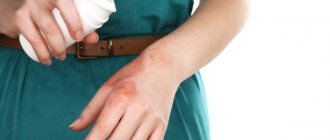
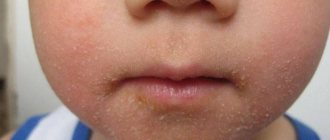
Eczema is an inflammatory skin disease of an allergic nature, characterized by a tendency to relapse and appearing in the form of burning, itching and rash on the skin in various places. Patients experience high skin sensitivity to various irritants, which explains the progression of eczema, often burdened by concomitant diseases.
The pathogenesis of the disease is similar to the mechanism of manifestation of allergic dermatitis. Often the latter is a disease that precedes the onset of eczema. The formation of eczema on the leg is one of the most common areas where it is located.
What does microbial eczema look like, what is the disease?
Microbial eczema of the lower extremities is a pathological phenomenon of a skin disorder, characterized by inflammation, the formation of red spots of different sizes, which then turn into wounds with a crust-like or film-like coating. Very often such phenomena show themselves around poorly healing wounds and cracks in the skin. For example, the foot may be affected due to cracks on it, which are very difficult to heal. In addition, microbial eczema on the legs, a photo of which can be studied in more detail in this material, can also occur after some underlying illness.
The skin must fulfill its main function - a kind of barrier to the entry of various bacteria and microbes into the body. But in the presence of such eczema, this function sharply worsens, so self-infection of the body occurs. That is why doctors always pay special and careful attention to this disease. The disease is classified in the classification of all eczemas (Classification “ICD-10”) as a unit that has its own code – L20-L30. In terms of contagiousness, such a disease is only transmitted by contact in cases where it is caused by a herpes or staphylococcal infection.
External signs of microbial eczema on the legs
In general, the following symptoms of the disease are distinguished:
- severe itching of the skin;
- rash;
- bubbles - vesicles;
- when the vesicles burst, serous fluid with an unpleasant odor flows out of them;
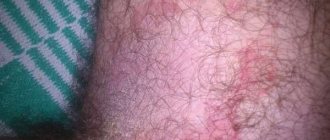
- redness in spots of different sizes or diameters;
- inflammation of the skin in the form of swelling above the surface of healthy areas of the epidermis;
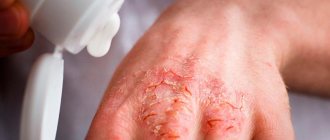
- open wounds;
- thin or thick crusts on oozing purulent wounds, peeling off over time;
- dry peeling on damaged skin;
- cracking of the skin with the formation of erosions and ulcers.
Foci of inflammation often have sharply defined boundaries, on the periphery of which there is a large accumulation of dying cells that turn into scales.
FOR REFERENCE: Depending on the localization of the rashes or vesicles themselves, they can merge into single “islands”, “lakes” with several screenings nearby - a couple of bubbles located not far from a continuous inflammatory accumulation.
Varieties
The types of this disease can also be called stages characteristic of the course of such a pathology, so they are easily classified according to the degree of development:
- Acute stage – duration from 2-3 weeks to 3 months. The developed spot on the skin itches, becomes wet, and itches.
- Subacute stage - noticed over a period of 3 months to 6 months. Peeling and thickening of crusts on the wounds are already occurring.
- Chronic stage – accompanies the patient for 6 months or more. Diseased skin is dense and differs in color from healthy skin.
If you focus on the symptoms of pain, itching, bleeding wounds, peeling and other things, then eczema that arises from microbial soil can be classified into the following types:
- Coin-shaped or nummular. The lesions are sufficiently isolated from each other by clear round boundaries 1-3 cm in diameter, similar to coins. It occurs less frequently on the legs than on the arms, but it still occurs.
- Varicose type. The primary cause will always be varicose veins in the legs. Affects the lowest part of the limbs.
- Paratraumatic variety. When postoperative wounds, leg ulcers, abrasions and other skin injuries on the legs do not heal well.
- Fungal mycotic eczema.
- Sycosiform. Caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: Weeping eczema erosions on the legs do not always accompany the disease. It may be completely absent, and the process may be dry, causing only wounds and peeling.
Possible complications
The greatest danger is the addition of a secondary infection - fungal or bacterial, as well as purulent inflammation of the skin. In this case, symptoms may be present: increased temperature (general and local), deterioration of the general condition, the appearance of purulent blisters and other signs. When the bubbles open, they emit an unpleasant odor. If such a clinical picture is detected, it is necessary to urgently seek medical help, which, as a rule, is provided in a hospital setting.
It is also possible to develop erythroderma. This pathological condition is characterized by the spread of the eczematous process to other areas of the skin and to the entire skin. This situation can occur due to improper treatment or excessive scratching of the affected areas.
Untimely treatment also has a negative impact on the course of the disease - necrosis or sepsis of diseased tissues may occur.
How is diagnosis carried out?
Before prescribing any ointment to a patient or choosing a method for treating microbial eczema on the lower extremities, doctors conduct a full examination to finally establish this disease.
Diagnostics proceed as follows:
- Visual inspection.
- Blood tests.
- Biopsy of a damaged area of skin.
- Laboratory tests are carried out to identify or exclude a particular pathogen - infection.
- Scraping to identify fungus.
- Bac sowing.
- Examination of skin cells by a histologist.
Such an examination is carried out not by one doctor, but by several specialists. The infectious disease specialist must understand which microbes visited the patient’s feet. The histologist will look for the cause in the correct development of epidermal cells. An allergist will rule out or identify the presence of substances that cause the rash. A nutritionist will prescribe proper nutrition and so on.
FOR REFERENCE: Finding the specific causative agent of progressive eczema is extremely important in order to then correctly prescribe antibiotics.
What provokes the development of dermatosis on the soles and heels?
Eczema on the heels, like any other types of dermatosis, affects the epidermis. As a rule, in this area of the body the disease is accompanied by peeling and painful cracks. The dry form of heel eczema in most cases is also characteristic of the acute, subacute, and chronic stages. Affecting the skin in any, even hard-to-reach areas of the human body, the disease is often localized on the sole and heel.
Eczema on the heels is a type of dermatosis
Among the reasons that doctors consider to be the main ones, there are several most likely factors:
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- genetic predisposition;
- constant stress, nervous experiences;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- weakened immune system;
- chronic diseases;
- infectious processes.
Often, heel eczema is the result of a complicated allergic reaction to detergents, cosmetics, socks, tights, low-quality shoes and other irritants. Sometimes eczematous signs can be detected due to a change in climate zone. Sudden temperature changes can also serve as an impetus for the development of pathology.
What treatment can there be for microbial eczema on the legs?
Any eczema, and especially microbial, should be cured only with an integrated approach. There is no such thing that the disease can be eliminated solely by some kind of antibiotic or a special diet - all treatment works when medications, ointments, children, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and so on are used. A pathology such as microbial eczema on the legs, the treatment and photo of which can be found here, can be healed using both traditional medicine and folk methods. But in order to treat such a disease as effectively as possible, it is best to immediately consult a professional doctor and diagnostician. Let's consider these several treatment options, which, by the way, can be combined or used alternately.
Remove microbial eczema of the lower extremities using classical medicine
A systematic approach to eliminating a disease always first of all takes into account the main and secondary causes that led to its formation. Therefore, those drugs are prescribed that are either aimed at eliminating one or more causes, or have a wide spectrum of action.
The following main approaches can be distinguished:
- The use of local anti-varicose agents.
- External use of antifungal agents.
- Adding antibiotics to eliminate the cause of the inflammatory process.
- To eliminate weeping, antiexudative drugs for external use are used.
- Any auxiliary products made on the basis of natural ingredients, such as, for example, birch tar or naphthalan oil, serve as excellent antibacterial drugs.
By the way, almost all antibacterial drugs also dry out eczema wounds. Any treatment of microbial eczema on the legs should be accompanied by medical supervision. This is extremely important, because for example, if he prescribed hormonal ointment, then he is obliged to monitor the patient’s condition with a certain regularity and frequency.
Physiotherapeutic approaches include:
- Skin treatment with ultraviolet light.
- Application of laser therapy.
- Connection of ozone therapy.
- Use of magnetic therapy.
Among the many medication options that may be prescribed are:
- any sedatives that can calm the patient’s nervous irritation, as well as irritation of the skin itself;
- vitamin complexes or a separate intake of vitamin B;
- antihistamine creams, ointments or tablets reduce the risk of allergic development;
- desensitizers such as Diazolin, Loratadine, Suprastin.
IMPORTANT! When the disease is of a fungal nature, antibiotics cannot be taken orally, and it is also impossible to use external agents based on antibiotics.
What ointments are used for illness
A popular way to get rid of the disorder is treatment with drugs used externally. This includes creams, gels, ointments.
Medicinal ointments
Ointments are produced for eczema of the feet. It is difficult to navigate among the assortment and choose the right drug. It is important to choose an effective and reliable tool. It is better to trust a doctor who will help you choose an option in a particular case. Let's consider effective and proven ointments for eliminating the disease.
Microbial eczema on the legs treatment with folk remedies
Additional treatment methods that periodically exert their auxiliary effective influence on healing are non-traditional approaches, the use of traditional medicine recipes. In fact, there are a lot of them now, but when choosing something from those proposed by non-traditional specialists, you should always consult with your doctor. After all, some masks, poultices, ointments, made with your own hands at home, may not be compatible with pharmaceutical medications. The most rational approach when eliminating microbial eczema on the legs, treatment and ointment, its selection should always be carried out taking into account the patient’s individual tolerance of certain ingredients.
In general, treatment with folk remedies is almost equally effective for everyone when:
- A product such as fish oil is used in the form of applications. Lotions are made for 3 days in a row.
- Applications with resorcinol and boric acid are also good, if they are still produced by pharmaceutical companies.
- Chamomile lotions are very effective in relieving inflammation.
- Bathing in a bath with infusions of string, chamomile, and celandine can remove inflammation, kill germs and bacteria, which is key in healing this disease.
- Coniferous poultices, if the wounds are not yet open, or from the leaves of a tree such as a walnut.
- Drink yarrow infusion or make lotions.
- Compresses made from elderberry leaves and many other options that are easy to find on the Internet on the websites of trusted specialists with good patient reviews.
IMPORTANT! At home, the use of alternative medicine alone will not completely cure microbial eczema.
What is the preventative method: 10 warnings?
To prevent the appearance of a microbial skin disorder on the legs, a photo of which can be seen here, you just need to remember simple rules and follow them. We suggest studying 10 preventive preventative measures:
- Avoid damaging the skin of your feet.
- Maintain personal hygiene regularly.
- Try as much as possible not to be nervous or worry.
- Move actively, visit baths, saunas, play sports - do everything to ensure that blood flow normally circulates throughout the body.
- Do not wear synthetic clothing, do not wear tight or poorly breathable shoes, so as not to cause unnecessary irritation and diaper rash of the skin.
- Regularly checking your hormonal levels is necessary to prevent many other diseases, not just leg eczema.
- Work in hazardous or harmful production exclusively in protective clothing to avoid contact of the skin of your feet (or hands, face, etc.) with chemicals, poisons and other pathogenic substances.
- You shouldn’t put any physical activity on your legs, and if you feel tired after a working day, take tonic foot baths or apply any cream that relieves tired legs.
- The first signs of varicose veins are the formation of “stars” on the legs. You should immediately consult a doctor for treatment before the veins become swollen and nodes form on them.
- Sleep with your legs elevated on a slight elevation. It is enough to place a small sofa ottoman or pillow under your feet so that your feet can fully rest during the night.
And most importantly, always contact your doctor in a timely manner so that you can rush to treat the sore in time. Because in an advanced or chronic condition, it can be very difficult to eliminate the severity of the disease, and in other cases it is even impossible. You shouldn’t prescribe or buy foot cream for yourself. After all, it is still unknown what the true reason led to the active development of microbial eczema. Therefore, to begin with, it is better to undergo a full examination, then get the doctor’s recommendations and carefully follow them.
Characteristic symptoms as heel eczema progresses
The inflammatory eczematous process developing on the heel is almost impossible to confuse with something else. As already mentioned, dermatosis in this area of the leg is manifested by dryness and peeling.
Signals that alert the patient that it is necessary to urgently contact specialists are the following manifestations:
- tissue hyperemia, slight swelling;
- unbearable itching;
- thickening of the skin;
- peeling of the keratinized epidermis;
- burning and pain, especially when walking.
Despite the fact that the disease is not dangerous to others and is not transmitted to others, the disease can spread throughout the patient’s body in fairly short periods of time. Timely therapy, adherence to the rules of a healthy diet, hygiene and routine will help to avoid the progression of the disease and the occurrence of eczematous symptoms in other parts of the body. It is worth noting that if the disease is not treated, the patient’s psychological state suffers. The discomfort that the patient constantly experiences causes irritability and insomnia, which can lead to headaches and general weakness of the body.
Eczema on the heels (dermatosis) is not dangerous to others and is not transmitted