What is skin nevus?
A nevus is a benign formation developing from pigment cells on the skin or mucous membrane, called a birthmark or mole. As a rule, it does not cause any physical discomfort, remaining invisible under clothing. There are many signs associated with the appearance of moles on one or another part of the body: some promise happiness in life, others promise health and longevity. Is it really?
Pigment or nevus cells are formed in the prenatal period of development. They are precursors of normal melanocytes, but remain in the deeper layers of the dermis, forming special clusters. Under the influence of a number of factors, nevus cells actively produce pigments that are visible on the skin as moles.
Modern medicine claims that ultraviolet rays that enter the skin during a person’s life are of great importance in the appearance of birthmarks. They are stimulators of modified melanocytes of the dermis, clusters of which lie dormant in its different layers. Having received the necessary dose of UV rays, these pigment cells begin to intensively produce melanin, which manifests itself in the form of various brightly colored spots - moles.
In addition, it should be noted the influence of hormonal levels on the development of nevi. Thus, during pregnancy, adolescence and with hormonal therapy, the number of moles increases. In addition, existing moles may slightly increase in size and change shape under these conditions.
In young children, birthmarks can hardly be found on the body, but in their dermis there are already accumulations of altered melanocytes awaiting stimulation. The older a person is, and the more time he spent in the sun, the more moles can be found on his body. The average person can find about 20 different types of nevi, sometimes their number exceeds a hundred, or moles merge into one huge spot. It is interesting that moles are much more common among representatives of the Caucasian race; in a person with dark skin, the number of nevi is several times less.
Reasons for education
Factors that cause changes in the DNA of skin cells can be:
- The influence of hormonal drugs taken by a woman before pregnancy (contraceptives).
- The influence of hormonal medications used by a woman during pregnancy (steroid ointments).
- Hormonal imbalance in the body caused by pregnancy.
- Alcohol and nicotine abuse by the expectant mother. The poison accumulates in the body for so long that it takes up to 2 years to cleanse it. That is, a safe pregnancy can occur 2 years after a woman gives up bad habits.
- Diseases of a sexually transmitted nature that are present in the mother’s body, including in a chronic form.
- Fungal and viral diseases of the female genitourinary system.
- An abundance of foods high in preservatives and artificial colors in a pregnant woman’s diet.
- Increased levels of radiation and severe air pollution with chemicals.
- Excess ultraviolet radiation to which a pregnant woman is exposed.
- Nevus in children can be hereditary, that is, transmitted at the genetic level from one of the parents.
A nevus can be non-pigmented, i.e.
invisible Education can be invisible. Such a non-pigmented nevus appears in an adult person under the influence of external factors - ultraviolet radiation, radiation, severe stress, change in climate or diet. In women, such formations appear during pregnancy against the background of hormonal imbalances. This nevus is also congenital, but becomes visible much later.
Types and types of nevi
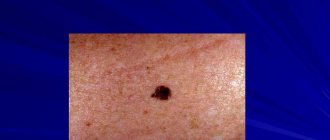
There are 3 types of moles:
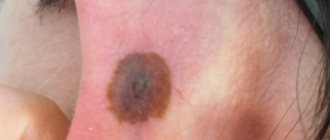
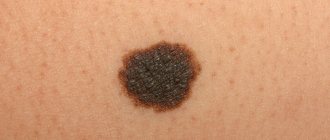
- Intraepidermal nevus is the most common. This is a flat, rounded formation with clear boundaries, uniformly colored from light to dark brown. As a rule, such a nevus appears in the first two decades, and gradually becomes depigmented in adulthood. The size of an intraepidermal mole during life is directly proportional to the increase in height and body weight, and the color of its surface may change.
- An intradermal nevus is distinguished by its dome-shaped shape; it is a formation of different colors, uniform in color, rising above the surface of the skin. The appearance of moles of this type is typical after 30 years; their size can vary from several mm to 5-10 cm. The dome-shaped shape is often created by the presence of a so-called stalk, which increases the risk of injury to the formation.
- Complex (mixed) nevus is a transitional form of intradermal and intraepidermal formations. It almost always has a round, spherical shape, dense consistency, and clear boundaries.
Several types of nevi should be distinguished, all of them have a benign course:
- vascular (strawberry, strawberry),
- dysplastic,
- papillomatous,
- Becker's nevus
- Setton's nevus
- blue.
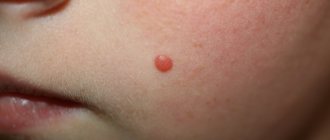
Vascular nevus appears as a result of abnormal growth of the walls of blood vessels. In this case, a spot of a reddish hue appears on the skin, dense to the touch, without hair. Due to its color, this mole is called strawberry mole.
Dysplastic nevus can appear on the skin throughout a person’s life. This is the result of the chaotic life of nevocytes under the influence of stimulating factors: UV rays, hormones, radiation, etc. Such a mole is small in size, as a rule, its color varies from red to dark brown. Their group arrangement on the body is characteristic.
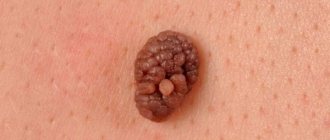
Papillomatous nevus has the appearance of a papule, with uneven outlines and a rough surface, often hair grows on it. Located mainly in the neck area.
Becker's nevus occurs mainly in young men during puberty due to the intensive production and entry into the blood of large quantities of male sex hormones. Its appearance is preceded by the formation of several brown spots on the skin, which then merge. Thus, Becker's nevus has uneven contours and is large in size. Over time, its surface becomes uneven and hair appears.
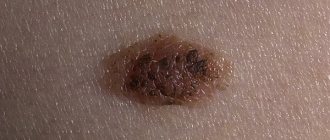
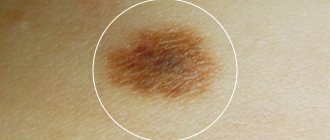
Setton's nevus is a brown nodule, up to 10 mm in diameter. Its distinctive feature is the presence of a rim of depigmentation (white circle) surrounding the mole along the periphery and is 2-3 times larger in diameter.
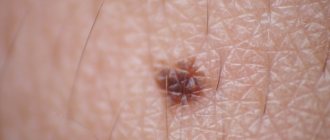
Blue nevus is called so due to its color. This is a small nodule with clear boundaries, always smooth.
Also, all nevi should be divided by size into:
- small (5-15 mm),
- medium (up to 10 cm),
- large (10-20 cm),
- gigantic, occupying the entire anatomical area.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis and treatment of skin diseases is carried out by dermatologists and cosmetologists in specialized clinics. An external examination of the birthmark is carried out to determine its location, size, shape, and color. Then the doctor interviews the patient, finding out hereditary predisposition, living conditions, and the presence of provoking factors.
To make a correct diagnosis, the following procedures may be necessary:
- examination using a dermatoscope;
- taking smears from the surface of the nevus;
- blood test for tumor markers;
- CT scan.
Differential diagnosis is necessary to separate the nevus from other formations on the skin - warts, molluscum contagiosum, basal cell carcinoma. After removal of a mole, it is sent for histological examination and biopsy to ensure its benignity or to determine signs of degeneration.
Nevi in newborns
Congenital nevi are essentially benign tumors. They are quite rare: in only 1-5% of cases you can find a nevus on the body of a newborn baby or a baby under one year old. At birth, the skin already contains accumulations of changed melanocytes, awaiting any stimulation for their further development. Most often they appear during hormonal changes in the body and under the influence of ultraviolet rays.
Congenital nevus, as a rule, has a round shape with clear boundaries. Its color is always uniform and can be light, dark brown, or black. The size of such a mole is from 5 mm to 2 cm. The surface is smooth or slightly bumpy, with slight hair growth. Also, a birthmark can reach gigantic sizes, occupying the entire anatomical area of the body, while its surface will be soft and velvety to the touch.
If a newborn child has many moles on his body, or birthmarks occupy a large part of the body, this is a reason to carefully monitor them, since there is a high risk of malignancy and degeneration into melanoma or another tumor. Consult a specialist.
Malignancy of nevi is possible with the constant influence of a number of irritating factors on it.
They most often are:
- chronic traumatization of a mole,
- frequent exposure to aggressive chemicals,
- disturbances in the level of hormones, most often sex hormones,
- adverse physical effects, UV rays, etc.
With malignancy (transition into a malignant tumor), the nevus causes concern. This may be associated with a feeling of burning, tingling or itching in the area of the mole, or rapid growth of its volume.
If the process of malignancy has already begun, then the nevus acquires characteristic signs:
- bleeding and wetting of the surface,
- rapid increase in size,
- ulcerated contours, unclear boundaries,
- uneven pigment coloring,
- lumpy surface, dome-shaped growth.
If disturbing symptoms appear, you should consult a specialist. With the help of a medical examination, the doctor can reliably determine the nature of the birthmark and select the necessary treatment.
What danger do white moles pose to children and adults?
It is worth considering that white moles are an individual feature of a separate organism and do not pose any danger, but you need to be on guard with such formations. Any external changes, damage, enlargements or pain require immediate medical examination.
If non-pigmented moles appear in children, this is not always critical. White formations are congenital or form before the age of 10. As a rule, they are benign and do not pose any danger. Watch the white spots grow. If they increase as the child develops, then this is normal. If you have other symptoms of degeneration, be sure to consult a doctor. If a white spot or mole appears on an adult, this has more alarming reasons, because it can alert about a disease called Vitiligo.
Vitiligo disease is a pigmentation disorder that causes white spots to form on any part of a person’s skin. This ailment is not common and is often a common skin defect. Light spots appear gradually, and their number increases. The hair on such areas of the skin also changes color. The first mistake that patients often make is ultraviolet exposure. Doctors categorically prohibit sunbathing, as the disease can only get worse. The nature of the disease is not fully understood.
Nevus removal
Moles that cause various types of discomfort must be removed. There are several methods for getting rid of moles - these are traditional medicine recipes, cryodestruction, and excision with a scalpel or laser. The most proven methods are surgical removal and the laser method, since they provide almost 100% elimination of nevi. You should definitely consult a specialist; the doctor will be able to choose the best treatment option for you.
There are a number of indications, in the presence of which an experienced dermatologist will advise getting rid of the nevus. First of all, this is due to oncological alertness, since nevi quite often become malignant.
It is recommended to remove moles if:
- their frequent traumatization, which is typical for nevi located in the groin and axillary areas, on the head, in places where belts and bras are worn.
- a sharp increase in the size, borders, and color of the birthmark.
- increasing discomfort, itching, burning, tingling, wetting, bleeding.
- high risk of malignancy, for example, if it is a giant congenital nevus.
- for prophylactic purposes.
In addition, removal of a mole is possible at the patient’s request, which is especially common when the nevus is located in an open area of the body or when it is large. Then getting rid of this formation will be a cosmetic operation with an aesthetic purpose.
Treatment method
If white birthmarks are located in inconspicuous places, do not bother a person and do not have a tendency to develop into malignant ones, then there is no need to carry out any therapeutic measures.
If a mole causes discomfort or can lead to undesirable consequences, it is necessary to get rid of it.
Therapeutic methods
Drug treatment of moles with therapeutic methods can neither remove them nor stop their growth. Therefore, to remove nevi, they resort to drastic methods - surgical or minimally invasive .
Nevus removal with laser
Laser excision of moles is now very common. This is a fairly reliable, proven method. Laser can be used to remove small moles located on any part of the body.
The essence of the technique is this: laser radiation penetrates exactly to a given depth in the required place. The procedure is painless, and there are no common complications such as scars, burns and cicatrices.
But there is also a significant drawback of this technique - when a large volume of nevus is removed, a whitish (depigmented) spot remains on the skin.
Why do birthmarks occur?
The mechanism of formation of congenital skin defects has not yet been fully studied. It is assumed that the causes of the appearance of nevi are disruptions in the body that occurred during the development of the child’s circulatory system, as well as premature birth. The risk group, which includes children who are at high risk of developing a birthmark, includes babies with white skin, premature babies, and girls (hemangioma is 3 times more likely to occur in them).
It is believed that in some cases the cause of this type of nevus is the fetal position taken closer to childbirth, when the fetus, instead of the usual bending of the head to the chest, throws it back. As a result, the presenting part becomes the face rather than the crown.
Before being born, the baby experiences pressure from the wall of the uterus and the mother’s pelvic bones. In some places it is so great that there is a disruption of the blood supply to the tissues of the area that is present. With the occipital, this is the area of the neck at the border with the hairline (“stork bite”), with the facial – the nose, bridge of the nose, chin, upper lip.
According to some doctors, birthmarks are formed due to fluctuations in hormones during pregnancy, infections of the genitourinary organs, and unfavorable environmental conditions.
New growths that appear in babies differ in shape, color, and texture. When examining a newborn's nevus, the doctor first determines its character. There are the following types of such moles.
Surgical removal of nevus
Surgical excision of nevi is still most commonly used. This method is reliable and convenient because it does not require special expensive equipment. Basically, large nevi are excised in this way.
The main disadvantages of the procedure are:
- cosmetic defect on the skin. Since the dermatologist must remove at least 3-5 cm of healthy dermal tissue around the nevus, scarring is almost inevitable.
- Excision of a nevus, if it is small in size, is performed under local anesthesia; in other cases, as well as in childhood, surgical removal of a mole is possible only under general anesthesia.
Complex pigment
Along with borderline pigmented and intradermal nevi, complex (pigmented) nevus is one of the main types of melanocytic formations of epidermal origin. The growth of such moles begins in the upper layer of the skin - the epidermis, then they grow directly into the dermis. This means that a complex pigmented nevus is simultaneously located in both the dermis and epidermis. Hence the name - dermoepidermal (mixed or complex) nevus.
This type of mole is benign, but according to various experts, in 50-80% of cases these formations can degenerate into melanoma.
This is why mixed (complex) skin nevus is considered melanoma-dangerous.
Caring for neoplasms
If your baby has a small to medium sized spot on his head, you don't have to worry. Such moles do not cause discomfort and do not require special care.
important to carefully comb the baby and put on hats that will not damage the nevus. Your main task is to eliminate accidental injury to the mole.
That’s why you shouldn’t forget that you can always show your child to a specialist, namely a dermatologist, who will determine the future fate of the pigment spot on the head.
There are some important tips to follow if your child has a mole on his head:
- You should not use scrubs and shampoos with small exfoliating particles, so as not to injure the nevus area.
- When combing your hair, you should avoid the mole without applying pressure or force in this area of the skin.
- An accessory to protect the head, as well as glasses, should not come into contact with the mole and cause discomfort when worn.
- It is important to measure the size of the mole once a month, and also pay attention to its color.
- You cannot get rid of it yourself, otherwise it can lead to the formation of a tumor, which will lead to negative consequences.
If a danger is detected, the dermatologist will suggest removing the mole on your child’s head. The reason for such actions may be not only a malignant tumor, but also cosmetic discomfort. Also, during the research process, he will be able to understand how large the percentage of its degeneration and influence on the baby’s life is.
Total information
Giant pigmented nevus is one of the congenital diseases. The frequency of birth of a child with this disorder is 1 in 500 thousand newborns. But according to some data, in fact, the pathology is diagnosed in 1-2% of the world's population. Official statistics do not correspond to real ones, since quite often patients ignore the presence of this tumor and do not consult a doctor. It can be detected when a patient visits a clinic for some other pathology, but the diagnosis cannot be recorded anywhere. In countries with low economic development, the presence of a nevus is not considered a disorder at all, so this diagnosis is also not recorded anywhere.
Males and females get sick with approximately the same frequency. Endemicity (more frequent occurrence in a certain region) has not been identified for the same reasons that the exact incidence has not been determined.
note
A peculiarity of a giant pigmented nevus is that it transmits a predisposition of genes to the occurrence of spontaneous mutations.