This article was checked and edited by pediatrician Olga Aleksandrovna Shushlebina.
Pigment spots, moles or nevi in children form in utero due to the accumulation of melanocyte cells in the skin. However, they are so insignificant in size that they are rarely detected by eye in newborns. Characteristic marks can be found on the baby’s body a few weeks after birth or even after 1 year. A new “wave” of mole appearance often occurs at 5-6 years of age and during adolescence.
Nevi come in various shapes, sizes, shades and most often do not pose a danger to children. But in some cases, such pigmented neoplasms can become malignant (degenerate into melanoma), then they should be removed immediately. Fortunately, this happens very rarely in children.
The doctor will determine whether the nevus is dangerous or not, and he will also recommend the method of treatment and the advisability of surgical intervention. Even if removal is not indicated, regular medical monitoring of the birthmark is necessary - this will allow timely recognition of the process of malignancy and avoid malignancy.
What is a nevus and why does it appear?
A benign tumor, or more precisely, a developmental defect that often occurs in the embryonic period due to the migration of melanoblasts from the neural tube to the basal layer of the epidermis. Those. - these are the precursors of nervous tissue that accidentally ended up in the skin.
They contain melanin; some of the nevi actively synthesize it, which determines the intense color of most of these formations. The names of the various types of nevi are associated with the specific cells that make up the formation, for example, a melanocytic nevus is formed by melanocytes, etc.
If these were ordinary melanocytes, then there would be no problems as such. However, these cells are not full-fledged, poorly differentiated, and therefore prone to growth and malignancy. Depending on the cellular component of the nevus, doctors divide these formations into absolutely dangerous, potentially dangerous and safe for the health of the child.
Nevi can disappear on their own or appear unexpectedly in other areas of the skin, since the cellular structure of these formations is not stable due to their low differentiation. Thus, doctors consider nevi to be a relatively unstable group of cells that usually do not escape the total control of the body.
The number of such formations directly depends on the hormonal background of a particular person - in adolescence, for example, previously dormant groups of cells often appear. If a new nevus appears on the skin of a child, this is not a metastasis, not a tumor, but simply inactive colonies of melanocytes that entered the skin during the embryonic period.
With age, the number of visible nevi increases significantly; by the age of 16, almost everyone has them, so operating on all emerging nevi is absolutely futile and not beneficial for the child’s body.
Complications of pigment formations
The most important and unfavorable complication of nevi is associated with the initiation of the oncological process in the event of exposure to unfavorable factors or even for no apparent reason. The risk increases with injury or unskilled removal. Complications also include bleeding after removal and infection in the postoperative wound.
- How to get rid of nail fungus at home. Quick relief from nail fungus
- Tablets to boost immunity for adults - list
- Homemade Tiramisu cake
Why do small children get moles?
Moles and age spots on a baby’s body are formed from melanocytes.
These pigment cells are present in the body of every person, regardless of age. The place of their localization is the space between the outer and inner layers of the epidermis. Thus, the presence of pigment cells is not a deviation; it is normal for childhood. If such moles have formed in multiple numbers, there is no need to worry. But formations with a diameter of more than 1.5 cm with unclear edges and uneven tonality require consultation with a pediatrician or dermatologist.
Expert opinion
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
Modified nevi are dangerous due to possible degeneration, so it is important to take timely measures to prevent or remove the problem area.
It happens that a mole disappears on its own and suddenly. If a small pale spot takes its place, the child should be shown to a doctor. Such unexpected behavior of a nevus may signal the beginning of the development of a skin disease.
When should you expect moles to appear?
Pigment cells fill a small organism during intrauterine development. Scientists say that the appearance of nevi is possible immediately at the moment of human birth. But these are such rare cases that it is not worth focusing on them. But by about 4 years old, children can already notice specific spots on their bodies.
If a child has many moles during the transition period, these changes in the body are identified with changes in the hormonal balance of the teenager. Over the course of several years, formations can form very actively. In the third decade, there are already many moles on the human body, then the process slows down.
It is impossible to answer unequivocally when moles appear in children. The mechanism of their development depends on the specific organism, and only attentive parents can know exactly at what point in the baby’s life path this or that element appeared.
In general, the process of formation of nevi depends on several factors:
- frequency of sun exposure;
- stage of active child development;
- hereditary predisposition.
Why do moles appear in a child? Genetics is one of the main reasons that determines the age at which nevi appear. Doctors believe that if a person’s moles appear in adulthood, then in children of this individual they will also form late.
Expert opinion
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
Dermatologists say the same thing about the multiplicity of formations. The more moles the parents have, the more of them there will be on the child’s body.
Medical statistics have recorded an early age for the appearance of moles - 1 - 2 years. Such children are already taken on country and beach holidays, where they are exposed to ultraviolet radiation. Short-term street walks that expose a child’s body to sunlight can cause the formation of new nevi.
Factors influencing the appearance
Experts believe that the formation of all moles occurs in the womb. During pregnancy, fetal defects occur:
- due to impaired cell division;
- hereditary predisposition;
- after contact with toxic substances (including smoking and alcohol);
- due to chronic diseases of the female genitourinary system;
- due to sexually transmitted infections.
Some of them appear from birth, others throughout life under the influence of certain factors:
- fluctuations in hormonal levels in the body (during puberty, conceiving a child, after long-term use of contraceptives);
- excess ultraviolet radiation;
- radiation;
- stress;
- weakened immunity;
- viral skin diseases.
With age, moles become pale, and by old age they completely disappear.
Nevi in children: is it worth sounding the alarm?
All moles in newborns are classified as follows:
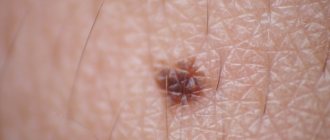
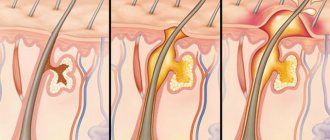
- Borderline nevi are nodules with clear boundaries, the color of which is not only brown and black, but also dark purple. The elements rise above the skin and do not cause pain when pressed. Hair does not grow on the surface of such moles, which distinguishes them from other types. The diametrical size of border nevi varies from a few millimeters to 1 cm. Occasionally they grow up to 5 cm. The danger lies in possible malignancy.
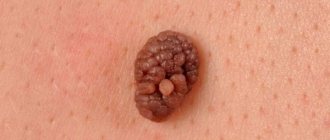
- Experts classify intradermal moles in infants as ordinary birthmarks and indicate their shape. It can be either a speck spread on the skin surface and having a diameter of several millimeters, or a large folded formation similar in appearance to a blackberry. In some children, the intradermal nevus has a characteristic stalk. Its color can be red, black, pale brown or natural flesh.
- Complex, also known as mixed form, is a transitional type between the types described above. A dense neoplasm with a spherical or dome-like shape is characterized by a dark brown, dark red and black color and a size of about 1 cm in diameter. Complex nevi are distinguished from epidermal moles by the presence of hairs. Their risk of transformation into melanoma is minimal, but they still require increased attention.
- Congenital nevi are a common phenomenon. Doctors link their formation to a disruption in the mechanism of transformation of cells that were originally the skin of the embryo into melanin. A congenital mole is immediately noticeable and attracts the attention of doctors even in the maternity hospital. The risk of malignancy of such a birthmark is determined by its position relative to the epidermal layers.
Giant nevi of the congenital type are very rare in newborns. They develop more often in girls than in boys. Moles grow with a child's body and stabilize in size as a person grows older.
Kinds
Moles on a child’s body can come in a variety of shapes, sizes and shades. The most common types of neoplasms are:
- Pigmentation in the form of red spots (also called “stork pinch”) forms on the baby’s head and face immediately after birth. This happens due to friction of the baby's skin against the mother's birth canal. Such nevi disappear on their own in the first year of a child’s life.
- An ordinary birthmark is formed in utero and can appear at the time of birth or some time after birth. Such a nevus in a child comes in different forms - borderline (a slightly convex neoplasm with clear edges with a diameter of up to 1 cm), intradermal (the surface of the mole is smooth or somewhat wrinkled), complex (a round, rather dense nevus from which hairs often grow).
- Purple (wine wine) spots on a child's face or body represent overgrown blood vessels. This pigmentation is growing rapidly, so it is recommended to remove it as early as possible.
- Superficial hemangioma can be congenital or acquired - the color of the neoplasm is red, the structure is smooth, pliable, localized in the upper layers of the skin, and tends to grow rapidly.
- Cavernous hemangioma is located in the deeper layers of the dermis, has a blue tint and is also a type of nevus. In addition, on the buttocks or lower back, children may develop greenish spots resembling bruises (they are called Mongolian, since the formation tends to occur predominantly in dark-skinned children), usually by the age of 3 the pigment disappears on its own.
If any “suspicious” spots appear on the child’s body, you should consult a doctor, but parents should not panic - not all nevi are potentially dangerous to the health and life of the baby.
Symptoms of nevus in a child
Congenital pigmented nevi usually grow slowly, and often stop growing by puberty. Pigmented nevi develop at the age of 5-10 years and are spots or compactions of various sizes and shapes, brown, brown and black.
An increase in size, compaction, increased pigmentation, the appearance on the surface of the formation of dense nodules, pigment spots around it, enlargement of regional lymph nodes are a sign of malignant degeneration of the nevus.
It may manifest as dysplastic nevus syndrome or familial atypical multiple nevus syndrome. It is characterized by a large number of large pigment formations, with irregular edges and different colors. Has a tendency to become malignant.
A linear nevus is a developmental anomaly characterized by papillomatous growths or hyperkeratosis of the skin along the nerves. Nevus of the sebaceous glands is presented in the form of hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands on the scalp or face in the form of dense nodular formations. In 10-15% of cases they tend to become malignant.
Forecast
The prognosis for giant pigmented nevus varies. In the absence of complications, it is favorable - the nevus does not cause any inconvenience, except for disturbing the aesthetic appearance of the skin. With malignancy, the prognosis worsens.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
8, total, today
( 70 votes, average: 4.16 out of 5)
Dühring's dermatitis, or dermatitis herpetiformis: symptoms and treatment
Diaper rash under the breasts: why it occurs, how to treat it
Related Posts
Diagnostics
The study of congenital nevi is always a difficult task.
This is due to the fact that only histological examination can provide the most reliable information about a nevus. However, it is extremely dangerous to carry out if melanoma is suspected, because trauma to the tumor can lead to a sharp jump in tumor growth and the spread of metastases throughout the body, as a result of which the chances of a successful cure are sharply reduced. It is for this reason that histological analysis is usually carried out after removal of the tumor.
It is possible to obtain cellular material from a congenital nevus only if there is an ulcer or weeping area on its surface. To do this, the doctor places a glass slide on the tumor, which is then sent to the laboratory for further examination under a microscope.
Expert opinion
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
Modern safe and accessible methods for studying moles today include radioisotope analysis. In this case, the patient is given a sodium phosphate-based medicine that has been labeled with radioactive phosphorus.
A day after this, the patient undergoes contact radiometry of the tumor and the skin that is located near it. The fact is that melanoma selectively accumulates phosphorus. This is the difference that the study shows.
In addition, a thermometric diagnostic method can be used. In melanoma and other malignant tumors, metabolism is slightly increased. Because of this, the temperature in this area also increases. Typically, the temperature difference between melanoma and healthy skin is about 4 degrees. This is what thermometric analysis is based on.
What is the danger of skin nevus?
Skin nevus at rest does not pose a threat to human life and health.
With a small size of the birthmark, he does not even consider it a significant cosmetic defect. However, the danger exists and it is quite real. The fact is that some types of nevi are prone to degeneration under the influence of unfavorable environmental factors and the internal hormonal status of a person. In this case, a rather dangerous oncological disease, skin melanoma, occurs.
The easiest way to prevent the development of a malignant tumor is at an early stage of its development. Therefore, every person with moles should constantly monitor them carefully. At the first signs of degeneration, you should seek medical help from an oncologist.
These may be the following signs:
- sudden increase in the area of the nevus;
- change in color of its surface;
- the appearance of a porous structure resembling a wart or a head of cauliflower;
- pain and skin itching;
- the beginning of hair growth from the neoplasm;
- the appearance of multiple new elements of pigment accumulation;
- separation of skin flakes;
- bleeding or discharge of lymph fluid.
Expert opinion
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
The degeneration of a skin nevus can be triggered by both external unfavorable factors and changes in a person’s humoral and hormonal status.
Most often, melanomas develop under the influence of:
- nevus injuries;
- prolonged exposure to ultraviolet sunlight (a particular danger lies in the use of solariums);
- taking hormonal drugs, including birth control pills;
- reducing the level of the body's immune defense;
- pregnancy and induced abortion;
- menopause;
- harmful production conditions.
It is not uncommon for melanoma to develop against the background of a nevus after the use of aggressive cosmetic methods. This can be chemical and mechanical cleaning, the use of potent creams.
In diagnosis, the structure of the skin tumor, clinical symptoms and histological examination data are important. If you see several differences compared to your mole, see your doctor. This will allow you to recognize a dangerous disease at an early stage.
Prevention
Since the disease is congenital, there are no specific methods of prevention. But you can reduce the risk of a nevus if you ensure normal pregnancy conditions. The main principles of such prevention are:
avoiding exposure of pregnant women to aggressive physical and chemical factors;- prevention, timely detection and treatment of infectious and somatic diseases;
- refusal of the expectant mother from bad habits;
- living in environmentally friendly conditions;
- avoiding stressful situations and exposure to occupational hazards;
- healthy lifestyle in general.
Indications for removal
It is not worth removing moles from a child without medical indications - aesthetic discomfort is not a reason for surgical intervention.
If the nevus is painless, soft and smooth, with clear edges, its size is less than 1.5 centimeters, it is absolutely safe for the baby, and there is no need to eliminate it. Moles should be removed if they:
- located in inconvenient places and are often subject to injury;
- intensively increase in size;
- daughter growths appear on the surface;
- the structure and color of the neoplasm changes;
- the borders of the nevus are blurred (the first sign of malignancy);
- there is itching, peeling or cracking;
- there are signs of an inflammatory process;
- there is pain on palpation;
- exudate is released from the nevus;
- the skin around the pigment is discolored, existing hairs fall out.
Even if a mole is safe for medical reasons, but is localized in places where there is a danger of injury, doctors recommend removing such tumors.
Is it possible to remove a mole from a child?
It is not always necessary to postpone the removal of moles in children for a long time; sometimes it needs to be done as early as possible, especially if the nevus has become dangerous and can degenerate into melanoma. However, there are no special age restrictions for removing nevi, although it is advisable to do this only for medical reasons from specialists.
The problem of getting rid of a mole in infancy can be the appearance of a keloid scar, which is difficult to resolve and is removed in the office of a plastic surgeon. Removing nevi in children of different ages is no different from the methods of removing moles in adults.
The same methods of getting rid of the tumor, including pain relief, can be used. This coincidence also stands out - like the ban on removing pigmented spots at home, using folk methods and in a beauty salon. In some cases there is no necessary knowledge and compliance with sanitary requirements, in others there is an increased risk of injuring the nevus rather than curing it.
In fact, there is no way to cure the skin of moles; they can only be completely removed, making it impossible to appear on the body again. If moles in a 2-year-old child become dangerous, then they simply need to be removed without delaying them to a later age.
But a simply ugly stain may not be removed in order to prevent the formation of marks after the operation, which will become an even greater problem for the child.
And to prevent other nevi from suddenly starting to bother you, you should avoid frequent and long periods of exposure to direct sunlight, although exposure to ultraviolet rays can be obtained even in the shade, so try to walk with your baby before 10-11 a.m. and after 4-5 p.m. .
Treatment methods
Having removed a potentially dangerous pigment from a child, in order to avoid problems in the future, parents should adhere to some rules aimed at preventing malignancy.
The following types of nevus removal are used.
Excision with a scalpel
Before the procedure, the baby is given premedication to prepare for general anesthesia. The surgeon removes the nevus, capturing several centimeters of healthy skin around it.
This is the most radical method (used in exceptional cases), but at the same time the most effective. After the intervention, the child remains in the hospital. The rehabilitation period is long, scars remain.
Cryodestruction
The procedure is performed on relatively small nevi under local anesthesia (sometimes without it). In essence, the neoplasm is frozen, after which the pigment gradually dies off with the formation of a crust on its surface. Over time, the scab falls off, revealing thin, healthy skin. There are no traces left.
Electrocoagulation
The mole is cauterized, after which it dies, becoming covered with a scab, which subsequently falls off on its own. The procedure takes place under local anesthesia. There is no bleeding, and traces after exposure are not visible.
Laser removal
This method is most suitable for eliminating pigmentation in children. Painlessness, absence of bleeding, disinfection of the wound - these are not all the advantages of laser therapy.
Only the neoplasm is eliminated; healthy skin is not treated. The rehabilitation period is only a few days; there are no scars or other traces of exposure.
Radio wave surgery
The method has many advantages, but at the same time there is one disadvantage - it is impossible to eliminate a large tumor using a radioknife. During the procedure, the surgeon removes the mole without affecting healthy skin.
Anesthesia is not always required as the procedure is virtually painless. There is no blood loss, the wound is disinfected at the same time. There is a minimum rehabilitation period, there are no marks or scarring.
How to prevent malignancy
Regularly inspect your baby's body for the formation of new moles.
In addition, you should know that there is a so-called risk group of children susceptible to melanoma. Be careful and conduct regular medical and self-monitoring if:
- there is multiple pigmentation on the child’s body;
- the size of at least one nevus exceeds 7 centimeters;
- there is a genetic predisposition to malignancy;
- frequent relapses of dermatological diseases occur;
- neoplasms are localized in a traumatic location (neck, armpit, groin, foot, head).
Expert opinion
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
If your child meets at least one of the five points, be careful - beware of walking in the open sun during the period of its greatest activity, immediately treat the mole with an antiseptic in case of injury and never cover the pigment with an adhesive plaster, this will only activate the production of melanocytes.
Any modification of the nevus is a reason to consult a doctor - timely treatment will prevent malignancy and save life.
Preventive measures
preventive measures. First of all, it is worth regularly examining the condition of the skin for changes in moles and their number.
You should also plan your regime in the summer, so you should not be in the sun from 12 to 16 hours of the day. It is necessary to use sunscreens that protect the skin from UVA and UVI rays (they are the most dangerous in terms of the development of cancer pathology). A special cream is applied so that it protects the skin evenly. Everything should be treated, including the ears, neck and face. If you are constantly in the sun, apply the cream every two hours.