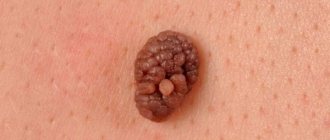
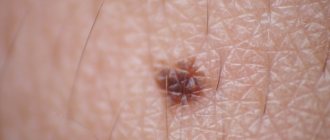
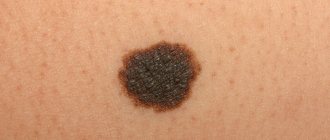
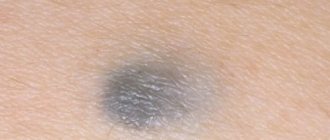
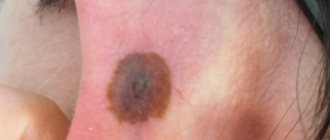
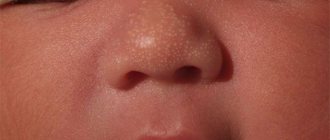
A papillomatous nevus is a bumpy mole that stands out above the surface of the skin and has a similar appearance to a papilloma. Most often it is located on the head, but it can also have other locations. Nevus can be diagnosed using dermatoscopy; in some cases, a biopsy may be necessary. This neoplasm is benign in nature, it can be congenital, or it can appear during life. The likelihood that it will develop into melanoma is almost zero.
A nevus is removed more often because it is easy to injure; it can also be caused by inflammation or a desire to get rid of it as a cosmetic defect. There are several removal methods.
general characteristics
Papillomatous nevus is a tuberous nodule, the structure of which includes papillary growths of a warty nature. This formation is attached to the epithelium with a wide base. Most often it is localized on the scalp, face or neck. However, in some cases it can be seen on other parts of the body.
This form of nevus, like most other types of moles, falls into the category of congenital formations. In this case, a papillomatous birthmark may remain invisible for a long time. However, this type of nevus gradually increases and reaches its final size at 20-30 years.
Such moles are benign and do not pose a health hazard. However, in medicine there are rare cases where such a nevus has transformed into melanoma.
It should be borne in mind that this convex mole causes a lot of inconvenience. Since in most cases it affects the head, there is a high probability of damage when combing, dressing or washing the hair. This increases the risk of the nevus degenerating into a malignant formation or developing an inflammatory process.
Alarm Signals
For those with a small congenital nevus, the risk of it degenerating into melanoma is approximately 5%. And the transformation of a giant nevus into melanoma occurs in 40%.
Mechanical damage - picking, scratching, as well as radiation - sunbathing in direct sunlight and going to a solarium are very dangerous and undesirable.
You should be wary if:
- the pigment spot has increased in height or width
- the mole has lost its clear outline
- the birthmark has changed its color, becoming more or less pronounced
- nodules and crusts appeared on the surface of the nevus, and it also began to bleed
- enlarged lymph nodes in the groin, armpits and neck
In what cases are pigmented nevi removed for preventive purposes?
- It is better to remove nevi in childhood before puberty
- if the mole is located where it can be accidentally torn off or damaged
- the size of the nevus is more than 1.5 cm
- mole color brown or black
A timely removed mole with the above signs will not allow the formation of a malignant tumor in this place.
Removal of pigmented nevi is one of the operations performed in the Diamed network of Moscow clinics. Doctors with extensive experience will be able to painlessly rid their patients of skin lesions. The procedure is carried out at the Diamed Shchelkovskaya and Diamed Maryina Roshcha clinics.
The selection of medications for the treatment of pigmented nevus is carried out only by a doctor and strictly on an individual basis, based on the type, age and characteristics of the patient’s body.
Causes
Experts have been studying the mechanism of development of this benign formation for many years. However, the exact reasons for its appearance are still a controversial point. Currently, the most reliable version is a congenital disorder of intrauterine development.
If there is a failure in the formation of the fetus, an increased amount of pigment accumulates in certain areas of the skin. Over time, this leads to the appearance of an intradermal nevus. Under the influence of certain factors, this formation increases in size and becomes more obvious.
The most common causes of fetal defects include the following:
- exposure to increased doses of radiation;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- contact with chemicals;
- entry into the body of toxic fumes.
Differences between papilloma and nevus
To distinguish a mole from a papilloma, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist. Only a specialist can accurately determine the nature of the formation on the skin. However, a person can make a preliminary diagnosis independently, based on the following features:
- Moles can occupy an entire part of the body or be literally a few millimeters in size. In this case, the papilloma usually reaches 2-15 mm, increasing to 5-6 cm only in case of damage.
- Nevi have a hard and dense structure, while papillomas have a loose consistency and are soft to the touch.
- The basis of moles are skin cells, and papillomas include blood vessels.
- A mole is a feature of every person; in some cases, birthmarks are inherited. In this case, the spread of papillomas is carried out exclusively by infectious means - through household and sexual contact.
- Nevi can have different shades - pink, light, black, brown and even bluish. Papillomas are always light in color - flesh-colored or pink.
- Moles can affect any part of the body, including mucous membranes. The main localization area for papillomas is the mucous membranes and areas of strong friction.
- Moles should have an even, symmetrical shape - round or oval, while papillomas can have different shapes.
- Nevus appears at birth or in the first years of life. Papillomas develop several months after infection. Rapid formations can occur after 1-2 months, and protracted ones - after 4 months.
Symptoms
Papillomatous nevus has a number of characteristic symptoms:
- The mole has a convex structure and resembles a tubercle in shape, which protrudes above the surface of the skin and is attached to it with a wide stalk.
- The integumentary epithelium is thickened. In this case, the mole is quite dense to the touch.
- In most cases, papillomatous nevus has a bumpy surface and a granular structure. Its basis is made up of elongated epidermal processes. This can easily be seen during microscopic examination.
- The neoplasm is distinguished by clear boundaries of arbitrary shape.
- Papillomatous nevus can have different shades - there are flesh-colored, brown, brown formations. Sometimes black moles are observed. This is determined by the amount of melanin that is present in the cells.
- Birthmarks can be single or multiple.
- The dimensions of this formation are quite impressive - from 1 cm.
Content:
- Common acquired pigmented nevus: Borderline,
- Difficult,
- Intradermal.
- dysplastic,
- Surgical,
Classification
There are different principles for classifying papillomatous nevi. So, depending on the appearance, such moles can have the following varieties:
- pigment type - a dark-colored mole that appears on the hairless part of the body;
- hair type - there may be several hairs that grow from the nevus and have an impressive length and a dark shade;
- verrucous type - in appearance it resembles a warty formation, but differs in a more lumpy structure and deep folds.
In addition, experts identify the following forms of papillomatous formations:
- Organic – occurs quite often. Benign moles of this type have a small base and rise slightly above the surface of the skin. As a rule, you can see single moles, which can have different variations of brown color. This formation includes several outgrowths that are covered with a stratum corneum.
- Disseminated - consists of many dirty-brown plaques that are localized on different parts of the body. This species may pose a certain danger to the human body.
The fact is that lumpy nevi, which are similar in appearance to warts, are often evidence of serious disorders in the functioning of the central nervous system and even epilepsy. Such formations often increase in size. In some cases, they dry out and fall off for no apparent reason.
Signs of degeneration into skin cancer
Papillomatous growths rarely degenerate into a malignant tumor. But since there is still a possibility, you need to treat neoplasms very carefully. Here are a few signs that may indicate malignancy:
- Excessive elevation above the surface of the skin;
- Blurry boundaries;
- Hair loss from a mole;
- Rapid increase in size;
- Change in color (lightening or darkening);
- Bloody discharge from the growth;
- The appearance of small spots and dots on the mole;
- Inflammation of the edges of the growth;
- Burning, pain, itching, tingling in the nevus;
- The formation of new small moles, cracks, and ulcers on the nevus.
You should go to the doctor when at least one of these signs appears. Melanoma is considered one of the most aggressive types of cancer; it progresses very quickly and almost immediately gives multiple metastases throughout the body. To recover and survive, you need to start treatment immediately after diagnosis.
Diagnostics
Even if a nevus does not cause discomfort, it must be shown to a dermatologist. To eliminate the risk of developing melanoma, it is necessary to accurately diagnose the type of formation.
As a rule, experienced doctors can determine the shape of a mole based on its examination and dermatoscopy. Thanks to this, it is possible to differentiate papillomatous nevus from papilloma, melanoma, filiform wart and other formations with similar symptoms.
Siascopic examination will also help to distinguish this formation from a pigmented nevus. In difficult cases, a tissue biopsy of the nevus can be performed. Even slight doubts about the diagnosis should be a reason to contact a dermato-oncologist, who will help rule out melanoma.
Complications
You should be wary of the mole degenerating into a malignant neoplasm, so there is an urgent need for timely excision of the nevus using surgical methods. In addition, the characteristic growth in everyday life is systematically exposed to damage, which is accompanied by dangerous inflammation and infection of the dermis. The appearance of fibroepithelial nevi is especially dangerous. Among potential complications, doctors also identify the following pathological processes:
- severe pain and redness of the dermis;
- risk of scarring after scratching the nevus;
- infectious skin diseases, skin infection.
Papillomatous nevus of the scalp
In most cases, this formation affects the scalp. However, sometimes it is detected on other parts of the body. Papillomatous nevus has irregular outlines and different shades. Sometimes it can be very pigmented - brown and even black.
Such nevi appear on the human body in both single and multiple quantities. This is influenced by the physiological characteristics of the body. Often, such moles form in early childhood and gradually increase throughout life.
Treatment and removal of papillomatous nevi
As a rule, it is recommended to remove such moles if there is constant injury, psychological discomfort, or the development of inflammation. If, as a result of diagnostic studies, it was not possible to completely exclude melanoma, it is also recommended to remove the nevus. In this case, histology of the formation must be performed.
To remove this type of mole, various methods are used - laser, radio wave exposure, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation. Surgical excision may also be performed. In any case, the use of local anesthesia is indicated.
If the papillomatous nevus is localized on the neck or face, laser removal is usually used. If you properly care for the wound after surgery, you can achieve the best cosmetic effect. However, in doubtful cases, this intervention is not performed, since it does not make it possible to obtain material for histology.
The use of cryodestruction to remove such a formation is indicated when localized on the scalp or those areas that are usually hidden by clothing. This technique can only be used by qualified specialists. This is due to the fact that deep exposure of the skin to liquid nitrogen provokes a cold burn and leads to scar formation. Carrying out histology in this case is also not possible.
Excellent results can be achieved using the radio wave method of removal. After this procedure, the tissues heal completely without scarring. This allows you to achieve excellent cosmetic results. In this case, the removed nevus can easily be sent for histology.
Electrocoagulation of a nevus is used quite rarely, since after it a noticeable scar is usually formed. However, after this procedure, histological examination can be carried out without problems.
A mole of impressive size is an indication for surgical removal. After such an operation, cosmetic stitches are applied, which avoids the appearance of a large scar.
Surgical operations
Large papillomatous nevus undergoes surgical excision. The application of small cosmetic stitches after the removal operation guarantees minimal cosmetic defects. The possibility of relapse is excluded, since along with the nevus, the doctor also captures part of the healthy tissue when removing it. Giant nevi are also treated surgically. They are rare, but the risk of developing cancer in them is very high. Treatment of giant pigmented nevus is carried out in stages, with the involvement of plastic surgeons for further cosmetic operations.
Papillomatous nevus in pregnant women
To prevent negative health effects, pregnant women should avoid exposure to negative factors. These include:
- radiation exposure;
- exposure to toxic substances on the body;
- significant change in hormone levels;
- infectious lesions of the urinary system.
The impact of these factors on the body of a pregnant woman can lead to a change in the structure of the nevus and the development of an inflammatory process.
The appearance of a papillomatous nevus can cause serious discomfort to a person, especially since such formations are often located in prominent places. In such cases, the mole is removed. If education does not bother a person, it can be left alone. But in any case, the slightest changes in the structure of the nevus should be a reason for a visit to an experienced dermatologist.