Rheumatologist of the 1st category. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Shishkina
Irina Alexandrovna
9 years experience
Rheumatologist of the 1st category. Candidate of Medical Sciences. Awarded a Certificate of Honor from the Kirov city administration for high professionalism and many years of work in providing assistance to the population, 2018. Winner of the regional stage of the All-Russian Doctors Competition in the “Best Therapist” category, 2021.
Make an appointment
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an inflammatory disease associated with the production of autoimmune antibodies and immune complexes to the tissues of one’s own body. At risk are patients aged 20 to 40 years. According to statistics, the disease is more often detected in women. The prevalence of the disease is no more than 2-3 cases per 1000 people.
Drug-induced lupus
About 10% of people with SLE experience symptoms due to a reaction to certain prescription drugs. According to Genetics Home Reference
, about 80 drugs can cause this condition.
These include some of the drugs that people use to treat hypertension. They also include some thyroid medications, antibiotics, antifungals, and oral contraceptives.
Medicines that are commonly associated with this form of lupus:
- Hydralazine;
- Procainamide;
- Isoniazid.
Drug-induced lupus usually goes away after a person stops taking the drug.
Neonatal lupus
Most babies born to mothers with SLE are healthy. However, about 1% of women with lupus autoantibodies will have a child with neonatal lupus. Sjögren's syndrome is another autoimmune condition that is common with lupus. The main symptoms include dry eyes and dry mouth.
At birth, babies with neonatal lupus may have skin rashes, liver problems, and low blood pressure. About 10% of them suffer from anemia.
The lesions usually resolve within a few weeks. However, some babies have cardiac problems and the baby may need a pacemaker. This can be a life-threatening condition. Women with SLE or other related autoimmune diseases require constant medical supervision during pregnancy.
What kind of disease is lupus erythematosus?
The disease refers to skin infections of the autoimmune type.
When manifested, it has the following types of characteristics:
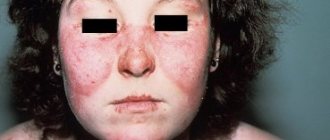
- Manifests itself as a red rash , which is localized in the cheeks and nose;
- As the disease progresses, the body begins to intensify the production of antibodies and damage healthy cells;
- The human body recognizes healthy epidermal cells as infected and starts the process of eliminating this type of cell;
- Females under 30 years of age are most often affected.;
- It is a rare type of disease and is hereditary;
- and epithelium are damaged
The disease tends to reduce and increase its symptoms, and is transmitted from mother to child at birth.
Causes of lupus
The immune system protects the body and fights antigens such as viruses, bacteria and germs. It does this by producing proteins called antibodies. White blood cells or B lymphocytes produce these antibodies. When a person has an autoimmune condition such as lupus, the immune system cannot distinguish between unwanted substances, antigens, and healthy tissue. As a result, the immune system directs antibodies to both healthy tissue and antigens. This causes swelling, pain and tissue damage. The most common type of autoantibody that develops in people with lupus is antinuclear antibody (ANA). These autoantibodies circulate in the blood, but some of the body's cells have walls that are permeable enough to allow some autoantibodies to pass through.
Autoantibodies can then attack the DNA in the nucleus of these cells. Several genetic factors likely influence the development of SLE.
Some genes in the body help the immune system function. In people with SLE, changes in these genes can interfere with the functioning of the immune system. One possible theory involves cell death, a natural process that occurs when the body renews its cells, according to Genetics Home Reference
.
Some scientists believe that due to genetic factors, the body does not get rid of dead cells. These dead cells that remain can release substances that cause the immune system to malfunction.
Causes of systemic lupus erythematosus
Why this disease occurs is still unknown. Doctors believe that a combination of several factors may somehow influence:
- heredity;
- hormonal changes, including puberty, pregnancy, childbirth;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- some medications (isoniazid, methyldopa, hydralazine, novocainamide, etc.);
- viral infections.
It is still unknown how these factors (individually or in combination) cause changes in the immune response. The body begins to produce antibodies to the nuclei of connective tissue cells, and it is the antibodies that damage the cells that cause inflammation.
Risk factors: hormones, genes and environment
Lupus can develop in response to a number of factors. They may be hormonal, genetic, environmental, or a combination of these.
The US National Institutes of Health notes that women are nine times more likely to have lupus than men. Age: Symptoms and diagnosis often begin between the ages of 15 and 45. However, 20% of cases appear after age 50, according to Genetics Home Reference.
Since 9 out of 10 cases of lupus affect women, researchers are looking at a possible connection between estrogen and lupus. In a review published in 2021, scientists observed that estrogen can influence immune activity and induce lupus antibodies in mice that are susceptible to lupus. This may explain why autoimmune diseases affect women more often than men.
There is not yet enough evidence that estrogen causes lupus. If there is a link, estrogen-based treatments may regulate the severity of lupus. However, more research is needed before doctors can suggest it as a treatment.
Researchers have not proven that any specific genetic factor causes lupus, although it is more common in some families.
A person who has a first- or second-degree relative with lupus will have a higher risk of developing it.
Scientists have identified genes that may contribute to the development of lupus, but there is not enough evidence that they cause the disease.
Environment
Environmental agents, such as chemicals or viruses, can trigger lupus in people who are already genetically susceptible.
Possible environmental triggers include:
- Smoking: The increase in incidence in recent decades may be due to higher levels of tobacco exposure.
- Exposure to sunlight: Some believe this may be a trigger.
- Drugs: About 10% of cases may be related to drugs, according to Genetics Home Reference.
- Viral infections: This can cause symptoms in people who are prone to SLE.
Lupus symptoms
Lupus symptoms occur during flares. Between outbreaks, people usually experience periods of remission when there are few or no symptoms.
- fatigue;
- loss of appetite and weight loss;
- pain or swelling in joints and muscles;
- swelling in the legs or around the eyes;
- swelling of the glands and lymph nodes;
- skin rash due to bleeding under the skin;
- mouth ulcers;
- sensitivity to the sun;
- fever;
- headache;
- chest pain when breathing deeply;
- hair loss;
- Raynaud's syndrome;
- arthritis.
Effect on other body systems
Lupus can also affect the following systems:
Kidneys
: inflammation of the kidneys (nephritis). 1 in 3 people with lupus have kidney problems. Lungs: Some people develop pleurisy, which causes chest pain, especially when breathing. Pneumonia may develop.
Central nervous system:
lupus can sometimes affect the brain and central nervous system. Symptoms include headaches, dizziness, depression, memory problems, vision problems, seizures, stroke or behavioral changes.
Vasculitis, or inflammation of the blood vessels, may occur. This may affect blood circulation.
Blood
: Lupus can cause anemia, leukopenia (reduced number of white blood cells), or thrombocytopenia (decreased number of platelets in the blood, which help blood clot).
Heart
: If inflammation affects the heart, it can lead to myocarditis and endocarditis. It can also affect the lining that surrounds the heart, causing pericarditis. Chest pain or other symptoms may occur. Endocarditis can damage the heart valves.
Symptoms and signs
Depending on the type of manifestation of the disease, there are various symptoms and signs of lupus erythematosus.
Each patient may experience individual symptoms and signs of disease development, which depend on the general state of the immune system and the characteristics of the body.
Manifestation of dermatological type
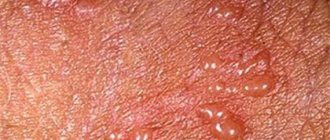
Characteristic manifestations of this type of lupus are the presence of a rash of varying intensity on the skin.
The first signs of disease formation:
- Itching of the epidermis;
- Swelling of the skin;
- Pain when touched;
- Manifestation of single formations in the face and neck.
Symptoms of the disease:
- Formation of a rash on the face that affects the nose and cheeks;
- The appearance of redness of the epidermis;
- Formation of scales;
- The appearance of red spots with a gray coating;
- Manifestation of veins and swelling of the legs;
- Violation of the integrity of hair and nails;
- Spider vein formation;
- General weakness;
- Temperature increase;
- Formation of a red line along the contour of the lips;
- Formation of ulcerative lesions of the mucous membranes of the mouth and nasal cavity.
The person may feel a lack of appetite and an upset stomach. Very often, such symptoms can lead to long-term headaches. A rash throughout the body can appear in the genital area, arms and abdomen.
Manifestation of orthopedic type
Very often, with advanced and complex types of lupus erythematosus, a decrease in the functions of the human skeletal system occurs.
Signs:
- Burning in joints;
- Painful symptoms at the end of the day;
- Violation of bone integrity;
- Rheumatology;
- When moving the limbs, unpleasant symptoms occur.
The following symptoms are observed:
- Inflammatory formations in the area of small joints;
- Damage to the elbow and knee joints;
- Tendon deformity;
- Specific crunching in the joints;
- Painful sensations.
The person experiences decreased joint function and frequent pain symptoms. The joint area becomes red and the skin becomes swollen.
Hematological signs of the disease
The development of the disease lupus erythematosus can be manifested by the following symptoms:
- Anemia;
- Formation of blood clots in blood vessels;
- Leukopenia.
In rare cases, damage to the walls of blood vessels and a reduced level of blood clotting may occur.
Manifestation of heart character
On the part of the heart organs, the manifestation of the disease lupus erythematosus can be manifested by the following symptoms:
- Endocarditis;
- Tachycardia;
- Pericarditis;
- Atherosclerosis;
- Myocarditis.
Signs:
- A sharp increase in heart rate;
- Pain in the chest area;
- General weakness.
The symptoms are chaotic in nature, often go away on their own, after which they appear with renewed vigor. Very often these types of symptoms are confused with other types of heart muscle damage and inappropriate treatment is used.
Significant factors associated with kidneys
In cases where lupus erythematosus disease affects the kidney area, the following symptoms may appear:
- Frequent urination;
- Pain in the lumbar region;
- Diseases of the genitourinary system;
- Swelling of the limbs;
- Hematuria;
- Pain during urination;
- Itching in the genital area
Symptoms:
- Swelling in the eye area;
- Observation of a large amount of protein in the urine;
- Pyelonephritis;
- Kidney disease.
Very often, the manifestation of such symptoms affects all nearby organs and disrupts the normal functioning of the genitourinary system.
Manifestation of a neurological nature
The disease can manifest itself with neurological symptoms:
- Dizziness;
- Epileptic seizures;
- Mental disorder;
- Stroke.
Signs and manifestations:
- Disturbance of normal sleep;
- Irritability;
- Overexcitement;
- Nervousness.
In addition to nervous system disorders, symptoms of indigestion, breathing problems and pain in the stomach are very common.
Situations can often be observed when the patient suffers from partial loss of vision or the formation of inflammatory processes in the visual organs.
Other complications
Having lupus increases your risk of a number of health problems:
Infection
: Infection becomes more likely because lupus also weakens the immune system. Common infections include urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, yeast infections, salmonella, herpes. Bone osteoporosis: This occurs when the blood supply to the bone is reduced. Eventually, the bone may break down. This most often affects the hip joint.
Pregnancy complications: Women with lupus have a higher risk of pregnancy loss, premature birth, and preeclampsia, a condition that includes high blood pressure. To reduce the risk of these complications, doctors often recommend delaying pregnancy until lupus has been under control for at least 6 months.
Diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus
There are special criteria of the American Rheumatological Association that take into account certain clinical manifestations of the disease (rash, damage to the joints, kidneys, central nervous system, etc.). Based on the combination of these criteria, the doctor makes a diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. The diagnosis is confirmed laboratory by the following tests:
- analysis for antinuclear antibodies - antibodies to various components of the cell nucleus;
- antibodies to native (unmodified) DNA;
- antiphospholipid antibodies.
To clarify the patient’s general condition and identify damage to specific organs, it is recommended:
- general blood analysis;
- biochemical blood test: determination of the level of creatinine, c-reactive protein, total protein, glucose, urea, ALT, AST;
- general urine analysis;
- ECG.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe additional tests: determination of daily proteinuria (the amount of protein excreted in the urine), Echo-CG, chest x-ray, and so on.
Treatment and home remedies
There is currently no cure for lupus, but people can manage their symptoms and outbreaks with lifestyle changes and medications.
Goal of treatment:
- prevent or control outbreaks;
- reduce the risk of organ damage.
Medicines can help:
- reduce pain and swelling;
- regulate the activity of the immune system;
- balance hormones;
- reduce or prevent damage to joints and organs;
- manage blood pressure;
- reduce the risk of infection;
- control cholesterol.
The exact treatment will depend on how lupus affects a person. Without treatment, flare-ups can occur, which can have life-threatening consequences.
Classification of systemic lupus erythematosus
At the beginning of the clinical course, the disease can be:
- acute - sudden onset, rapid onset of symptoms from most organs, including kidney damage, rapid deterioration of the patient's condition;
- subacute - gradual onset, wavy course, relatively slow spread throughout the body;
- chronic - begins with damage to one organ, usually the skin, persists for a long time at one level of severity, and spreads slowly to other systems.
According to the intensity of manifestations, 3 degrees of activity are distinguished:
- minimum,
- moderate,
- expressed.
Forecast
People who have a history of lupus do not usually survive more than 5 years. Now, however, the treatment can significantly increase a person's life expectancy, according to the National Institutes of Health.
Effective therapy can also help manage lupus so a person can live an active, healthy life.
As scientists learn more about genetics, doctors hope they will one day be able to identify lupus at an earlier stage. This will make it easier to prevent complications before they occur.
Scientists believe that lupus increases the risk of developing cervical cancer in women.