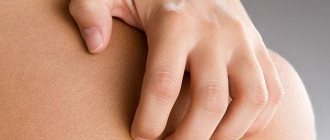
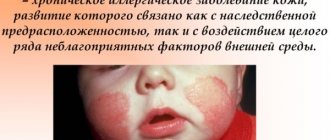
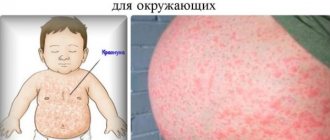
Throughout life, a person acquires many diseases, but there is a group of diseases that are inherited. One of these diseases is atopic dermatitis in adult patients (pictured).
The incidence of dermatitis among adults is 5-10%, but in countries with a developed industrial system the incidence rate can reach 20.
Every year there are more and more cases of atopic dermatitis. As a rule, atopic dermatitis very rarely occurs as an independent disease. In 35% of cases it is complicated by asthmatic diseases, 25% by rhinitis, and 10% by hay fever. Women get sick much more often than men.
Factors in the development of atopic dermatitis
This disease is most often inherited - from mother to child. As a rule, most patients who suffered from atopic dermatitis in childhood experience similar symptoms as adults. Often, as a result of atopic dermatitis, there are causes for allergies and asthmatic diseases.
The most common causes of atopic dermatitis:
- genetic predisposition;
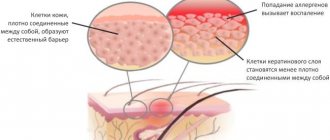
- increased sensitivity of the skin;
- functional and biochemical disorders of the epidermis;
- sometimes the causes of the disease are directly related to stressful situations and psycho-emotional stress;
- poor nutrition;
- poor environmental conditions (pictured).
In addition, atopic dermatitis in adults can be triggered by numerous allergens (animal waste products, dust mites, synthetics, pharmaceuticals, plants, etc.).
Eczema
Eczema is a complication of dermatitis that appears against the background of nervous breakdowns and individual irritants. In its mild form, a pale rash appears on the skin and flaky spots appear.
In severe forms of the disease, the color of the spots on the skin becomes more intense, a rash appears moist to the touch, and blisters appear. Touching the discharge can crush the blisters, which can lead to infection. For this reason, the disease often becomes severe. With improvement, crusts and sometimes scars form.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis
The main symptoms of the disease are expressed by the following manifestations:
- There is a painful itching, which most often occurs at night. This can cause scratching and lead to the development of staph and streptococcal infections;
- The patient experiences increased dryness of the skin. At the same time, the skin begins to peel off and its color may change;
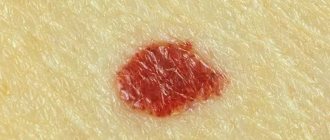
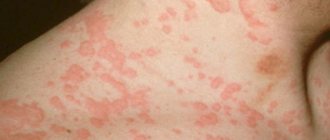
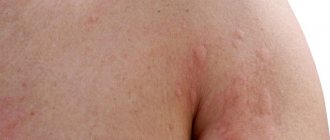
- In adult patients, atopic dermatitis is characterized by hyperemic rashes in the acute period. It is characteristic that if in infancy the rash is localized in the popliteal cavity, on the arms and legs, then in adults a more dense structure and relief appears (pictured).
At each age there are characteristic symptoms. In newborns, they appear as red spots only on the face, arms and legs. In adolescence, the rash is pronounced on the arms and neck. In adults, rashes can appear on any part of the body, but most often on the head, hands, elbows, face, neck and legs. Very rarely, the rash appears on the back, chest and feet.
Dermatitis caused by internal causes
Among the skin diseases that arise due to internal causes, the following can be listed:
- Eczema and seborrheic dermatitis (forms in areas where sebaceous glands are concentrated and can even affect the scalp and genitals).
- Infectious (reaction of the human body in the form of a rash to exposure to infection).
- Rash at the vaccine injection site.
- Inflammation of the skin due to pathologies of internal organs (kidney disease, pancreas disease, etc.).
- Neuropsychic effects (itching for a short period of time, up to several hours).
- Food (the body's response to food allergens; old, stale foods; food with a lot of dyes and chemical additives, for example, synthetic crab sticks or sweet fizzy drinks).
- Medication (allergic response of the body to some drug; heavy dose of medication; incorrectly selected medications).
Treatment of atopic dermatitis for adults
Therapeutic measures to relieve the symptoms of atopic dermatitis are prescribed taking into account the severity of the disease, the presence of chronic infections and the age of the patient. As a rule, the treatment of atopic dermatitis in adults today includes the use of many drugs that act in different directions.
These include:
- First of all, antihistamines are prescribed (Fenkarol, Zyrtec, Cetirizine, Tavegil, etc.), which can neutralize the acute symptoms of the disease. It is important to consider that first-generation antiallergic drugs have a number of side effects such as lethargy, drowsiness and inability to concentrate. In addition to antihistamines, it is recommended to take membrane stabilizers (Ketotifen, etc.). Drugs in this group smooth out the immune reaction to the allergen;
- It is imperative to treat dysbiosis, since the beneficial intestinal microflora is suppressed by numerous pharmacological drugs. Most often, a course of Hilak, Linex, etc. is prescribed. In addition, enzyme preparations Mezim-Forte, Panzinorm, Festal, etc. are prescribed together with dysbacteriosis;
- in cases where atopic dermatitis is accompanied by secondary infection and complicated symptoms of the disease are observed, treatment with antibacterial agents (Erythromycin, Sumamed, etc.) is recommended. When weeping wounds and hard scabs appear, therapy with anti-inflammatory and disinfectants is recommended. Rubbing the skin with a brewed solution of chamomile has a positive effect;
- if an acute attack of the disease has developed as a result of a stressful situation, dermatitis can be cured, in accordance with medical prescriptions, in complex therapy by taking sedative tablets as prescribed by the doctor - Novopassit, Persen, valerian infusion, motherwort;
- Treatment of adult patients and children is often carried out with steroids, both general and local. However, before using hormonal ointments, you should consider a number of contraindications for their use. Glucocorticosteroid drugs (Lokoid, Advantan) for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in young children are allowed from 6 months. After reaching 2 years of age, Elokom, Momat and Laticort can be used. In adulthood, hormonal ointments Mometasone, Triderm and Celestoderm are prescribed. If treatment with the above pharmaceuticals is ineffective, it is recommended to prescribe Interferon and Cyclosporine. It should be remembered that, despite their effectiveness, steroid drugs are not allowed to be used for long;
- In addition to steroid drugs, non-hormonal ointments and creams are actively used in the treatment of dermatitis (Eplan-cream, Bepanten, Pantoderm, Panthenol, Skin-Cap cream). Antifungal cream Exoderil is often used. Non-hormonal external agents (ointments and creams) have less effect on dermatitis, but they are preferred in therapy, since they have virtually no side effects.
To strengthen the body's defenses, vitamins (B, C, E) are prescribed. Vitamins can be taken either orally or by injection. In addition, therapy with medications, including ointments and creams, includes physiotherapy (magnetic therapy and phototherapy). If an allergic reaction to medications develops, reflexology and treatment with homeopathic remedies are recommended.
Symptoms of the disease
Atopic dermatitis is characterized by:
- rashes on the head, face, cheeks, lips, elbows and knees, shoulders and back, feet;
- very dry skin, peeling;
- intolerable itching, burning;
- transformation of redness into weeping blisters (experts call this process “wetting”);
- thickening of skin areas after inflammation is relieved, formation of cracks, enhancement of the natural “pattern” of the skin;
- dependence of relapse on the time of year (remission usually occurs in summer).
Chronic dermatitis is characterized by swelling and redness of the feet (called “winter foot symptom”).
Other symptoms are also possible: “fur cap” - when hair falls out on the back of the head, Morgan's symptom - when the lower eyelids “cut through” deep wrinkles.
Video about the treatment of dermatitis in a child from Dr. Komarovsky’s school:
Folk remedies for atopic dermatitis
Folk remedies (potions, lotions, compresses) have a positive effect in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. However, it should be remembered that children and adults can only be treated with them in combination with traditional therapy.
The most commonly used folk recipes are:
LOTION. Dermatitis can be cured by using medicated lotion as an aid. In order to prepare it, you should take 1 tbsp. l. Veronica officinalis and pour 200 ml. hot water. The solution is left to infuse for 3-4 hours, after which it is filtered. It is recommended to wipe the affected skin with the prepared lotion up to 6 times a day. The medicinal solution is absolutely safe and has no side effects.
COMRESS. It is recommended to use compresses from folk remedies in treatment. A compress with raw potatoes, which is very easy to prepare at home, has a positive effect. It is necessary to wipe 1 raw potato (previously washed and peeled), wrapped in gauze and applied to the affected area overnight. You can prepare a cucumber compress in the same way.
OINTMENT (ANTIPRITIC). To relieve itching and hyperemia of the skin, it is recommended to prepare a special ointment. You need to take 1 tbsp each of butter and glycerin. + 2 tbsp each chamomile, fireweed and pre-boiled hay dust. Chamomile and fireweed should be poured into 800 ml. boiling water and boil over a fire for at least 10 minutes, after which dust, glycerin and oil are added to the solution. The mass is boiled over low heat until it becomes a thick porridge. The prepared ointment should be stored in a cool, dark place. It is recommended to lubricate the affected areas up to 4-5 times a day.
FOR INTERNAL RECEPTION. Traditional recipes provide for any form of treatment, including oral treatment. To prepare a medicinal solution for oral administration, you can take equal proportions of herbal powder:
peppermint, tricolor violet, oregano, elecampane root and chamomile. Pour this mixture with hot water in a ratio of 1 tsp. l: 1 tbsp. boiling water After cooling and filtering, it is recommended to take 100 ml of the solution. after eating.
In addition, patient reviews note an improvement in their general condition after ingesting a decoction of raw oats. To prepare the solution, take oats and add water in a ratio of 1:5, after which the solution is boiled for 10 minutes and then squeezed until mucus is obtained. It is recommended to take this remedy for 1 month before meals. Adults – 2 tbsp. spoon, children - 1 tbsp.
It should be borne in mind that the treatment of atopic dermatitis with traditional therapy and folk recipes is a rather lengthy process and important importance is assigned to the strict implementation of all medical recommendations and adherence to a hypoallergenic diet.
Williams criteria for diagnosing AD
According to the Williams criteria, to diagnose atopic dermatitis, it is necessary to establish whether itching has occurred within the last year and at least 3 of 4 symptoms:
- involvement of skin folds (elbow and knee), changes in the neck or around the eyes;
- coexistence of other atopic diseases, for example, bronchial asthma or hay fever (when diagnosing children under 4 years of age, atopic diseases in 1st degree relatives are taken into account);
- general dry skin throughout the year;
- visible inflammatory changes in the flexion areas of the limbs and on the cheeks/forehead and elongated parts of the limbs in children under 4 years of age or onset of the disease before the age of 2 years (not applicable if the child is under 4 years of age).
Recommended Diet
Diet for atopic dermatitis in adults is a prerequisite for treatment. It must be taken into account that with atopic dermatitis, adults must have a balanced diet in order to maintain the necessary complex of vitamins and minerals.
With the development of the atopic form of the disease, foods that cause an acute allergic attack should be excluded from the diet. The most common provocateurs of the disease are:
- canned and pickled foods;
- sausages and smoked meats;
- milk products;
- chicken eggs;
- You can’t eat fatty fish and meat;
- citrus fruits, strawberries;
- vegetables and fruits (including freshly squeezed juices) of bright color;
- sauces, hot spices;
- bee products, chocolate, nuts, cocoa;
- red wine, soda, fast food.
SAMPLE MENU IN THE TABLE FOR ATOPIC DERMATITIS FOR ADULTS:
A nursing woman should exclude white bread and whole milk from the menu. Patients with atopic dermatitis need to include in their diet foods with unsaturated fatty acids that are present in fish. However, it is highly allergenic, so it is recommended to use vegetable oils enriched with omega acids, which are found in flaxseed oil and olive oil.
In addition, the diet should contain fermented milk products, since they contain useful microelements that are not received by the body as a result of intolerance to cow's milk. An additional advantage of fermented milk products is their beneficial effect on the intestinal microflora, since dysbiosis contributes to the complicated course of the disease.
It is recommended to cook food in a steam bath, as this cooking method reduces the allergenicity of foods. Sometimes a patient who cannot eat fresh red vegetables (tomatoes, peppers) responds normally to the use of thermally processed vegetables in their diet.
Atopic patches (ATP)
Atopic patches are a type of epidermal patches in which specially prepared allergens are applied to the uninjured skin of the patient's back and sealed. They are used to detect delayed allergenic reactions that cannot be detected by skin prick tests.
Atopic patches are a very good addition to the diagnosis of AD with substances that the patient must eliminate from life in order to reduce the symptoms of the disease.
Atopic patches
Preventive actions
- To prevent the appearance of atopic dermatitis, it is recommended to spend a lot of time outdoors, engage in dosed physical activity, and relax in a maritime climate, since sea air has a beneficial effect on the body.
- Atopic dermatitis requires the exclusion of synthetic clothes and bedding. Patients are recommended to use natural cosmetic products, without adding fragrance or dye.
- You should avoid temperature changes and refuse to keep pets that can provoke an allergic reaction.
It is necessary to follow the doctor's recommendations when treating the disease with traditional therapy and folk remedies. This is the only way to prevent relapses of atopic dermatitis and get the most positive result.
Forms of eczema
Since the causes of eczema are numerous, the forms are also varied:
- neuropathic eczema (as a result of a weak nervous system);
- reflex eczema;
- paratraumatic disease (after injuries);
- microbial (consequence of infection);
- professional (as a result of contraindications for work activity).
The most difficult things to cure are atopic dermatitis and eczema (the difference between them is minimal - only a doctor can make a diagnosis), the causes of which have not been fully studied by doctors until now. There are speculations that the cause of the disease is the insufficiently effective functioning of the immune system. In addition, the disease can pass from parents to children.
There are many similarities between atopic dermatitis and childhood eczema. However, each disease has its own specific characteristics. There is a big difference between atopic dermatitis and eczema. The atopic form is included in the group of childhood dermatitis, united by several symptoms. They depend on the patient’s age and the individual characteristics of the child’s health. During the inflammatory process (especially when combined with respiratory allergies), people show greater sensitivity to a whole range of food, household and pollen substances.
Eczema of atopic dermatitis manifests itself from birth to two years. At the same time, patients are also often diagnosed with manifestations of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and other organs and systems.
Disease prevention
For patients in remission, doctors provide preventive therapy. This delays the onset of the acute stage, and sometimes completely relieves a person from an unpleasant disease.
Prevention includes a hypoallergenic diet, relaxation in a sanatorium, and baths with sea salt. It is also necessary to exclude any contact with allergens that can cause an outbreak of the disease.
For adults, and especially for children, hygiene and the use of natural rather than synthetic underwear are extremely important.
The best ointments and creams
The doctor should select products for external use, based on the general condition of the skin and the degree of its damage by the disease.
| A drug | Action |
| Isis | An effective antiseptic. Relieves inflammation on the skin. Increases skin resistance to negative environmental factors. |
| Akriderm | Corticosteroid. Relieves itching, inflammation, reduces swelling and redness. |
| Flucinar | Hormonal ointment that has a drying effect. Reduces redness, swelling, has contraindications. |
| Celestoderm | Reduces inflammation, itching, the ointment is effective for all types of dermatitis. |
Treatment of atopic dermatitis on the face should begin after the first signs of the disease appear. This will allow you to quickly relieve unpleasant symptoms and alleviate the condition. Taking medications, using ointments and following a diet will allow you to achieve long-term remission without relapse.
Treatment of neurodermatitis
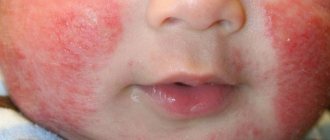
The main thing in therapy is the elimination of the allergen, including through menu correction. It is very important to reconsider the diet of a nursing mother if the atopic dermatitis shown in the photo is allergic and is observed in infants.