At least 80% of the world's population have encountered at least once in their lives unpleasant and not at all aesthetic growths on their skin and mucous membranes. And not everyone pays attention to the emerging tumors, but this could be HPV 6. Moreover, this is done in vain. After all, the appearance of growths on our body signals that the body is infected with the human papillomavirus (HPV), a very unsightly and even sometimes dangerous disease that may not show itself for quite a long time.
With strong immunity, the human body copes with any bacteria, including this infection, and when the immune system is undermined, for many reasons, such as:
- exposure to stress;
- presence of bad habits;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics;
- hormonal imbalances.
HPV types
The papillomavirus begins to actively multiply, causing us enormous aesthetic and physical discomfort. This manifests itself not only in women, but also in men, which is so unfortunate. Therefore, it is necessary to treat HPV first of all by strengthening the immune system, and then, with the permission of the doctor, you can use other methods - removal, taking medications, folk remedies, etc.
There are more than 120 types of HPV, some of which are less dangerous - these are warts and papillomas that arise and grow on the surface of the skin. But others that affect the mucous membrane, genital warts, are among the most dangerous formations. Because for many reasons, even simple trauma (breakage, tearing and other damage to the growth) and due to weakened immunity can cause the appearance of cancerous tumors.
Types of HPV that do not cause cancer are: HPV 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 28, 49. These include childhood warts, growths on the soles and hands.
HPV strains with a low risk of cancer are: HPV 6, 11, 13, 32, 34, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 51, 72. Types of the disease such as papillomavirus with an average risk of cancer are: HPV 26, 30, 35, 52, 53, 56, 58, 65.
High-risk HPV strains are: HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 45, 50, 59, 61, 62, 64, 68, 70, 73.
Condylomas and warts that appear on the genitals are most dangerous for women. Thus, HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 45 and 59 can become precursors of cervical cancer (73% - 90%). And HPV 61, 62, 68, 70 and 73 become the culprits of precancerous urological and gynecological diseases.
These are the so-called genital warts and flat warts on the genitals and other human mucous membranes. Some types of infection can be a “surprise” for men as well. They are transmitted sexually. HPV 6 also belongs to these strains.
Causes
As mentioned above, type 6 papillomavirus can be transmitted through contact with an infected person, during natural birth from mother to baby, as well as through the use of other people's personal items. That is, infection can be caused, for example, by simply trying on new clothes that an infected person had previously tried on.
The incubation period of HPV of the low oncogenic type can be up to ten years; during this period of time, the pathogenic flora is in a state of suspended animation in the body, without manifesting itself in any way. However, against the background of certain factors, the virus is activated. The following aspects can serve as an impetus for launching the mechanism:
- The presence of chronic diseases of the reproductive system or digestive tract.
- Infectious diseases of viral or bacterial etiology, occurring in an acute form.
- The presence of bad habits, which include not only smoking, drinking alcohol, but also poor nutrition.
- Long-term use of potent medications.
- Hormonal imbalances.
Despite the fact that HPV type six is not associated with a risk of developing cancer, treatment for the disease, the main goal of which is to remove growths, should be mandatory.
At the same time, it is important to contact a specialist when the first signs appear, that is, individual small growths.
Symptoms of HPV 6
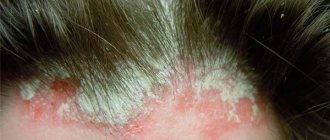
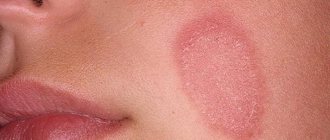
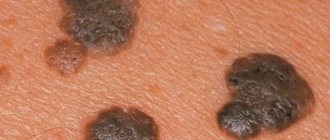
HPV strain 6 appears in the form of flat, whitish warts and thin thread-like, elongated, light-colored, soft to the touch, small growths (condylomas). Their danger lies in the fact that their presence can only be detected by examination by a doctor:
- gynecologist;
- urologist and dermatovenerologist for men;
- proctologist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- pediatrician;
- ENT.
We recommend reading:
- HPV type 58 in women
- Suppositories for HPV
- HPV type 39 in women
They are most often localized on the male genital organ, in the female vagina or in the anus. Remember that, for example, when a therapist detects moles, he gives a referral to all of the doctors listed above. Additionally, you should take into account the fact that you can go to a specialized clinic where they will use the method of excision, removal, etc.
Methods for diagnosing the virus
Diagnosis of papillomatosis includes an examination by a gynecologist, urologist or dermatologist. If malignancy is suspected, the doctor will refer the woman to an oncologist.
The following studies are shown:
- a smear of discharge from the urogenital tract - to exclude STDs, dysbacteriosis, fungal infections;
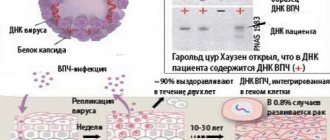
- PCR analysis – confirmation of the fact of HPV infection, determination of its type, oncogenicity and viral load. Any liquid media is used - a smear from the vagina, urethra, amniotic fluid, sperm;
- a blood test for antibodies is an optional procedure; it only indicates the presence of antibodies to HPV;
- Digene test is an analogue of PCR analysis. Only discharge from the urogenital tract is used as a sample.
Additionally, colposcopy is indicated to exclude cervical dysplasia. An ultrasound is performed if inflammatory processes in the uterus, ovaries, or fallopian tubes are suspected.
Diagnosis of HPV type 6
If neoplasms are detected during examination, the doctor will refer the person for the following tests:
- PCR test (smears from the mucous membrane of the penis or vagina);
- qualitative analysis test (detects whether papillomavirus is in the body);
- DNA test (determines the quantitative and qualitative components of the HPV strain).
As a rule, based on the results of primary tests, when dangerous changes in the human body are identified, a number of tests are done to determine the degree of danger of oncogenic formations, namely:
- cytology (determining the presence or absence of cancer cells under a microscope);
- biopsy (histology) (examination of a piece of growth to determine the degree of degeneration of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one).
And after receiving the results of all tests, the most appropriate treatment for each specific case is prescribed. If the sixth strain is detected in women or men, the doctor prescribes therapy depending on the malignancy or benignity of the formation.
Effectiveness of prevention
Compliance with precautions and hygiene measures help prevent the body from becoming infected with the virus. This is, first of all, an orderly sex life, without casual relationships and frequent changes of partner. It is necessary to use protective equipment, such as a condom.
The pathogen can enter the body in a public toilet or bathhouse. You need to use disposable toilet seat covers and wash your hands thoroughly after visiting. In the sauna or swimming pool, you must wear tight swimming trunks.
In a family, it is unacceptable for all members to share the same towel, washcloth, or toothbrush. The child should also be accustomed to washing his hands after using the toilet, not touching his face with them, and not putting dirty fingers in his mouth. Children do not have sufficient protective forces and are easily infected with various types of HPV.
Treatment of papillomavirus type 6
When treating HPV, its viral nature must be taken into account. After all, a healthy and strong immune system copes with viruses on its own, so treatment should be comprehensive, namely:
- antiviral;
- immunostimulating;
- aimed at removing growths.
It should be understood that if the genitals are affected by HPV, self-medication is extremely undesirable and very dangerous.
Today, clinical excision methods are widely used, such as:
- removal with a laser beam (today this is considered one of the most effective and expensive operations, because it is innovative technology that can eradicate the growth so that it will not only be invisible, but also cases of relapse will be reduced to zero);
- freezing (removal using liquid nitrogen, this method is used in most cases in beauty salons, and the cosmetologist must have permission to use and use this substance, so before carrying out the procedure, it is better for the client to read the documentation and verify everything personally);
- extermination by electric current (this method is carried out in hospitals and other medical institutions, it involves eradicating the growth using electric current with a special device, however, noticeable scars may remain after the operation);
- surgical (they resort to it when the papilloma has reached a level of high oncogenicity).
The most effective and inexpensive method is removal using a laser beam and electric current. These methods do not require prior anesthesia and leave virtually no traces.
Treatment
If HPV 6 is present, the patient is prescribed antiviral therapy; one of the methods for removing pathological growths is additional procedures.
If you have been diagnosed with human papillomavirus type 6 or 11, do not try to remove growths yourself, consult a specialist
How to treat neoplasms, the appearance of which is caused by infection activity?
There are several ways to remove growth:
- surgical intervention;
– laser method;
– cryodestruction – low-temperature exposure;
– diatherocoagulation – use of an electric knife;
– surgical method
All of the listed methods of getting rid of pathologies must be carried out by a specialist in a medical institution. It is important to follow the appropriate recommendations for caring for the damaged area after removal of pathologies.
Individual therapy and a variety of effective treatment methods for men and women separately are developed for each patient.
Drugs that help with HPV 6 in women and men
Drug treatment is aimed at cauterizing a growth such as papilloma. It is recommended to use the following drugs:
- "Solcoderm";
- "Doufilm"
- "Superclean";
- "Kondilin";
- others, based on acids and alkalis.
Their action is aimed at burning out growths so that they disappear. But you should be careful to apply medications directly to the tumors so as not to damage healthy areas of the skin.
Recommended antiviral drugs include:
- "Allokin-alpha";
- "Groprinosin" (or analogues);
- "Epigen intimate spray";
- "Panavir";
- others having an antiviral nature.
These drugs basically fight bacteria and have an antiseptic and disinfectant effect.
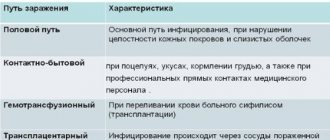
Routes of infection and localization of growths
The route of infection with the virus is contact, household contact. There is a chance of catching a sore while using the same towel for everyone.
Typical localization is:
- in men: head of the penis, frenulum, area around the external opening of the urethra;
- in women: vulva, labia, pubis, anorectal area, inguinal folds, clitoral area.
Condylomas are found on the mucous membranes of the rectum, mouth, and pharynx.
How to boost your immune system if you have HPV?
To increase immune defense when infected with HPV DNA, you can use the following medications:
- "Immunal".
- "Pooxidonium".
- "Roncoleukin."
- "Interferon".
- "Viferon".
- other immunostimulants.
The use of this kind of drugs stimulates and enhances the natural protective functions of our body.
Something to remember! The course of treatment lasts from 5 days to 2 months. Any medications and drugs must be purchased from pharmacies and used strictly as prescribed by a doctor or according to the instructions. This is especially true for children.
In folk medicine, when infected with HPV DNA, celandine juice (lotions or direct drops of juice) and garlic (compresses from crushed plants) are widely used. They are done several times a day, for one month. Tinctures and mixtures of fruit and vegetable juices (apple juice, raw potatoes, garlic) are taken orally to increase vitality.
If the papillomavirus, or rather its manifestation, a wart in women or men, darkens, shrinks and falls off after treatment, then the result has been achieved. A person may not worry about HPV type 6. However, even with a positive effect, it is necessary to take into account the risk of relapse and degeneration of condyloma (warts) into a malignant growth. But it is impossible to diagnose a neoplasm at home.
PCR for HPV with concentration
A more accurate diagnostic method is PCR.
True, it makes sense to conduct this research only using a quantitative method.
Qualitative PCR does not have much informative value.
The very fact of the presence of HPV 6 in the skin does not mean anything.
The virus may be present in minimal quantities.
Then it does not pose a health threat.
Accordingly, on the basis of such an analysis it is impossible to decide whether treatment is needed, how it should be carried out, and whether monitoring of the patient is required.
A much more informative test is quantitative PCR.
It allows you to determine the viral load.
PCR is performed for:
- primary diagnosis of HPV;
- determining the type of papillomavirus;
- assessing the degree of danger of the disease (based on viral load);
- assessing the dynamics of the disease (viral load increases or decreases);
- assessing the success of the treatment.
PCR is often done several times.
If diagnostics are carried out at certain intervals, then comparison of the results allows you to see how the disease develops.
If the number of HPV 6 increases, this means that the pathology is progressing.
The patient may develop additional condylomas or enlarge existing formations on the skin.
It is contagious to others.
In addition, complications are possible in the future.
With a decreasing load, the doctor assesses the dynamics as positive.
This means that the person is recovering.
Under the influence of your own immunity or ongoing treatment, HPV 6 will soon leave the body.
Preventive measures for the occurrence of the disease
Compliance with personal hygiene standards in public places, a healthy and correct lifestyle, strengthening the immune system, regular visits to specialist doctors (at least once a year) will save a person and his family members from such unpleasant health “surprises” as infection with such an ailment as papillomavirus.
Remember that if a girl has not yet had sexual relations, you can always get vaccinated at an earlier age. This is done from 10 to 14 years of age. In addition, it will protect in the future from any strain entering the body, and even if the bacteria penetrates, the vaccination in most cases stops the infection and prevents it from progressing, but on the contrary, destroys it.
Among the preventive measures are an active lifestyle, proper nutrition, and proper drinking regimen.
If a person takes all this into account, then no viruses are scary to him. Just remember that everything needs to be done in moderation - excessive treatment or prevention is also not necessary, so as not to aggravate the situation. Please note that if you accidentally tear off a tumor and it will bleed, it is better to disinfect it with 3% hydrogen peroxide and contact a doctor. The article has been verified by the editors
How the disease is transmitted
HPV infection can occur from a sick person to a healthy person in 3 ways:
- infection of a child during childbirth from the mother (or while still in the womb of a pregnant woman);
- during sexual contact (vaginal, oral, anal);
- contact and household path through abrasions, scratches on the body.
You can become infected with HPV from a carrier of the virus who has growths on the body.
Contraceptives will not help protect against human papillomavirus, since during sexual intercourse the skin near the genitals comes into contact. But it is still necessary to use barrier methods of contraception to prevent other sexually transmitted diseases.
At the slightest damage to the skin, the virus enters the body. However, contraceptives reduce the risk of HPV infection.