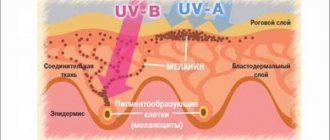
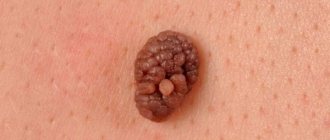
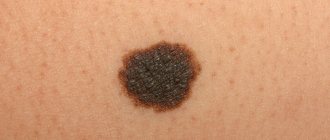
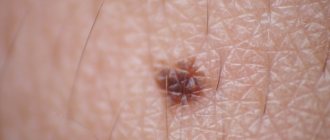
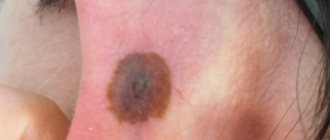
A blue mole is a small formation on the skin that is blue or bluish in color. This color is associated with an excessive number of cells in the dermis that produce melanin. As a rule, they are found singly, but sometimes group formations are observed.
A mole gets its blue color from excess melanin.
Despite the fact that a blue nevus is a benign formation, there is still a possibility of the mole degenerating into melanoma.
Reasons for appearance
A blue nevus is a cluster of cells in which the quantitative composition of melanin is increased, located in the deeper layers of the skin. Dark blue nevus is a benign formation. However, due to various factors, there is a risk of its transformation into a malignant tumor. This means that if there is a blue mole on any part of the body, or there is the slightest change in it, you should immediately contact a dermatologist.
The main reasons for the appearance and changes of this type of moles include:
- regular exposure to ultraviolet rays on the skin (not only direct sunlight, but also visiting a solarium);
- diseases of the urinary system that are caused by infections and have a chronic form;
- hormonal imbalance occurs when a woman reaches menopause, during pregnancy, as well as in adolescents during puberty;
- systematic use of hormonal or contraceptive drugs;
- an allergic reaction that affects the skin of an adult or child;
- an inflammatory process that occurs on the human skin and has an acute form.
With the prolonged presence of one or more factors, the process of degeneration of a purple mole into a malignant growth, that is, melanoma, may begin. Blue nevus can be distinguished not only by color, but also by size, which ranges from 2 to 4 centimeters. Such a mole does not have clearly defined boundaries, and the surface is smooth. There are single blue moles on the body, but there are cases when a person can have more than five of them. Such moles most often appear on such areas of the body as lips, cheeks, head, arms and legs, and shoulders.
Based on their forms, blue nevi are divided into:
- Cellular. Size from 1 to 3 centimeters.
- Melanocytic. A bluish mole that includes various pigments. As a result, the color looks uneven, and there are no clear boundaries of the growth.
- Simple. Moles are small in size (about 1 centimeter). The top layer is smooth and the color is dark blue. A birthmark may also appear on the mucous membranes.
Types of formations
The form of blue nevus can be cellular, simple or combined:
- The simple form looks like clusters of cells saturated with melanin. A single nodule protruding above the skin is small, no more than a centimeter. The shade can vary from dark blue to light gray, and the surface is smooth. The most popular place is the neck; nevus may appear on the arms and face.
- The cellular form is represented by a cluster of large cells less filled with pigment. The diameter of the formation is larger, can reach 3 cm. Uneven dark tones and lack of brightness are typical. The surface is rough. The main places of damage are the hands, feet, buttocks, and lower back.
- The combined form is the result of combining blue nevus with its other varieties (for example, intradermal). The appearance resembles a knot; there is an interweaving of brown and blue tones. This type is characterized by surface heterogeneity and blurry edges. Affected areas are the lumbar area, neck, palms.
Is blue nevus dangerous?
It is extremely rare for a blue mole to transform into a malignant tumor. However, medical practice confirms such cases. The danger of degeneration threatens a person with cancer, which in later stages is difficult to treat and can cause negative health consequences.
In order to promptly recognize the transformation of a nevus into an oncological disease, it is necessary to remember the following symptoms that are inherent in this process:
- The mole changes its size to a much larger one.
- Change in color.
- The appearance of hairs on the birthmark.
- Painful sensations occur on palpation.
- The nevus itches, itches and burns.
- The surface of the growth becomes bumpy and rough.
- Pus mixed with blood is released from the growth.
The most dangerous is the blue nevus, which is located in places subject to constant mechanical stress. Namely: face, back, neck, arms. When a nevus in such a localization is injured, there is a risk of introducing an infection into it, which can provoke its change into a cancerous formation.
To avoid negative consequences, you should take hormonal and contraceptive medications with caution, and do not stay in direct sunlight for a long time between 10 and 17.00. This especially applies to people with a light skin tone and the presence of multiple blue, brown or red birthmarks on the body. And also, to avoid consequences, you should limit your visits to the solarium and monitor the hormonal balance in the body.
If there are suspicious signs when a mole turns blue, you should urgently consult a doctor who specializes in moles, a dermatologist or oncologist. He will conduct a personal examination, a number of other examinations, and determine what actions should be taken in relation to the blue nevus.
Types of moles (nevi) on the lips
What kind of moles are there on the lips? Such formations on such a sensitive area of the skin are divided into two types:
- Vascular moles are formed due to abnormally rapid proliferation of capillaries.
- Pigmented - appear with strong melanin production.
In addition to these two typologies, moles differ from each other in size, shape and degree of color:
- Flat - such formations are practically invisible and do not cause discomfort.
- Convex moles are already formed in the deeper epidermal layer and often have hair follicles.
- Vascular nevi usually have a blue-violet color and increased density.
- A hemangioma is similar in structure to a harmless wart. However, such a mole on the lip requires special attention, because a bunch of blood vessels are collected inside it, it is often injured and bleeds.
- Pigmented moles are mostly congenital in origin, sometimes reaching quite large sizes.
Could there be dangerous moles on the lips from all of the above? Definitely yes.
Pigmented moles are especially dangerous; hemangioma is less dangerous. Their common unpleasant feature is that both of them tend to degenerate into cancerous tumors.
Is it necessary to remove a blue nevus?
The question of whether a blue mole needs to be removed or not is decided by a specialist after a certain examination. To determine that it is a blue nevus, it will not be difficult for a doctor, since it is distinguished by the corresponding color. Next, the doctor will perform a dermatoscopy. It is carried out using a special device, a dermatoscope. It will enlarge the image of the mole several tens of times, which helps determine the exact structure of the growth and its depth.
The need to remove the blue formation will help determine the ultrasound. Ultrasound diagnostics helps to identify the amount of melanin, how deep the growth lies, and the presence of pathologies. A method such as histology is carried out after removal of the growth. The removed nevus is sent for testing, which can determine whether it is benign or malignant. If the latter option is detected, the analysis will determine at what stage the cancer is located.
In case of skin cancer, the doctor prescribes removal of the nevus. This procedure can be carried out if the bluish formation is located on a visible area of the body, causing aesthetic discomfort to the person. Today medicine carries out removal using several methods:
- Radio waves. Radiation can remove cells with large amounts of melanin.
- Electrocoagulation. High-frequency electric current cauterizes the blue nevus.
- Laser. A safe procedure that uses a laser beam. Used for small formations.
- Cryodestruction. Liquid nitrogen destroys nevus tissue and prevents its further development. It is used in the presence of small blue moles.
- Surgical intervention. A scalpel is used. The downside is the presence of scars after the operation.
Diagnosis of blue nevus
There are no difficulties in diagnosing a blue nevus; its external manifestations help: the color of the nevus and the pronounced boundaries of the formation.
Dermoscopy and siascopy allow for in-depth studies. The first procedure reveals the structure of the formation, its possible changes and depth. Using siascopy, the direction in which melanin is located on the damaged area of the skin is determined. Ultrasound is sometimes used to study the growth of the nevus and the risk of its transformation into a malignant neoplasm.
After the nevus has been removed, doctors conduct additional histological examination. It is necessary to identify the concentration of melanin in the deep layers of the skin. Since melanin sometimes accumulates in cellular tissues, these cells become enlarged and group together, leaving connective tissue bridges between the clusters.
Can a blue nevus turn into cancer?
Often people who have a cyanotic formation on their body wonder what a blue nevus is and whether it can turn into cancer. A blue birthmark is not a malignant tumor. However, the presence of factors such as inflammatory processes, hormonal imbalance, chronic diseases of internal organs can provoke changes in the spot.
If the growth begins to change its structure, turn red, hurt or itch, this is a reason to contact a specialist. In the absence of medical care, a blue mole may begin the process of degeneration into an oncological disease, which is fraught with dangerous consequences for human health and life.
Removing moles on the lip
When deciding to remove a mole on the lip, it is strictly forbidden to resort to traditional methods or the services of a salon cosmetologist.
All the risks lie not only in the subsequent formation of an unsightly scar instead of a mole, but also in provoking all kinds of complications. Currently, medicine has proposed the following methods for removing moles on the lips:
- surgical intervention;
- use of laser;
- radio wave method;
- electrocoagulation;
- use of liquid nitrogen.
All of the above methods have their own characteristic pros and cons. To make a more correct choice, doctors use the diagnosis and test results of the owner of the mole.
Among other things, not every patient is recommended to resort to the destruction (removal) of a mole. This procedure has contraindications for children and pregnant women, patients with acute respiratory disease, and hypertension. It is also possible to have an allergic reaction to the pain reliever.
As for the correct timing for this small operation, it would be better to choose winter or autumn, when ultraviolet radiation is not so bright and effective.
Diagnosis of blue moles
To prevent a benign blue mole from degenerating into melanoma, it is important to determine the nature of the blue spot. Blue nevi are often located far from other formations, which is their distinguishing feature. Only a doctor can describe the correct clinical picture with the help of research and laboratory tests. Diagnostic methods are listed in the table below.
Blue moles.
It is because of this pigment that the color of the neoplasms is determined: blue (blue), black and gray. Most often, this type of nevus is single, however, there are cases of multiple manifestations. A blue mole is a benign tumor.