
The first thing therapy begins with is avoiding contact with the allergen. Only this guarantees the effectiveness of treatment. It is recommended to avoid, among other things, contact with mechanical irritants that injure the epidermis. To do this, you should choose only loose clothing made from natural fabrics.
You need to pay special attention to the choice of washing powder. It is recommended to give preference to products with the least aggressive formulations. Such products should be free of phosphates and other similar components.
It is also recommended to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet. Berries, fruits and vegetables of red and orange color should be excluded from the diet. The consumption of citrus fruits is unacceptable. It is also recommended to avoid honey, nuts, seafood, coffee, chocolate and so-called junk food containing dyes and preservatives. In this case, the menu should contain:
- porridge;
- lean meat and fish;
- permitted vegetables and fruits;
- vegetable soups;
- milk and products made from it with a low mass fraction of fat, if there is no allergy to cow protein.
Antihistamines
The use of antihistamine medicinal products is one of the points of treatment for dermatitis on the legs. These drugs relieve itching of the epidermis, redness and rashes. Antihistamines are taken orally and used externally. Most often, doctors prescribe Tavegil, Zodak, Loratadine, Suprastin, Fenistel gel for topical use and others.
Topical corticosteroid ointments
The use of such ointments for dermatitis on the legs is only relevant if the pathology is severe. Hormone-based drugs quickly improve the condition of the epidermis. Products such as creams and ointments relieve itching and burning, relieve rashes and peeling, and also relieve swelling of soft tissues.
Corticosteroid drugs have side effects, so such products are used only as prescribed by a doctor and for a short period.
Usually the course of treatment does not exceed 5 days, but the exact period is determined by a specialist, depending on the subjective characteristics of the body and the severity of the pathology.
The ointment is applied to the affected epidermis in a thin layer, without affecting healthy areas of the skin. If such therapy does not bring the desired result, the doctor may prescribe oral anti-inflammatory hormonal drugs.
Among the most popular corticosteroid ointments are Advant and Lokoid. Prednisolone is most often prescribed for oral administration.
Desensitizing drugs
Such remedies help rid the body of toxins. Medicines are prescribed when the disease enters the acute stage. Most often, the doctor prescribes injections with calcium gluconate.
Vitamin and autohemotherapy
Taking vitamins speeds up the treatment process, improves the condition of the epidermis, and also has a positive effect on the condition of all organs and systems. Usually, for dermatitis on the legs, complexes are prescribed that contain vitamins B, A, C, E and D.
Autohemotherapy is a course of physiotherapy procedures. This method of treatment is aimed at increasing the body's defenses.
Traditional methods of treating dermatitis on the legs
If we talk about how you can treat dermatitis on the legs with the help of traditional medicine, then this can only be done in consultation with a doctor.
Such drugs should only be used as additional therapy. Below are recipes for the most effective remedies for treating dermatitis on the legs.
Infusion based on hops and string
To prepare the product you will need:
- string - 50 g;
- hops – 50 g;
- water – 500 ml.
The plants are combined, placed in a thermos and filled with boiling water. The product is left to infuse for 6-8 hours. Next, the product is filtered and used as a compress.
Decoction based on oak bark
Required components:
- crushed oak bark – 50 g;
- water – 300 ml.
The oak bark is poured with boiling water and set to boil for 10-15 minutes. After this, the broth is left to cool and filtered. The resulting product is used to treat the affected areas of the epidermis several times a day. The manipulation is carried out until the condition improves.
Infusion based on viburnum berries
To prepare the drink you will need:
- crushed viburnum berries – 2 large spoons;
- water – 1 glass.
The berries are poured with boiling water and left to infuse for 4 hours. Over time, the drink is filtered. The product is consumed 100 ml 4 times a day.
Rosehip compress
To prepare the product you will need rose hips. The fruits are crushed to a pulp, wrapped in gauze or bandage and kept for several minutes on the affected area of the epidermis.
Herbal infusion
Required components:
- corn silk – 20 g;
- juniper fruits – 20 g;
- nettle – 10 g;
- sage – 10 g;
- plantain – 10 g;
- wormwood – 5 g;
- water – 1 l.
All plants and berries are combined and poured with boiling water. The product is infused for 12 hours. Next, the drink is filtered and consumed 100 ml three times a day.
Burdock root decoction
Required Products:
- chopped burdock root - 1 small spoon;
- water – 500 ml.
The plant is placed in a thermos and boiling water is added. The product is left to infuse for 7-8 hours. The product is filtered and used externally and for oral administration. The infusion is used to treat the affected epidermis several times a day, and also consume 100 ml three times a day.
Sea buckthorn oil
This is one of the best remedies for dermatitis on the legs. Sea buckthorn oil is recommended for oral use. The product is consumed 2 ml twice a day in the morning and evening. The product is also suitable for external use. In this case, the drug is treated with the affected areas of the epidermis several times a day until recovery.
Cranberry juice
To prepare this remedy you will need a handful of fresh berries. The cranberries are wrapped in gauze, then crushed and the juice is squeezed out. The resulting drink is used to wipe the affected areas of the epidermis. The manipulation is carried out several times a day. The course of therapy is until the condition of the skin improves.
Traditional methods of treatment
Along with traditional medicine, traditional methods of treatment are also actively used. It is recommended to use them only if the child is over 3 years old.
Despite the effectiveness demonstrated by folk remedies, examination and doctor’s recommendations should not be ignored, especially since some doctors recommend traditional treatment methods as a complementary therapy to the main treatment.
The following tools are trusted and popular:
- ointment from the herb St. John's wort for external use;
- a mixture of honey and Kalanchoe;
- potato juice in the form of lotions;
- infusion or decoction of chamomile flowers (recommended to be added to water when a child takes a bath);
- oak bark in the form of a decoction - successfully relieves inflammation on the surface of the skin;
- decoction of string leaves;
- weak manganese solution
- flaxseed oil;
- potassium permanganate solution.
Most of the remedies are decoctions and solutions that relieve irritation and inflammation. Oils, ointments and lotions are more suitable for moisturizing the skin and relieving itching.
Diet for the treatment of dermatitis in children
Compliance with diet is the most important condition for the effective treatment of allergic dermatoses in children of all age categories.
Parents sometimes despair, wondering whether the disease can be cured at all. However, it is the correct diet that sometimes determines how quickly an allergic disease will disappear and whether a relapse will occur.
The menu for a child 2–5 years old suffering from allergic dermatitis looks approximately as shown in the table.
| Breakfast | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner | Before bedtime | |
| 1st day | Buckwheat porridge, Dutch cheese, tea without sugar, a slice of black bread with butter | Potato soup with sour cream, meat puree, boiled rice, compote | Fruits | Steamed meat cutlets, mashed potatoes with sour cream, compote or tea | Kefir or unsweetened yogurt |
| 2nd day | Liquid rice porridge, cottage cheese, unsweetened tea or compote, black bread with butter | Cabbage soup with fresh cabbage, steamed meat cutlets (preferably rabbit or turkey), pasta with butter | Fruits, yogurt | Cabbage salad with butter, boiled potatoes with sour cream, boiled or baked meat with herbs | Kefir |
| 3rd day | Oatmeal, tea, cheese, bread and butter | Potato soup with sour cream, steamed meatballs, compote | Fruits | Lazy cabbage rolls with rice and dietary meat, children's cottage cheese with fruit, compote | Yogurt |
| 4th day | Mashed potatoes with butter, cabbage salad, cheese, tea | Vegetarian barley soup, steamed meat cutlets, cabbage salad | Fruit or yogurt | Boiled potatoes, steamed meat balls, salad, tea | Curdled milk |
The menu is quite arbitrary, but from it it becomes clear that a child can eat tasty and healthy, even suffering from allergic dermatosis of any origin.
Children over 3 years old should receive a variety of foods, depending on their origin, vitamin and chemical composition. Adequate nutrition will give you strength and allow you to quickly cope with the problem.
Diet
It is impossible to overcome the disease without following a diet, especially during periods of exacerbation. Considering that most often the problem is provoked by food, strict control over what the child eats becomes mandatory. If the baby is breastfed, then the mother should follow the same recommendations.
Products with a high allergenic index include:
- all citrus fruits;
- fruits and berries that are red in color, including apples;
- nuts and honey;
- large amounts of sugar and salt in the diet;
- fatty, spicy and smoked foods.
If a child is bottle-fed, atopy can also occur with lactose intolerance. In this case, it is necessary to replace the mixture produced on the basis of goat milk or milk with vegetable protein. It is also important to introduce complementary foods correctly - one product every few days.
It is very important to control and observe how the child reacts to the innovation.
If you are allergic to dust or pollen, it is not possible to completely limit the access of the allergen to the body. The only way out is to change your place of stay during periods of exacerbation of the disease and carefully care for the house to neutralize dust. In cases of allergies to household chemicals, cosmetics and diapers, it is necessary to replace and select more suitable cleaning products and baby care products.
Physiotherapy
When treating atopic dermatitis in a child, doctors prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures. They must be carried out under the strict supervision of a specialist.
Procedures recommended for children include:
- applying special bandages to damaged areas;
- ultraviolet irradiation under a special lamp;
- paraffin therapy.
This also includes water procedures performed using traditional medicine. Lasting results are also achieved by sanatorium-resort treatment, which is carried out in combination with the choice of the most suitable living conditions during the treatment period. Most often, the results of such therapy are long-lasting.
Can it be cured forever?
The disease is considered chronic. However, if the necessary measures are taken in advance, then the likelihood of lifelong remission is very high.
Treatment measures include activities such as:
- full comprehensive examination;
- correct treatment;
- compliance with doctor's instructions;
- diet, especially during periods of exacerbation;
- maintaining hygiene at home, which will eliminate dust and pollen during flowering periods.
In the future, the symptoms of the disease will appear less frequently or disappear completely.
Skin care features
If atopic dermatitis occurs at an early age, it is important to pay special attention to caring for the child’s skin. The baby’s body is still weak, and it reacts in the most unexpected way to minor influences. It is important to maintain personal hygiene and, following the pediatrician’s recommendations, bathe the child in herbal decoctions, whose action is aimed at relieving inflammation.
Don't get carried away with shampoos, soaps and wet wipes. Even when there is an indication of hypoallergenicity, they may not be suitable for a particular child.
You also need to be careful when choosing diapers for young children. If the manufacturer recommends changing them every 4 hours, then this requirement cannot be ignored, even if there is not enough discharge. If any rash is detected on the child’s delicate skin, you should consult a doctor and replace the hygiene product.
Despite the growing number of cases of atopic dermatitis in children, it is wrong for parents to limit their child from possible allergens, ensuring complete sterility. The result will be a weak immune system that did not receive the necessary training during its formation period.