Doctors have identified more than 100 different types of HPV. All of them are divided into 3 broad groups. The first group includes formations that do not cause the development of oncology, but only cause aesthetic discomfort to the infected person. The second group of human papillomavirus has a low percentage of tumors degenerating into cancerous tumors. Most often, this may be due to genetic predisposition, injury to papillomas, or secondary infection. The third group of the virus poses a threat to human health, as it contributes to the development of cancer. This includes HPV of high oncogenic risk, which requires mandatory treatment.
What is oncogenic HPV?
HPV develops under the influence of different strains of the virus, which can be expressed on the skin or mucous membranes in small formations of a different nature (from flat spots to warts). The possibility of cells degenerating into malignant depends on the type of pathogen. That is, the virus can exist in the human body without causing any special changes in the tissues.
In the oncogenic type, the pathogen affects the nuclei of cells, provoking changes and mutations in them at the genetic level, as a result of which the likelihood of tissue degeneration into cancer cells increases. With non-oncogenic HPV, the immune system can independently eliminate the virus. This period can take up to 2 years.
The course of the disease in men and women
The clinical picture is somewhat different in women and men.
Among women:
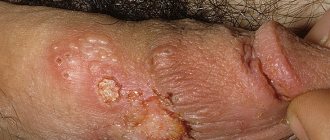
- genital warts;
- flat condylomas;
- genital herpes;
- papillomas;
- skin rashes of various locations;
- itching;
- feverish condition;
- redness;
- signs of cervical disease.
For men:
- warts on the frenulum of the penis;
- inflammatory processes of the foreskin;
- polyps in the genital area;
- itching of intimate organs;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- burning when urinating.
What types of HPV are classified as a high oncogenic risk group and where are papillomas located?
HPV of high oncogenic risk can be observed in approximately 2-3 people out of 20. In other cases, the virus may be absent or have a low or average probability of degeneration into oncological formations.
Characteristics of HPV by risk groups:
| Risk group | HPV numbering | Characteristics according to the probability of degeneration |
| Low | 1, 2, 3, 4 | The likelihood of HPV degeneration into oncology is practically absent. The pathology is expressed by the appearance of small single growths on the skin, which cause mainly a cosmetic defect. |
| Average | 6, 11, 42, 43, 44, 52, 58 | The risk of HPV degeneration into cancer cells is 1%. |
| High | 16, 18, 26, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 53, 56, 58, 59, 66, 68, 73, 82 | The probability of cells degenerating into malignant is more than 50%. Species 16 and 18 occupied a special place. They are the most dangerous and cause the development of cervical cancer in women after 40 years of age in 70% of cases. Their danger lies in the absence of symptoms. |
Group 3 HPV poses the greatest danger, although group 2 is also oncogenic. Therefore, if they are present, constant monitoring of their external condition and general well-being is required. The research method has identified about 130 types of viruses, among which only 80 stamps have been studied (according to their effects on the body). To detect HPV, it is important to know their external characteristics.
In appearance, HPV has the following division:
| HPV numbering | Characteristics of appearance and localization zone |
| 1, 2, 3, 4, 63 | It is expressed by the appearance of warts, similar in characteristics to a callus. Localized mainly on the sole. |
| 10, 28, 49 | Flat warts appear on the skin. They can be located on any part of the epidermis. |
| 27 | Convex warts of different colors and shapes can also be localized on any part of the skin. |
| 6, 11, 13, 16, 18, 30, 33, 35, 39 | They affect the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs in the form of ordinary or genital warts. |
HPV can be located on any part of the skin, but with oncogenic risk they are localized predominantly:
- near the anal area and in the rectum;
- on the cervix and vaginal mucosa;
- labia or penis with scrotum;
- lips and oral mucosa.
To determine the type of virus, it is important to undergo a full examination with specialized tests. Visual examination and donation of urine or blood do not give accurate results and do not determine the type of pathogen.
Symptoms
The manifestations of the 35th strain of the virus do not differ from the signs of the presence of other strains. They consist in the formation of growths:
- Warts . A large number of warts may indicate the presence of any type of infection.
- Genital warts . Most often they appear in people over 18 years of age; they can form on various areas of the skin and mucous membranes, but in most cases they can be observed in the intimate or anal area.
- Flat condylomas . HPV strain 35 rarely causes such tumors, but if they are present, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible - such growths may indicate the onset of an oncological process.
In addition, humans have:
- fever without manifestation of bacterial or viral infection;
- itching and redness are observed in places where the growth forms;
- Women may experience inflammatory diseases of the genital organs.
Methods of infection
HPV is an infectious disease and can develop when the pathogen enters the body in the following ways:
- during sexual contact. This method of infection ranks 1st. The likelihood of a woman getting infected from a man is higher than a man getting infected from a woman. This is due to the fact that during intimacy, the vaginal mucosa is more often exposed to microtraumas into which the pathogen penetrates. The virus can enter the body not only during sexual intercourse (vaginal, anal or oral), but also through kissing;
- during natural childbirth. If a woman in labor has HPV, then when passing through the birthplace, the infection can enter the child’s body. Therefore, before planning a pregnancy, it is important to exclude HPV in both parents;
- when breastfeeding a child, if the mother is also a carrier of HPV;
- upon contact with a carrier of infection or through hygiene items with which he was in contact (including in beauty salons). The pathogen can enter the body only through damaged mucous membranes or wounds on the skin. But the likelihood of infection with HPV with a high oncogenic risk, with this method of transmission, is minimal. The appearance of warts is more often noted; the possibility of degeneration, which is low.
It is important that animals do not carry HPV.
HPV symptoms
When infected with the virus, patients do not experience noticeable discomfort; the disease does not manifest itself with a clear picture of the disease. In women, the infectious cell appears more often than in men. HPV with highly oncogenic DNA causes dysplasia and cervical cancer. Development is based on cell division under the influence of a group of factors. Symptoms of a viral process:
- condylomas and papillomas on the skin surface and mucous tissues;
- atypical discharge, vaginal bleeding;
- pain in the abdomen and vagina during and after sexual intercourse;
- general weakness in the body, malaise;
- During a gynecological examination, the uterine cervix changes and the process of inflammation develops.
Papillomas are included in the group of non-oncogenic or low-oncogenic HPV. The process of transmission of viruses to others occurs through close household contacts. The formation does not require removal. Papilloma does not cause harm or discomfort to the patient.
Condylomas cause viral pathology when infected during sexual intercourse. Condyloma is indicated for removal. The growth destroys the mucous membranes, is regularly injured and is highly likely to recur. Papillomavirus rarely affects men. More often they are carriers of HPV. 0.3% of cases of infection by bacteria with a high oncogenic risk result in the formation of condylomas, cancer of the genital organ and perianal area. Homosexuals and bisexuals are on the danger list.
Viral infection is common among heavy smokers. When viruses appear in non-smokers, the disease is associated with the activation of oncogenic HPV. The main signs of infection are the appearance of formations such as warts, papillomas, and cervical dysplasia. Patients have applied signs of pathology. Penetrating into the female body, the high carcinogenic risk papillomavirus significantly changes the tissue structure of the genital organs. The following signs are noted:
- discomfort during menstruation, heavy menstrual bleeding;
- the appearance of non-menstrual bleeding between menstrual cycles;
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes and ectopic pregnancies;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- impossibility of conceiving a fetus.
Reasons for activation of papillomavirus
HPV of high oncogenic risk, after entering the body, can remain in it secretly, without showing symptoms (the period can take from 3 weeks to 10 years). At this time, the immune system fights the pathogen. A complete recovery is possible without taking medications (by the body’s own efforts).
If the immune system weakens, the pathogen becomes active and begins to multiply, which is expressed by the appearance of formations on the epidermis. With further development of the pathology, the affected cells can develop into malignant ones, that is, cancer begins to develop.
Probable reasons for HPV activation:
- frequent violation of the integrity of the skin. This not only increases the likelihood of HPV activation, but it is also dangerous for new types of viruses to enter the body through open wounds;
- the presence of chronic pathologies (or frequent infectious diseases), both dermatological and internal organs. With long-term illnesses, the immune system weakens;
- diseases of an endocrine and autoimmune nature;
- HIV and radiation therapy. Accompanied by virtually no immunity;
- the presence of hormonal imbalance (during adolescence, menopause or pregnancy);
- abuse of alcohol, nicotine or drug use. As a result, the likelihood of additional infection increases, and bad habits also contribute to a decrease in immunity;
High-oncogenic risk HPV can be activated by alcohol, tobacco or drug abuse. - living in an environmentally polluted area or working in a hazardous industry. Due to slagging in the body, the activity of the immune system decreases;
- frequent overheating or hypothermia;
- genetic predisposition to HPV and cancer;
- taking medications to reduce the functioning of the immune system.
Long-term depression, constant stress, irregular sex life (or frequent change of sexual partners) also contribute to the intensification of HPV reproduction.
Preventive measures
No preventive measure can provide a 100% guarantee that the body will not produce antibodies to HPV in the next 10 years. However, there is a preventive measure that can reduce the likelihood of the formation of secondary infectious foci. Vaccination is carried out at the request of people.
Foreign countries have been prescribing recombinant vaccines to strengthen the immune system for 10 years:
- Cervarix – intended for women;
- Gardasil is prescribed for the prevention of viral infections in patients of both sexes.
Both vaccines are characterized by an affordable price category. The substances include an inactivated virus that protects against strain types 16 and 18. In fact, the products show effectiveness in treating other dangerous types of microbacteria. Vaccination is prescribed for adolescents from 9 to 14 years of age and women under 30 years of age.
The procedure is carried out over six months in three stages. Vaccines have individual drug administration regimens that allow achieving maximum results from the properties of the vaccinations. General preventive measures involve strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations:
- Refusal of casual sexual contacts, it is recommended to adhere to monogamy.
- Use of barrier methods of contraception.
- Quitting bad habits.
- Strengthening immune defense when the body is weakened after fighting diseases.
- Complete rest.
- Healthy food filled with vitamins and beneficial microelements.
- Regular physical activity.
- Gynecological examination. A woman should be examined by a gynecologist twice a year and have a smear to check the condition of the body and the presence of characteristic elements in the smear.
- Maintain hygiene, especially when visiting a bathhouse, sauna or swimming pool.
Among the negative consequences of HPV are systematic disturbances in hormone levels and the use of immunosuppressants, which have a detrimental effect on the immune system.
In what cases does cancer develop?
The most important reason for the development of cancer cells in the presence of HPV with a high oncogenic risk is a severe weakening of the immune system. After the pathogen enters the body, its DNA penetrates the nuclei of human cells and disrupts the division process.
As a result, damaged cells begin to divide chaotically, forming tumors containing the virus (warts of different shapes and textures are formed). These neoplasms are benign, but when the above factors are combined, the likelihood of cells degenerating into cancer increases.
High-risk HPV is more often the cause of the following cancers:
- cervical cancer;
- rectal cancer;
- penile cancer;
- breast cancer;
- laryngeal cancer.
To avoid the development of oncology, it is necessary to promptly diagnose the degeneration of HPV into cancer.
Danger of HPV
In men, the mucous tissues of the genital organ are protected. Therefore, the likelihood of a man contracting HPV HCV is low. When a viral infection enters the mucosal cells, the pathology rarely develops into penile cancer. The formation of tumor growths provokes the development of:
- erectile dysfunction;
- acute process of inflammation in the urinary canal;
- erosions form on the shaft of the penis after injury to condylomas and exposure to bacteria;
- infertility.
The spread of carcinogenic viruses in the female body can cause cervical dysplasia. The disease develops in 3 stages. At an early stage, 1/3 of the mucous tissue of the uterus is destroyed and individual growths form. The middle stage is characterized by the destruction of more than 50% of the mucosa. At the last stage, the pathology becomes malignant. As a result, women experience cervical cancer.
Symptoms of high oncogenic risk HPV in women and men?
HPV can be accompanied by different symptoms depending on gender and the severity of oncogenic risk (the most pronounced signs appear when cells are predisposed to degenerate into cancer with a high probability).
Symptoms characterizing the presence of HPV in the body (in men and women):
- the presence of growths on the skin or mucous membranes (genital organs, mouth) in the form of warts, especially those with an irregular shape;
- a sudden change in color of the formations, their uncharacteristic growth, the appearance of redness and signs of inflammation near the growths (possibly slight bleeding from them);
- painful urination;
- Women may experience heavy discharge between periods with blood;
- feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- unpleasant sensations in the vagina or penis during sexual intercourse or after its completion, as well as during hygiene procedures;
- soreness in the groin;
- itching or burning sensation on the genitals.
If these signs are present, it is recommended to undergo a full examination with the necessary tests, which not only determine the presence of HPV in the body, but also their type.
Types of HPV
There are several types of formations that appear when infected with HPV.
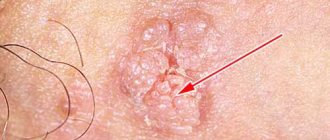
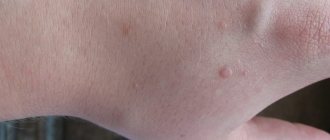
Warts
These are benign formations that have a dense structure and a wide base. They reach a diameter of 2 - 10 mm. They can be round or irregular in shape, have clear outlines, and a rough surface.
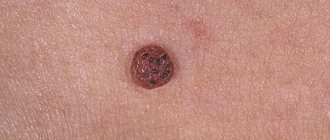
Papillomas
This is the type of HPV that is most common. They reproduce on a stalk or have a wide base. They can be multiple or solitary. Color varies from flesh to brown. Malignant papilloma most often has a dark brown or black tint.
Condylomas
This type of virus is pedunculated genital warts. They are soft to the touch and most often have a pink tint. They are localized on the genitals or in the anal area. They grow quickly, affecting large areas of human mucous membranes.
Analyzes
The specialist performs a visual examination of the formations in order to determine their condition (appearance, location), and also clarifies additional symptoms. To confirm the presence of HPV in the body and determine its type, tests are required, which are described below.
PCR
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) does not require special preparation. To diagnose the virus, blood, urine, and a scraping/smear from the urethra and vagina are taken.
Based on the results of studies of these materials (prepared from 1 to 3 days), it is possible to confirm or deny the presence of HPV, as well as determine the type of virus. But it is impossible to determine the amount of pathogen in the body. Therefore, additional examination will be required.
Digene test
The examination is carried out after 30 years. No preparation (except for hygiene procedures) is required to carry it out. The test involves taking mucus from the cervix in women or from the urethra in men. As a result of the examination of the material, HPV can be confirmed or excluded, as well as the oncogenicity of the virus can be identified.
If the indicator is in the range from 0.1 to 3, then the likelihood of developing cancer is practically absent. If the value is from 3 to 5, then the risk of developing cancerous papillomas is more than 50%. An indicator above 5 means a high probability of HPV degeneration into oncology or the beginning of the development of a cancer process. The examination results are ready only on the 8th day.
PAP test
The examination allows you to detect HPV with average oncogenicity in the body. The test is used primarily to diagnose women. No preparation required (only hygiene procedures).
For the study, mucus is collected from the cervix. The result can be found out in 2-3 days. It is possible to examine men; material is taken from the anus for diagnosis.
Genotyping
It is carried out mainly using a PCR test. The purpose of the examination is to identify only the most dangerous HPVs in the body (these are 16 and 18).
ELISA
For diagnosis, blood is drawn. The test is aimed at detecting antibodies to HPV, not the virus itself. This allows you to determine not only the presence of the pathogen in the body, but also to assess the degree of neglect of the pathology (that is, how long the infection has been in the body).
The procedure does not require special preparation. To get results you need to wait 2-3 days. The method is used to monitor the dynamics of therapy.
Additional tests
If the above analyzes do not give the necessary results, then the specialist may prescribe additional procedures:
- colposcopy. Suitable for women. Using a colposcope, the gynecologist evaluates the external condition of the cervix and identifies the presence of abnormalities. The examination does not accurately confirm or refute the presence of HPV;
- biopsy. Papillomas tissue is examined to identify cancer cells in them. The duration of diagnosis can take up to 14 days.
Additionally, urine, feces and blood tests are prescribed to determine the general condition of the body (detection of chronic pathologies and assessment of the state of immunity).
Diagnostics
For timely detection of the virus, it is recommended to diagnose the disease at least once every three years. Informative and reliable methods for identifying oncogenic type HPV are:
- Polymerase chain reaction. One of the most reliable methods by which not only the presence of pathogenic flora is determined, but also the strain of the virus.
- Daijin test. One of the innovative and expensive diagnostic methods, which is currently used only in large medical centers. It is the most informative, allows you to determine the number of viral microorganisms in the blood, strain, oncogenic risks.
- Dad - test. It is also a fairly reliable method for detecting oncogenic HPV, used primarily for diagnosing infectious diseases in women.
- ELISA. This method allows you to determine the level of viral load on the body, strain and oncogenic risks of infection. In addition, the method is one of the few on the basis of which it is possible to create a complete picture of the disease and determine the duration of infection, that is, the presence of HPV in the body.
Often, for additional diagnostics, the genotyping method is used, which makes it possible to determine the identity of the pathogenic flora. More often, this method is relevant if there is a suspicion of oncogenic type HPV infection.
Conservative treatment
HPV of high oncogenic risk at the initial stage can be detected only after undergoing a course of tests. If its presence is confirmed, a doctor can prescribe complex treatment using medications, hardware therapy, or using folk remedies. Self-medication is prohibited.
Antiviral drugs
HPV is an infectious disease of a viral nature, so a specialist may initially prescribe antiviral drugs.
For example:
- Acyclovir. For treatment, tablets, ointment or cream are prescribed. The products destroy viral infections and are approved for use from 2 years of age. The drugs have a large list of side effects that you need to familiarize yourself with before use. The course of treatment is 5-10 days;
- Ribavirin. For HPV, tablets or capsules are prescribed. Intravenous administration of the composition is possible (but only in a hospital setting with an advanced form). The product is approved for use after 18 years of age. It also contains a large list of contraindications. Duration of therapy is about 6 months;
- Viferon. Used in the form of suppositories, ointments or gels. Allowed for use from birth. Contraindications and side effects include an allergic reaction to the components. The course of treatment is from 3 weeks to 6 months;
- Kipferon. Suppositories not only eliminate the virus, but also help strengthen the immune system. The drug has no age restrictions. Allergies are a contraindication and a negative reaction. Duration of treatment is 7-10 days;
- Panavir. It is prescribed in the form of suppositories, gel, and in stationary conditions in the form of injections. The drug has contraindications and adverse reactions, which you should familiarize yourself with before use. Cannot be used under 18 years of age. Course from 5 to 14 days.
The type of antiviral drugs and the course are prescribed by the attending physician according to the dynamics of therapy.
Immunostimulating drugs
HPV can be present in the body for a long time during the incubation period, but when immunity decreases, it immediately begins to multiply.
Therefore, to prevent activation of the virus, it is necessary to take medications to strengthen the immune system:
- Immunal. The solution and tablets have an immunostimulating effect and also have a weak antiviral effect. Approved for use from 1 year. For lung pathologies and allergies, the drug is not prescribed. The drug must be taken from 2 to 8 weeks;
- Lavomax. The tablets have an antiviral and immunomodulatory effect. Under 18 years of age and with allergies, the medication is not used. Course 1 month;
- Isoprinosine. The tablets destroy viral infection and help strengthen the immune system. Use is prohibited for children under 3 years of age and for those with kidney pathologies. Duration of therapy is 5-14 days.
Additionally, it is recommended to increase the amount of fresh fruits and vegetables in the diet, as well as drinks made from them.
Ozone therapy
Ozone therapy is a physiotherapeutic treatment, the effect of which is based on the disinfecting effect of ozone. For HPV, therapy can reduce the activity of the virus and increase immunity. The method has no contraindications or side effects. Ozone can be administered intravenously with special formulations or external irrigation.
Treatment methods
There is no complete cure for the papilloma virus. If a virus infection occurs, it will remain in the person’s body for the rest of his life. The entire fight against the virus that exists at the moment is based on suppressing its development and suppressing the activity of the infection. Self-medication is unsafe, so consultation with a doctor is required.
Depending on the course of the disease, the doctor may prescribe the following therapy :
- The use of traditional medicine, which can be effective only at the very beginning of the development of pathology.
- Drug treatment. Antiviral and immunostimulating therapy is prescribed.
- Surgical removal of growths.
As for traditional medicine, celandine juice is most often used, which is used to lubricate the tumor several times a day. It is important to remember that celandine is a poisonous plant, so you need to use it very carefully and strictly follow the doctor’s instructions.
Also considered effective:
- Castor oil;
- garlic juice;
- aloe juice;
- ammonia;
- tincture of green walnuts.
If surgical intervention is necessary, manifestations of papillomavirus are eliminated in the following ways:
- removing the growth with a scalpel;
- laser cauterization;
- electrocoagulation;
- radio wave method;
- cryotherapy;
- cauterization with chemical compounds (Solkvagin).
Radical treatment
HPV of high oncogenic risk in an advanced form is difficult to respond to drug therapy, so a specialist may prescribe more radical methods of treatment.
Laser excision of growth
With the laser method, the beam excises formations and seals the vessels without leaving scars. To prevent the re-development of HPV, it is necessary to take a course of antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs.
Cryodestruction
Cryodestruction is based on cauterization of papillomas with liquid nitrogen. It freezes formations that gradually fall off on their own (they cannot be torn off). The procedure may cause skin burns and scars (depending on the qualifications of the specialist). But due to the deep effect on the tissue, the likelihood of relapse of the disease is reduced.
Electrocoagulation
The method is similar to cryodestruction, but instead of nitrogen, high-frequency current is used for cauterization. The procedure may also cause burns and subsequent scarring.
When choosing this method, give preference to modern devices that minimize the risk of developing a negative reaction, even with low qualifications of the specialist.
Radiotherapy
To treat formations, mainly X-ray radiation is used, which destroys HPV cells. The method is practically painless, the likelihood of scar formation is minimal, and due to the sealing of blood vessels, rapid tissue restoration is noted.
Surgery
With the surgical method, papillomas are eliminated by cutting. The method has contraindications, as well as the risk of blood loss and scar formation. During surgery, there is a possibility that HPV cells will be partially removed, so relapse of the disease is possible in a short time.
Features of treatment and prognosis
If during the study, HPV of a highly carcinogenic type was identified, then special treatment is indicated even in the absence of any symptoms. In this situation, an integrated approach is used, including conservative, invasive methods, as well as folk remedies.
First of all, patients are prescribed a course of drug therapy aimed at suppressing the vital activity of the virus and stopping its reproduction.
For this purpose, drugs of the following groups are used.
- antiviral - Acyclovir, Ribavirin, Cidofovir, as well as interferons;
- immunostimulants – “Immunal”, “Lavomax”.
Advice! It is mandatory to take the combined action drug “Isoprinosine” or its analogue “Groprinosin”. It slows down cell division, enhances antiviral effects, and stimulates the body's own defense reactions.
If rapid growth and reproduction of the virus is suspected, cytostatics are prescribed to suppress this process:
- "Podofilin";
- "Vinblastine";
- "5-fluorouracil."
According to patients, medications for general and local use are equally effective. The latter are used to treat growths formed on the skin and epithelial tissues.
Mechanical removal of growths using any of the modern methods is considered an effective method of therapy:
- electroexcision – burning out formations with electric current;
- radiotherapy – excision of the tumor by exposure to waves of different frequencies;
- laser removal - cauterization of the growth with a beam of rays;
- cryodestruction – removal of growths using liquid nitrogen.
No less popular is the chemical method - treating the tumor with a potent agent, which ultimately leads to its disintegration. Such drugs as Solcoderm, Feresol and Condilin are widely used. To avoid burns, the product must be applied only to the surface of the growths. To prevent the re-formation of papillomas, it is recommended to use the transdermal immunostimulating cream "Aldara" (Imiquimod).
Folk remedies
Folk formulations can be used only in the absence of contraindications; consultation with your doctor is necessary.
The most effective and popular recipes:
- dandelion. You can lubricate the growth 4 times a day with fresh dandelion juice. It disinfects and burns HPV cells. The juice should not get on healthy cells due to the likelihood of developing a burn;
- chamomile and St. John's wort . Steam 10 g of chamomile and St. John's wort in 1 liter of boiling water. Insist. Use for sitz baths (to get rid of HPV on the genitals and rectum) or for foot baths. Before use, you need to dilute the composition with 2 parts of water;
- aloe _ Squeeze fresh aloe juice and make lotions with it for 10-15 minutes 3-4 times a day.
The duration of treatment is determined individually based on the dynamics of therapy.
Prevention of HPV 35 infection
The main directions in preventing infection with the human papillomavirus are maintaining a healthy lifestyle and boosting immunity. First of all, it is necessary to streamline sexual relations: to exclude casual relationships and frequent changes of partners. Next, you should get rid of bad habits, balance your diet, and establish a daily routine.
Rest should be sufficient, and it is good to include physical exercise in your routine. You should definitely undergo preventive examinations with a doctor; testing for HPV is necessary every three years. This allows you to significantly reduce the risk of developing genital cancer.
Living with a person infected with HPV 35 requires certain precautions. Sexual partners must always use condoms. All rules of intimate hygiene should be observed. Sharing towels, toothbrushes, and washcloths is prohibited.
It is mandatory for all family members to give up bad habits and maintain a healthy lifestyle. A balanced diet and sufficient amounts of fruits and vegetables are required. You should conduct regular examinations with a gynecologist, urologist, and diagnose the virus in the blood.
Forecast
It is almost impossible to completely eliminate HPV from the body. After eliminating formations from the skin (medication or hardware), the probability of relapse is more than 50%. To prevent the occurrence of malignant tumors due to the degeneration of HPV of high oncogenic risk, timely relief of pathology is recommended.
HPV is a viral pathology that manifests itself as formations on the skin. Papillomas (with medium and high risk of oncogenicity) can have different structures and can degenerate into malignant cells. Therefore, it is necessary to promptly examine formations and undergo tests to reduce the likelihood of developing cancer.
Author: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Why is papillomavirus dangerous?
The potential threat in viruses of this type is primarily the risk of growth of tumors of the urinary tract and genitals.
Slightly less commonly, viruses are responsible for tumor growth in the oropharynx area.
The long-term existence of the virus in epithelial cells sooner or later changes their structure and ability to divide uncontrolledly.
Any episode of infection should be diagnosed, monitored and, if possible, treated.
Errors in immune defense can occur at any stage of life.
In addition to external provoking factors, they can be caused by natural hormonal fluctuations.
Therefore, today there is an urgent question about creating artificial protection against papillomaviruses by vaccinating high-risk groups or children.