Skin diseases have accompanied humans for thousands of years. Various types of dermatitis and non-infectious skin diseases significantly complicate a person’s life. Guttate psoriasis is a type of psoriasis that does not damage the nails. A teardrop-shaped rash appears on the torso and limbs and then spreads throughout the body.
The teardrop shape is a complication after suffering from ordinary psoriasis. This form of the disease is called wandering because it is impossible to understand where the scaly papules will appear. The disease must be treated as soon as the first pathological symptoms appear, otherwise it will become chronic.
What is the disease
Guttate psoriasis is one of the types of psoriasis.
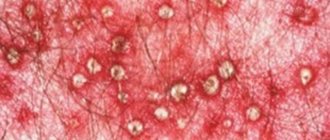
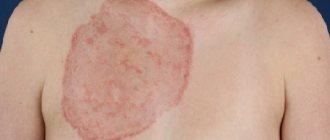
Of all forms, it ranks second and is also non-infectious in nature. It appears on the skin as papules, which can be pinkish, red, and sometimes purple. Lesions appear above the skin level and often spread over large areas.
It is impossible to predict further damage to healthy areas of the skin, and this complicates the treatment process.
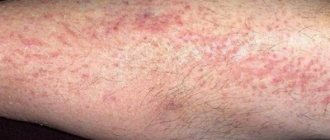
The disease can manifest itself at any age, but more often it affects young people and adolescents (from 16 to 27 years old). With guttate psoriasis, the characteristic manifestations are a rash of a round shape or in the form of a drop, which is why it is also called droplet psoriasis.
Moreover, large plaques are not observed; instead, small rashes appear in the form of dry red or purple spots. The lesion covers large areas, most often appearing on the back, shoulders and hips.
Guttate psoriasis (another name is “droplet”) is a specific form of scaly psoriasis, the peculiarity of which is the sudden appearance of scaly and itchy rashes of a round shape throughout the body, except for:
- faces;
- nail plates;
- soles;
- palms.
Guttate type psoriasis, like others, is of an autoimmune nature. The disease is caused by inadequate functioning of the immune system, during which it attacks skin cells, which causes them to die prematurely and are too quickly renewed by the same immature, defective cells.
Symptoms of guttate psoriasis appear in people at different ages, even in infancy, and are often very acute. Multiple small papules quickly appear in the form of droplets of pink, scarlet and burgundy color. Gradually they unite and form large plaques with a grayish stripe along the edges. When you peel off an element of the rash, you can detect the “psoriatic triad”:
- On top there is a white scale (peeling), which is easily removed.
- Underneath there is a damp, glossy surface. It is called terminal film.
- Under the glossy layer is a wound surface with protruding droplets of blood. This is "bloody dew".
The disappearance of the rash cannot be taken as recovery. Psoriasis is incurable and can recur at any time. This is especially likely if the sick person neglects the rules of prevention. Exacerbations of guttate psoriasis are seasonal - observed mainly in spring and autumn.
Drip psoriasis in newborns has its own peculiarity. It forms small inflamed lesions, which are often localized in the genital area. Because of this, psoriatic rashes are confused with diaper dermatitis.
What is the prevention?
To prevent various forms of psoriasis, the following measures are used:
- Dry skin is lubricated with moisturizing creams, this is especially important after water procedures in order to normalize its hydrolipidic membrane;
- Treat your skin with care, avoid wounds, cuts, scratches;
- Nutrition. Eliminate or reduce fried, fatty, salty foods in your diet. Consume complete proteins contained in lean meat, fish, legumes, fermented milk products with a small percentage of fat content: kefir, cottage cheese, milk, whey. Eat more vegetables, fruits, berries;
- Increase the body's immunity: do exercises, gymnastics, harden;
- Include fish and fish oils in your diet, which contain omega-3 fatty acids. They help reduce inflammatory processes in the body;
- Quitting bad habits: smoking, alcohol;
- Taking baths using various herbs;
- Consuming a large amount of liquid (at least 1.5-2 liters per day);
- Avoiding stressful situations. If something causes discomfort, then try to get rid of it or change the situation in a more favorable direction. In severe cases, seek help from a psychotherapist.
At the first signs and symptoms of guttate psoriasis described above, you should go to the doctor and consult for further diagnosis and prescribing the correct timely treatment. It is important to prevent the disease from becoming more severe and to begin preventing complications.
About the causes
Dermatologists still argue about the etiology of drip psoriasis. Most believe that the main cause of the disease is past infectious diseases, which include viral (ARVI), streptococcal and staphylococcal infections:
- otitis;
- tonsillitis (tonsillitis);
- pharyngitis.
Often, the first symptoms of a chronic epidermal disease appear at the age of 14-16 years, 15-20 days after a bacterial or viral infection. The theory described above is supported by the fact that scrapings from a psoriasis rash always reveal a bacterial pathogen. Despite this, it is impossible to become infected with guttate psoriasis from another person.
Infections lead to the first exacerbation of the disease or to the transformation into a drop-shaped form of other types of psoriasis. Additional factors that increase the likelihood of developing guttate psoriasis:
- stress;
- physical stress;
- metabolic disease;
- endocrine pathologies;
- genetic predisposition (presence of psoriasis in parents);
- allergies;
- chronic skin injuries;
- bad habits and unhealthy diet.
The causes of the teardrop form of psoriasis are the reason for much discussion among dermatologists. They agree only that the impetus for the activation of the disease comes from a recent illness of viral or bacterial etiology (most often influenza, otitis media or tonsillitis).
This is confirmed by the fact of mandatory detection of infectious agents in cultures of a smear taken from a patient during the progressive stage of drip psoriasis.
Guttate psoriasis is a type of psoriasis that appears as red, scaly papules that look like small sores (blobs).
They are located in such a way that it is impossible to predict where new inflammation will appear.
Guttate psoriasis is a chronic disease, so a complete cure is impossible. An exacerbation can only be replaced by a temporary period of remission.
As a rule, the disease worsens in the autumn-winter period.
Stages of the disease:
- Mild psoriasis. This stage is expressed by single papules. The skin is affected by rashes in less than 3%.
- Moderate psoriasis. At this stage, skin damage can be up to 10%.
- Severe form. Skin damage at this stage is more than 10%. Treatment of this form is complex, and therapy is selected individually.
At the first stage, single, small-sized inflammations appear. And as the disease progresses, the plaques increase.
One of the main reasons is a hereditary predisposition to the disease. However, there are other prerequisites:
- Disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system.
- Psychological breakdowns.
- Presence of infectious diseases: streptococcal and staphylococcal infections.
- Metabolic disease.
- Viral infections.
- Weakening of the immune system.
- Cold intolerance.
Any of the above reasons can trigger the appearance of guttate psoriasis.
Complication
Untimely treatment of guttate psoriasis can cause the development of serious pathological complications for a person:
- hypertension;
- diabetes mellitus;
- kidney diseases;
- atherosclerosis;
- heart and vascular diseases;
- hepatitis A;
- skin cancer
Drip psoriasis often causes psychological discomfort in patients. The patient avoids communication with people, becomes irritable and aggressive. Over time, alienation and loneliness lead to nervous breakdowns, stress, and depression.
Complex therapy for guttate psoriasis contributes to a noticeable improvement in the condition of the skin. Correctly selected treatment guarantees long-term remission.
Severity
There are 3 forms of the disease:
- Soft, which is characterized by a small area of skin damage (no more than 3%). The limbs are covered with single pinkish papules, which cause itching and burning. Suppressing the symptoms of the mild form of the disease does not cause difficulties.
- Medium – characterized by a large affected area (up to 10% of the skin). In this case, intensive manifestation and significant growth of plaques occurs. Moderate guttate psoriasis is more difficult to treat than mild forms of the disease.
- Severe - the lesion covers 20% of the total area of the skin. The disease is represented by lesions in the form of violet-lilac plaques, reaching a diameter of several tens of millimeters.
There are no visible reasons for the formation of psoriatic elements in any type of disease.
Depending on the severity of the pathology, there are mild (less than 3% of the skin is affected), moderate (3 to 10%) and severe (more than 10%) forms. Advanced forms are less amenable to treatment, and in such situations, a dermatologist decides how to treat guttate psoriasis based on the general health of the patient.
The severity of the manifestations of the pathology is determined by the severity of inflammation of the skin and varies from single small elements of rashes to huge flaky spots covering almost the entire body.
Doctors distinguish three degrees of guttate psoriasis according to severity:
- Mild – a maximum of 1-3% of the body is affected, the rash is sporadic, minimally disturbing and disappears quickly. Mild psoriasis can be confused with irritation or hives.
- Moderate – 5-10% of the body is affected, the rash is multiple, and confluence of papules is noted.
- Heavy. A severe course of the disease can be called a condition in which more than 15% of the skin is affected. Rashes all over the body merge into huge skin defects, cause severe itching and burning, and can transform into more severe forms of the disease.
In addition to degrees of severity, psoriasis has stages of progression. There are only three stages of the disease:
- Progression stage - elements of the rash appear, the affected areas itch, and when the skin is damaged, new rashes form.
- Stabilization - the rash calms down, new elements do not appear, all symptoms subside.
- Resolution stage - skin defects actively heal and disappear without a trace. Pigmented spots may remain in their place, especially in children, but they also pass quickly.
Then a full (absolutely no symptoms) remission occurs, when psoriasis goes into “sleep mode”. Remission can last for months or even years.
The stage is determined depending on how severely the skin is affected. Experts distinguish three stages in the development of the disease:
- The initial stage is known as “mild psoriasis”. It is characterized by a single rash and papules in different places on the body.
- The middle stage is known as “moderate psoriasis”. It is determined by the presence of a rash and partial fusion of papules, most of the skin remains free.
- The third stage is characterized by a severe form of the disease, the presence of a large number of fused papules, and serious skin damage.
During the progression period, itching, new spots on the skin, as well as papules around fresh lesions appear. During the stabilization period, new spots do not appear, and the itching gradually decreases. At the stage of resolution, practically no traces of psoriasis remain.
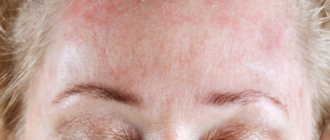
Psoriasis on the scalp (scalp)
This form of the disease occurs in almost half of patients with psoriasis. The severity of the clinical picture can also be very diverse: from thin whitish crusts that turn into thin small scales and flaking in the form of dandruff, to coarse and thick plaques that form equally large scales. Against this background, the skin is red, especially after exfoliating a large number of scales at the same time. This form occurs both in isolation and in combination with other types of psoriasis.
Symptoms of psoriasis on the head
Symptoms of the process often extend beyond hair growth, spreading to the skin of the forehead, back of the head and ears. Requires differential diagnosis with seborrheic dermatitis, in which the crusts have a yellowish tint, in contrast to the whitish appearance of psoriasis. There are no particular difficulties in making the correct diagnosis.
Causes of psoriasis on the head
The causes of psoriatic inflammation of the skin in the scalp area are associated with impaired maturation of the surface layers of the epidermis and the release of keratin. The following factors can lead to this:
- Microtraumas and irritation of the scalp;
- Incorrectly selected hair care cosmetics or changing them frequently;
- Dry scalp;
- Severe stress effects;
- Changes in climatic conditions;
- Drug influences;
- Violation of dietary recommendations regarding psoriasis;
- Dishormonal and metabolic disorders in the body.
How to treat psoriasis on the head?
If the process is represented only by a local lesion on the head, then local effects on the inflamed areas will be quite sufficient. The following methods work well for this:
- Cryotherapy is the effect of ultra-low temperatures on inflamed areas. In this case, simultaneous destruction of inflamed and defective keratinocytes occurs. After a few days they come off in a single layer;
- Ultraviolet irradiation. Conventional quartz lamps or ultraviolet combs are used. The shorter the hair length, the better the effect;
- Shampoos and soaps. They are an auxiliary method and complement the basic techniques. The most common: kertiol, tana, nizoral, friderm with tar. The only soap that is indicated for psoriasis is tar soap.
- Ointments and creams. Salicylic ointment in a 2% concentration well moisturizes dry psoriatic plaques and helps clear them of scales. Hormonal ointments based on glucocorticoids have proven themselves quite well: prednisolone, sinaflan, betamethasone, trimistin, triderm, flucinar. It is advisable to apply them to inflamed skin after removing the crusts.
- Traditional medicine methods - the use of various recipes based on elecampane, egg yolks, onions, and medicinal herbs.
Features of pathology in children
Children are susceptible to guttate psoriasis due to sudden climate change, frequent stress, and obesity can be the cause. It is important to give children more fruits and fresh vegetables; special vitamin complexes that support the immune system and strengthen it are also useful.
If you are diagnosed with guttate psoriasis, it is not recommended to carry out treatment on your own; be sure to consult a specialist and undergo treatment under constant supervision. Only a professional doctor will prescribe medications, a set of measures that will cure guttate psoriasis in children and adults, alleviate the condition, prolong remission, and help in case of complications.
The frequent development of psoriasis in children is explained by frequent infectious diseases (influenza, measles, chickenpox, tonsillitis and others). The teardrop form of psoriasis in a child manifests itself on the torso, upper and lower extremities, as well as on the head under the hairline.
There is severe itching, which, judging by the reviews of parents, noticeably worsens the quality of sleep during an exacerbation. Plaques can persist for a long time, periods of remission can last up to ten years.
Guttate psoriasis is diagnosed in children no less often than in adults. Children and pregnant women should not use hormonal medications for treatment. Psoriatic rashes can be treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory creams, such as Anthralin and Akrustal.
Additionally, ointments with disinfecting and wound-healing effects are used: salicylic, naphthalan, sulfuric. During pregnancy, any treatment must be agreed with your doctor.
Most often, the disease occurs in adolescents, less often in young children. The signs of psoriasis in children are the same as in adults. The only difference may be the area of the affected areas. In childhood, the disease can be caused by:
- streptococcal perianal dermatitis;
- superficial bacterial infections of the anus or perianal area.
Recommendations for treatment and nutrition
To effectively treat psoriasis at home, you must follow the recommendations:
- It is imperative to visit a doctor and adhere to his recommendations, no matter how experienced the patient is in treatment and what knowledge he has in this area;
- When treating children, the most important thing is to exclude the provoking factor ;
- Treatment should take place intermittently and on schedule;
- Carefully remove peeled crusts from the surface of the skin and moisturize with cream.
Diet plays an important role in the treatment of psoriasis.
You should exclude the following from your diet:
- Alcoholic drinks;
- Soda;
- Products with caffeine;
- Red fruits and vegetables;
- Citrus;
- Chemical food additives;
- Chocolate.
During periods of exacerbation of psoriasis, you should follow a strict hypoallergenic menu.
Signs and symptoms of guttate psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis and its symptoms have many similarities with other forms of the disease. The patient may report the following complaints:
- The appearance of scaly rashes;
- Intense itching (often characterized by an acute onset of the process);
- The growth of pathological elements on the skin.
An important sign of this form is a rash. The spots differ from the usual plaques of psoriasis, are characterized by smaller sizes and often acquire a dotted character.
Note! A more severe course of the disease, as a rule, occurs in the winter. In summer, symptoms may subside in a shorter period of time.
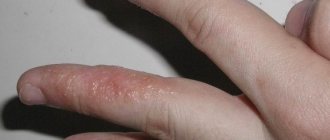
Psoriasis on hands
Symptoms of psoriasis on the hands
Very often, psoriatic rashes spread to the skin of the hands. The back surfaces and skin between the fingers are most often affected. Inflammatory rashes on the palms are less common. The appearance of psoriatic plaques on the hands does not differ from processes in other localizations. On the palmar surface they take on the appearance of rough red calluses with large scales.
Causes of psoriasis on the hands
The reasons for the spread of psoriasis to the hands are mainly associated with violation of the rules of hand care and constant microtrauma of the skin in this area. This is especially true for people who already have psoriasis. Hand contact with toxic chemical compounds is important.
How to treat psoriasis on the hands?
Since isolated psoriatic lesions of the hands are extremely rare, treatment should be local and general:
- Hand skin care using moisturizing and softening ointments (based on Vaseline, salicylic ointment);
- Refusal to keep your hands in a damp environment and wear rubber gloves for a long time;
- Treatment of inflamed skin with hormonal ointments (Triderm, Flucinar, Trimistin, Kremgen);
- Antihistamines: loratadine, Erius, Claritin;
- Systemic administration of glucocorticoids and cytostatics;
- Physiotherapy methods in combination with photochemotherapy.
Symptoms
The age of people who develop the guttate type of the disease ranges from 17 to 30 years.
The randomness and inability to determine the location of the rash make it difficult to carry out treatment procedures.
The first symptoms of guttate psoriasis most often appear in a patient who has recently (two to three weeks ago) suffered from an illness of infectious etiology: scarlet fever, tonsillitis or influenza.
The surface of his torso, arms and legs suddenly becomes covered with many pale-colored papules (the color of the rash can vary over a wide range - from light pink to soft lilac).
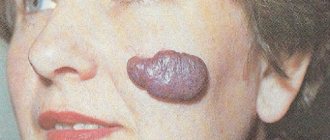
Psoriatic rashes are extremely rare on the face.
The size of the papules, whose shape resembles droplets of water, is equally variable: they can be small dots or nodules with a diameter of one to ten mm. In some patients, along with papules, large (up to ten cm in diameter) spots may be observed.
Being single at first, psoriatic plaques steadily increase in size, and sometimes, merging with each other, they occupy new islands of skin.
In the development of psoriatic rashes there are:
- A progression stage characterized by intense itching and the appearance of fresh rashes. Patients experience Koebner's symptom, which consists of the appearance of new rash elements at the site of skin damage.
- The stabilization stage, accompanied by a decrease or cessation of itching and the absence of new rashes. Old psoriatic plaques begin to turn pale and flatten. This process is accompanied by the formation of a slightly colored skin rim around them.
- The resolution stage, during which the lesions gradually disappear, leaving behind either depigmented or hyperpigmented areas.
Unfortunately, the disappearance of the rash does not mean the patient’s recovery. Guttate psoriasis is a chronic disease, the clinical course of which is characterized by alternating periods of remission and seasonal exacerbation (in some patients, exacerbation occurs in the spring, in others in late autumn).
Methods of modern therapy are not yet able to ensure complete recovery of the sick. However, this disease, which is not infectious, is completely safe for others.
In most cases, guttate psoriasis appears in teenagers. The disease can be triggered by a previous infectious disease, for example, otitis media, tonsillitis. The first symptoms appear 3-5 days after recovery from an infectious disease.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The causative agents of the teardrop form of psoriasis are streptococci. The skin disease begins to develop 2-3 weeks after infection with bacteria. These microorganisms often infect humans during adolescence. Causes of the disease:
- hormonal disorders;
- genetic predisposition;
- metabolic problems;
- constant psychological tension and stress;
- alcoholism and smoking;
- unbalanced diet.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
Guttate psoriasis is diagnosed by identifying the patient’s characteristic complaints: the presence of a rash, itching, peeling.
A blood test reveals nonspecific signs of the inflammatory process.
A biopsy of the affected areas of the skin reveals a thickened outer layer of immature cells, immune elementary units (T-lymphocytes).
A simple examination and questioning may be sufficient for an experienced doctor to make a correct diagnosis. The doctor learns about the history of the disease, clarifies all medications taken, and examines the skin.
Usually this information is enough to establish or exclude a diagnosis. If additional information is needed, a general blood test and a throat swab may be performed to check for the presence of streptococcus.
In doubtful cases, a skin biopsy is performed.
Interesting to know! The stains may disappear on their own within 2-3 weeks. However, specific therapy may be required to relieve symptoms and prevent underlying infection.
How to treat guttate psoriasis? There are several ways to combat dry and flaky skin, which is accompanied by swelling and itching:
- Corticosteroid-based cream reduces the inflammatory response and reduces itching;
- Special shampoos nourish and moisturize the scalp;
- Coal tar lotions are effective in combating irritated skin;
- Regular moisturizing creams help;
- Prescription vitamin D and vitamin A supplements may be recommended.
How to treat guttate psoriasis in more severe cases (when more than 10% of the skin is affected)? In such situations, oral medications may be prescribed:
- Corticosteroids.
- Methotrexate.
- Cyclosporine.
Phototherapy is another effective treatment option. For this purpose, special devices for ultraviolet irradiation are used.
Note! Direct sunlight helps effectively combat rashes. Avoid sunbathing; it is recommended to stay in the sun for no more than 20-30 minutes a day.
For diagnosis and treatment of guttate psoriasis, you should consult a dermatologist. The doctor will examine the elements of the rash, take a medical history, and order tests, which will include:
- general standard blood test - the indicators are almost the same as normal, but in severe and moderate cases it shows an increase in ESR, as well as eosinophils and leukocytes;
- bacterial culture - shows the presence of pathogenic bacteria;
- histological analysis of the epidermis in the affected area shows the immaturity of skin cells.
Diagnostics is carried out in three stages:
- anamnesis analysis;
- general examination of the person;
- clinical and laboratory studies.
The patient is examined by a dermatologist. In most cases, an external examination is sufficient to identify the disease. Most often it is confused with fungal diseases, so a skin analysis is done.
Analyzes
Without tests, the doctor will not be able to provide the correct treatment.
Instrumental diagnostics
A dermatoscope is most often used in the diagnostic process. It allows you to display skin pictures on the big screen. Doctors will be able to examine and study the condition of the skin in more detail.
Who to contact
Guttate psoriasis is a skin disease that is diagnosed by a dermatologist. But depending on the level of severity, other specialists also participate in treatment. A referral to a dermatologist is issued by a therapist, who, due to his absence, can prescribe treatment. Complex forms are characterized by joint damage. In this case, therapy should take place with the participation of a rheumatologist.
Folk remedies for drip psoriasis
Medicines prepared at home using natural ingredients are part of the treatment regimen for skin lesions. Psoriasis is distinguished by the presence of an allergic component. To avoid complications, it is important to coordinate the recipes of traditional healers with your doctor. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable. To eliminate symptoms it is recommended:
- take baths with oak bark, string, chamomile flowers - relieve itching and inflammation;
- drink an infusion of valerian root for calm;
- Apply lotions with Kalanchoe and aloe juice to speed up healing.
In case of drop-shaped skin lesions, it is useful to take decoctions of medicinal herbs orally to relieve inflammation and increase immunity. The following remedies eliminate the symptoms of the disease:
- ointments, creams based on tar, grease to restore the epidermis;
- sea buckthorn oil - take orally, on an empty stomach, a teaspoon and lubricate the affected areas of the skin;
- tea with linden flowers to reduce temperature and eliminate fever.
Cream with propolis
The beekeeping product, which has an anti-inflammatory and bactericidal effect, is used in the recipes of traditional healers for the treatment of numerous diseases. A cream containing active ingredients for drop-shaped psoriasis is applied twice a day until the symptoms disappear. The use of a composition with propolis is due to its effect on the skin:
- wound healing;
- regenerating;
- immunomodulatory.
All components of the healing cream for psoriasis are thoroughly mixed and kept in a water bath until a homogeneous structure is formed. The basis of the drug is butter with the addition of bee products. The medicinal composition includes the following components:
- butter – 80 g;
- propolis – 50 g;
- wax – 10 g;
- royal jelly – 10 g;
- pollen – 10 g.
Ointment with grease and birch tar
Traditional healers recommend preparing a medicinal ointment at home that eliminates the symptoms of psoriasis. The components in its composition improve the condition of the skin and speed up recovery. The components of the recipe have the following medicinal properties:
- grease – eliminates peeling, burning, normalizes the process of tissue restoration, reduces the affected area;
- birch tar – activates cell regeneration, improves blood circulation, stops itching.
For teardrop-type psoriasis, apply a thin layer of prepared ointment to the rash and leave without a bandage for 2 hours. The composition is washed off with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, and you can take a bath. The procedure is performed every day until the symptoms disappear. To prepare the ointment, the components are mixed in a ceramic container and left in a dark place for three days. The composition includes ingredients:
- grease – 150 g;
- birch tar – 50 g;
- children's cream – 10 g;
- sulfur powder – 10 g.
Bath with string, chamomile and celandine
Medicinal plants, due to their healing properties, are used for internal and external use. Baths containing herbs and flowers have a healing effect on the skin. For guttate psoriasis, they produce the following effect:
- chamomile flowers - soothe, relieve itching, soften the epidermis, heal;
- celandine – eliminates inflammation, pain;
- series - speeds up metabolic processes, eliminates redness and rashes.
Baths containing these medicinal plants must be taken 3 times a week, for a course of 15–20 procedures. The duration of the session is no more than 15 minutes. To prepare the composition you will need:
- Take 50 g of each plant.
- Add 0.5 liters of boiling water.
- Leave for 10 minutes.
- Strain.
- Add to a bath with a water temperature of 40 degrees.
Herbal mixture for oral administration
Regular use of a decoction of medicinal plants will help cope with the manifestations of skin rashes. It is taken as a monthly course, and after 10 days the treatment is repeated. The dosage of the healing composition is 100 ml 30 minutes before each meal. To prepare the herbal medicine, take a spoonful of the mixture, pour a glass of boiling water, and leave for 2 hours. The medicinal composition includes the following herbs in equal parts:
- violet;
- sage;
- celandine;
- series;
- calendula flowers, chamomile.
Bran bath
Water treatment procedures using bran for teardrop-shaped psoriasis help eliminate inflammatory processes on the skin. Regular use softens scales, reduces the rate of formation of papules, and eliminates itching. To make a bath, you need:
- Place a glass of wheat bran in a cotton bag.
- Add 50 grams of grated tar soap.
- When taking water into the bath, pass it through this composition.
- Perform the procedure every other day for 20 minutes.
- After the session, do not wipe yourself, let the skin dry.
- The course of treatment is 20 baths.
Treatment
Guttate psoriasis is difficult to treat; it requires a comprehensive approach, using medications simultaneously with phototherapy, plasmapheresis, and immunomodulators. The treatment process will be long, especially with large lesions of the skin.
Using ointments and lotions alone will be ineffective, because, according to scientists, the problem is not just in the skin, with psoriasis there is a metabolic disorder, and serious pathological changes in the immune system occur.
Therefore, combining drugs with physiotherapy and folk remedies will bring the greatest effect. Of course, there is no talk of a complete cure, but to alleviate the condition, prolong remission, reduce symptoms - this is possible if certain conditions are met.
External preparations
External products that prevent excessive division of epidermal cells, soften the skin, and relieve itching are popular. The drugs used include:
- hormonal agents - reduce inflammation, inhibit the reactivity of the immune system;
- vitamin D - most effective in combination with ultraviolet irradiation;
- tar - for the treatment of lesions located in the scalp;
- activated zinc - helps eliminate skin itching and also helps reduce redness;
- immunomodulators - increase hemoglobin levels, strengthen the body’s resistance to infection.
In the acute course of the droplet form of psoriasis, plasmapheresis may be prescribed - complete blood purification.
Different types of therapy
They are used in a system with drugs; several types are used:
- Hirudotherapy - the use of leeches helps improve blood circulation and normalize immune reactions.
- Ichthyotherapy - the doctor fish cleanses the skin of rashes; the entire surface layer of plaques is eaten by fish when the infected area is immersed in water.
- Cryotherapy - placing the patient in a chamber with a temperature of -1300 C, reduces itching, relieves swelling and inflammation.
- PUVA therapy - a drug is administered that accumulates the ability to regenerate, and the affected areas are irradiated with ultraviolet light.
External means
The patient is prescribed hormonal and non-hormonal ointments and lotions. Ointments are prescribed in combination with injections and medications. Treatment of guttate psoriasis is a long process; ointments alone are not enough; they will not cure it completely, but will help alleviate the condition and reduce symptoms.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies based on herbs are welcome, because such ointments and infusions can be used for a long time, which is useful for chronic psoriasis, unlike hormonal drugs and antibiotics, the course of which is limited for treatment.
Therapy for guttate psoriasis is complex and consists of:
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- diets.
You can try folk remedies. You should also definitely fight the cause of exacerbations of lichen planus, if it is a chronic ENT infection (for example, tonsillitis) or another. Means to combat the primary disease are selected individually.
Medication
Treatment of guttate psoriasis with drugs should begin immediately at the first manifestations. In severe cases of the disease, hormonal anti-inflammatory ointments are used:
- Hydrocortisone;
- Triderm cream based on betamethasone;
- Flumethasone;
- Dermovate.
Drug therapy includes drugs with calcitriol for external use: Daivonex, Forcal. To generally strengthen the body and immunity, in particular, retinoid vitamins are used, intended for oral administration: Tigason or Neotigason.
Due to the fact that, at the current level of development of medicine, complete healing of patients is not yet possible, treatment of guttate psoriasis consists of achieving a stable remission, characterized by the absence of external manifestations of the disease.
google2
The complex of therapeutic measures includes:
- glucocorticosteroids that reduce inflammation;
- antihistamines that soften the effect of mediators of the inflammatory process;
- vitamins D, A and E;
- cytostatic drugs that slow down the process of cell division;
- to eliminate itching and relieve pain, the surface of the skin is treated with ointments containing steroids and salicylic acid;
- the patient is regularly given a subcutaneous injection of monoclonal antibodies or administered through an IV. The effects of these drugs help neutralize the body's autoimmune reactions.
To improve the effectiveness of drug therapy, patients undergo procedures:
- Plasmophoresis is a blood purification technique that allows you to remove ballast substances and toxic immune complexes from it.
- Ultraviolet irradiation of psoriatic plaques. In some cases, this technique is used as an independent procedure, and sometimes it becomes part of a PUVA therapy session. During these sessions, natural substances – psoralens – are introduced into the patient’s body, which are activated only after irradiation with ultraviolet light. As a result of the reaction with epidermal cells, excess DNA production is suppressed.
- Local cryotherapy using liquid nitrogen.
It is recommended to treat the teardrop form of psoriasis with folk remedies:
- It is necessary to take herbal baths. Celandine, chamomile, and string are suitable for this.
- Drink herbal teas that have a calming, anti-inflammatory effect. Herbs: linden blossom, chamomile, mint, lavender, etc.
- Sea buckthorn oil is very useful. It should be taken orally (1 tsp on an empty stomach) and smeared on the affected skin.
- Areas of skin affected by plaques should be lubricated with celandine tincture, preferably red wine.
Monastic tea has an excellent effect on guttate psoriasis, as its herbal composition promotes recovery and relieves inflammation in the body. It relieves itching, is an anti-allergenic agent, restores normal blood circulation, etc.
Treatment of drip psoriasis is conditional, since the disease is chronic. The goal of therapy is to achieve a state of remission in which symptoms are minimal. To cure the disease, general and local effects are used. Proper treatment can control symptoms and also prevent triggers.
Medicines
The disease can be treated at home. In case of a complex form, it is necessary to stay in the hospital. The most popular medications used for treatment are:
- Cortisone - available in the form of cream and ointment. Requires targeted application to affected areas of the skin, relieves itching and inflammation.
- Lotions (Belosalik, Elokom, Diprosalik, Skin-Cap, Daivonex, Calamine, Fufan, Lycan).
- Tar shampoos to combat dandruff, flaky skin and papules (Friderm Tar, Tar 911, Tana, Sebozol, Dandruff, Nizoral, Sulsena, Vichy, Skin Cap).
- Creams containing vitamins A and D, as well as medicinal creams (Triderm, Dermovate, Travocort, Elokom, Lokoid Lipokerm).
- Products for moisturizing the skin (baby creams are suitable).
There are no tablets aimed solely at eliminating guttate psoriasis. The doctor prescribes immunomodulators, vitamins in capsules, and the drug Daivobet.
Vitamins
Vitamin D3 is the most effective topical therapy. It stops inflammation and inhibits the development of the disease. To strengthen the immune system, it is recommended to take vitamin C. Vitamins A and E restore the epidermis and accelerate the growth of new cells. Vitamin B is essential for the creation of new skin cells. The necessary vitamins are determined after tests and prescribed by the attending physician.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is used in cases where home treatment with standard treatment does not produce the desired effect. Physiotherapeutic procedures are based on treating the skin with soft ultraviolet light.
Complex physiotherapy is carried out using:
- photochemotherapy;
- laser therapy;
- electrosleep;
- magnetic therapy;
- plasmaphoresis - in particularly difficult cases.
Folk remedies have varying levels of effectiveness and must be approved by a doctor.
It is necessary to treat guttate psoriasis comprehensively, using all possible methods.
These include:
- use of external preparations (ointments, sprays, gels);
- prescription of immunomodulators;
- plasmapheresis;
- Ural Federal District;
- antihistamines.
Due to the damage to a large area of skin, treatment of the disease requires a long time and it is almost impossible to cope with it using external means alone.
- First of all, the acute symptoms of psoriasis are neutralized with the help of a diet that excludes fatty, spicy, salty, smoked and sweet foods from the diet. Nutrition, especially for children, should be balanced, with a sufficient amount of proteins, vitamins and microelements, which should be obtained from lean fish and lean meat, fermented milk products and vegetable oils;
- To relieve itching and swelling, the use of antihistamines (Diazolin, Claritin, Erius, etc.) is recommended. If there is a confirmed connection between the development of guttate psoriasis and staphylococci, the patient is given a course of vaccination. To compensate for vitamin deficiency, vitamins of group E, D, P, C, A, and B are prescribed. To prevent the proliferation of superficial epidermal cells, it is recommended to take retinoids (Neotigazon, etc.);
- a mild form of guttate psoriasis can be treated with external medications (Bepanten, Zinocap, etc.). In case of a progressive form, plasmapheresis and the prescription of external glucocorticosteroids (Elocom, Diprosalik, Advantan, Triderm, etc.) are required;
- in case of regressive course of guttate psoriasis, creams and ointments (Psorkutan and Daivonex) containing vitamin D3 (calcitriol) are additionally prescribed, which prevents the growth of skin particles.
In addition, physical therapy is recommended, which involves exposing the affected areas to long-wave ultraviolet rays. Before this procedure, a preparatory stage (PUVA therapy) is carried out with the prescription of drug treatment that increases skin photosensitivity.
Treatment of guttate psoriasis is quite effective using traditional medicine recipes.
OINTMENTS. Honey – 10 gr. fresh Kalanchoe juice – 10 ml. eucalyptus oil – 30 gr. All ingredients are mixed and infused for 3 days, after which it should be applied to areas affected by psoriasis.
When treating guttate psoriasis, a systematic approach is used, which includes step-by-step treatment.
First of all, the patient is recommended to try local treatment - ointments, gels, creams, folk recipes. Then (if there is no effect) phototherapy is prescribed. If the first two methods do not help, potent drugs are prescribed - topical steroids (hormones), monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of psoriasis and psychotropic drugs.
The first two methods are often combined for better results and lasting remission.
Let's look at each method in more detail.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods of treatment have a great advantage - their natural composition and therefore the absence of side effects. You can choose several treatments for yourself from the full review: “53 folk recipes for the treatment of psoriasis.”
Let's look at recipes that are convenient for treating guttate psoriasis.
The course of healing the body will be long and labor-intensive. First, the doctor finds out the cause of the rash. Only when it is established can you receive quality treatment.
The first step is to eliminate the cause that triggered the onset of the disease, and then prescribe a course of health procedures that will help cleanse the skin of the “rash” and restore the body.
Guttate psoriasis requires an integrated approach to treatment. The patient is prescribed a strict diet to normalize the metabolism in the body.
The main directions of treatment are PUVA therapy and plasmapheresis.
PUVA therapy is a procedure in which the affected areas of the body are exposed to ultraviolet radiation together with the use of topical medications. Irradiation is carried out only under the strict supervision of the attending physician.
Plasmapheresis is the purification of blood from harmful substances. Completing this procedure helps reduce relapses and effectively relieves exacerbation of the disease. This method is based on the use of immunomodulator drugs. They prevent the cell from dividing, which causes the affected areas of the skin to shrink.
The following methods of treatment for psoriasis are also used:
- Physiotherapy treatment.
- Supporting the body by taking vitamin complexes.
- Prescribing medications to support the immune system.
- The use of drugs with monoclonal antibodies.
There are many ointments and gels for external use that are prescribed when a person has guttate psoriasis. Treatment is carried out in combination with a diet; further adherence to proper nutrition is necessary.
Recently, the Chinese ointment “King of Skin” has become widespread in use. It is actively advertised and discussed by both patients and doctors.
The ointment contains clobetasol propionate and ketoconazole, sandalwood oil, neem tree leaves, tulsi (holy basil), kapuru kachari, turmeric, licorice, talc.
“Skin King” ointment is available in small jars and is intended for the treatment of psoriasis of any type.
The drug works in this way:
- Reduces itching.
- Reduces skin dryness.
- Fights inflammation and prevents the recurrence of inflammation.
- Eliminates peeling and evens out the skin.
However, it must be remembered that any treatment should begin after consultation and under the supervision of a doctor.
Seborrheic psoriasis
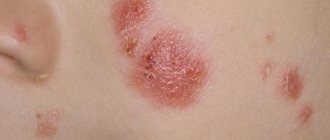
Sometimes the clinical course of psoriasis resembles seborrheic dermatitis. In this case, it is called seborrheic psoriasis. Symptoms of the disease look like this:
- The scalp or behind-the-ear areas are affected;
- Inflamed plaques look like whitish crusts against the background of reddened skin;
- Rubbing plaques leads to the formation of a large number of small scales;
- After removing the crusts and scales, hyperemic, thin, shiny skin remains;
These symptoms are the main diagnostic differences between ordinary seborrhea and seborrheic psoriasis.
Psoriasis - how to get rid of a deadly autoimmune disease?
Judging by the fact that you are reading these lines now, victory in the fight against psoriasis is not yet on your side...
Have you already thought about radical treatment methods? This is understandable, because psoriasis can progress, resulting in the rash covering 70-80% of the body surface. Which leads to a chronic form.
Red blistering blisters on the skin, itching, cracked heels, peeling skin... All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand. But perhaps it would be more correct to treat not the effect, but the cause? We found an interesting interview with a dermatologist at the Russian Dermatology Center. Read the interview
Systemic therapy
If more than 10% of the body surface is involved in the process, and the symptoms are severe, then we are talking about a systemic effect on the body. Systemic medications are used.
In practice, the following classical groups of drugs are used to combat guttate psoriasis:
- Cytostatics (Methotrexate). Medicines are folic acid antagonists. They block cell division and reduce the number of teardrop plaques. They have many side effects and contraindications.
- Immunosuppressants (cyclosporine Sandimmune). They block the autoimmune factor in the development of pathology. They combine well with antibiotics, taking into account the bacterial effect on the development of guttate psoriasis.
- Systemic retinoids (Tigazon). An effective group of medications that regulate the processes of growth, maturation and rejection of keratinocytes. They are one of the basic means for combating psoriasis.
In parallel, symptomatic medications are used to stabilize the patient's condition. Antihistamines - to combat itching, sedatives - to normalize the emotional background, vitamins and minerals - to strengthen the body.