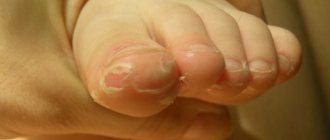
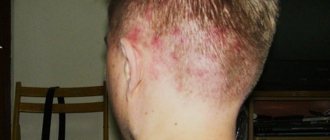
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic allergic disease with periods of exacerbation and remission. The most characteristic symptoms of the disease are persistent itching of the skin and red lesions that resemble lichen. Atopic dermatitis is most often diagnosed in young children; adults get sick less often.
Other terms for atopic dermatitis, such as atopic eczema or formerly used scabies, bring together the nature and specific symptoms of this disease in the name itself. People suffering from AD suffer from chronic itchy skin. Scratching that is difficult to control causes the skin to break down, weakening its protective barrier function. As a result, there is an excessive loss of water from the deeper layers of the skin (drying out), and allergens have a greater chance of entering the body.
What is atopy?
The content of the article
Atopy is an abnormal response of the body to an allergen, leading to an overproduction of IgE antibodies responsible for the allergic reaction. Atopic dermatitis belongs to the group of atopic diseases, like bronchial asthma, urticaria and hay fever.
Patients prone to atopy usually have several allergic diseases at the same time. The body of a person with AD responds to very low doses of allergen (molecules that can trigger an immune response) in the environment. The disease can be caused by many factors that surround us: dust mites, pollen from flowers, animals and food.
Dermatitis on hands
Dermatitis on the hands is a common skin disease that is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. The pathology is characterized by severe itching, the appearance of itching and rash on the skin. The skin becomes severely inflamed, and pain in the area of the dermis is possible. The disease occurs in both small and large patients.
The cause of development can be various external factors affecting the human body. What other features does dermatitis have?
Causes of dermatitis
Dermatosis manifests itself in the form of an allergic reaction to external irritants. The main factors provoking the development of pathology include:
- Physical - abundant contact with water, temperature and pressure surges, sun rays and radio emissions.
- Biological - interactions with plants such as garlic, nettle, ash.
- Chemical – interaction with chemicals: varnish, paint, household chemicals, acid.
- Obligate – mineral acids, alkalis, toxic substances.
Dermatitis on the elbows can also be triggered by other irritants:
- Poisonous, toxic substances transmitted by airborne droplets, plant pollen.
- Cosmetics for skin care.
- Allergenic products containing dyes and preservatives.
- Psychological factor (emotional instability, stress, depression).
- Taking antibiotics and dietary supplements.
Be careful, sometimes removing external signs does not help to completely get rid of the problem. Inside the body, the disease can rapidly progress and affect the autoimmune system.
Because of this, severe pathologies that are dangerous to human health can develop.
Dermatitis can cause the development of a cancerous tumor, so do not delay treatment and go to the hospital in a timely manner.
In addition, often the cause of the development of dermatitis is a hereditary factor. It is for this reason that the disease can appear in infancy. It will be chronic. In this case, it is better to protect the patient from factors that provoke the progression of the disease.
Remember! Upon initial contact with the irritant, no visible signs appear on the body, as the body quickly begins to produce antibodies that fight the allergen. Regular contact with an irritant provokes a severe allergic reaction that affects the skin and immune system.
Symptoms of dermatitis
The development of pathology is accompanied by the manifestation of visible symptoms. Dermatitis on the fingers is characterized :
- The appearance of redness in the area of irritation.
- Hands swell.
- In severe cases of pathology, watery blisters with cloudy liquid appear on the body.
- After the blisters burst on the skin, erosive areas appear on the dermis.
- Severe itching.
- Dry hands.
- Crust on damaged areas.
- A bluish area of the dermis.
Simple contact dermatitis in the normal course of the disease does not cause complications. The only thing that can happen in this case is severe damage to the skin. There may be scars or welts on your hands. In some cases, pigmentation or calluses may appear.
With prolonged development of the disease and exposure to the allergen, severe complications and consequences are possible. If proper treatment is not started, then the formation of necrosis, deep damage to the epidermis, infectious or viral infection, and the development of fungus are possible. In severe cases, the development of eczema and sepsis is possible.
Types of dermatitis on the hands
Depending on the factor affecting the body, hand dermatitis is divided into several types:
- Simple contact dermatitis on the hands. External manifestations appear on areas of the skin that have been in contact with the allergen. The development of the disease subsides when protected from the irritant.
- Atopic form.
This type is caused by a hereditary factor. This form of allergic dermatitis on the hands is characterized by the appearance of specific neoplasms on the skin. - Actinic type. It is characterized by damage to the dermis of the hands due to regular contact with different types of radiation.
- Seasonal.
It is divided into two types: solar lichen (manifests itself with prolonged contact with the sun's rays), cold eczema (an allergic reaction that develops during cold weather, the skin begins to dry, itch and crack). - Allergic type.
The body's reaction to external irritants in the form of cosmetics, chemicals, paint, toxic substances.
The duration of treatment, the drugs used and further prognosis will depend on the type of pathology. Most often, patients are diagnosed with contact and allergic types of pathology. To find out the nature of the disease, you should undergo a diagnostic examination and be tested for allergens.
How to treat dermatitis on the hands
Only a doctor can tell you how to treat dermatitis on the hands of children and adults. Therapy should be beneficial and not harmful to the person. Therefore, self-medication in this case is strictly contraindicated.
The task is not to delay a visit to a dermatologist.
Before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to undergo a complete examination. Tests will help determine what type of disease the patient has. After diagnosis, the attending physician prescribes a course of therapy and prescribes the necessary medications. Typically, therapy lasts for 7-10 days, with conservative treatment. If the problem is neglected, purulent ulcers may appear on the hands.
Non-hormonal drugs
Most often, a cream or ointment for dermatitis on the hands is used to eliminate visible symptoms. The most popular and effective means include:
- “Zorka” is available in the form of a cream and is made from natural plant ingredients. Helps restore damaged areas, softens and nourishes the upper layers of the dermis.
- "Eplan" is a cream with a pronounced antiseptic effect, it disinfects the skin well and heals wounds.
- “De-panthenol” is available in the form of cream and spray. Well softens and heals the dermis, helps quickly eliminate cracks and wounds.
- Exoderil cream is prescribed for infectious types of pathology.
- "Radevit" - a product in the form of an ointment is used to treat inflammatory areas and severe itching, relieves irritation.
- "Gistan" is a dietary supplement, taken orally, used to strengthen the immune system.
- "Losterin" is an antifungal ointment that helps eliminate signs of dermatitis.
- "Desitin" - ointment has an antiseptic and analgesic effect. Quickly relieves pain, itching and irritation.
- "Skin-Cap" is an antifungal ointment that eliminates germs on the skin and prevents the development of eczema.
All drugs are non-hormonal. Therefore, they are approved for use by children and adults. It is prohibited to use medications without the knowledge of the attending physician, as there is a risk of harming the body and aggravating the situation.
Hormonal drugs
In severe cases of the disease, hormonal drugs can be used. This group of medicines includes:
- "Celestoderm" is an ointment based on glucocorticosteroids, used for the treatment of contact type of pathology that manifests itself on the hands.
- Advantan is a medicine used to treat skin hypersensitivity or dermatosis.
- "Flucinar" is used in the treatment of dry dermatitis of non-infectious origin.
Treatment in children
Treatment of dermatosis in children takes place in several stages. It is carried out with extreme caution, since children's skin is very sensitive and delicate. The child is protected from the irritant, the damaged areas are smeared with healing ointments or powder. It is also recommended to regularly carry out preventive measures.
Depending on the clinical picture and course of the disease. The patient may be prescribed sedatives to facilitate the course of therapy. Children should be prescribed medications by a pediatrician, as some products are not suitable for children's skin.
During exacerbation
In case of exacerbation of the chronic form of the pathology, traditional healing methods can be used in combination with healing ointments and gels. You can use chamomile tinctures, lotions or herbal baths to relieve pronounced signs of the disease. They effectively relieve visible signs of the disease, however, they do not help get rid of the allergen from the inside.
Causes of atopic dermatitis
The first symptoms of atopic dermatitis in almost half of patients appear between the third and sixth months of life, in most cases the disease appears before the age of five. The origin of atopic dermatitis is complex and its development is a combination of environmental, genetic, immunological and non-immunological factors.
In AD patients, there is a genetic defect in the epidermis that causes abnormalities in the composition of the superficial layer of the skin. As a result, the patient's skin is overexposed to allergens and becomes dry, overly sensitive and itchy.
Atopic dermatitis
The disease is genetic, which means that if one or two parents had atopic dermatitis or any other atopic disease, the likelihood of children inheriting a tendency to atopy, including atopic dermatitis, is high.
First symptoms
A person is unlikely to immediately notice redness and rashes on the skin behind. Unfortunately, people pay attention to such problems only with the onset of burning, itching, and discomfort. This is far from the initial stage of the disease.
The mother will see a rash and dermatitis on the child’s back faster, but in the initial stages it can be confused with prickly heat, chicken pox or diaper rash.
The first signs of dermatitis are usually itching and changes in some areas of the skin. In more complex or advanced situations, the skin thickens, acquires a red tint and becomes rough.
What are the symptoms of atopic dermatitis (AD)?
The most common symptom of atopic dermatitis is eczema, an inflammation that appears as papules on reddened skin. Skin lesions usually appear in groups and in irregular shapes.
Scratching causes damage to the skin. Chronic lesions lead to lichenification (thickening) of the skin and its hyperkeratosis, that is, ichthyosis (keratosis pilaris, ichthyosis). In very severe conditions, erythrodemia may occur, that is, general inflammation of the skin, enlarged lymph nodes and fever.
Depending on the age of the patient, the course of the disease can be divided into three phases: childhood, adolescence, and adulthood. The location of changes differs from time to time. In children, symptoms of atopic dermatitis are often visible on the cheeks and forehead, while in adults it is mainly visible in the flexures of the lower and upper limbs. In addition, adults may develop other symptoms of AD, such as whitish dandruff, which does not occur in children.
Features of traditional treatment
If the first alarming symptoms occur, you should consult a dermatologist. It is this specialist who provides information on how to get rid of atopic dermatitis. If necessary, the doctor will issue a referral to an allergist.
The treatment regimen for atopic dermatitis includes the following points:
- Oral or local use of glucocorticosteroids. These drugs are most often prescribed for atopic dermatitis. The attending physician should inform you what to apply to the rash.
- Taking or administering antihistamines. Examples of drugs: Suprastin, Loratadine, Clemastine.
- Taking or topical use of immunosuppressants.
- The use of moisturizers.
Additionally, membrane stabilizing and sedatives may be prescribed, as well as medications whose active components have a beneficial effect on intestinal function.
According to reviews, atopic dermatitis in adults is not a death sentence. But in order to achieve stable remission, it is necessary to follow medical recommendations and adhere to the principles of a therapeutic diet.
How to recognize atopic dermatitis?
Tests often used in diagnosis are skin tests and atopic patches, but a negative test does not always mean that the disease is not present, it may only mean that the allergen has not yet been detected.
The laboratory also performs total serum IgE determinations, which determine the patient's allergies. Since atopic dermatitis is an allergic disease, we cannot completely cure it, we only treat it symptomatically. In some cases, it is possible to desensitize the patient.
Causes
The reasons for the exacerbation of dermatitis in the fall are associated with the intensive operation of heating devices, which make the air dry and deprive the skin of moisture.
At this time of year, the functioning of the immune system deteriorates, which leads to an exacerbation of chronic pathologies.
The exact causes of the development of this disease are currently unknown, but the following predisposing factors are identified:
- Genetic predisposition, the presence of this disease in close relatives;
- Frequent stressful situations, neuroses and other mental disorders;
- Poor nutrition, eating large amounts of allergenic foods;
- Use of low-quality cosmetics;
- Working with harmful production factors;
- Pathologies of internal organs, including the digestive system;
- Autoimmune pathologies.
How to prevent and treat recurrent inflammation in AD?
Treatment of AD is complex and requires constant monitoring of skin condition. This is especially important for children, who most often cannot determine which foods they are allergic to and in what situations. Patients must minimize exposure to allergens, which is not easy due to the multiplicity of allergens and their prevalence.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis increase in response to stress, so to prevent relapses, it is recommended to avoid stressful situations, especially when it is chronic.
During an exacerbation of symptoms, it is necessary to consult a dermatologist who will select appropriate antihistamines, which also have antipruritic properties, and other drugs that inhibit the development of allergies - for topical or general use (for example, immunosuppressants).
Treatment of recurrent inflammation in AD
It is worth taking care to exclude from the diet foods that make patients feel unwell and give a rash. Avoiding allergens in powders and mouthwashes that are highly irritating to already affected skin is also key.
Avoid clothing made from wool and other “caustic” materials. The quality of the bed linen on which the patient sleeps is important. It should also be soft and non-irritating. Hygienic and cosmetic procedures also affect the condition of the skin in AD. Avoid exfoliating cleansers and soaps and moisturize and lightly lubricate your skin regularly.
Back allergy treatment
Rashes on the body are an unpleasant thing, but dermatitis on the back is an even more problematic condition: you cannot scratch it or treat it yourself. In addition, this part of the body comes into contact with clothing and is often covered with sweat, which corrodes the inflamed epidermis.
Allergic or atopic dermatitis on a child’s back is difficult to treat, since the baby spends most of the time in a horizontal position, but babies cannot scratch itchy spots or rashes, unlike adults.
Having discovered symptoms of allergic dermatitis in adults, it is advisable to begin treatment by eliminating the provoking factors. Therefore, all contact with the identified allergen must be excluded. For example, if washing powder caused rashes on your hands, you should replace it with a more environmentally friendly one or wash it with gloves.
However, if it is not possible to determine the exact cause of allergic reactions, it is necessary to conduct a series of specific allergy tests that will identify the sensitizer.
To effectively treat allergic dermatitis, the following remedies are used:
- First of all, this is an ointment that has an antifungal and antimicrobial effect, which allows you to quickly relieve itching and alleviate the patient’s condition. It is worth paying attention to Zyrtec, Telfast, Erius, etc. In addition to the above ointments, the most popular and effective are Advant, Lokoid, Elidel, which are prescribed for skin lesions.
- If local treatment is not effective, the adult is prescribed antihistamines such as Cetrin, Zodak, Claritin, as well as their analogues. They will help reduce swelling and itching. Although their role in the treatment of this type of allergic reactions is secondary.
- For very severe reactions, oral corticosteroids may be prescribed. The duration of treatment and dosage of drugs in this case can only be determined by a doctor.
READ MORE: Rash on a child’s back without fever
The back is a hard-to-reach area of the body; it is more difficult to treat due to its inaccessibility. Treatment for allergies depends on the cause of its occurrence. When treating allergies, first of all, it is necessary to remove:
- The suspected allergen causing the allergic reaction. Eliminate contact with the allergen. Once the allergen is removed, the symptoms of allergy (dermatitis) will disappear. And the skin will become clear again.
- Foods that can increase an allergic reaction: citrus fruits, chocolate, eggs.
- During treatment, medications must be prescribed that reduce the risk of developing allergies, as well as its symptoms. They are called antihistamines. These include: Claritin, Zyrtec, Zodak, Suprastin, Tavegil and others.
If it is impossible to independently establish the cause and identify the allergen, then you need to contact a specialist. After all, only special diagnostic methods will reveal the cause of the development of allergies on the back. Only a doctor can correctly prescribe treatment and get rid of this disease.
First of all, you need to be careful about self-medication, especially if the cause of dermatitis is unknown to you. Medicinal plants and beekeeping products, popular for home treatment, can themselves cause allergies, thereby increasing the manifestations of dermatitis. Therefore, before selecting remedies and medications, you need to visit a doctor.
Treatment for dermatitis is selected depending on the type, stage and cause. It can be general and symptomatic. The minimum treatment period for dermatitis, even local, is three months.
If you stop treatment when the symptoms go away without completing the full course, the dermatitis can become chronic and will recur again and again.
Symptomatic treatment is aimed at eliminating the results of dermatitis - skin lesions, eczema, rashes, ectopia, peeling, etc. These are hormonal, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antimicrobial or combination ointments and sprays.
Hormonal drugs against dermatitis include:
- Prednisolone. Used for contact and atopic dermatitis. The active ingredient is prednisolone. Cannot be used for systemic fungal infections. The course of treatment is 4-5 weeks. The dosage is determined by the doctor.
- Flucinar. It is used for contact, atopic and seborrheic (fungal) dermatitis. The active ingredient is flucinolone. The course of treatment is no more than two weeks (can be repeated after a break). When used on the face, the course of treatment is no more than one week.
- Lorinden. Used as an anti-inflammatory agent for atopic dermatitis. The active ingredients are flumethasone pivalate and salicylic acid. The ointment continues to be applied until the symptoms of dermatitis completely disappear, after which treatment is stopped after another 3-4 days.
- Fluorocort. A remedy against allergic dermatitis, manifested in the form of dry and weeping eczema. The active ingredient is triamcinolone. The course of treatment lasts from five to ten days; if there are no results, it can be extended to 25 days, but should not last more than a month.
They are very effective in relieving the symptoms of dermatitis; they are most often used in advanced forms of the disease or in cases of large areas of skin damage.
Hormonal ointments should be used only in short courses, as they cause a number of complications. If you can do without them altogether, it’s better to do so.
Anti-inflammatory drugs include:
- Akriderm. It is used for both allergic and simple contact dermatitis. Can be used for occupational dermatitis (caused, for example, by permanent exposure to chemical pathogens on the skin) and for solar erythema (burns and redness). Cannot be used for perioral dermatitis. The active ingredient is betamethasone. The course of treatment is up to three weeks.
- Advantan. It is used for all types of dermatitis: simple contact, allergic, as well as true (when the cause is not established) dermatitis. Perioral dermatitis is also a contraindication for use. Active ingredient: methylprednisolone aceponate. The course of treatment ranges from two weeks to three months.
- Triderm. Used for all types of dermatitis. The drug relieves redness and inflammation, kills bacteria and suppresses the activity of fungi, if any. Helps with infection in areas affected by dermatitis. Active ingredients: betamethasone, clotrimazole, gentamicin. The course of treatment is two to three weeks. If after this period the symptoms do not go away, you need to consult a doctor again to clarify the diagnosis.
READ MORE: Atopic dermatitis candidiasis
These ointments relieve itching and inflammation and accelerate skin healing.
For allergic dermatitis, treatment is aimed not only at eliminating the symptoms, but also at the cause of the disease. Therefore, therapy mainly includes antihistamines, including: Claritin, Zodak, Diazolin, Suprastin, Tavegil, Fenistil, Telfast and others.
If allergy tests reveal a specific pathogen, it should be eliminated from everyday life. If we are talking about food allergies, the product must be excluded from the diet.
For seborrheic dermatitis, which is caused by fungi, antifungal and antiseptic drugs are prescribed.
When identifying a pathogenic fungus as the causative agent of dermatitis, the following means are used:
- Mycozoral. Ointment with a fungistatic effect, i.e. slowing down the growth of fungi. The active substance is ketoconazole. The course of treatment is from two weeks to a month (sometimes longer).
- Mycozon. The product controls the proliferation of fungal flora and has a bactericidal effect. The active substance is miconazole nitrate. The course of treatment is from two weeks to two months.
- Akriderm GK. Complex action ointment: relieves redness and itching, destroys fungi, kills bacteria. Active ingredients: betamethasone, clotrimazole, gentamicin. The course of treatment is from two weeks to one and a half months.
In the treatment of dermatitis, the main thing is to see a specialist in time so that he can determine the cause and prescribe treatment. If you relieve the symptoms with folk remedies or ointments, but do not cure the root cause of the dermatitis, it will appear again and again until it becomes chronic, which can be very difficult to treat.
Atopy is not only a disease of the body
Atopic dermatitis is a disease that can have a negative impact on the patient’s psyche. Children and adolescents diagnosed with AD are more likely to have problems being accepted in their community. It is difficult to explain to your peers where the red spots and scars come from after an exacerbation of the disease.
Fortunately, only about 30% of patients continue to have symptoms into adulthood. In the remaining 70%, the symptoms disappear completely or appear in a milder form, which the patient can control with the help of a good dermatologist.
Symptoms and types of disease
Science knows exudative, seborrheic, erythematous, erythematosquamous simple, erythematosquamous with lichenification and lichenoid-pruriginous forms of atopic dermatitis.
Manifestations of the disease most often occur on the legs, elbows, head, neck, face, shoulders, hands and arms. The patient experiences severe itching, which may be complicated by a secondary infection.
Dryness, exfoliation of tissues, thickening and discoloration of the skin can also be accompanied by bubbles of liquid, which take a long time to become wet after the outer shell ruptures and, when dry, form a yellow crust.
We recommend reading: How to treat eczema at home
The main symptoms of exacerbation of atopic dermatitis are:
- the appearance of papules, rashes on various areas of the skin, erosion and erytomatous spots;
- exacerbation of diseases such as bronchial asthma, nipple dermatitis, cheilitis and conjunctivitis;
- hypoglycemia, hypotension, sudden weight loss, constant fatigue, adynamia and impaired gastric secretory function;
- deterioration of immunity, an increase in the volume of leukocytes and eosinophils in the blood and a decrease in the number of T-lymphocytes.
The main problem of atopic dermatitis is that the disease gene is able to survive under any conditions. Even if the allergen is accurately identified and isolated, the disease will subside only for a while, attacking the body with renewed vigor after some period of time.
Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis (AD): skin tests
When diagnosing atopic dermatitis, in addition to analyzing symptoms and laboratory tests, a series of skin tests, such as skin tests, atopic patch tests, or nutritional skin exposure tests, are performed to identify substances responsible for an excessive allergic reaction.
The diagnosis is confirmed by immunological laboratory tests - determining the concentration of IgE antibodies - and a number of skin tests that can identify allergens responsible for an excessive allergic reaction.
Sample menu for the day
At first it is quite difficult to adjust your diet. However, within a few days, each person will be able to create a menu that meets all requirements. You just need to remember the list of allowed products (or print it out and hang it on the refrigerator) and learn how to combine them.
Sample daily menu for atopic dermatitis in adults:
- Breakfast - porridge cooked in water (buckwheat, oatmeal or pearl barley); baked apple.
- Lunch - vegetable puree soup; 50 g boiled beef. It is recommended to make soaked potatoes, cauliflower and zucchini the basis of the first course. Cook the ingredients until done. The soup can be seasoned with vegetable oil. This is a simple recipe for atopic dermatitis, but it meets all the requirements.
- Afternoon snack - 200 ml kefir; cracker.
- Dinner - rabbit or turkey cutlets; braised cabbage. You can add fresh cucumber to the meat dish. The recipe for making cutlets is simple. Simply chop the meat, salt it, and add herbs to taste. The cutlets can be steamed or baked in the oven with a minimum amount of oil.
You need to eat 4 times a day with equal intervals between meals. In adults, the menu for atopic dermatitis is identical to that for children.
Skin testing (STP)
Skin prick tests test for a specific allergen. This test is based on the fact that IgE antibodies are present on the surface of immune system cells. The purpose of the test is to bring such cells into contact with the allergen.
A solution containing the allergen is applied to the patient's skin, and then it is pricked with a special lancet. Typically, this test tests several substances at the same time, such as dust, hair or pollen.
Skin tests
This test is no different from a test that determines an allergy to any substance. Therefore, the presence of a positive allergic reaction does not automatically mean atopic dermatitis. In addition to the allergic reaction, other symptoms such as dry and itchy skin should also appear. Additionally, a negative test result does not mean that the disease is not AD; it only means that this set of substances does not cause allergic reactions.
Traditional methods of treatment: compresses
It is important to understand that the use of unconventional methods does not relieve a person of the need to seek competent medical help. Treatment of atopic dermatitis in adults with folk remedies only leads to a weakening of the severity of clinical manifestations. But it significantly improves the quality of life.
The most effective recipes:
- Grind Veronica officinalis. Take 10 g of raw material and place it in a glass or enamel container. Pour boiling water (200 ml volume). Close the container tightly and wrap it with a towel. Let it brew for 3 hours. Strain the prepared liquid. Soak a cotton swab in the infusion and apply to pathologically changed areas of the skin. It is recommended to carry out the procedure 5 times a day.
- Peel a few potato tubers. Wash them thoroughly. Grind the tubers, but do not use metal objects. Transfer the resulting mass into cheesecloth. Apply to affected areas and secure. It is recommended to apply the compress at night.
- Collect pear tree leaves. Dry them and grind them. Take 1 glass of raw material and pour boiling water (0.5 l) over it. Place the container on the fire. Boil for about 5 minutes. Let it brew for 12 hours. Soak a cotton cloth in the liquid and apply it to the affected area. Secure with cling film. This remedy is effective in the treatment of atopic dermatitis on the hands. It is enough to take baths with a decoction several times a day.
- It is recommended to use calendula tincture as a compress. To prepare it, you need to take 10 g of raw material, place it in a glass jar or bottle and fill it with 100 ml of medical alcohol or vodka without additives. Close the container tightly. Place it in a dark place. Let it brew for 1 week. Use the prepared calendula tincture as a compress. If a burning sensation occurs, dilute it with clean boiled water in a 1:1 ratio.
- In autumn, it is recommended to use pumpkin to treat atopy. Grind its pulp and wrap the resulting pulp in cotton cloth or gauze. Apply compresses to the affected areas at night.
- Grind fresh St. John's wort herb. Take 200 g of raw material and squeeze the juice out of it. Add 20 ml of pre-softened butter to the resulting liquid. Use the finished product as a compress at night.
- Grind the celery roots in a blender. Squeeze the juice from the resulting pulp. Soak a piece of cotton cloth or gauze in the healing liquid. Apply a compress for a quarter of an hour.
- Take 30 g of oatmeal. Pour 150 ml of boiled hot milk over them. To stir thoroughly. Allow the product to cool. Wrap it in gauze and apply to pathologically changed areas. Secure with adhesive tape or cling film. After 20 minutes, remove the compress and wash the skin with warm water.
- Grind mint leaves to a powder consistency. Take 20 g of raw material and mix it with 20 ml of warm water. Apply the resulting paste daily to the affected areas. The product must be washed off after 20 minutes.
- Sea buckthorn fruits have excellent anti-inflammatory and regenerating properties. It is recommended to grind them to a paste-like consistency. Apply the resulting mass to the affected areas for 20 minutes. After the specified time, rinse off the product with warm water. To enhance the healing effect, it is recommended to simultaneously drink a decoction of sea buckthorn. To prepare it, you need to pour a glass of boiling water (200 ml) over several berries and simmer over low heat for about 15 minutes.
The main rule in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in adults with folk remedies is regularity. The procedures must be done daily until the clinical manifestations completely disappear.
Atopic patches (ATP)
Atopic patches are a type of epidermal patches in which specially prepared allergens are applied to the uninjured skin of the patient's back and sealed. They are used to detect delayed allergenic reactions that cannot be detected by skin prick tests.
Atopic patches are a very good addition to the diagnosis of AD with substances that the patient must eliminate from life in order to reduce the symptoms of the disease.
Atopic patches
The problem is obvious
I'm 17 years old and my problem is acne. Tell me, can they be cured with the help of medicinal cosmetics? Or is it necessary to be treated by a dermatologist?
Vasilisa Ananyina, Komarovo
Dermatologist Guzel Kulikova answers:
– Acne can occur in both mild and quite severe forms. Patients with moderate and severe forms of acne have to take medications orally: antibiotics (necessarily in combination with agents that normalize microflora), agents that regulate sebum secretion (usually contain zinc, sulfur, etc.), vitamins A and B. Women Combined oral contraceptives are often prescribed. However, such treatment is carried out strictly according to indications, after a thorough study of hormonal levels.
But moderate and mild acne, fortunately, can be cured with external therapy alone. Firstly, it is important to take proper care of your face. If you are predisposed to acne, you should avoid alcohol lotions and oily decorative cosmetics and creams. For washing, you need special gels, not milk and soap, which form an alkaline film on the skin, preventing it from breathing. Masks with kaolin are useful - they dry out and adsorb fat. You should be careful with tanning. Ultraviolet in modest doses is useful, but in large doses it is the opposite.
Secondly, it is recommended to limit foods and drinks that increase the secretion of sebum (fatty, sweet, pickled, smoked, coffee, alcohol). Acne sufferers benefit from foods containing polyunsaturated fatty acids (for example, sea fish and vegetable oils), vegetables (especially pumpkin), and dairy products.
And finally, it is necessary to apply externally special preparations for problem skin. Thanks to them, it is possible to extinguish the inflammatory process.
Skin application with SAFT nutrition test
SAFT is a food allergy testing method primarily used for young children. The technique involves eating the food that is suspected of causing the child's allergy and monitoring symptoms.
If erythema, itching and swelling of the skin occurs during use, this indicates a positive result, that is, an allergy. Most often, this test is carried out on allergenic fruits, vegetables, milk, chicken eggs and nuts.
Diagnostics
In order to know what and how to treat allergic dermatitis, you must first recognize which substance is the allergen. Setting up an individual patch test (application tests) will help with this.
This is a special diagnostic method using sets of allergens and placing them on the skin of the forearm or middle third of the back for 48 hours. Such tests are carried out only by doctors.
The first thing you need to do is visit a therapist, who will issue a referral for detailed urine and blood tests and, most likely, refer you to a dermatologist.
A dermatologist may prescribe a scraping from the lesion site for laboratory tests (histology, bacteriological examination).
If you suspect a household or food allergy, you should visit an allergist to undergo testing for different types of allergens.
Diagnostic problems in diagnosing blood pressure
Atopic dermatitis poses diagnostic challenges because some of the symptoms of atopic dermatitis are common to other skin diseases. Atopy is sometimes confused with psoriasis, symptomatic scabies, or a mild rash. The Williams or Hanifin and Raike AD diagnostic criteria sets are useful in making a diagnosis.
It is also not always easy to identify the allergens responsible for the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms. A negative skin test does not always mean that the disease is absent, it can only indicate that the sensitizing allergen has not yet been detected. Meanwhile, it is the correct choice of substances that the patient should eliminate from life in order to reduce the symptoms of the disease that is the key to improving his well-being.
Vitamins are wasted
I heard somewhere that with some diseases the absorption of vitamins in the body is impaired and therefore, no matter how much vitamins you take, everything will be useless. Is this true and what kind of diseases are they?
Kira Stepanyan, Urengoy
Physician Irina Sergeicheva answers:
– Indeed, many ailments increase the risk of hypovitaminosis. For example, in diseases of the stomach with low acidity, the body most often experiences a lack of vitamins B, B1, B3, C, and in case of high acidity - A, B3, B12, C. In case of cholelithiasis, chronic hepatitis, there may be a lack of fat-soluble vitamins A, D , E and K.
Problems with the intestines cause an increased need for vitamins A, K, E, D, H, C, group B. Vitamin reserves quickly “burn out” also in infectious diseases with fever, chronic diseases of the respiratory system, liver, kidneys, during treatment with antibiotics and sulfonamides . In these cases, it is necessary to additionally take vitamins A, C, B1, B2, B6.
However, uncontrolled use of vitamins in large doses can lead to intoxication of the body, in addition, cause an allergic reaction, including the development of anaphylactic shock. Particularly dangerous is an excess of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K, which accumulate in reserve in the liver and fatty tissues. Therefore, taking vitamins, like any other drug, must be coordinated with your doctor.
Determination of total concentration of IgE antibodies
The simplest test performed to diagnose AD is to determine the total concentration of IgE antibodies in the blood. This concentration is indicated in IU, and the standard is 100 IU/ml. In patients with atopy, the total concentration of IgE antibodies increases by 80%. There is often a relationship between IgE concentrations 10 times normal and the clinical condition of the patient's skin. The higher the antibody concentration, the worse and more severe the skin changes.
Therefore, patients with atopic dermatitis can be divided into two groups: those with elevated antibody levels and those with normal antibody levels (about 20% of patients).
- In the first case, we talk about extrinsic atopic dermatitis (extrinsic atopic dermatitis - EAD) because the symptoms are caused by allergens coming from the environment.
- Less commonly we deal with internal AD (intrinsic atopic dermatitis - IAD), where symptoms arise from non-immune causes, such as a skin defect or a nonspecific inflammatory response. This means that an IgE result within the normal range does not necessarily rule out atopic dermatitis.
Pharmacy from the garden
I spend the whole summer at the dacha. Of course, I have some medicines there, but I try to use folk remedies. Can you tell me which of the things that grow in the garden can be used to treat a throat?
Serafima Ilyina, Ufa
Naturopathic doctor Svetlana Olkhovskaya answers:
– You can grate fresh beets and add a tablespoon of 9% vinegar to it. This remedy should be infused for about four hours and strained. You should gargle with the resulting juice every three hours during the day. Usually, after such treatment, the sore throat subsides.
It is tasty and healthy to take lemon juice with honey, drink tea with ginger. Or suck on a piece of ginger root, fresh or dry. This refreshes, warms and disinfects the throat.
A good proven method for the first pain in the throat is to dissolve a piece of onion at night for 15–20 minutes, after which it can be chewed and swallowed.
How is atopic dermatitis diagnosed? Criteria for diagnosing blood pressure
When diagnosing atopic dermatitis, in addition to immunological laboratory blood tests, the key is to analyze the patient's skin condition and its symptoms in accordance with the criteria of Williams and colleagues or the criteria of Hanifin and Raika.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic disease with a complex cause. Its appearance is influenced by immunological, genetic, non-immunological and environmental factors. Therefore, this is not just an allergic reaction. For this reason, the basis for correct diagnosis of AD is the overall picture of the disease, especially the appearance of the skin.
Atopic dermatitis is a disease that causes diagnostic problems - similar symptoms can occur with other types of dermatitis, such as seborrheic or sweat dermatitis, contact eczema, mycosis or psoriasis. The most common diagnosis of atopic dermatitis is the so-called Williams and colleagues criteria or Hanifin and Reike criteria.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Psoriasis
Consumer Reviews
VashaNyasha (otzovik.com)
“Good day, friends and readers of the site!
I would like to share a review of our lifesaver, La-Cri emulsion. Starting at 3 months old, my boys were diagnosed with atopic dermatitis. They prescribed a diet and the use of emollient, of course they recommended expensive products. We used them, but the expense was high, and they were not cheap. And one day they advised me to try La-Cree emulsion.
The age on the tube is 0+, that is, suitable for children from birth. The composition includes extract of string, licorice, walnut, violet, jojoba oil, bisabolol, d-panthenol. The properties are written on the tube. A small pea of emulsion is enough for a large area of skin and is well absorbed. It copes with its properties with a bang.
It is also suitable for mother’s skin, both the face and the whole body. Relieves dryness, after the emulsion the skin is moisturized and soft. It lasts a long time. In general, I recommend it for use."
calm66 (otzovik.com)
"Hello! I would like to share my impressions of the La-Cri cream for sensitive skin from the VERTEX company. In fact, this is an excellent series containing not only creams, but also shampoos, lip balm, washing gels, etc. I was attracted by the fact that the products are also suitable for children and people suffering from dermatitis, which is very important for me ! I have dry skin on my face and the skin around my mouth often turns red. I tried many creams until I found this one. I read about it on the Internet, read reviews and decided to try it. And for good reason! The cream is light, absorbs very quickly, and does not leave an oily sheen. not Marat's clothes. I apply it at night and in the morning before applying makeup. My skin is prone to dermatitis, my face often turns red, itches, and flakes. this is very unpleasant. The cream moisturizes well, relieves itching and redness. Checked! The cream is not white, as we are all used to, but light beige, one might say flesh-colored, not greasy.”
Sources:
- A.N. Pampura, A.A. Chuslyaeva, Modern approaches to the treatment of atopic dermatitis in children https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/sovremennye-podhody-k-terapii-atopicheskogo-dermatita-u-detey
- Yukhtina N.V., Modern ideas about atopic dermatitis in children https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/sovremennye-predstavleniya-ob-atopicheskom-dermatite-u-detey
- Kamasheva G.R., Khakimova R.F. Valiullina S.A., Methods for assessing the severity of atopic dermatitis in young children, Dermatology journal, 2010 https://cyberleninka.ru/article/v/metody-otsenki-stepeni-tyazhesti-atopicheskogo-dermatita-u-detey-rannego -vozrasta
Photos of dermatitis
Photo album on the diseaseWilliams criteria for diagnosing AD
According to the Williams criteria, to diagnose atopic dermatitis, it is necessary to establish whether itching has occurred within the last year and at least 3 of 4 symptoms:
- involvement of skin folds (elbow and knee), changes in the neck or around the eyes;
- coexistence of other atopic diseases, for example, bronchial asthma or hay fever (when diagnosing children under 4 years of age, atopic diseases in 1st degree relatives are taken into account);
- general dry skin throughout the year;
- visible inflammatory changes in the flexion areas of the limbs and on the cheeks/forehead and elongated parts of the limbs in children under 4 years of age or onset of the disease before the age of 2 years (not applicable if the child is under 4 years of age).
Treatment of lesions with homemade ointments
For many years, humanity has known a highly effective antipruritic agent. To prepare it you will need the following components:
- Flowers of fireweed and chamomile.
- 400 ml of decoction based on hay dust.
- 800 ml of clean water.
- Glycerol.
- 10 g butter.
Mix crushed fireweed and chamomile flowers. Take 1 tbsp. l. raw materials, fill it with water. Cover the container and place on low heat. Boil for 5 minutes. Add a decoction based on hay dust and butter to the resulting product. Put it back on the fire. Cook, stirring, until the mixture reaches a uniform consistency. Mix the resulting mass with glycerin in a 1:1 ratio. Apply ointment to areas of pathology up to 4 times a day. Store the product in the refrigerator.
Propolis has proven itself well in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. This is a remedy that can stop many inflammatory processes occurring in the body. Algorithm for preparing the ointment: grind 30 g of propolis and mix it in a glass container with vegetable oil (120 ml), then place the dish in the oven for 20 minutes. Cool the resulting product. Treat foci of pathology with the prepared ointment. The duration of treatment is not limited. The procedure must be carried out until the clinical manifestations of the disease completely disappear.
In some cases, atopic dermatitis affects a large area of skin. In this case, rubbing is effective. It is necessary to prepare a decoction from the string (for 60 g of dried herb there should be 250 ml of boiling water). Strain the resulting product and dilute with water (2 l). Soak a towel in it and wipe off. At the end of the procedure, take a shower, cleansing the skin with tar soap. Rubbing is recommended to be done once every 3 days.
Criteria for diagnosing blood pressure according to Hanifin and Raike
The Hanifin and Raik criteria assume the existence of 3 of 4 core symptoms and 3 additional symptoms.
Main symptoms:
- itching;
- typical appearance and location of lesions;
- chronic and recurrent disease;
- presence of atopy in the patient's family.
Additional symptoms:
- dry skin;
- increase in IgE antibodies;
- follicular keratosis or ichthyosis;
- increased susceptibility to infections (mainly staphylococci);
- immediate skin reactions;
- positive skin tests with allergens;
- manifestation of symptoms since childhood;
- tendency to recurrent skin infections;
- cataract;
- tendency to relapse of conjunctivitis;
- changes in the color of the eyelids and skin around the eyes;
- wool intolerance;
- certain food intolerances;
- exacerbations in stressful situations;
- itching after sweating;
- white dermographism;
- thickening of the folds on the neck;
- facial erythema;
- cheilitis;
- keratoconus;
- Denny-Morgan sign (additional fold of skin below the lower eyelid);
- white dandruff;
- inflammation of the nipples;
- tendency to nonspecific inflammation of the skin of the hands and feet.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter