It is unpleasant when papillomas appear on the body of adults, but papilloma in an infant looks much worse. Papillomas are a virus commonly referred to by the acronym HPV. The disease is common, occurring in more than 70% of the population; usually the disease goes away on its own within a few months and does not cause any inconvenience to its carriers. Because of this, if the tumor has not grown on the face or genitals, people do not try to fight the infection and do not go to the doctor.
Modern treatment methods allow you to gently get rid of papillomas, including in newborns
A short-sighted decision, given that the tumor can lead to the development of cancer. There is no need to panic, this disease can be easily treated. The growths are usually benign and easy to remove. Modern methods for removing papillomas are gentle, painless and leave no marks on the skin.
What papillomas look like in newborns - types of papillomas and their typical locations
What does papilloma look like?
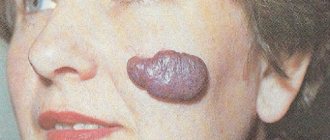
Papilloma is a benign formation on the skin or mucous membranes, having the shape of a papilla, a soft shapeless sac on a stalk or a dense lump.
Basically, papilloma has the color of the tissue on which it originated, sometimes it can be a little darker or lighter.
Papilloma can be a single formation or multiple , localized on any open parts of the body (except the scalp) and mucous membranes.
It must be borne in mind that papilloma or papillomatosis is not a single disease, but a complex pathology associated with HPV infection.
Types of papillomas in newborns and their locations
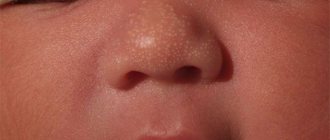
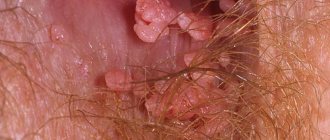
- Thread-like papillomas, or acrochords , are located singly or in groups on any area of the skin, most often on the cheeks, around the eyes and mouth, on the forehead, neck, eyelids, armpits, and in the folds of the groin area. If they are small, they may not be noticed immediately. These are very thin and delicate formations that can easily separate from the skin during hygiene procedures or rubbing clothes against the skin. Blood will appear at the site of the torn papilloma. Filiform papillomas are a type of formation in this group, which is most often congenital and not acquired in the postnatal period.
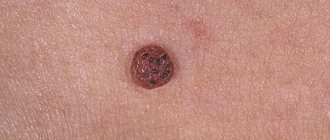
- Flat papillomas (or in common parlance - warts) are dense formations in the skin that may protrude slightly above the surface, but do not form a stalk. Most often, flat papillomas are located on the face. They cause itching and bother the baby with pain. In addition, these papillomas are more likely than others to become inflamed due to the child scratching the skin.
- Vulgar papillomas are most often localized on the buttocks and palms. They are round in shape and rise slightly above the skin. The top layer of papilloma is quite dense, similar to a wound crust.
- Plantar papilloma usually appears in older children. They differ from other types of formations in that they are located on the plantar surface of the foot. They can merge and occupy quite large areas of the skin. Quite painful and very difficult to treat.
- Epithelial hyperplasia forms on the mucous membrane of the mouth, palate, tongue and soft palate. This is a single or multiple papillary formation that can become inflamed, damaged during eating, and painful.
- Laryngeal papillomatosis is nodular and papillary formations localized in the glottis and on the posterior wall of the larynx. Due to constant irritation of the airways, it can cause swelling and lead to a life-threatening condition.
- Warty dysplasia appears mainly in children aged 3 years and older. The rashes are localized mainly on the hands and fingers. Mostly multiple, can merge into clusters. The formations are rough, round, and occasionally pigmented. These warts are dangerous because, more often than others, they degenerate into cancerous tumors over time.
Should a child be treated for papillomavirus: doctors' opinion
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Parents are concerned about the question: is it worth treating their child for a dangerous papillomavirus. Most doctors come to the conclusion that there is no need to immediately get rid of papillomatosis in infancy; one should monitor the progression of the disease and assess the exact stage of development. It is necessary to remove the warts when the warts instantly grow, enlarge, and cause discomfort in the form of itching and severe pain.
Causes of papillomas in newborns and routes of transmission - but is HPV always to blame?
If you noticed, at the beginning of the article we mentioned papilloma-like formations. In this case, we are talking about all defects of the baby’s skin and mucous membranes, which in appearance are very similar to papillomas, but in fact are other diseases with causes different from HPV.
What is it easy to confuse papillomas with, including in newborns?
- Nevi (moles), which often look similar to papillomas. Congenital nevi are found in 1% of all babies (the pathology affects exclusively representatives of the Caucasian race).
- Molluscum contagiosum in the postnatal period, which sometimes closely mimics papilloma in appearance, having a stalk or an elongated shape. Unlike papilloma, the mollusk spreads extremely quickly over the skin and is much more actively transmitted to others through any contact, including through household contact.
- Melanoma is congenital, or appears in the first weeks after birth. Outwardly, it may look like a papilloma and rise above the surface of the skin or mucous membranes in the same way, but in the vast majority of cases, melanoma has dark pigmentation. Although there are also discolored options.
- Congenital small skin defects with papillary growths that are not a consequence of HPV infection.
In order to diagnose the above diseases , manifested by papilloma-like formations, and differentiate them from true neonatal papilloma, the necessary set of examinations is prescribed in each specific case.
Only a specialist should make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment!
Factors contributing to HPV infection in newborns:
- Acute immune deficiency.
- Errors in the functioning of the digestive system.
- Allergoses.
Viral infection with HPV can occur at the time of birth of a child or in the postnatal period.
It is necessary to keep in mind that the virus in a child’s body can remain dormant for a long time, and cause the appearance of formations on the skin and mucous membranes already at the age of one year and even later.
An important factor in the prevention of papilloma in a newborn is to undergo examination before pregnancy, and, if necessary, treatment!
Until quite recently, almost the only cause of all papilloma-like formations on the skin of newly born children was categorically considered to be infection with the human papilloma virus, which occurs when the child moves through the mother’s birth canal and contact of his skin with her mucous membranes.
However, not so long ago it was established that the virus can penetrate the placenta during pregnancy and provoke the appearance of papillomas in the fetus - which means that the child can be attacked by the virus in utero.
Proof of this fact is the latest medical statistics, according to which quite a lot of children are born whose papillomas are diagnosed immediately after birth. And this was confirmed by data on the birth of children by cesarean section, in whose anamnesis the fact of contact with the mother’s birth canal was completely excluded.
In the postnatal period, the virus can also be transferred to the baby’s body from medical personnel carrying HPV, through dirty instruments and household items - that is, by contact.
The cause of papillomatosis is the introduction of HPV into epithelial cells. The disease is contagious and can be transmitted both through direct contact with the patient’s skin or mucous membranes, and through household items, clothing, water, and untreated medical instruments.
How is HPV transmitted to a child in utero?
The very high ability of HPV to be transmitted from body to body is explained by its very small size - the virus can penetrate even through 3-5 micron pores in condoms (therefore, alas! - even this method of protection during sexual contact may not protect against the HPV virus).
In addition, there are more than 100 types of HPV - of which some types are more inert regarding infection, others are more aggressive.
It has been established that HPV can “skillfully” camouflage itself in the body and for the time being not manifest itself in laboratory tests - this is the so-called “non-productive type” disease .
The high ability of the virus to be transmitted from one person to another even through touch or other objects, its integration into the body in such a way that it becomes part of its cells, subjugating even the genome, makes HPV simply invulnerable - both for diagnostic methods and for therapy.
We have to talk about quite common cases of the unrecognized presence of HPV in the body of the expectant mother, as well as conservative treatment with positive diagnostic data for the virus, which does not bring the expected results.
Therefore, if a child is born with a skin defect caused specifically by HPV, then there is only one reason for this: intrauterine infection from a mother in whose body the virus is present .
According to the latest data, intrauterine infection of a child is possible with HPV types 6 and 11. There is currently no data on the mechanism of intrauterine transmission of HPV to the fetus; this issue is being studied.
Video on the topic
Amina Pirmanova / article author
It occurs quite often in children and adults. Like any other virus, HPV enters the body unnoticed. It can manifest itself under favorable conditions.
Important! It is necessary to distinguish between Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) and Papilloma formation.
- Papilloma is a benign formation.
- Exophytic condyloma (wart, anogenital wart), associated with HPV.
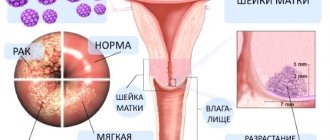
- Precancer and cervical cancer.
If the last two formations can and should be treated, then Papilloma PL is considered a benign formation. This virus causes troubles and problems when it manifests itself on internal organs - kidneys, urinary tract, vagina, mucous membranes. Papilloma, unlike warts (condylomas), has a stalk - thin, wide, and very rarely the stalk is absent.
A child may develop viral PL at the time of birth if the mother has such formations in the vagina or cervix. A child sometimes takes his first breath while walking along paths. At this moment, the virus can enter a small organism that does not yet have protective barriers.
Diagnosis of HPV in a newborn - how to recognize infection?
When it comes to preparing for the birth of a child and preventing HPV, it is extremely important to carry out a specific examination of the woman even during pregnancy planning , so that there is time to undergo treatment if the diagnostic data are positive.
It is better if the woman undergoes examination at least six months before the expected conception . It should be borne in mind that the full course of treatment for HPV takes 4 months - this is exactly the period of development in the body for this virus.
So, a woman can be prescribed the following diagnostic procedures:
- Gynecological examination to detect external signs of infection - warts, genital warts.
- Cytological examination of smears from the vagina and urethra may show abnormal cells that are present in cases of HPV infection.
- Vaginal swab for PCR (Polymerase chain reaction).
- Screening Digene test is a cytological examination of epithelial cells from the cervical canal, taken by scraping. Shows both the degree of concentration of the virus in the body and its oncogenic activity.
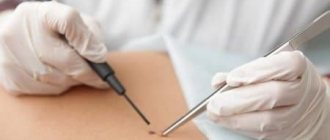
- Histological examination of tissue samples taken by biopsy.
There are frequent cases of false-positive or false-negative diagnostic results for the human papillomavirus, especially in the absence of external symptoms. In these cases, if the presence of HPV is suspected, a complex of examinations using several methods is necessary, as well as repeated examinations after a certain period of time.
How is a child tested for HPV?
Papillomas in the throat of a newborn
If characteristic papilloma-like formations are detected on the skin of a newborn child, the diagnosis can be made immediately, with a visual examination.
To confirm the presence of human papillomavirus in the body of a newborn child and for differential diagnostic purposes, it is sometimes necessary to perform a PCR screening test .
To confirm laryngeal papillomatosis, a diagnostic procedure of direct laryngotracheoscopy .
Preventive measures: basic rules
A very important step in the treatment of papilloma on the child’s ear
is further prevention of the disease.
To do this you must follow the rules:
- the child must have a healthy and nutritious diet;
- frequent walks in the fresh air;
- participate in outdoor games;
- strictly adhere to hygiene rules;
- Before reaching the age of one year, it is better to protect the child from close contacts with a large number of people.
It is very important that the baby feels care, love and happiness in the family.
Removing papillomas under the arms at home: how to safely carry out the procedure
Previous post
What they look like and how to get rid of condyloma in intimate places: modern and traditional methods
Next entry
Treatment of HPV and papillomas in a newborn child - is surgery necessary?
Research on the human papillomavirus began not so long ago, and medicine cannot yet offer systemic conservative therapy that could completely eliminate HPV in the body.
There is simply no specific therapy with a 100% guarantee against HPV today.
But treatment, even with positive test results for HPV, is not always required - more often it is simply necessary to monitor the child and repeat screenings after certain periods. Moreover, medicine knows of numerous cases of self-healing from HPV, especially in childhood and adolescence.
It is necessary to immediately treat papillomas in children in the following cases:
- Papillomas on the skin or mucous membranes grow very quickly and/or change color to red or black.
- Signs of severe pain at the papilloma site.
- Swelling of the tissue around the papilloma, spider veins on the skin.
- Papilloma is located in places where the risk of damage is highest - near the anus or in skin folds, on the child’s face, around the mouth and eyes, as well as formations on the oral mucosa.
- Papilloma has an irregular shape.
- Laryngeal form of papillomatosis, when there is a threat of blocking the airways with papilloma formations and edema.
Modern treatment of human papillomavirus infection in newborns has 3 main directions:
- Increasing the child's immunity.
- Antiviral conservative therapy.
- Elimination of formations on the skin and mucous membranes - papillomas, warts, papilloma clusters.
There is no standard treatment regimen - in each case, treatment is prescribed by a doctor , based on the child’s age, his condition, concomitant pathologies and the degree of HPV progression.
For single papillomas, the child is prescribed conservative therapy, which includes:
- Taking immunomodulators.
- Complex of vitamins.
- Local applications with ointments, lotions.
With an increase in the child’s immune responses, papillomas can be regressed and often disappear completely, without relapses in the future.
Methods for surgical removal of papillomas in a child:
- Cryoapplication with liquid nitrogen is a non-surgical method based on the destruction of pathological areas of the skin. It has many advantages over others, in particular - it is bloodless, is performed quickly and does not leave scars on the skin.
- Excision of a papilloma or cluster with part of the adjacent tissue is performed using the classical method (using a surgical scalpel), or with a pulsed dye laser. Laser excision is preferable as it has good results in terms of faster wound healing, less blood loss and a low likelihood of typical post-operative complications. The scalpel is used only when it is necessary to take material for further histological examination.
- Radiosurgery is the irradiation of pathological tissues with a high dose of ionizing radiation. This method is practically not used for papillomas in newborns, but radioknife is used to treat laryngeal papillomatosis.
- Electrocoagulation is not used in the treatment of papillomas in children.
Does my child need to be vaccinated, and which ones?
Under no circumstances should you try to remove or cauterize papilloma in a newborn on your own! You should also not use traditional methods without the advice of a specialist!
Symptoms
If papillomas appear in the mouth, they cannot always be noticed, since they can grow in places inaccessible to the eye. Appetite may deteriorate, and in rare cases, you may experience a complete refusal to eat.
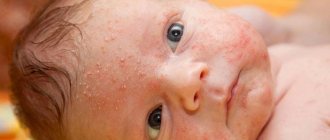
If papilloma appears in a newborn baby, then parents notice excessive tearfulness and often observe a lack of sleep. Older children may complain of scabies in certain areas. Upon examination, you can notice small growths, the color of the skin.
Sometimes flat papillomas appear or have a sharp end, reminiscent of a sharpening thread. Remember - if you see a single papilloma, then almost always a second one appears, and then the next ones.