Blisters in the groin with herpes type 2
The most likely cause of a vesicular rash is a herpes infection.
It is considered one of the most common STDs, ranking second after trichomoniasis.
Blisters in the groin area do not appear immediately after infection.
The incubation period lasts for 1 week.
This is the time that passes from the moment of sexual contact with an infected partner until the first symptoms appear.
These are the subjective sensations: itching, burning, tingling.
This is the prodromal period, when there is no rash yet.
She appears a day later.
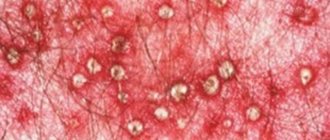
Watery blisters form in the groin, surrounded by an area of hyperemia.
They contain a clear liquid.
Vesicles are grouped.
Almost all of them are formed at the same time.
In the future, if there are any additions, they are insignificant.
Bubbles appear wherever the virus enters the skin.
This can be not only the groin area, but also the labia majora, pubis, and anal area.
In men, watery blisters in the groin are complemented by a vesicular rash on the head of the penis and scrotum.
After a few days the contents become cloudy.
The bubbles become sluggish.
Then they open up.
Ulcers form, which transform into crusts.
After they leave, temporary hyperpigmentation remains.
Herpes infection is not completely cured.
Although its symptoms go away after 1-2 weeks, the virus remains in the body.
Existing drugs do not allow for its complete elimination.
Therefore, for most people, herpes recurs from time to time.
Features of relapses:
- are milder than the primary infection
- may vary in frequency among individuals, occurring within 80% within 12 months of infection
- the severity and frequency of exacerbations correlates with the severity of the initial episode of the disease
How herpes will progress largely depends on the full functioning of the immune system.
In people with strong immunity, bubbles may form in small quantities and last only a few days.
The illness lasts only a few days.
In the future, there are no exacerbations at all, or they are so mild that they go unnoticed.
In people with weak immune systems, the disease is severe and often worsens.
HIV-infected people may experience severe complications, including those associated with brain damage.
Pathogenesis of inguinal athlete's foot
Under favorable conditions, the pathogenic fungus invades and begins to multiply in the skin. Important importance is attached to the enzyme keratinase produced by fungi, which allows them to penetrate the cells of the epidermis.
After introduction, the fungus germinates in the form of branched mycelium; if the rate of exfoliation (desquamation) of the epithelium is low, the mycelium of the fungus spreads further over adjacent areas of the skin. Otherwise, either spontaneous recovery or asymptomatic carriage occurs. The decisive point is the state of local immune defense (macrophages, T cells, IgA secretion). Dermatophytes contain carbohydrate wall molecules (β-glucan) that are recognized by innate immune mechanisms such as Dectin-1 and Dectin-2, which activate similar receptors 2 and 4 (TLR-2 and TLR-4) and trigger the immune defense mechanism. Unsaturated plasma transferrin (inhibits dermatophytes by binding their hyphae), complement, opsonizing antibodies and phagocytosis by neutrophils have a certain role. All these mechanisms prevent the involvement of deep tissues in the process, and therefore dermatophytes never penetrate beyond the basement membrane of the epidermis. In typical cases, the rate of mycelial growth significantly exceeds both the desquamation of the epithelium and the time for the formation of an immune response, resulting in the formation of ring-shaped foci with a peripheral zone of active fungal reproduction and with a central, apparently healthy skin, where the process is partially or completely suppressed by local immunity. .
Are blisters in the groin dangerous due to herpes during pregnancy?
A herpetic infection is extremely unpleasant for most people, but still not dangerous.
But if blisters in a woman’s groin occur during an existing pregnancy, this is an unfavorable prognostic sign.
Surely you know that all expectant mothers are tested for TORCH infections in the first trimester.
The letter “H” in this abbreviation stands for herpes.
This is one of the most dangerous infections of the gestational period.
It can lead to spontaneous abortion, developmental defects, complicated pregnancy, and premature birth.
Sometimes the fetus becomes infected with a herpes infection and develops severe neonatal herpes.
The greatest threat is when a woman becomes infected after conceiving a child.
While a recurrence of herpes is much safer for both the mother and the fetus.
In this case, protective antibodies exist in the blood.
Therefore, although there are risks, they are minimal.
How do you know if you are infected for the first time, or if this is an exacerbation of herpes that you may have been infected with many years ago?
First, you can strain your memory and remember if you have had blisters in your groin before.
Secondly, you must be tested for antibodies to herpes during pregnancy.
If there are IgG antibodies, but not IgM, this is a relapse of herpes, and not a primary infection.
In case of relapse, the risk of intrauterine infection is very small.
But there is a risk of transmitting herpes to the newborn during childbirth.
Therefore, all women who develop blisters in the groin in late pregnancy are subject to drug treatment.
In some cases, the presence of genital herpes becomes an indication for cesarean section.
Otherwise, the child becomes infected.
In the natural course of neonatal herpes, the mortality rate of children reaches 50%.
In the case of the development of a disseminated form of infection, it is even higher – 90%.
After treatment, children usually survive, but neurological impairment may persist.
Bibliography
- Drake LA, Dinehart SM, Farmer ER, Goltz RW, Graham GF, Hardinsky MK, et al. Guidelines of care for superficial mycotic infections of the skin: Tinea corporis, tinea cruris, tinea faciei, tinea manuum, and tinea pedis. Guidelines/Outcomes Committee. American Academy of Dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol 1996;34(2 Pt 1):282-6
- Jaradat SW, Cubillos S, Krieg N, Lehmann K, Issa B, Piehler S. Low DEFB4 copy number and high systemic hBD-2 and IL-22 levels are associated with dermatophytosis. J Invest Dermatol 2015; 135:750-8
- Foster KW, Ghannoum MA, Elewski BE. Epidemiologic surveillance of cutaneous fungal infection in the United States from 1999 to 2002. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004 May. 50(5):748-52
- Patel GA, Wiederkehr M, Schwartz RA. Tinea cruris in children. Cutis. 2009 Sep. 84(3):133-7
- Dahl MV. Dermatophytosis and the immune response. J Am Acad Dermatol 1994;31(3 Pt 2):S34-41
- Tainwala R, Sharma Y. Pathogenesis of dermatophytoses. Indian J Dermatol 2011; 56:259-61
- Dermatovenerology. National leadership / ed. Yu. K. Skripkina, Yu. S. Butova, O. L. Ivanova. – M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2014. – 1024 p.
- Rodionov A. N. Fungal skin diseases: a guide for doctors (2nd ed.). – St. Petersburg: Publishing House “Peter”, 2000. – 288 p.
- Wan SJ, Lara-Corrales I. An unresponsive rush to topical steroids: tinea incognito. Arch Dis Child. 2021 Jan;103(1):13
- Federal clinical guidelines. Dermatovenereology 2015: Skin diseases. Sexually transmitted infections. — 5th ed., revised, and additional. - M.: Business Express, 2021. - 768 p.
- Sahoo AK, Mahajan R. Management of tinea corporis, tinea cruris, and tinea pedis: A comprehensive review. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2021 Mar-Apr;7(2):77-86
- Hazlianda C, Muis K, Lubis I. A Comparative Study of Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism and Fungal Culture for the Evaluation of Fungal Species in Patients with Tinea Cruris. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2021 Nov 21;5(7):844-847
- Weitzman I, Summerbell RC. The dermatophytes. Clin Microbiol Rev 1995; 8:240-59
- Sergeev A.Yu., Sergeev Yu.V. Fungal infections. Guide for doctors. – M.: “BINOM”, 2003. – 440 p.
Blisters in the groin due to heat rash
Miliaria is a reaction of the groin skin to overheating.
There is a blockage of the sweat glands.
Miliaria can be crystalline and red.
In the case of crystalline prickly heat, blockage of the sweat glands occurs at the level of the stratum corneum of the skin.
In this case, small bubbles with transparent contents are formed.
Usually they do not exceed 1 mm in diameter.
Miliaria rubra is an even deeper process.
Therefore, in addition to the blisters, papules appear.
Miliaria itself is not considered a disease.
This is nothing more than a skin reaction to overheating and humidity.
After eliminating the pathogenetic factors, the skin is restored without treatment.
But prickly heat is a predisposing factor for secondary infections.
If bacterial flora attaches, sweat gland abscesses can form.
They require surgical treatment.
Treatment
If symptoms of the above diseases are detected, it is recommended to immediately consult a venereologist. It is the specialist who will be able to correctly diagnose and prescribe appropriate treatment. As a rule, doctors prescribe:
- anti-allergy drugs - “Suprastin”, “Zodak”;
- eliminating fungus - “Clotrimazole”, etc.;
- antiviral agents - “Acyclovir”, “Valacyclovir”;
- broad-spectrum antibiotics in the form of tablets, injections;
- antiseptics.
The basis of prevention is maintaining a healthy lifestyle, maintaining personal hygiene and avoiding promiscuity. If there are minor deviations in the skin in the groin area, it is recommended to immediately consult a specialist.
Blisters in the groin due to dermatitis
Contact dermatitis can cause blisters to form.
This is a form of skin inflammation that is associated with exposure to a toxic substance.
Most often, contact dermatitis occurs on the hands and is associated with work activities.
If bubbles appear in the groin, we are not talking about occupational hazards.
With a high probability, such a lesion is caused by attempts at self-medication, when all kinds of “folk recipes” are used.
Sometimes people try to remove warts and moles with caustic chemical compounds containing alkalis or acids.
The acute form of contact dermatitis develops with short-term exposure to a chemical substance in a toxic dose.
Plaques appear on which there are many small bubbles located nearby.
Some of them are opened.
Therefore, an erosive surface is formed, from which the ichor is released.
Subsequently, the surface dries out and crusts form on it.
Dermatitis can also occur in subacute or chronic form.
But they are not accompanied by the formation of bubbles.
Definition of disease. Causes of the disease
Athlete's inguinal rash is a parasitic, infectious skin disease caused by pathogenic fungi, characterized by itching and rash in the area of mainly the inguinal folds.
In domestic dermatology, epidermophytia inguinalis, eczema marginatum is identified as a separate disease, the cause of which is infection with the parasitic fungus Epidermophyton floccosum. In world dermatology, this term is not used, since damage to the inguinal and other folds of the body, in addition to E. floccosum, is often caused by other pathogenic fungi, such as Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton tonsurans and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Therefore, in practice the term mycosis of large body folds (Tinea cruris) is used.
Routes of infection:
- Direct - transmission of the pathogen directly from the carrier or patient through close bodily contact.
- Indirect - a more common route of infection through various objects on which there are skin flakes with pathogenic fungi (sheets, wooden benches, clothes, towels, toilet seats, beach beds, medical instruments).
- Autoinoculation is the transfer of the pathogen from lesions on the arms or legs.
Blisters in the groin due to allergies
An allergic skin reaction is very similar to simple contact dermatitis.
The only difference is that after the skin reddens, papules first appear on it, and only after that do they turn into blisters.
While there are no papules on the skin upon contact with a toxic chemical, blisters form immediately.
An allergy that appears only in the groin and nowhere else is highly likely to have resulted from direct skin contact with an allergen.
The inflammation zone repeats the area where the substance that provoked the reaction came into contact with the skin.
Unlike simple contact dermatitis, the blisters extend somewhat beyond the area of its impact.
Symptoms of inguinal athlete's foot
For inguinal epidermophytosis it is characteristic:
- Acute onset of the disease with transition without treatment into a sluggish chronic process.
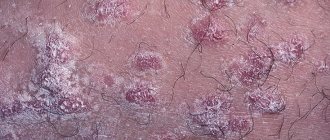
- The appearance of symmetrically located pink-red spots, sharply limited from healthy skin, with a flaky surface, which, due to rapid peripheral growth, form extensive lesions up to 10-15 cm in diameter.
- Formation of ring-shaped or garland-shaped lesions with a peripheral confluent or intermittent red edematous ridge consisting of papules, pustules, vesicles, scales and with a central zone of apparently healthy skin.
- The rash is localized in the area of the inguinal folds and the inner surface of the thighs, and the scrotum in men is often involved in the process, and lesions of the skin of the penis are not observed. Less commonly, rashes can be localized in the armpit, perineum, intergluteal fold, or in the folds under the mammary glands.
- In some patients, additional lesions may appear outside the main lesion—the so-called dropouts.
- Approximately half of the patients have mycosis of the feet.
- Itching and pain in the affected areas, which intensifies when walking.
Athlete's inguinal rash should be distinguished from:
- Erythrasma is a chronic skin disease caused by Corynebacterium minutissimum;
- Diaper rash (intertrigo, intertriginous dermatitis) - dermatitis from mechanical irritation of the skin due to friction of contacting folds of the body;
- Streptococcal intertrigo, often occurring in children and obese adults;
- Limited neurodermatitis, which can manifest itself in the inguinal-femoral folds, on the inner surface of the thighs, on the skin of the scrotum;
- Candidiasis of the folds, which occurs more often in patients with diabetes;
- Acanthosis nigricans associated with obesity;
- Histiocytosis X in children is a genetically determined disease;
- Allergic dermatitis of large folds, resulting from skin allergies to various substances contained in underwear, clothing, deodorants, toilet soap, medications;
- Inversion psoriasis of the folds;
- Seborrheic dermatitis when localized in skin folds;
- Benign familial chronic pemphigus Gougerot–Hailey–Hailey is a hereditary bullous dermatosis.
Bubbles in the groin with pemphigus
Pemphigus is a severe autoimmune disease.
Without treatment, deaths are common.
In most cases, the oral mucosa is primarily affected.
Subsequently, blisters appear throughout the body, including in the groin.
There is no itching.
Blisters on the skin cause pain.
The most typical places for the rash to form:
- scalp
- armpits
- groin
- face
- breast
After the blisters open, painful erosions form.
The elements have different sizes and shapes.
They are arranged randomly.
When you press on the bubble with your finger, its area increases (Nikolsky's symptom).
The disease requires the use of immunosuppressants.
Blisters in the groin due to an STD
Most sexually transmitted infections do not cause blisters in the groin.
The exception is herpes.
Much less often, blisters with purulent contents appear against the background of candidiasis.
Other STDs mostly affect not the skin, but the urethra and internal genital organs.
But sexually transmitted diseases are not only infectious, but also parasitic.
Among them is scabies.
It is caused by the scabies mite.
People become infected through sexual intercourse or through bedding.
There are two main complaints:
- itching
- rash
The rash usually appears as papules.
If bubbles appear, they are caused by a secondary bacterial infection.
They can occur if streptococcus is attached.
Then blisters with flaccid lining and purulent contents appear on the skin.
Forecast. Prevention
The prognosis for inguinal athlete's foot is favorable. With timely and correctly prescribed treatment, recovery occurs quickly. However, if the risk factors are not eliminated, re-infection is possible, since immunity is not formed after the illness. Therefore, in order to avoid a new infection and the occurrence of the disease, it is necessary to exclude all risk factors and follow preventive measures:
- do not use other people's bed linen, towels, washcloths;
- when visiting swimming pools, saunas, baths, beaches, use sheets and pads;
- when visiting public toilets, use special covers on toilet seats;
- fight obesity and sweating;
- try not to wear tight and tight-fitting clothes;
- after bathing, dry the groin area thoroughly with a towel or hairdryer;
- At the first signs of illness, consult a doctor.
What tests should I take for blisters in the groin?
To understand why the bubbles appear, you need to get tested.
The doctor takes a scraping from the rash.
The material is examined using the bacterioscopic method.
It may contain mites, fungi or other pathogens.
Signs of a bacterial infection (for example, streptococcal pyoderma) are also determined.
The most likely cause of the blisters is herpes.
PCR is used to detect the virus.
It allows you to get ahead of the type of herpes virus (first or second).
Often the blisters are caused by allergic reactions.
A doctor can confirm the allergic origin of skin inflammation using a blood test.
In the future, it is important to identify the allergen in order to eliminate further contact with it.
For this purpose, allergy tests are carried out.
But they do this not immediately, but after eliminating the symptoms of skin inflammation.
The person comes to the clinic after 2 weeks.
Various allergens are applied to the skin and the reaction to them is assessed.
If dermatological diseases are suspected, a skin biopsy may be required to verify the diagnosis.
Complications of inguinal athlete's foot
A frequent complication of the chronic form of inguinal epidermophytosis is lichenification, which occurs from scratching with severe itching, in which the process resembles limited neurodermatitis.
Another complication is the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, which leads to erosion of the lesions, the appearance of pustules (pustules), weeping, and severe pain. In advanced cases, extensive ulcers may appear.
In some cases, secondary infection with yeast-like fungi Candida occurs, which complicates the course of the disease and its treatment.
How to anoint the blisters in the groin?
There is no universal ointment that can be applied to the skin and all blisters will go away, regardless of the reasons for their occurrence.
There are a large number of diseases that lead to the formation of vesicles in the groin.
They are all treated differently.
Moreover: the wrong choice of therapy can lead to serious complications.
For example, if a person is trying to treat his allergies, but he actually has streptococcal pyoderma, this will most likely lead to the formation of deep inflammation and an abscess.
Because the antiallergic drugs used suppress the immune system.
The use of antibacterial drugs against the background of an existing fungal infection can aggravate its manifestations.
Because competitors of the fungal flora that inhibit its growth are destroyed.
Thus, therapy can only be prescribed after a thorough diagnosis, otherwise it can be harmful.
If a herpes infection is detected, therapy is carried out with acyclic nucleosides.
The patient is prescribed oral administration of acyclovir or its analogues.
Its use begins as early as possible, ideally during the period of prodromal phenomena.
It is also possible to use topical acyclovir in addition to systemic therapy.
In the future, this drug is prescribed for each relapse of herpes.
For bacterial skin infections, antibiotic ointments are used.
If the depth of inflammation increases, oral antibacterial drugs are indicated.
Streptococcal pyoderma, which causes blisters in the groin, is easy to treat in most cases because streptococci are susceptible to most antibiotics, including penicillins.
For scabies, insecticides are prescribed topically and treatment of clothing and bed linen.
In case of allergy development, local glucocorticoids are used.
Be sure to identify the allergen and eliminate contact with it.
Diagnosis of inguinal athlete's foot
Diagnosis of inguinal athlete's foot is based on medical history, clinical picture and results of laboratory and instrumental studies.
- The most common and generally accepted diagnostic method is a microscopic examination of a native preparation of skin flakes from lesions treated with a 10-15% solution of caustic alkali (KOH), with which the mycelium and spores of the fungus can be identified. This method allows you to quickly confirm the diagnosis; the disadvantage is low sensitivity (a false negative result is observed in 15% of cases).
- A cultural study with inoculation of material from lesions on a special Sabouraud medium, which allows you to determine the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to antimycotic drugs. The disadvantage of the method is the duration of the study (from 3 to 6 weeks).
- Recently, the method of determining the DNA of the pathogen using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) has been used to diagnose athlete's foot. The most promising diagnostic method, but the main disadvantage is the high cost of the study and the presence of a specialized laboratory.
- In difficult cases, a biopsy from the lesions followed by histological examination can be used.
- Examination with a Wood's lamp allows one to differentiate inguinal athlete's foot from erythrasma, in which a coral-pink glow of the lesions is noted.
In all cases, the diagnosis of the disease must be confirmed by laboratory research methods.