Papillomas in intimate places are a common phenomenon. Neoplasms of this type can appear on the genitals, on the skin of the perineum, and in the anus. If papilloma appeared in the intimate area, then this was most likely due to infection from a sexual partner with the human papilloma virus.
Speaking about what such neoplasms look like, it is worth noting that almost all papillomas and warts that are localized in the intimate area are genital warts. They develop from squamous epithelial tissues. Therefore, noting what types of papillomas there are, we can also distinguish two more varieties: thread-like growths (occur in the groin area, look similar to elastic threads, there can be quite a lot in one area), flat viral formations (look like miniature lumps, painful, may itch).
If you do not know which doctor removes papillomas in intimate places, then you should contact a urologist, proctologist, or gynecologist (depending on where exactly the viral growths have formed due to HPV). The listed specialists will first treat the disease and then, if necessary, remove the tumors.
Causes of papillomas in the intimate area
Papillomas, or genital warts, in intimate places in women have a viral etiology. HPV is transmitted exclusively from person to person and leads to changes in the pattern of tissue growth. There are many types, or strains, of the virus that cause the growth of benign warts in women and provoke cancer of the vagina, cervix, and anus.
All strains of the virus are divided into groups according to their ability to induce malignant transformation of tissues.
| Degree of oncogenic risk | Type of human papillomavirus |
| Low | 3, 6, 11, 13, 32, 34, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 51, 61, 72, 73 |
| Average | 30, 35, 45, 52, 53, 56, 58 |
| High | 16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 50, 59, 64, 68, 70 |
The growth of genital warts in most cases is provoked by HPV strains 6 and 11.
What does papilloma look like?
It is not difficult to determine the presence of papillomas on the external genitalia. The neoplasms look like a small process, transparent or flesh-colored. Usually, papilloma in an intimate place does not appear one by one. Its body is soft, loose, and easily damaged.
There are several types and forms of papillomas:
- Pointed - papilloma appears in the groin, on the pubic part and on the genitals themselves. They rise above the surface of the skin by 0.5-1 cm, while their diameter is several times lower. The main danger of such neoplasms is rapid growth. Papillomas can grow together, forming conglomerates that degenerate into tumors.
- Flat – genital papillomas are localized on the cervix, glans penis and rectum. They appear in clusters, causing severe itching, pain, swelling and redness of the affected areas of the epithelium.
The following types of genital papillomas are less common:
- Thread-like - barely noticeable neoplasms of a transparent or flesh-colored color, having a diameter of up to 5 mm and a height of up to 2 cm. These papillomas in the groin can develop without much harm to overall health.
- Pedicled papillomas - the neoplasm itself is attached to the surface of the skin with the help of a special thread-like process.
There are a lot of varieties of papillomas, which differ in shape, color and pathogen that provoked the appearance of papillomas on the genitals.
Routes of infection
HPV is very easily transmitted from person to person. Entry into the body occurs in several ways.
| Method of infection | Description |
| Sexual | When genital warts occur in intimate places in women, this is the main method of infection. The virus can enter the body through oral-genital and anal contact. |
| Contact and household | The virus can survive for a short time in exfoliating skin cells, so the presence of damage to the skin and mucous membranes, even of a microscopic nature, allows viral particles to penetrate the human body. Infection occurs when visiting public toilets, swimming pools, baths, and gyms. |
| Autoinfection | The woman herself can spread the virus to new areas of the skin when shaving and epilating. This route of infection is also called autoinoculation. |
| From mother to child | The viral infection can be transmitted from mother to child during childbirth. This causes the appearance of papillomas in a newborn on the mucous membranes of the mouth, pharynx, genitals, and in the anus. |
The likelihood of infection increases in the presence of predisposing factors.
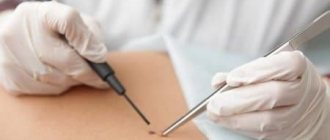
Removal methods on female organs
The selection of a method for removing the growth is made based on the size and signs of oncogenicity of papillomas, the severity of the disease and the condition of the patient’s body at the time of the procedure.
Hardware solutions are optimal. For large volumes, surgical excision is used along with healthy tissue to prevent further spread of papillomatosis.
The removal process is carried out exclusively in a medical facility by a qualified doctor.
Surgery
The operation to excise the focus of papillomatosis, surrounding affected and parts of healthy tissue, lasts from 40 minutes to several hours.
After surgery, the recovery period is 14-30 days, the postoperative wound is healed by surface tension. It is necessary to carefully observe the rules of intimate hygiene and treat the area with antiseptics (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin) until the wound surface is completely healed. The disadvantages are that scar tissue and an extensive scar may form, which may require further plastic surgery in the area of surgical correction.
Minimally invasive methods
The optimal choice for eliminating the external manifestations of HPV:
- Laser method. The laser beam coagulates the papilloma as quickly as possible (from several minutes to half an hour), without the formation of a scar. Recovery takes from 1 to 10 days, the method is bloodless. If necessary, local anesthesia is performed using subcutaneous injections of Lidocaine, Ultracaine.
- Freezing at extremely low temperatures using a jet of liquid nitrogen. The impact is targeted, without damaging healthy tissue. The range of application on the mucous membrane of the genital organs is limited, the effect is aggressive.
- Radio wave method using excision (actually burning with a radio wave) using a radio knife - the Surington apparatus. Minimally painful, bloodless with a recovery period of up to 7-10 days.
Probability of infection
HPV infection of the genitals and perineum is highly contagious, or contagious. Infection during a single sexual contact with a partner who has the virus occurs in six out of ten cases. The possibility of genital warts increases even more in the presence of a number of conditions.
| Predisposing factor | Characteristic |
| Young age | Most often, clinical signs of HPV infection appear in patients aged 20 to 24 years. In general, the age range from 17 to 33 years is the most likely for women in terms of the growth of papillomas in intimate areas. |
| Early sexual debut | Early onset of sexual activity, when the processes of hormonal changes have not yet been completed, is a factor that increases the risk of genital papillomatous formations. |
| Frequent change of sexual partners | A large number of sexual partners, frequent and promiscuous sexual contacts significantly increase the chances of contracting human papillomavirus infection. |
| Unprotected sexual contacts | Barrier contraception - the use of a condom - still remains the only easily accessible and relatively inexpensive means of possible, but not absolute, protection against HPV. It is impossible to completely get rid of the likelihood of infection with its help, since a condom may not isolate all contacting areas of damaged skin. But unprotected sexual intercourse is an almost guaranteed infection. Unprotected anal sex is an even greater risk factor, as it is often accompanied by microtrauma to the mucous membrane and skin. |
A combination of factors greatly facilitates the possibility of infection.
Causes
Genital papillomatosis is often hidden and is activated under conditions that reduce the immune system, for example, hormonal imbalance, influenza. There can be many reasons for the development of this pathology. The disease is transmitted through a handshake, clothing, bedding, personal hygiene items: washcloth, toothbrush, towel.
You can also become infected with the disease in a bathhouse, swimming pool, sauna, public shower or during a gynecological examination. However, the main reason for the appearance of formations on the genitals is intimate relationships with an infected partner.
Since the skin on the genitals is thin, easily injured and has a moist environment, the infection can exist for a very long time in such favorable conditions. Barrier contraception cannot completely protect the body from HPV invasion.
Causes of infection:
- oral, anal and genital contact with a carrier of infection;
- prolonged use of medications;
- disorder of the genitourinary system;
- colds;
- use of hormonal contraceptives;
- HIV infection;
- stressful situations;
- pregnancy;
- allergy;
- diabetes;
- exercise stress;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- unfavorable working conditions;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, smoking;
- incorrect diet.
Forms of existence of HPV in the body
Once in the female body, the virus penetrates the epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes, where it can exist in two forms.
| Form of existence of HPV | Characteristic |
| Episomal | The inactive stage of virus development, which is considered benign. Viral particles are located outside the cell's chromosomes. Observed in asymptomatic carriers of the virus. It is observed in patients with good general body resistance. |
| Introsomal | The active stage of HPV development is regarded as a malignant form of parasitism of viral particles in the body. The virus integrates into the genome of epithelial cells and begins to control the cellular genetic material for the reproduction of HPV-encoded proteins, which leads to the appearance of clinical symptoms. |
During pregnancy
In rare cases, the development of papillomatosis occurs during pregnancy, which negatively affects both the process of bearing a child and the woman’s health. Most often, infection is caused by a physiological decrease in immunity during pregnancy.
Characteristic signs that should alert a woman will be heavy vaginal discharge, which is associated with hormonal imbalances that are aggravated by a viral infection that has entered the body.
It is unacceptable to carry out treatment on your own - thereby a pregnant woman exposes the fetus developing in the womb to danger. When the first signs of papillomatosis develop, an examination and consultation with a gynecologist must be followed. The attending physician will suggest the best option for removing papillomas, and will also prescribe medications that strengthen the body (vitamin therapy).
Variants of the course of HPV infection
Contact with human papillomaviruses, even those dangerous in relation to cancer, does not always lead to the appearance of genital warts and the development of malignant diseases. Recovery may occur over a period of 6 to 12 months or long-term carriage without symptoms may occur. Papillomas in women appear in intimate places, and then quickly grow when the virus awakens. A decrease in the body’s defenses and the activation of HPV are promoted by:
- prolonged hypothermia;
- excessive physical and psycho-emotional stress;
- abuse of strong alcohol, smoking;
- viral, bacterial, fungal infectious diseases;
- traumatic injuries;
- pregnancy;
- malignant tumors;
- hormonal diseases;
- taking antibiotics, hormones, cytostatics.
In more than half of patients, characteristic growths in the genital area appear 1–3 months after intimate contact with a partner infected with HPV.
Prevention and care after removal
To avoid relapses and complications, the wound must be cared for after removal. After surgery, a crust forms at the site of the tumor. It is necessary to avoid damaging it, as it protects the wound from infection. In order for the crust to form faster, constant ventilation is needed. The scab should not be lubricated or wet with anything. You should also avoid exposing it to ultraviolet rays.
To prevent relapses, you need to carefully monitor your immunity. Avoid hypothermia, overheating, and drafts. Treat concomitant pathologies in a timely manner. Switch to a healthy diet and give up bad habits. Perform hardening procedures and exercise daily.
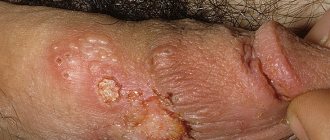
Symptoms
Genital papillomas in women can be single or multiple (see photo), small or large in size. Usually, during initial growth, they look like small flesh-colored or pink nodules, and later turn into growths in the form of papillae, similar in appearance to the comb of a rooster or cauliflower inflorescences. They are soft in consistency and have a so-called stem. Sometimes they grow up to several centimeters in diameter. The most common sites of localization in women:
- vaginal part of the cervix;
- walls and vaults of the vagina;
- labia;
- urethra;
- perineal skin;
- area around the anus;
- groin area.
Genital warts often exist asymptomatically. In this regard, women do not complain, especially with small lesions. Bleeding and weeping appear when the growths are traumatized, itching, pain, and sometimes an unpleasant odor - when ulceration and the addition of a secondary bacterial infection. Discomfort during urination occurs when papillomas are localized in the urethra, and during defecation - in the anus.
Classification of formations
Since we are talking only about the intimate area, the types of papillomas will be described only from this area. Papillomas on the genitals are soft, located in groups, and are rarely isolated. Types of urogenital papillomas:
- Condylomas acuminata are flesh-colored tubercles, formations on legs, have a cone-shaped shape, which is why they got their name. What do papillomas look like? They are flesh-colored or pinkish in color, rise above the skin in the form of a cockscomb or grow like a head of cauliflower. Usually localized on mucous membranes and transmitted only through sexual contact.
- Lesions in the form of papules are round in shape and can be up to 1 cm in size. They are located on the skin of the genitals.
- In the form of spots - they can be of different colors: from pink and gray to red and brown. Also found on the mucous membranes of the genitals.
- Bowenoid papulosis - may appear as macules and papules, ranging in color from gray to brownish-black. It can grow both on the skin and on mucous membranes, in women - on the clitoris and labia, in men - on the penis. Has a high oncogenic risk.
- Giant condyloma is a wart that resembles a head of cauliflower. It consists of many papules and nodules connected to each other.
The virus can exist inside a cell, infecting its nucleus - the introsomal form. Then it integrates into its genome and acts on the chromosomes; this form of morphology is malignant. In the episomal form, the virus does not invade chromosomes; this type is benign.
Diagnosis of papillomas in intimate places in women
When genital warts appear in the genital area, patients usually turn to a dermatologist and gynecologist. When conducting diagnostics, the doctor:
- interviews the patient;
- studies the history of the development of the disease;
- examines the external genitalia;
- takes a cytological smear (scraping of cells from the cervical canal and vaginal part of the cervix for evaluation under a microscope);
- conducts a gynecological examination;
- performs a colposcopy (examination of the vagina, cervix and the initial part of the cervical canal using an optical device - a colposcope);
- takes material for histological examination if he suspects the malignant nature of the formation;
- recommends taking blood to determine HPV type using polymerase chain reaction (PCR);
- screens for sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
If genital papillomas located in the urethra are detected, an examination by a urologist and urethroscopy may be necessary. It is mandatory to screen your sexual partner for the presence of HPV and STIs.
Destruction options
It is impossible to remove large growths in 1 session. If there are many formations, long-term therapy is needed. The required result can be obtained quickly only when hardware methods are used. Such manipulations are allowed if it is determined that there is no risk of malignancy. The procedure is performed only by experienced specialists in a hospital setting.
When it turns out that a wart can develop into a tumor, the patient requires surgical intervention. The operation is also carried out if there are a lot of growths. In this case, the surgeon uses a scalpel. Before mechanical removal, a local anesthetic is injected into the skin. At the end of the procedure, a small scar remains.
Hardware methods are a gentle option for removing growth. Laser therapy is the most popular today. The laser beam acts on the growth and removes it completely, regardless of the location and depth of germination in the tissue. There is no scar left after the manipulation. Other hardware techniques:
- Electrocoagulation. According to this method, using an electric current of constant frequency, tumor tissue is removed, and the vessels are sealed. Capillaries also overlap in healthy tissues located nearby. Electrocoagulation is considered a bloodless method. It leaves a small wound that heals in a matter of days.
- Cryodestruction. Genital tumors are removed with liquid nitrogen through freezing. This local effect is very effective, but is used only for the external genitalia. If HPV has infected the cervix and vaginal mucosa, then freezing with liquid nitrogen is prohibited.
- Radio wave destruction. It involves the use of the Surgitron apparatus, which generates radio waves. They destroy pathological areas of the skin and mucous membrane, but have no effect on healthy tissue.
All these methods make it possible to remove areas of growth on certain parts of the body, but do not fight relapses. Condylomas may appear again after removal if immunity decreases. To avoid their occurrence, it is enough to take immunomodulators and antiviral drugs for a certain duration. The duration of the course of treatment is determined by the doctor.
Treatment of genital papillomas
Therapy for genital papillomas should solve the following key problems:
- improve immunity;
- remove existing papillomas;
- prevent the appearance of new growths.
It is extremely difficult to completely get rid of papillomavirus due to its variability and significant species diversity, so treatment is predominantly symptomatic and restorative.
It is necessary to treat not only the woman, but also the sexual partner.
The main goal of therapy is to convert the virus into an inactive, or dormant, state.
| Medical direction | Ways to achieve |
| Boosting immunity | A decrease in the protective properties of the immune system contributes to the appearance of genital warts in the genital area in women. With good immunity, the body is able to cope with HPV contained in cells in 80-90% of cases within 24 months. The effectiveness of the local immune response can be increased with antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs: Interferon, Isoprinosine, Allokin-alpha, Cycloferon, Genferon, Epigen Intim, Lykopid, Aldara, Immunomax, etc. It is possible to use various dosage forms: injection solution, tablets, vaginal and rectal suppositories , ointments, creams, sprays. |
| Removal of papillomas | Therapy cannot be limited to just removing existing papillomatous growths. The patient should be treated comprehensively. The disappearance of small papillomas and regression of large papillomas can sometimes be achieved with immunostimulating and antiviral treatment. In addition, papillomatous formations should not be removed without systemic treatment, as this promotes infection of adjacent areas of the skin and mucous membranes, increasing the possibility of relapse. Removal of papillomas in intimate areas can be carried out in several ways: surgically, using alternating electric current, laser, liquid nitrogen, using coagulation with chemicals. |
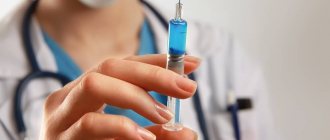
| Prevention of HPV infection | A healthy lifestyle is a factor that helps increase nonspecific immunity, and it is necessary to reliably resist HPV infection. You should create the correct stereotype of sexual behavior: choose one sexual partner, avoid casual relationships, use a condom. For primary prevention, there is a vaccine called Gardasil, which is effective against HPV types 6, 11, 16 and 18. Vaccination is effective only for preventive purposes and is not intended to treat an existing disease. The best result is achieved if vaccination is carried out before the onset of sexual activity. Side effects when administering the vaccine are minor. |
Gardasil is a vaccine that allows you to protect against papillomavirus, which is responsible for the formation of papillomas in the intimate area
Medications
There are a number of pharmacological agents that can remove papillomas and other formations on the skin. But it is not recommended to use them independently without a doctor’s prescription, especially in the intimate area, since there is a high probability of side effects. In addition, applying medications to the genitals is inconvenient for the person himself, so it is best to seek the help of medical professionals.
According to experts, the following are considered effective medications:
- Condilin. A solution for the local treatment of genital papillomas, cauterizing them and causing cell necrosis. The skin around the formations is lubricated with Vaseline or any ointment. The drug is applied using a plastic applicator. The procedure is carried out twice within 3 days. If necessary, repeat after a week's break. If the child is under 12 years of age, Condilin is used only as directed by a doctor. This rule also applies to women during pregnancy and lactation.
- Solcoderm. The product contains oxalic and acetic acids, which burn out tumors. The drug is aggressive, so it is recommended to use it simultaneously on an area of no more than 2 cm2. Contraindicated in cases of suspected degeneration of papillomas, as well as for children under 5 years of age.
- Fluorouracil. Available in the form of an ointment with 5% active substance content. It is applied to tumors using an applicator, avoiding contact with healthy skin. Apply once a day until the growth completely disappears, but no more than 7 days. If necessary, the course is repeated after 2 weeks. Not for children, pregnant and lactating women.
- Imiquimod. The cream is applied pointwise to the papillomas in the evening and throughout the night. The course of treatment is up to 4 months. While using the drug, it is recommended to avoid contact with ultraviolet radiation on the skin to avoid burns. Contraindicated in children and adolescents under 18 years of age, as well as during pregnancy and lactation.
All external preparations intended to remove tumors are toxic and can cause irritation to the delicate skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs. Therefore, they should be used strictly following the instructions and only as prescribed by a doctor.
Traditional methods
There are many folk recipes that allow you to get rid of papillomatous formations at home (which in no case should be torn off). For removal use: celandine, garlic, lemon juice, hydrogen peroxide. All of these products are dangerous for use in the intimate area. You should also remember that you cannot cure an infection simply by getting rid of visible growths. To combat the virus, systemic therapy is necessary, so it is better not to self-medicate, but to contact specialists immediately.
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
With papillomatosis of the intimate area, complications may develop:
- decreased libido and disruption of hormonal regulation;
- secondary infection.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, undergo the necessary tests, and eliminate potentially dangerous papilloma of the genital area, the prognosis is favorable, cure occurs in 95-100% of all diagnosed cases. If formations appear, consult a doctor immediately to avoid dangerous consequences. Removal must be accompanied by a comprehensive effect on the body to avoid relapses.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors