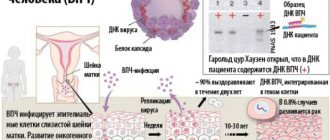
The spread of fungal infection in the groin area is an infectious process that in most cases affects the male body; in women, this form of mycosis is much less common. Many people try to solve the problem on their own, avoiding communication with a doctor, since the topic will affect the intimate area of the body.
But improper treatment significantly aggravates the process and can provoke unforeseen complications. Therefore, an important point in determining therapeutic measures when a fungus is detected in the groin is competent diagnosis within a specialized clinic. Since even a slight peeling in the pubic area can already be the first sign of the development of mycosis.
Photo
Prevention
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Careful observance of personal hygiene rules.
- Regular change of clothes and underwear, washing and ironing them.
- Fighting excessive sweating, using cosmetics (for example, talcum powder).
- Prevention of stress.
- More physical activity.
Important!
If you find suspicious spots and irritation in the groin, or feel itching, it is important to immediately consult a doctor. Self-medication, including self-prescription of medications, is unacceptable!
Prevention measures concern not only the person himself, but also his home . It is necessary to disinfect all contact surfaces, especially in the bathroom.
A colony of pathogens can only be destroyed by long boiling of bed linen and clothes with laundry soap.
It is important to teach yourself and your loved ones to dry yourself thoroughly after taking water procedures, and to use only personal towels.
When visiting public baths and saunas, use protective rubber shoes and take a shower after swimming. Immediately treat minor cuts and abrasions with an alcoholic infusion of calendula or salicylic acid.
Athlete's foot
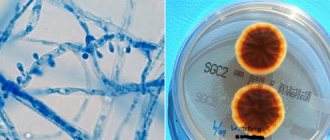
The causative agents are the fungi Epidermophytonfloccosum, Trichophytonmentagrophytes, Trichophytonrubrum. Most often they affect the groin area, but can be localized in the armpits, under the breasts, and on the inner thigh.
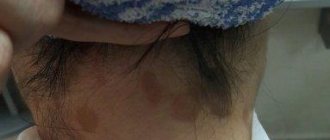
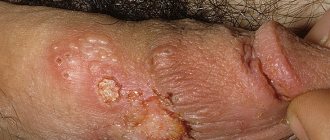
The disease begins with the appearance of small pink round spots. Their surface peels and itches. Gradually, the affected areas grow up to 10 cm in diameter and merge with each other.
Foci of inflammation have a clear convex border strewn with bubbles. In the center of the formation, the skin clears, pigmentation takes the shape of a ring. Patients suffer from itching, burning and pain, which intensifies when walking. If the pathology is not treated, fungus in the groin in women can last for several years.
Introduction
Fungus on the body is an extremely unpleasant dermatological disease, which, if diagnosed untimely, is very difficult to remove.
It is not dangerous to human life, but it creates an aesthetic problem and can cause concern for a long time.
Despite the fact that the percentage of sick men is much higher than women, no one is immune from such an infection. Let's look at the main causes of fungus, symptoms and, of course, take note of treatment methods.
Candidiasis
Infection caused by yeast-like fungi Candida albicans and others of the genus Candida. All of them are part of the normal microflora of the vagina, oral mucosa and intestines. They are classified as opportunistic microorganisms.
Once in the human body, mushrooms may not make themselves known for years until a favorable environment for their reproduction arises. This usually occurs when immunity is reduced or a sweet environment is created (for example, with diabetes).
Most often, candidiasis affects the genital area and causes fungus in the groin in women. The clinical picture includes itching and burning, redness and swelling of the labia and vaginal vestibule, and cheesy discharge. Pain occurs during sexual intercourse and urination. A red rash appears on the genitals, which, when scratched, turns into numerous ulcers.
In the absence of adequate treatment, the disease enters the chronic stage with frequent relapses. In advanced cases, damage to the organs of the reproductive system may occur, leading to infertility.
Types of fungal infection
In practice, several types of pathogens of fungal flora are diagnosed, which form the development of mycosis in the groin area, affecting in most cases people in the middle age category.
Athlete's inguinal
It is provoked by one of the representatives of inguinal fungi, which is Epidermophyton floccosum, forming a small percentage of disorders among the entire group of mycoses. The pathogen is transmitted by contact, through direct interaction with infected things or people. Provoking factors that contribute to the activation of a pathogenic microorganism are the following conditions:
- Excessive sweating.
- Use of tight underwear.
- Endocrine pathologies, in particular diabetes.
- Long-term treatment with glucocorticoids.
- Prolonged stay in a humidified environment.
The fungal pathogen settles in the groin area, armpits, folds of skin under the mammary glands and the gluteal area, somewhat less frequently on the back of the knee bends. With the development of a pathological disorder, the fungal zone of tissue damage most often spreads to areas adjacent to the groin. In childhood, the disease is diagnosed extremely rarely, but cases of the development of epidermophytosis are recorded during puberty.
Rubromycosis
The disease is caused by Trichophyton rubrum. The pathogen is able to penetrate the systemic bloodstream, causing extensive lesions in different parts of the body. It is usually localized between the fingers and in the fingernails and toenails, but can cause inguinal fungus in women.
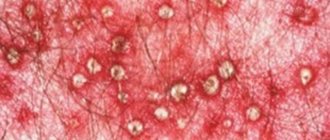
The pathology appears in the form of large red spots with a flaky surface. In the affected areas, compactions and vesicles with serous fluid inside form. The capillaries in these places expand. Unbearable itching appears.
The edges of the lesions swell and become covered with crusts and rashes. The central part acquires a yellowish, bluish or brown tint. The disease has a sluggish nature with exacerbations in the warm season. If left untreated, it can drag on for a very long time.
What treatment therapy should I use?
Restorative measures necessarily include the use of medications, which include antifungal ointments and creams, antihistamines and systemic immunomodulatory tablets.
The treatment course has a long interval for superficial treatment of the affected areas using drugs such as clotrimazole, miconazole, terbinafine, triderm. Each product, dosage and application regimen are determined by the doctor in accordance with the results of laboratory diagnostics, establishing the specifics of the current fungal infection.
Erythrasma
For a long time it was believed that this disease was caused by fungi. But now it is classified as pseudomycosis. Scientists have found that the causative agent is the bacterium Corynebacterium minutissimum, which lives on the skin of almost all healthy people.
In its effects, the microorganism resembles fungi. It is localized in areas with diaper rash and dermatitis and most often affects those who are overweight. The bacterium has a detrimental effect only on the upper layers of the skin.
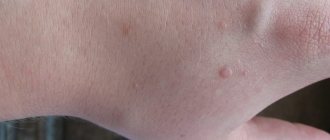
External manifestations are also similar to mycotic diseases. Round spots of brown, red or yellowish hue appear on the body. The diameter of the neoplasm reaches several centimeters. Gradually they merge with each other, forming large foci.
The affected area has a smooth surface covered with pityriasis-like scales. Over time, the center of the pigmented area turns pale or brown.
The disease does not cause physical discomfort, so patients rarely seek medical help. Pathological processes last for more than 10 years, periodically subsiding. Exacerbations usually occur in the summer.
When rubbed or dirty, the affected areas become infected. Complications include burning, itching, pain and inflammation.
Causes and routes of infection
The causes of inguinal fungus are varied. The main factor becomes infection from an external carrier. The fungus is transmitted through direct contact with an infected partner or indirectly through:
- use of common household items and premises;
- wearing someone else's clothes or shoes;
- visiting public places where there is a high risk of infection.
But for the intensive development of infection, additional conditions are required that simulate the spread of the fungus and its activity:
- body hyperhidrosis;
- regular diaper rash;
- wearing underwear made of synthetics and small sizes;
- too hot climate;
- overheating of the body from overly warm clothing.
All this entails a weakening of local immunity and creates a favorable environment for the pathogen. The causes of fungal infection may be associated with the vulnerability of the general immune system due to exacerbation of chronic diseases, colds, prolonged use of hormonal drugs and antibiotics.
Features of treatment
When your pubic skin is itchy and itchy, you should seek advice and treatment from an experienced dermatologist or mycologist. The doctor will offer external ointments or creams, which within a few weeks will relieve the patient of unpleasant symptoms and return to a normal rhythm of life.
The most common and effective are:
- Econazole;
- Miconazole;
- Ketoconazole;
- Mycozolon.
Miconazole cream for fungus
At any stage, with a large area of damage, experts recommend using tablets. They will help the patient defeat candidiasis or epidermophytosis from the inside. It is enough to take them for 5–10 days to get a good lasting effect and get rid of inflammation.
Treatment is more difficult in women if inguinal mycosis manifests itself in the vagina. External creams should be supplemented with special suppositories with antifungal components: Terzhinan, Livarol or Pimafucin. Drugs for pregnant or lactating women are selected with caution so as not to harm the baby.
You can reduce the discomfort of itching with the help of antiallergic medications: Suprastin, Diazolin or Claritin. Baths with decoctions of oak bark, which will reduce sweating and dry out inflamed skin, can alleviate your general condition.
Before going to bed, the groin is treated with iodine tincture, calcium chloride or natural antifungal compounds: tea tree oil, a decoction of eucalyptus leaves or St. John's wort, diluted propolis.
Folk recipes
- You can treat inguinal fungus yourself using traditional medicine.
There are several simple but quite effective methods: Birch infusion. To prepare it, you will need to take about 15 leaves of this tree, pour in 100 ml of vodka and let it brew for 5 days. The resulting composition should be used to treat the rash 2 times a day until it completely disappears. Related article: Birch tar as a remedy for fungus - Herbal compress. To prepare it, take 2 parts of oak bark, the same amount of yarrow stems and 1 part of flax seeds. All this is mixed in a container, poured with boiling water (1 liter) and left for 30 minutes. The infusion is used for a compress, which is done daily before bed.
- Herbal decoction. To cure mycosis, mix chamomile, St. John's wort, eucalyptus and yarrow in equal amounts. All herbs are poured into 0.5 liters of boiling water and infused for half an hour. The resulting decoction is taken orally, 100 ml 3 times a day. More details
But do not forget, traditional medicine recipes can be used as independent treatment only at the initial stage of the disease. In the future, they will be ineffective and will only lead to complications, since the correct treatment was not prescribed.