Herpes is considered the general name for a disease associated with a viral infection. Today, there are 8 types of the disease, which manifests itself in different parts of the body. Such an infection can live in the body of almost any person, and can also affect almost any organ. At the very beginning of life, children, as a rule, do not develop such a disease; this is due to the fact that their body is under reliable protection, which is nourished by maternal antibodies. But children who are 3-4 years old may already be affected by the disease. Since personal antibodies can be produced in a child’s body only by the age of 5.
All children, like adults, can be susceptible to herpes. In this case, infection can come from both parents and other children in the kindergarten or school. Although the virus has several types, children are often exposed only to primary herpes.
Clinical picture
The virus enters the child's body from an infected person. This happens when using shared dishes, towels, and most often through kissing.
The disease occurs in several stages:
- At first, a feeling of discomfort and itching of the skin appears.
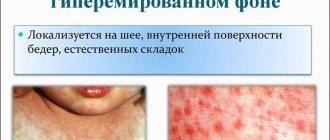
- Hyperemia - the area where herpetic blisters will soon appear, begins to turn red.
- The appearance of bubbles. They can be single or combined; serous fluid collects inside them. Bubbles appear about a day after the first symptoms appear.
- 3-4 days after the first signs appear, the process of ulceration begins and crusts form. The crusts go away in 5-7 days, the damaged areas of the skin are restored, and no traces remain of the previous rashes.
Herpes on the face in children is also accompanied by a change in the child’s general well-being. The baby loses his appetite, he becomes lethargic, does not want to play, and his skin becomes pale.
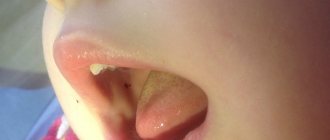
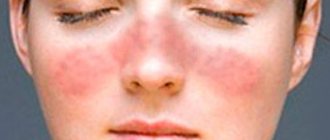
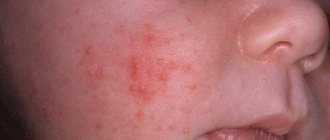
Lesions on the face can have different localizations: herpes often occurs on the cheeks and lips, but the rash can even spread to the forehead. When herpetic eruptions appear on the oral mucosa, the process of chewing and swallowing food becomes difficult, and an enlargement of the lymph nodes is observed.
When the virus spreads to the organs of hearing and vision, the central nervous system, and internal organs, serious complications may develop.
The herpes simplex virus can lead to encephalitis - it causes damage to parts of the brain, which leads to irreversible consequences.
Herpes infection
Any subtype of infection is highly contagious. The main method of contracting the virus is through close contact with an already infected person. For example, the reason could be a simple kiss from parents. Such a disease can also be transmitted through objects that are used in everyday life, where even the slightest fraction of the saliva of a sick person remains. This could be dishes, toys or a towel, etc. True, as the droplets with the virus dry out, the infection will die. As a rule, those people who suffer from an illness may not even suspect that it lives in the body and thereby infects other people.
Classification
There are several forms and types of the disease.
According to the form, herpes on the face of a child can be divided into:
- spicy;
- chronic.
The acute form is characterized by a severe course. With it, there is an increase in temperature, multiple rashes appear, and swelling of the face is observed. The child is capricious and crying. Nausea may occur along with a decrease in appetite.
In the chronic form of dermatitis, the symptoms are not clearly expressed. There is usually no increase in temperature, or it quickly returns to normal. The rashes are sporadic and disappear quickly. The child does not complain of a general deterioration in health.
There are several types of disease:
- primary;
- recurrent;
- neonatal.
Primary – the first manifestation of a herpes infection. Since the body has not encountered the virus up to this point, it can be severe. Deterioration in health may last up to several weeks.
Recurrent (repeated) herpes is characterized only by external symptoms; in general, the infection does not affect the child’s condition. Signs of the disease disappear after 8-10 days. Relapses can be repeated frequently, and even overlap one on one - in such cases, types of herpetic rash are found, characteristic of different stages.
Neonatal is diagnosed in newborns. Infection occurs as the child passes through the birth canal. These cases are very dangerous and require medical supervision.
Symptoms
The symptoms of herpetic lesions of the dermal layer of the face, including the lips, are quite specific. Among the characteristic manifestations are:
- Formation of a papular rash on the face. Papules have the appearance of dome-shaped transparent structures. They are filled with colorless or whitish (yellowish) exudate with impurities of pus. Develop in singular or plural. The size of the papules varies from 0.3 to 3 cm. When opened, they form a characteristic “well”; secondary infection of the wound is possible. If you do not scratch these wounds, scars will not appear.
- Increase in body temperature to subfebrile or febrile levels (slightly above 38 degrees). As a rule, this is observed with massive damage to the facial skin.
- Pain at the site of the rash. Burning, aching, shooting pain accompanies the patient throughout the course of the disease.
- Itching at the site of the lesion.
With mononucleosis and cytomegaly, other manifestations are possible. In this case, symptoms of damage to internal organs will be detected.
Etiology
Rashes on the face can occur due to 3 types of viruses: simple virus types 1 and 2, as well as chickenpox.
Virus particles penetrate most easily into loose, moist shells. Therefore, most often it penetrates through the lips. Virus particles that enter the body infect nerve cells and change cell chromosomes. After this, the body produces small numbers of viral cells throughout its life.
In response to such an invasion, antibodies are produced - this is how immunity to the virus appears. The infected cells produced are destroyed by the immune system, and there are no manifestations of the disease. However, when the immune system weakens, it cannot fight off infection.
Possible complications with herpes on the face:
- Otitis. There is a possibility of deterioration or complete loss of hearing.
- Damage to the cardiovascular system.
- Meningitis.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
- Pathologies of the digestive system.
Such consequences are possible if treatment measures are not taken in a timely manner.
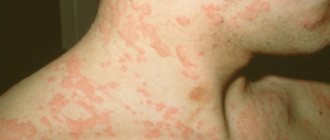
Rash on the body due to herpes
Herpes, popularly known as cold sores, is usually associated with blisters on the lips (type 1 virus), and blistering rashes on the skin of the body caused by the herpes virus go by other names.
There are several types of herpesvirus that cause diseases accompanied by rashes on the body. These include:
- Chickenpox and herpes zoster, caused by the varicella zoster virus and always accompanied by a rash;
- Cytomegalovirus , accompanied by a rash with weakened immunity;
- Infectious mononucleosis (Epstein-Barr virus ), accompanied by a rash when taking antibiotics necessary to treat the disease;
- Pseudo-rubella (roseola) , accompanied by an extensive rash and caused by the herpes virus type 6.
Chickenpox rash
During primary infection with the Varicella zoster
A disease occurs called chickenpox or chickenpox.
This well-known common disease is spread by contact or airborne droplets, so most children become infected with this virus before they reach 15 years of age. The incubation period characteristic of the disease lasts from 10 to 21 days
from the moment of contact with the patient. Symptoms of the disease are:
- Malaise that occurs a day or two before the appearance of the rash and manifests itself in moderate abdominal pain (optional), headache and fever;
- Rashes on the face and throughout the body.
Initially, herpes on the skin of the body looks like a red spot , which then transforms into a papule, and then into a single-chamber vesicle with a clear liquid in the middle (vesicle). After a day, the liquid becomes cloudy, and a depression forms in the center of the bubble. The vesicle then becomes covered with a crust, which falls off over time. Spots remain at the sites of the primary elements, disappearing after a week. A characteristic feature of chickenpox is the simultaneous existence on the skin of various stages of development of the elements of the rash (from spots to crusts).
Shingles rash
In children who have recovered from the disease, the chickenpox virus strengthens in the nerve cells and remains in a latent state, not manifesting itself in any way. With a significant decrease in immunity, a relapse of the disease is possible - herpes zoster. At the onset of the disease for 3-4 days
observed:
- Weakness;
- Digestive disorders;
- Slight increase in temperature;
- Pain localized mainly in the areas of future rashes.
Symptoms and degree of intoxication are individual.
At the next stage of the disease, a rash appears. Herpes on the skin usually appears along the peripheral nerves. Favorite locations:
- projection of intercostal nerves;
- facial trigeminal nerve.
The rash begins with the appearance of pink edematous spots , which within 3-4 days turn into groups of erythematous papules, giving way to blisters with clear liquid. At the same time, local lymph nodes enlarge and pain increases. By the end of the week, the bubbles dry out and form yellow-brown crusts. After the crusts fall off, slight pigmentation remains.
Possible postherpetic neuralgia, manifested in pain that is difficult to treat. Herpes on the skin of the face is sometimes accompanied by damage to the facial and oculomotor nerves.
The condition is characterized by a burning sensation, intense pain that intensifies at night, as well as a decrease in tactile sensitivity in the affected areas. There are cases of the disease that are not accompanied by pain. The severity of the disease depends on the state of the patient's immunity. An uncomplicated disease lasts 3-4 weeks.
Symptoms of herpes zoster:
- A small lesion (often looks like an itchy pink spot the size of the palm of your hand);
- One-way localization. Herpes on the skin of the back appears either on the left or right side, on one shoulder or on one side of the neck. Watery blisters on the skin of the legs and arms appear much less frequently.
Rash due to roseola, infectious monoculosis, cytomegalovirus
Roseola usually affects infants. This disease is accompanied by fever and profuse maculopapular (grouped, raised above the surface of the skin and reaching 1 cm) rashes throughout the body. When a rash appears, the temperature decreases. The itchy rash resembles a rubella rash. Treatment of herpes on the skin in this case is not required - the rash goes away on its own within a week, leaving no traces.
With infectious mononucleosis, a small percentage of patients develop a maculopapular rash on days 7-10 of the disease, which quickly disappears without leaving any traces. The rash does not itch and has no specific localization; it does not require specific treatment. It is provoked by the use of ampicillin.
With cytomegalovirus, a reddish-brown rash is usually located on the face , legs and arms, as well as in the mouth. The intensity and size of the spots depends on the individual characteristics of the organism.
How to treat?
Treatment of herpetic dermatitis is carried out using external agents. How to treat herpes in a baby should be determined by a specialist. The doctor not only makes a diagnosis, but also determines whether it will be enough to use exclusively external agents for recovery.
The most effective treatment will be if an integrated approach is implemented: drugs of not only local, but also systemic action are used.
It is not recommended to use brilliant green to treat herpes on the face in children. The solution has no effect on the virus itself, but can cause skin burns in the baby.
To prevent further spread of the viral manifestation, it is necessary to treat the skin on the face with an antiseptic drug that does not contain alcohol. This can be hydrogen peroxide 3%, chlorhexidine.
For treatment, you can use folk remedies: tincture of calendula, chamomile. Their use will help avoid the formation of pustules. In order to avoid the appearance of crusts, the bubbles are lubricated with essential oils. This could be oil of oregano, ginger, lemon.
Ointments that can be used to treat herpetic dermatitis on a child’s face:
- Acyclovir and drugs containing the active substance of the same name. It is possible to use such drugs as: Zovirax, Virolex, Acyclostad. All these drugs have the same composition and do not differ in pharmacological action.
- Ointments with Penciclovir. This is Fenistil Pentsivir. The effect of the product is similar to ointments based on acyclovir.
- Viferon. Available in the form of a gel and ointment, it contains interferon. It is characterized by two actions at once: antiviral and immunomodulatory. Treatment with this drug is well tolerated even by young children. It can be used to eliminate herpetic rashes in children under one year of age and has no contraindications for use. The only limitation may be individual intolerance to the drug. Viferon is applied throughout the entire treatment period.
- Panavir, Viru-Merz. The active ingredient in these drugs is Tromantadine. It is advisable to use these drugs at the initial stage of the disease, before bubbles appear.
Use of honey and propolis
You can treat herpes on a child's chin using beekeeping products. But such products are allowed to be used only if children are not allergic to honey. As soon as bubbles appear, they need to be lubricated with bee glue tincture. It must be prepared in advance. Pour 30 g of propolis into 1 glass of vodka. Leave for 14-16 days. Children can be given the drug for internal use. Cut 150 g of bee glue into cubes and add 500 ml of distilled water. Leave the product for 24-48 hours, then strain and take 15 drops daily. It is better for the child to add the drug to warm milk.
You can prepare a healing ointment for herpes on the face. 2 tsp. Mix wood ash with the same amount of honey and minced garlic. The resulting mass must be used to treat the affected areas. The procedures are performed 3-4 times a day. A remedy made from linden honey is popular. 2 tbsp. l. Mix sweet amber with 3-5 drops of fish oil. The ointment should be used to treat rashes every 3 hours.
If you know how to treat herpes in children, you can quickly and effectively cope with the disease. Therapy must be coordinated with a specialist so as not to harm the child’s health.
Tweet
Pin It
Tags:Children
- Development of herpes zoster in children: symptoms and treatment
- How to avoid getting shingles from others
- What is dangerous about shingles during pregnancy and how to cure it
- Is it possible to wash in the bathroom if you have shingles?
Preparations for oral use
Antiviral agents for internal use are used with caution in treating children. They are prescribed for herpes zoster or multiple rashes.
Treatment can be carried out using the following antiviral drugs:
- Acyclovir;
- Flavoside;
- Zovirax;
- Valtrex.
For a speedy recovery after a course of antiviral therapy, immunomodulators are additionally administered.
There is no point in using antibacterial drugs in this case. They have no effect on the virus, only helping with diseases caused by bacteria.
During treatment, the child should drink plenty of fluids. This will help remove toxins from the body faster.
How dangerous is the disease?
Speaking of the insidiousness of herpes, it is worth noting that, like many other diseases, herpes itself is not terrible - the serious consequences of this disease are dangerous. It is precisely they that can lead not only to an imbalance of the entire body, but also to disability or, even worse, death.
List of the most dangerous complications that can occur after herpes:
- Cerebral palsy. Often it begins to develop after a complicated course of the disease with herpes.
- Meningitis and encephalitis - these ailments can develop after illness in both newborns and older children. If emergency medical measures are not taken, death is possible in 90% of cases.
- Blood clotting disorder (DIC syndrome).
- Various eye diseases: corneal erosion, episcleritis, uveitis, chorioretinitis, iridocyclitis.
- Deep liver damage, up to chronic hepatitis.
- Gingivitis and stomatitis.
- Inflammation of the tonsils and herpangina.
Video from Dr. Komarovsky:
Folk recipes
Treatment of viral diseases can additionally be carried out using traditional methods. The following medicinal herbs can be used to combat the herpes virus:
- series;
- celandine;
- sagebrush;
- calendula;
- oregano
Strong decoctions are prepared from these plants for external use. Take 3 tablespoons of any herb, fresh or dry, and pour boiling water over it and leave for 20 minutes.
Wipes are moistened in the resulting infusion and applied to the area of the rash 3-5 times a day. Such lotions eliminate itching and pain. They also have a slight antiviral effect, but their use alone is not enough for treatment.
The bubbles can be smeared with a cut aloe or Kalanchoe leaf. Applications with juice are made every 3 hours. This remedy is quite effective - after a day, the serous fluid flows out of the blisters, and the healing process begins.
You can use the properties of medicinal herbs to strengthen the immune system. For this purpose, use:
- Rhodiola rosea roots;
- rose hips and hawthorn fruits;
- St. John's wort;
- lure root.
Mix a tablespoon of all ingredients, add boiling water and leave in a thermos.
The decoction is given 30 minutes before meals, warm, in a third of a glass. It should be taken throughout the entire period of relapse, cold.
There is a significant difficulty in treating children - maintaining hygiene. Children forget that they should not touch the affected area. After contact with virus particles, they may not wash their hands when touching other parts of the body - therefore, the likelihood of spreading the virus is high.
Aloe in the treatment of herpes virus
Aloe can be used to treat herpes in children. This plant has a rich composition that helps get rid of rashes quickly. Agave contains:
- amino acids;
- vitamin C;
- minerals;
- microelements.
Products made from aloe can remove herpes from the chin, lips and eliminate rashes on the cheek. Such drugs have an antibacterial effect, heal damaged areas of the skin and restore the structure of the epithelium.
A universal remedy that is suitable for any area of the face is agave tonic. Chop 1-2 leaves of the plant and pour 250 ml of boiling water. Leave the medicine for 60-120 minutes, then strain and apply to treat rashes every 2 hours. Aloe juice is often used to treat blisters. The extract is diluted with honey (1:1) and 2 tsp. vodka. The ingredients are mixed and applied to the affected areas of the skin.
If a child is infected with herpes on the lips, then a plant leaf cut in half (without prickly elements) should be applied to the pimples. The application must be secured with a band-aid and left overnight. The next morning, the compress should be removed and the skin should be treated with tincture of propolis or calendula in alcohol.
Treatment for dermatitis, which is similar to herpes, follows a remedy made from honey and aloe. It is necessary to grind the plant and mix it with a liquid bee product. The prepared mixture must be applied to a cotton pad, which should be used to treat the face or other location of the rash. Such procedures should be carried out 4-5 times a day. Before lubricating the skin, it should be wiped with alcohol. This must be done to eliminate germs and bacteria.
Children can also be given aloe juice orally. The drug should be drunk in its pure form up to 3 times a day, before meals. To prevent the product from becoming bitter, you can add linden honey to it.
Treatment with agave can effectively get rid of the disease and avoid its relapse.
Preventive actions
The virus is transmitted exclusively from person to person. Therefore, parents need to be careful: if the virus worsens in someone they know, do not allow the child to communicate with him. A healthy baby, even if infected, may not experience any reaction. It will appear only when the immune system is weakened.
This may happen in the following cases:
- ARVI;
- hypothermia;
- dysbacteriosis;
- poor nutrition;
- unorganized daily routine and lack of hardening.
Immunomodulatory drugs that can be used to strengthen the immune system include:
- Lycopid. The drug is given one tablet for 10 days.
- Derinat. It has no contraindications and is used to strengthen the immune system.
- Cycloferon. Can be prescribed to children over 4 years of age; use is possible only as prescribed by a doctor.
- Viferon. Used to treat young children. The drug is available in suppositories. Duration of therapy is 1 week.
When herpetic dermatitis appears on a child’s face, urgent measures should be taken. To determine a treatment regimen, you should contact an infectious disease specialist or pediatrician.
4.2 / 5 ( 5 votes)
Causes and development factors
The causes of this disease include:
- Infection . Penetration of the virus into the child’s body.
- Hypothermia . It negatively affects the baby’s immunity and leads to herpes.
- A recent infectious disease , cold or flu. The body does not have time to recover, and this is a favorable environment for the herpes virus.
- Stress . If a child often finds himself in stressful situations, this negatively affects the immune system and leads to the development of herpes.
- Lack of vitamins . If there is a lack of substances beneficial to the body, herpes may appear.
Risk factors include overheating, prolonged contact with sick people, and vitamin deficiency. Herpes often appears in children who often catch colds. Doctors also consider children who have an allergic reaction to be at risk.
You can learn about methods for preventing hypervitaminosis in children from our article.
Cold on the lip: how to treat it
If a cold has popped up on your lip, it causes a lot of discomfort. I would like to get rid of this problem as soon as possible
But in order not to aggravate the problem, it is important to know how to act correctly
Why does a cold on the lip occur?
Cold sores on the lips are caused by the herpes virus. It lives in the body of an infected person constantly and only waits until the immunity declines to make itself known. Causes of herpes on the lips: hypothermia; stress, lack of sleep, overwork; diseases that suppress the immune system (flu, HIV); menstruation in women; injuries in the lip area; contact with a person with herpes.
Precautionary measures
It is worth remembering that herpes is a viral disease. You can infect another person even with a kiss
Therefore, if you have a cold, you need to take the following precautions. Blisters on the lips should not be pierced or picked out, and sores that have formed should not be peeled off, as the virus may penetrate even deeper or enter healthy areas (into the mucous membrane of the nose or eyes). During illness, one must not forget about hygiene - use only a separate mug and spoon, wipe yourself exclusively with your own towel
During illness, one must not forget about hygiene - use only a separate mug and spoon, and dry yourself exclusively with your own towel.
Treatment for a cold on the lip
At the first sign of a cold, it is necessary to treat the painful areas with antiviral ointment. For example, one of the following drugs: Acyclovir, Zovirax, Panavir-gel, Vivorax. The ointment acts in two directions at once: it fights the virus and creates a protective shell at the site of the cold, which prevents the spread of the virus throughout the body and reduces the risk of transmitting it to others.
The resulting crust must be treated to soften it in the intervals between applying the ointment. For this purpose, you can use hydrogen peroxide, sea buckthorn oil or fatty cream. For a speedy recovery, it is necessary to avoid hypothermia, maintain immunity: take vitamins, drink natural juices, fruit drinks, herbal teas. If your temperature rises, or if colds appear frequently, it is better to consult a doctor. In severe forms of herpes, an antiviral drug is prescribed in the form of tablets orally.
Traditional medicine recipes
You can use folk remedies against colds on the lips. Garlic juice is a natural antiviral medicine. To use it, you need to chop a few cloves of garlic, add a teaspoon of honey and mix. Apply the resulting mixture to the place where the cold appears.
Juices of Kalanchoe and aloe plants. Take a leaf of the plant and smear the herpes-damaged area with the juice that has flowed from the fracture site. This will contribute to the speedy healing of sores.
Fir oil. At the first sign of a cold on your lips, you can start treating your lips with this remedy. Then there will be significantly fewer bubbles or they will be completely invisible.
KakProsto.ru>
Other articles
- How to treat an incipient cold
- How to treat a cold
- How to treat ear congestion during a cold
- How to treat a cold in the nose in an adult
- How to treat a severe cold
- How to treat a cold during pregnancy 2nd trimester
- How to treat a cold in the mouth
- Ears hurt when you have a cold - how to treat them
- What is the best way to treat a cold in an adult?
- How to treat a cold on the eye
- A cold has come out on my lip, how to treat it
- How to treat a cold without fever
Causes of herpes in children
The cause of the disease is primary infection with herpes or its activation against the background of weakened immunity. The virus is transmitted through direct skin contact or the exchange of body fluids. It is undemanding to the external environment and can live in the air or on surfaces for about a day. Herpes can also be transmitted to a child from the mother at birth.
Activation of the virus occurs due to the following factors:
- hypothermia, colds, acute respiratory viral infections, which reduce the child’s immunity;
- lack of vitamins, especially in winter and early spring;
- past infectious diseases;
- frequent stress, which also negatively affects the body's defenses.
Possible complications
The lack of timely and comprehensive treatment leads not only to a protracted course of the disease, but also causes complications. These include:
- inflammation of certain areas of the brain (meningitis, encephalopathy);
- herpetic conjunctivitis, keratitis;
- otitis;
- herpetic sore throat, stomatitis;
- mononucleosis;
- dysfunction of the digestive, cardiovascular, and nervous systems.
The herpes virus is present in a latent state in most people, regardless of age and lifestyle. Under the influence of unfavorable external or internal factors, the infection becomes more active. It is impossible to completely remove the virus, but you can create unfavorable conditions for its manifestation in a child. Active immunity and personal hygiene will help reduce the risk of infection. And if infection occurs, then the manifestations of the herpes virus will occur in a mild form.
Dr. Komarovsky about the herpes virus
Myths about herpes infection
With the onset of cold weather, more and more people with characteristic rashes on the lips appear. It would seem that this is a common and not at all mysterious disease, but the average patient knows nothing about herpes - except that “it’s a fever on the lips.”
Herodotus wrote about herpes a hundred years BC: it was the “father of history” who gave herpes its modern name (from the Greek “herpein” - to crawl) - due to the ability of herpetic ulcers to “spread” in different directions from the primary vesicle on the skin. Over many centuries of “communication” with herpes, this disease has become overgrown with myths.
Let's try to deal with the most common of them.
Myth 1. Herpes is not contagious.
Quite the opposite. Herpes is transmitted by airborne droplets (coughing, sneezing, talking), contact (kissing, sharing utensils, lipstick) and sexual contact. It is also possible that the child is infected from the mother while passing through the birth canal. Typically, this happens if the mother becomes infected with genital herpes during the third trimester of pregnancy. At the same time, her body does not have time to produce antibodies, which she passes on to the child. And if there is damage to the placenta, the child can become infected in the uterine period - this is called congenital herpes.
Myth 2. Herpes is a manifestation of a “cold.”
In fact, herpes is an independent disease that is caused by the herpes simplex virus. It is usually activated by hypothermia, stress, overwork, exacerbation of chronic diseases or a decrease in general immunity.
Myth 3. If rashes appear on the lips, the cold has subsided.
The popular view, however, has nothing to do with reality. In reality, rashes mean that a previous respiratory infection has weakened the immune system, and this has given the herpes virus the opportunity to be active.
Myth 4. If the rash goes away, herpes is cured.
This would be very cool, but, unfortunately, it is impossible to remove the virus from the body. It stays with a person for life, and you can only force it to be in a “sleeping” state. Therefore, 95% of people have the herpes virus, and the majority acquire it at the age of 3-4 years, but its manifestation is only in about 20% of people.
Myth 5. You can only get herpes if you have a rash.
Indeed, in the active phase of the disease, a larger number of viral particles are released and the likelihood of infection is higher. But infection can be transmitted at any time through invisible microtraumas of the skin and mucous membranes.
Myth 7. A condom completely protects against infection with genital herpes.
A condom does reduce the risk of infection, but, unfortunately, it does not provide a 100% guarantee. Transmission of the virus can occur through areas of the body not covered by a condom, or through certain defects in the “rubber friend” (for example, poor quality or excessively porous).
Myth 8. The best treatment is cauterization with alcohol, iodine or brilliant green.
Cauterization does not affect the herpes virus and its activity, but it is very easy to burn damaged skin and mucous membranes in this way. It is better to carefully lubricate the rash with an antiseptic that does not contain alcohol, so that a purulent infection does not occur. Namely, exacerbations of herpes are treated with special antiviral drugs, for example, acyclovir, which prevents the multiplication of the virus. For frequent exacerbations, medications that stimulate the immune system and restoratives are used.
Myth 9. Herpes is a harmless disease and only affects the skin.
In fact, herpes ranks second in mortality from viral infections, second only to ARVI. The herpes simplex virus is integrated into the genome of nerve cells, so the rash occurs at the sites of nerve endings and is accompanied by severe pain. Theoretically, herpes can appear anywhere there is nervous tissue, which means in almost any organ. With a decrease in general and local immunity, herpetic inflammation can develop in the mucous membrane of the mouth and larynx, cornea and conjunctiva of the eye, lymph nodes, internal genital organs, intestines, liver, kidneys, lungs and central nervous system. When the brain is damaged, most patients die or remain disabled.
In addition, with congenital herpes, multiple developmental defects and even the death of the baby are likely, and genital herpes significantly increases the risk of developing cervical cancer in women and prostate cancer in men.