Main features of the disease
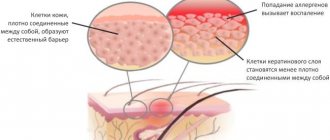
The top layer of skin becomes inflamed, and when it becomes chronic, irritation appears and scales form. Pathologies of this kind occur in skin areas with a denser distribution of sebaceous glands.
The main provocateurs of seborrheic (gneiss) dermatitis are yeast-like fungi, which are a component of the skin microflora. Fungi (Malassezia restricta, Malassezia furfur and Malassezia globosa) prefer a more nutritious environment, which is exactly what is found around the sebaceous glands.
With normal regulatory function of fungal populations, the epidermis responds normally to their presence. As for newborns, their fragile body cannot withstand the irritating effects of polyunsaturated acids secreted by fungi.
Prevention
To prevent seborrheic dermatitis, you must adhere to the following rules:
- During pregnancy, the expectant mother should lead a healthy lifestyle with good nutrition, avoid stress and contact with infections.
- Strictly follow all hygienic measures to care for the baby.
- When bathing your baby, use only hypoallergenic, fragrance-free baby soap.
- Avoid overheating the scalp by wearing numerous hats and scarves. At home, the baby's head should be open.
Seborrheic dermatitis is not a dangerous disease, but it is still not worth treating a child on your own without consulting a doctor.
Under the mask of harmless dandruff, other childhood dermatoses (atopic dermatitis and psoriasis) can be hidden, which without timely treatment become chronic forms that significantly worsen the child’s quality of life.
Causes of seborrheic dermatitis
The results of the studies have not yet made it possible to identify the etiology of the disease in question. Although the reasons for its appearance have been identified:
- Hereditary trait - the ability of the body to change the chemical composition of the secretion secreted by the sebaceous glands is transmitted. Thus, a condition is inherited that creates fertile soil for the development of gneiss. The child inherits a tendency to increased secretion, so excess sebum interferes with the normal functioning of the protective function of the epidermis.
- Stage of formation of hormonal levels. In the postembryonic period, the baby's blood contains hormones received from the mother at the time of intrauterine development. Their presence activates the functions of the sebaceous glands, which will provoke hyperfunction or hyperplasia.
- Weak immunity gives the green light to the sebaceous glands, which are present on the skin in the form of spores. Lipophilic fungi (Malassezia furfur) multiply, causing inflammation on the skin. With reduced local immunity, the sebaceous glands go into hyperfunction mode and secrete a huge amount of secretion. Such bursts of fungal activity contribute to the disruption of the natural process of rejection of dead cells. They remain on the skin, glued together with excess fat, forming scales and flaky crusts on the body, in particular on the baby’s head.
- Secondary immunodeficiency is infection of the fetus during intrauterine development.
- Impaired functioning of the gastrointestinal tract due to a lack of essential vitamins and microelements for normal metabolism, as well as due to dehydration of the body.
- Fatty, spicy, fried and sweet foods should not prevail in the diet of a nursing mother. When artificially feeding a baby, you should make the right choice of baby food.
- Infectious diseases suffered by the baby suppress the immune system, which becomes the cause of seborrhea.
- Taking antibiotics, glucocorticoids.
- Disturbance of intestinal microflora – dysbacteriosis.
- Failure to comply with hygienic requirements for caring for a newborn.
- Using detergents when bathing and washing a child’s hair that contain allergenic components. As a result of the destruction of the protective layer on the baby's skin, the increased work of the sebaceous glands is activated.
- Keeping your baby too warm will significantly increase sweating. This happens more often in the autumn-winter period, when parents make the unforgivable mistake of wrapping their child as warmly as possible.
- Dry and hot air in the room in which the baby is located.
All of the above reasons are provocateurs of the disease from which the baby suffers. It is enough to eliminate them or prevent them, and the child will easily cope with the disease in a natural way: gradually his body adapts, the functioning of all organs and systems will return to normal, and seborrheic dermatitis will not threaten him.
Why does the disease occur?
In infants, crusts on the scalp can appear under the influence of various factors.
- The main cause of the disease is considered to be hormonal changes. After birth, newborns accumulate hormones in their bodies that they received from their mother during fetal development. In the process of establishing your own hormonal levels, a malfunction may occur, which causes increased work of the sebaceous glands and the formation of crusts on the surface of the head.
- Dermatitis on the head in newborns can appear under the influence of external factors. Hats and bonnets worn during the period after birth lead to increased sweating and the appearance of gneiss. The development of the disease is also influenced by the detergents used when bathing. They dry out the skin, preventing the sebaceous glands from functioning properly.
- On the part of the head where hair grows, crusts may form if a nursing mother violates the rules of nutrition. An incorrectly selected mixture can have the same effect.
- If the fungus Malassezia furfur is attached to the crusting process, the rash may spread to other areas. It often appears on the face, where the skin becomes keratinized.
- The disease can appear in newborns with weakened immune defenses. In this case, it is easier for infections to enter the body, causing dermatitis.
In most cases, treatment for the disease is not prescribed. However, if there are disorders in the immune system, additional therapy may be required.
Constant wearing of bonnets and caps can lead to the appearance of seborrheic dermatitis on the head of a newborn.
Forms of manifestation of gneiss
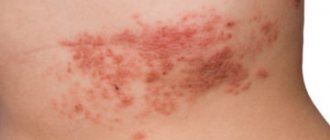
The main manifestation of this disease is fatty layers of yellowish-white color, which are located in the parietal region of the head (large fontanel). The same scaly formations can be on the eyebrows, forehead, cheeks, and also in the areas behind the ears. Less commonly, they appear on the chest of a newborn.
This skin disease can occur in various forms of severity:
- Mild degree. Dandruff is observed on the baby's head. If scales are present, they can be easily separated with a soft comb. The skin remains healthy. It is painless, there is no itching, the baby is calm.
- The average severity of the disease is characterized by the appearance of larger areas of damage. The layers are more dense, the scales turn into crusts, and are colored brown. After their removal, the skin turns red and an inflammatory process is noticeable. At this stage, seborrhea covers not only the scalp, it appears on the chest and almost the entire body.
- The severe degree is characterized by the presence of a thick scaly-cortical layer. The baby's head is covered with a “seborrheic cap”. After removing the layers, cracks and pockets of erosion form on the child’s skin. All this is accompanied by itching and pain. The baby sleeps poorly, slowly gains weight, becomes restless and tearful. With this form, secondary infection is possible.
In the first stage, the disease may resolve naturally without drug treatment. It is enough to follow the doctor’s recommendations on proper feeding and proper care of the newborn.
The second degree of the disease will require medical assistance, as a result of which a positive prognosis for complete recovery is guaranteed.
The most severe form can lead to unpleasant consequences in the form of complications: damage to the hair follicles. The most unpleasant thing may be baldness of certain areas of the head or alopecia. After intensive therapy, hair growth is restored.
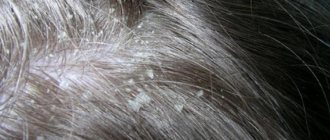
In this photo, seborrheic dermatitis of the parietal part of the head of a newborn is clearly recognized:
Gneitis on the baby's head
However, the most dangerous remains the possibility of secondary infection with streptococcus or staphylococcus. Considering the fact that the veins on the head are connected to the vessels of the brain through anastomoses, ulcers that appear on the skin can cause serious diseases such as encephalitis or meningitis.
Official medicine defines several types of seborrhea:
- Wet - the release of excess secretion due to excessive activation of the sebaceous glands.
- Dry – insufficient production of sebum.
- Mixed - in some areas of the baby's skin the secretion is released above normal, in others - below.
Complications
Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp in babies is a benign disease that often goes away on its own without treatment.
With extensive scaly layers, the hair follicles are also damaged. In such cases, partial alopecia or baldness is possible. After treating seborrhea, hair growth is restored.
But in severe cases, in a weakened child, a secondary infection of the pathological focus occurs with pathogenic bacteria - streptococcus, staphylococcus. Symptoms appear in the form of ulcers on the scalp, which is especially dangerous because the veins located here have anastomoses, that is, they connect to the vessels of the brain. If not diagnosed and treated in a timely manner, this can lead to the occurrence of such serious diseases as meningitis or encephalitis.
Carrying out diagnostics. Main symptoms
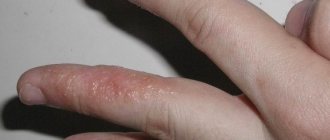
Seborrheic dermatitis in an infant
A pediatrician diagnoses seborrheic dermatitis on the body of an infant through a visual examination of formations on the skin. Main symptoms: arrangement of yellowish scales or crusts on the scalp.
On the eyebrows and other parts of the face, flaky, fine-plate scales have a whitish tint.
If the appearance of pathological changes on the skin is in doubt, you should consult a dermatologist. For diagnosis, a dermatoscope is used, which allows you to study the affected areas in more detail. Next, microscopy of the tissue of scales and crusts is performed.
Differential diagnosis will be needed if the gneiss does not go away in the first year of the child’s life. In this case, allergic or atopic dermatitis or psoriasis can be diagnosed.
Symptoms
The main clinical manifestation of gneiss is the presence of fatty yellowish-white deposits on the crown of the baby around the large fontanel.
The skin underneath is unchanged, sometimes hyperemic. Less commonly, scaly formations are located on the face: on the forehead, near the eyebrows, on the cheeks, on the chin, behind the ears. Itching is absent or very mild. The disease occurs in three forms: mild, moderate and severe.
- In mild forms, seborrhea in infants on the head looks like dandruff. The scales are easily separated from the skin, the epidermis underneath is not changed. There is no itching, the child’s general condition does not suffer.
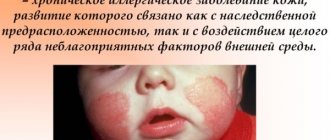
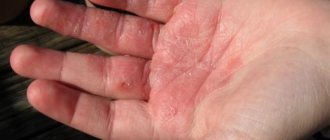
- The average form is characterized by more extensive skin lesions, the scaly-cortical layers are dense and brown in color. When the crusts are rejected, inflamed, bright red skin is exposed. The pathological process extends not only to the face (forehead, eyebrows, bridge of the nose, temporal areas), but also to the back of the head, neck, torso and limbs. In the photo below you can see the manifestations of seborrheic dermatitis on the face.
- The severe form is characterized by the formation on the scalp of merging powerful scaly-cortical layers that cover the skull in the form of a “seborrheic cap.” The superficial layer of the epidermis is affected. The skin after peeling off the crusts is inflamed, red with areas of erosion and cracks. With this form of seborrhea, a secondary infection may occur. The hair growing in the affected area is also damaged: it becomes brittle and falls out easily. The child's general condition deteriorates significantly: itching, interrupted sleep, poor weight gain, restlessness and frequent crying appear.
Treatment of seborrhea in newborns
The first stage of dermatitis in children does not require the use of medications, since it is physiological. The main method of treatment is to create comfortable conditions for the child. This is, first of all, normal air temperature (not higher than +20 degrees) and sufficient humidity, as well as compliance with hygiene rules. A diet that provides the child with the necessary vitamins and microelements. When breastfeeding, a healthy diet for the mother is important. With artificial milk, careful selection of milk formulas and the correct dosage.
For seborrhea in infants, procedures are carried out to help cleanse the skin of scales and crusts:
- Before water procedures (60 minutes before), it is necessary to lubricate the affected parts of the body with warm vegetable oil (olive, vaseline, burdock, castor, sterilized sunflower) and put on a cotton cap. After bathing, remove crusts with a soft brush. Such procedures are performed regularly once a week until all the scales disappear.
- Shampoos with an antifungal effect are allowed to be used no more than twice per 7 days: Ionil, Sebulex, Nizoral.
- On the recommendation of a doctor, use creams that have a drying effect: zinc ointment, Bioderma, Friederm.
- To eliminate seborrheic dermatitis on the baby's face, an anti-inflammatory and fungicidal agent is used - Bioderma Sensebio DS+ cream. It is applied to dry skin in a thin layer; there is no need to rinse it off. This product helps to activate sebum synthesis.
- Baby cream is applied at night. The next morning, wash your hair with a special shampoo for children, then comb it carefully.
Preventive skin care for babies
After about six months to a year, the disease will recede and leave no trace. Although sometimes it happens that seborrhea “lingers” in the body for up to three years.
A severe stage of the disease when infected with pathogenic bacteria requires drug therapy using antibiotics or other drugs.
If the above measures did not give a positive result, and the scales not only did not disappear, but papules and/or vesicles appeared, you will need a second consultation with a doctor and differential diagnosis.
Features of the disease in adolescents
Adolescence is special. The hormonal system of a young body changes. An unstable psycho-emotional state contributes to experiences and the occurrence of stressful situations. Violation of the regime, balance and calorie intake also causes activation of the sebaceous glands. That is why in adolescence there is a spread of acne on the face, peeling of the skin, and the appearance of dandruff. In addition, the appearance of seborrhea is influenced by:
- Failures in the functioning of the digestive organs due to a decrease in beneficial microflora in the intestines and an increase in harmful ones, which leads to disruption of metabolic processes at the cellular level, unbalances the work of secretion production by all glands, including the sebaceous ones;
- Activation of the sebaceous glands leads to an increase in the production of subcutaneous sebum and the abundant development of yeast-like fungi, the appearance of dandruff;
- The lack of vitamins A and E in a young body contributes to the disruption of the sebaceous glands in performing their functions in the direction of increasing secretion production;
- The wrong choice of shampoo, creams (especially foundations that close pores on the skin of the face), abuse of alcohol-containing cosmetics harm the skin, provoke the appearance of dandruff and acne;
- Neglecting hats in cold weather or prolonged exposure to the sun in the summer heat has a detrimental effect on the condition of the skin and the development of seborrheic dermatitis.
Like adults, children of all age groups suffer from seborrheic dermatitis of dry, oily and mixed types. In schoolchildren and adolescents, the oily type of seborrhea is more common, it is chronic, and after a year it is dry.
Based on the above, traditional medicine recommends that at the first sign of seborrheic dermatitis in a child of any age, use a qualified consultation in a medical institution.
Traditional healers recommend
Nature gives us many useful plants with which we can get rid of seborrheic dermatitis. However, any use of folk remedies is advisable only after consultation with a doctor, especially if it concerns the health of a child.
Infusion on the roots
Mix burdock roots, elecampane (15 g each), and several St. John's wort inflorescences. One tablespoon of the collection is poured into 250 g of boiling water and infused in a thermos for about 8 hours. Then the strained infusion is rubbed into painful areas after bathing.
Miracle Sage
For one glass of water, take 20 g of dried sage leaves, boil all this for 15 minutes. Allow to cool and apply as a lotion to areas affected by gneiss.
Oak bark will cleanse your skin
Keep a container with one glass of boiling water and 25 g of oak bark in a water bath for 5 minutes. After three hours of infusion, pass through the filter and rub into painful areas of the skin.
Flower medicine
One tablespoon of chamomile, calendula and crushed plantain leaves (in equal parts) is placed in a thermos and filled with boiling water (1.5 cups). It is infused for three hours, then the areas affected by seborrheic dermatitis are wiped with a gauze swab.
Before using folk remedies, it is essential to consult a doctor who will advise testing for individual tolerance to a particular folk remedy. To do this, just moisten the prepared infusion with a tampon and attach it to the baby’s wrist. After 24 hours, check the condition of the skin. If there is no redness, then this folk medicine is suitable for use.
Judging by the reviews of those who have used such home remedies, they can indeed have a positive effect, but you need to make the right choice in consultation with your doctor.
More information about the use of alternative medicine can be found in forums where those interested in curing seborrhea in newborns communicate. Here you can find reviews and different opinions that help you make the right decision.
Treatment
Drug treatment for seborrheic dermatitis in infants, as a rule, is not carried out until they reach one year of age. In most cases, the symptoms of the disease disappear by this time, and only in rare cases the unpleasant signs of seborrhea persist for up to 2-3 years.
To speed up recovery, it is enough to follow only general recommendations for caring for the baby:
- maintain optimal temperature and humidity in the room;
- dress the child according to the weather, do not overheat;
- for bathing, use only products intended for the care of children's skin;
- do not overuse baby soap and other care products, as this can provoke excess sebum production;
- If the facial skin is peeling, lubricate it with baby cream;
- soften and carefully comb out crusts from the scalp with a special soft brush (to soften, you need to treat the inflamed areas with sunflower or olive oil an hour before bathing);
- Wash your hair twice a week with a special antifungal shampoo.
It is strictly forbidden to roughly tear off or tear off the crusts. Such actions will lead to damage to the skin, infection, and the development of complications.
Shampoos
Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp in infants quickly disappears if special antifungal shampoos are used to wash the hair.
- Nizoral. Contains the antifungal component ketoconazole. Eliminates flaking and itching. It is used to treat seborrhea twice a week for a month, and to prevent relapse - once every 30 days. Has no age restrictions. Analogs: Sebozol, Ionel, Dermazol.
- Skin Cap. Contains zinc pyrithione as the main component. It has antifungal and antibacterial effects, suppresses cell division processes. Reduces peeling and itching, prevents the development of infectious complications. Prescribed to children over one year of age. The course of treatment lasts 2 weeks. Analogue: Friederm Zinc.
- Cynovitis. Contains a combination of zinc pyrithione, dexpanthenol, urea and climbazole. It has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and antifungal effects. Moisturizes the skin, promotes exfoliation of dead cells, activates tissue regeneration. Used twice a week for a month, then once every 30 days for prevention. Suitable for the treatment of oily and dry forms of seborrhea in children over one year of age.
Folk remedies
If your doctor allows, in addition to antifungal shampoos, you can use folk remedies to treat seborrhea in infants:
- sage decoction (pour a tablespoon of herb with a glass of boiling water, boil for another quarter of an hour, cool, strain);
- decoction of oak bark (pour 25 g of raw material with a glass of boiling water, simmer for 5 minutes in a water bath, then leave for another 3 hours, strain);
- infusion of chamomile, plantain, calendula (mix equal amounts of herbs, then pour 300 ml of boiling water over a tablespoon of the mixture, leave in a thermos for 3 hours).
Decoctions of medicinal plants are used for daily treatment of inflamed lesions. However, before using them, you need to make sure there is no allergy by treating the skin on the elbow. If the baby does not show signs of an allergic reaction, you can use the product.
Prevention of skin disease
In order for the birth of a baby to bring joy, and not endless worries about his health, you should take preventive measures seriously:
- During pregnancy, it is very important to avoid stressful situations, lead an active, healthy lifestyle, and follow a diet that contains foods containing vitamins and beneficial microelements for the normal development of the unborn child.
- Maintaining child body hygiene.
- Water procedures should be carried out only using products with a hypoallergenic effect.
- Keep the baby's head open indoors. When walking, do not wrap yourself up excessively to prevent overheating of the skin.
Diagnostic features
If yellowish, grayish dandruff and unusual dense crusts are detected, a visit to your local dermatologist is necessary. After a visual examination, the doctor will refer the patient for a diagnostic examination in order to determine the source of the unstable functioning of the sebaceous glands:
- clinical and biochemical blood tests;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland - as a procedure for detecting changes in the organ;
- analysis for hormonal balance - more often prescribed for adolescents;
- A bacterial analysis is taken by scraping from pathological foci and is necessary to identify the invading pathogen.
Therapeutic measures to relieve seborrhea are prescribed only to confirm the presumptive diagnosis.
Gneiss treatment forecasts
If the nature of the occurrence of seborrhea on the baby’s head and other parts of the body is physiological in nature, the prognosis is comforting. The disease goes away naturally without drug treatment. As noted above, it is enough to follow the recommendations for creating an appropriate environment and caring for the baby.
There is significantly less optimism in expectations of recovery in congenital seborrheic dermatitis. In such cases, it is quite difficult to achieve positive results. It is very difficult to correct an inherited genetic predisposition to such a disease. It will not be possible to completely get rid of it; the main thing is to prevent a severe form. To do this, periodically contact a dermatologist.
Features of treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in children
Self-treatment of seborrhea in children of any age does not always bring the expected result, since the signs of different dermatitis may be the same, but the treatment methods may be different.
On the baby's head
It is necessary to note the importance of child care in the first days and months of a child’s life. Regular water procedures, ventilation of the child’s room and air exercise, proper personal hygiene products are the key to the baby’s health. An important factor is the way a nursing mother eats and takes certain medications.
The first “bell” of seborrheic dermatitis is always the appearance of dandruff, small “foci” of flaky “milky crusts” on the child’s head, and their redness.
In this case, it is best to pay attention to the child’s hygiene: bathing, combing out loose crusts with a soft brush, removing loose scales with tweezers. To wash the baby's head, you can use special shampoos for infants. After water procedures for washing the baby’s head, you can use olive or special fortified baby oil, which the pediatrician will recommend. In some cases, the doctor attributes the use of antifungal children's ointments.
On the face of a baby
Often the rash spreads from the head, covered with hair, to the face and body of the little man. In this case, the child must be provided with bathing with limited contact of facial skin with water. Use only detergents (gels, soaps, shampoos) that do not irritate the skin. Water procedures must be completed by wiping the child’s dry body and face with specialized products, such as cleansing, skin softening, vitamin A-enriched creams, and antifungal products.
It is forbidden to remove peeling crusts with your fingernails.
It must be remembered: a child’s body is not a place for experimentation. All medical procedures must be carried out after consultation and prescription by a doctor.
Children over 1 year old
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in children of preschool and school age is carried out comprehensively. With strict adherence to personal hygiene and a special diet, medications for internal and external use are used in combination with physiotherapy. The specific treatment is prescribed by the doctor, guided by the tests and studies performed.
The necessity of using external agents depends on the form of seborrheic dermatitis and the age of the patient. This category of drugs includes medicated shampoos and softening creams, ointments and various cosmetic oils, medicinal baths.
Increasing the child’s immune defense, destroying yeast-like fungus on the body and scalp, eliminating factors contributing to the disease are the main areas of use of medicines and drugs:
- Calming the nervous system as a result of experiences and stressful situations;
- Antifungal ointments;
- Probiotics to improve the functioning of the digestive system by improving intestinal microflora and enhancing immunity;
- Vitamins A, E;
- Natural or synthetic agents that have a regulating effect on the immune system of the child’s body.
The latest developments in physiotherapy improve blood circulation in the skin and increase skin tone. Carrying out massages, applying a magnet to certain areas of the body, stimulating specific points with a laser beam, in combination with medications, can speed up the child’s recovery process.
Treatment in adolescents
The process of puberty in girls and boys is strictly individual. For some girls it starts at 8-9 years old and ends at 14-15. For boys, this process begins later - from 11-13 years old and ends by 18-20.
During this period, there is an increase in the secretion of the sebaceous glands, which becomes a breeding ground for yeast-like fungus and the cause of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp, face and other parts of the body.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in adolescents is not much different from treatment in adults. But sometimes it is enough to exclude chocolate, hot spices and seasonings, and pickles from the diet, and dermatitis stops its development. But it is better to consult a dermatologist, conduct a comprehensive examination of the body, and additional tests to carry out highly effective treatment measures.
A rash on a teenager’s body is often accompanied by the appearance of acne and itchy, scaly plaques. Constant scratching can lead to secondary infection.
During this period, it is necessary to normalize metabolic processes at the cellular level and stabilize the functioning of the digestive system. At the same time, therapeutic measures are carried out to cure chronic diseases, eliminate nervous shocks and eliminate stressful situations as much as possible.
Simultaneously with drug treatment, which includes the use of antihistamines, choleretic drugs, and a complex of vitamins, auxiliary physiotherapy is carried out. It is designed to improve the effect of medications, prevent relapse, and reduce testosterone levels during puberty in a young body.
Physical therapy may include:
- Administration of drugs through the skin of a teenager;
- Special treatment of affected areas of the body with infrared rays;
- Using liquid nitrogen to treat affected areas;
- Use of electric current;
- Breathing procedures with enriched oxygen to improve the metabolic process in the body.
An important role in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis is played by personal hygiene with special shampoos, gels, soaps, and creams.
Useful tips for parents
A nursing mother should strictly monitor her diet. It is necessary to reduce fatty foods, whole milk and fermented milk products with a high percentage of fat to a minimum. Do not get carried away with baked goods, sweets, and other dishes containing high levels of carbohydrates.
When feeding with ready-made formulas, you should not skimp on the baby’s health and do not buy cheap ones without the “hypoallergenic” sign.
To reduce the amount of time you bathe your baby using shampoo or soap, change diapers more often. Do not overuse wearing extra blouses and caps, so as not to cause increased sweating and not provoke the appearance of such an unpleasant pathology of the epidermis.
Share with friends
Rate this article