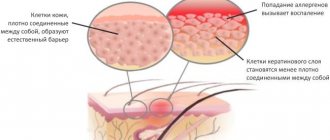
There are several different opinions about the group of diseases to which atopic dermatitis belongs. Some experts believe that we are talking about a skin disease, others insist that this is a genetic variation of the disease, and the third group points to the immune nature of dermatitis. In fact, all theories are true. Atopic dermatitis is a genetic disorder (complicated by heredity) that leads to a pathological immune response of the body, which appears as a lesion of the skin. Due to its prevalence, it is important to know what atopic dermatitis is (ICD-10, symptoms, difference from a number of other diseases).
Causes
The disease is mainly caused by heredity.
Problems that activate the process of exacerbation of the disease
The course of the disease is recurrent, alternating with stages of remission. The following factors especially aggravate it:
- environmental and climatic anomalies;
- unbalanced diet;
- expansion of the range of allergic reagents;
- nervous overload;
- immune disorders;
- early feeding of infants.
Dermatitis worsens as a result of a reaction to allergens and irritants.
Prevention measures
Prevention is designed to reduce the number of relapses to the minimum possible.
To do this you need:
- Avoid contact with causative allergens and limit contact with potentially dangerous ones.
- Control the humidity in the room and avoid dusty, dry air.
- Follow a diet, limit the consumption of allergy-provoking foods: chocolate, honey, citrus fruits, nuts and others.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Introduce taking vitamins in the form of complexes during periods of deficiency.
- Take proper care of your skin, keep it clean, avoid hypothermia, overheating, and direct contact with household chemicals and synthetic fabrics.
- Try to reduce the manifestations of possible chronic diseases to a minimum.
- Carry out preventive measures against helminth infection.
- During the flowering period of plants (April - June), monitor the manifestations of allergic reactions to pollen.
- Avoid stressful situations, do yoga, relaxation. If signs of nervous overload appear, take mild sedatives.
Treatment for atopic dermatitis can take quite a long time. The patient must follow strict rules during treatment and relapse of atopy, the cause of which may be a hidden chronic form of any disease.
It may take years to find her. It is important not to despair, not to be afraid to try different methods of therapy, to try to stop the exacerbation and to believe in a complete recovery. Simple optimism and faith in a cure is half the success.
Symptoms
The main signs appear on the surface of the skin.
- irritation;
- severe itching;
- dryness.
When scratching, a secondary infection (viral or bacterial) develops.
Most common symptoms:
| Symptom name | How it manifests itself |
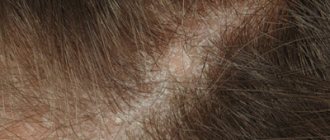
| "Fur hat" | Changes in the condition of the hair on the back of the head (becoming weaker, sparse) |
| Morgana | The appearance of deep wrinkles in large numbers on the eyelids of children |
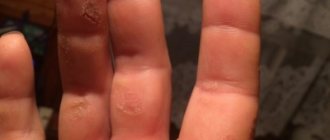
| "Winter foot" | Overflow of blood vessels of the soles, peeling, puffiness, cracks |
| "Polished nails" | The appearance of shine in the nails, grinding of their edges due to scratching |
Secondary symptoms are physical, psychological, domestic, cosmetic, emotional discomfort and complexes.
Periods of the disease
Dermatitis occurs especially often in older infants (from 2-4 months to 1 year). Before the age of 5 years, dermatitis occurs, but less frequently.
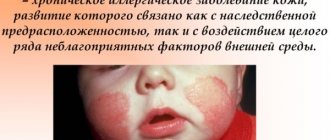
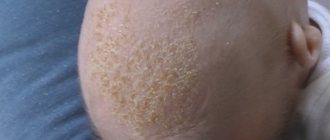
Atopic dermatitis in children
The early development of the disease is explained by the predisposition of infants to allergic diseases.
Atopic dermatitis in children: photo
Prerequisites for early dermatitis:
- poor nutrition and lifestyle of the mother during pregnancy;
- the child’s immature immune system.
The disease often resolves by age 4, but occurs in adolescents and adults. Before the age of 5 years, 90% of the manifestations of the disease are recorded.
Atopic dermatitis in adults
Symptoms tend to subside with age. However, the disease may manifest itself and even occur for the first time in adolescents and adults. By the age of 15-17 years, the disease recedes on its own in 70% of cases. Only 30% flows into the adult form.
Clinical indicators in different phases:
| Characteristics | Phase | |
| Infant and children | Adult | |
| The main manifestation is itching | + | + |
| Formation color | Hot pink | Pale pink |
| Places of formations | Face, buttocks, arms, legs | Area of the popliteal, elbow bends, face, neck |
| Forms of formations | Bubbles, wetting, crusts, scales | Papules, skin pattern, dry skin, peeling, cracks. |
The disease progresses differently, depending on the phase, cause, and other diseases.
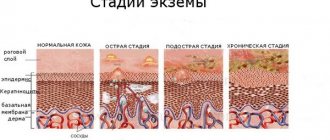
Seasonal exacerbations occur in spring and autumn. Stages according to the nature of the course: acute, chronic.
Atopic dermatitis, photo in adults
At the first suspicion of the occurrence of this disease, you should not isolate yourself from others. The peculiarity of the disease is that it is not at all contagious. Although, studying what atopic dermatitis is and looking at photos of bright rashes all over the body in adults, it is difficult to believe that they are safe for others.
Treatment
Since symptoms differ between children and adults, treatment also differs. The process is quite complicated. The basis is diet, drug therapy, specific hyposensitization (reduction of general sensitivity to the allergen).
Main objectives of treatment
- elimination of the allergic factor;
- relieving inflammation and itching;
- cleansing the body of toxic substances;
- prevention of complications and relapses.
When treating, age, the presence of concomitant pathologies, and clinical severity are taken into account.
Treatment methods
Treatment methods are selected by the attending physician in combination. The most common:
- drug therapy;
- use of laser;
- photochemotherapy (PUVA);
- blood purification (plasmapheresis);
- measures to reduce susceptibility to the allergen (hyposensitization);
- exposure to needles (acupuncture);
- diet.
Diet therapy
It is designed to regulate nutrition, which helps improve the condition and helps prevent exacerbation. Firstly, food allergens are completely excluded. Milk and eggs are not recommended, even if tolerated.
With a hypoallergenic diet, the following are completely excluded:
- fried meat and fish;
- vegetables, mushrooms;
- honey, chocolate;
- melon, citrus fruits;
- strawberries, black currants;
- canned food, spices, smoked meats.
Diet is especially important for atopic dermatitis in children . The following dishes should prevail on the menu:
- porridge: buckwheat, rice, oatmeal;
- cheese, cottage cheese, butter, fresh vegetable salads, fruits;
- vegetarian soups with sour cream;
- meat dishes: boiled meat, meatballs, cutlets and steamed meatballs;
- side dishes: boiled rice, pasta, stewed cabbage, mashed potatoes;
- drinks: tea, compote, kefir.
It is recommended to limit salt intake.
Drug therapy
Includes different groups of drugs:
| Group | Action | Recommendations | Name |
| Antihistamines | Relieves itching, swelling | Change weekly to avoid addiction | Loratadine, Clemastine, Hifenadine |
| Corticosteroids | Relieves attacks and unbearable itching | Appointed at the initial stage for a short period of time | Triamcinolone, Methyprednisolone |
| Antibiotics | Anti-inflammatory | For purulent complications | Metacycline, Doxycycline, Erythromycin |
| Antiviral | Fighting viruses | For viral complications | Acyclovir |
| Immunomodulators | Strengthening the immune system | If necessary | Echinacea, Ginseng |
| Sedatives | Relief of itching and general condition when affecting the nervous system | Prescribed when the disease is associated with stressful situations to relieve fear, depression, insomnia | Motherwort, Nozepam, Bellataminal |
Local treatment
It takes into account the nature and prevalence of the pathology, age characteristics, complications, and other factors.
Action of drugs : anti-inflammatory, decongestant, drying, antipruritic, disinfectant.
Forms : lotion, ointment, paste, cream.
Representatives : Losterin, Prednisolone, Flumethasone.
The use of emollients for atopic dermatitis in children
These are substances that soften and moisturize the skin, protecting it from irritants. Particularly effective in early childhood after bathing.
They are produced on the basis of hypoallergenic ingredients without the presence of harmful chemical compounds.
List of funds:
- A-Derma;
- Bioderma Atoderm;
- Topicrem;
- Oillan;
- Physiogel intensive;
- Dardia.
The use of emollients helps fight dryness, inflammation, and skin damage during manifestations of atopic dermatitis.
Atopic dermatitis on the face of a child (photo)
Dr. Komarovsky conducted extensive research on how to treat atopic dermatitis in a child . Among the important reasons, he identifies the child’s overeating, his intake of food in greater quantities than he is able to digest. For pathologies in children, Komarovsky suggests treating in three directions:
- Minimizing the entry of harmful substances from the intestines into the blood. Fighting constipation, dysbacteriosis, increasing meal times, reducing the concentration of infant formula, using activated charcoal, dosing sweets. The main thing is not to overeat.
- Avoid skin contact with irritating factors. Boiling water before bathing, using children's washing powders, natural fabrics, bathing with soap no more than 2 times a week, taking care of the quality of toys.
- Creating conditions to reduce children's sweating. Maintain temperature and humidity conditions, do not wrap yourself up excessively, and drink enough liquid.
Treatment with folk remedies
People practice decoctions for oral administration, means for local treatment, baths with special agents, and compresses.
Some folk recipes:
| Ingredients | Cooking method | Application |
| Bay leaves – 4 pieces, boiling water – 200 ml | Combine, leave covered until cool, then strain | Take 40 ml orally before bedtime for children, and 100 ml for adults; course – 10 days |
| Viburnum berries – 5 spoons, boiling water – 1000 mg | Combine, leave covered for up to 10 hours, strain | Drink 200 ml throughout the day for children, 400 for adults; course – up to 2-3 weeks |
| Oatmeal – 3 spoons, hot cow’s milk – 1 liter | Mix until smooth | Apply the substance to the skin for 20 minutes, then rinse and lubricate with nourishing cream |
| Veronica (medicinal herb) – 1 spoon, boiling water – 1 glass | Infuse, covered and wrapped, for 2 hours, then strain | Wash the affected areas with lotion up to 6 times a day; the course is not limited |
Also popular among the people are baths : coniferous ones, with chamomile and string, calendula, mint and other medicinal plants. It is practiced to add soda or starch to combat dryness. It is recommended to wash the skin on the face and other parts of the body daily in the morning with a 1:10 solution of vinegar and water.
Many folk remedies reduce symptoms and treatment becomes more effective.
Complications
They arise due to injury to the skin by scratching. Because of this, its protective properties are reduced, resulting in infections.
Types of complications
| By frequency of occurrence | Type of skin infection | Pathogen | Manifestation | Where does it occur? |
| 1 | Bacterial (pyoderma) | Different types of bacteria (cocci) | Pustules, crusts on the skin, malaise, fever | Head, any parts of the body, limbs |
| 2 | Viral | Herpes virus | Clear bubbles with liquid | Mucous membranes and skin of the face, surface of the throat, genitals |
| 3 | Fungal | Yeast-like fungi | Round rash lesions, thrush in children | Folds on the skin, nails, head, feet, hands |
Preventive measures help avoid complications.
Prevention Starts before the baby is born.
Primary – prevention of dermatitis
Natural feeding, limiting medications, and following a diet are necessary.
Secondary – prevention of relapses, exacerbations
- exclusion of causes and provoking factors;
- compliance with the prescribed diet;
- taking preventive medications;
- skin hygiene.
Interaction with other drugs
Possible interactions with the following drugs:
- Folic acid, cyanocobalamin – increasing the effectiveness of Potassium orotate.
- Cardiac glycosides – improving their tolerability.
- Potassium-sparing diuretics, ACE inhibitors - hyperkalemia may develop.
- Astringents and enveloping agents - reduce the absorption of Potassium orotate in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Glucocorticosteroids, muscle relaxants, oral contraceptives - reduce the effectiveness of Potassium orotate.
Hygiene features
Hygiene rules are recommended to keep the skin in order:
- do not wash with a washcloth every day;
- use hypoallergenic soap;
- prefer a warm shower to a hot one;
- blot with a towel rather than rub;
- moisturize the skin with special products;
- use clothes made from natural materials.
Complete recovery is considered to be the absence of symptoms for 3 to 7 years. The interval between the stages of exacerbations lasts from a month to several years.
If left untreated, there is a risk of developing bronchial asthma. It is necessary to carry out treatment under the supervision of a specialist.
Competent prevention and lifestyle protect against relapses. It is important to be attentive to your own body, follow a diet, and take care of the condition of your skin.
Diet
One treatment for atopic dermatitis is not always enough. A positive result will come faster if you follow a diet. You need to know what you can eat with atopic dermatitis without fear of exacerbation of the disease. Doctors advise completely removing allergenic foods from the menu: eggs, chocolate, alcohol, citrus fruits and fruits with red peels.
Video: Dr. Komarovsky “Atopic dermatitis.”