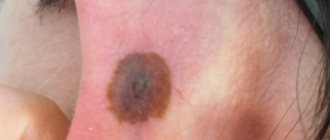
The malformation of epithelial buds is called epidermal nevus. Epidermal nevus is a benign neoplasm and can occur both during intrauterine development and throughout a person’s life. Damage to such parts of the body that are constantly visible causes severe cosmetic discomfort for a person.
Epidermal nevus (birthmark) can occur in utero or during life.
Why is a warty nevus dangerous?
Warty nevus is not classified as melanoma-hazardous, that is, the risk of its malignancy is low. But this does not mean that such a convex mole cannot be reborn at all. In the presence of provoking factors, it can cause the development of skin cancer.
When answering the question of why a warty nevus is dangerous, it is worth mentioning its high sensitivity to mechanical, chemical, and thermal effects. The reaction to the stimulus is tumor growth. The more often it is injured, the more it increases in size.
Moles are prohibited:
- scratch;
- to scratch;
- cutting down;
- cauterize;
- freeze.
In addition to tumor growth, these actions increase the risk of infection and the development of inflammatory processes.
What do experts advise?
Do not forget that aggressive growth of verrucous nevi can be malignant. This suggests that it is necessary to avoid any heating of the skin growths. Based on this, experts advise:
- refuse to visit baths and saunas;
- in hot weather, do not stay outside for a long time (from 11.00 to 16.00 - it is during this period of time that the exposure to ultraviolet radiation is greatest);
- protect yourself as much as possible from direct ultraviolet rays coming into contact with the affected skin;
- it has been proven that sun creams do not in any way provide protection against the appearance of cancer;
- Refusing to use a solarium to get a tan is harmful.
If you notice that the growths have changed their shape or have acquired a new shade, then you should immediately consult a doctor. With timely preventive treatment, the nevus will not be malignant, and its neutralization using modern methods will allow you to get rid of discomfort.
⛔ One important rule to remember is that self-medication can be dangerous to your health. Removing the tumor using any home method can provoke inflammatory processes or severe irritation of the epidermal layer.
Causes
A warty nevus is a benign neoplasm that appears as a result of disorders of embryonic development.
There are no atypical cells in the structure of the tumor. The deviation lies only in the amount of normal epidermal tissue. For this reason, this raised mole has another name - keratinocytic epidermal nevus.
According to a number of researchers, the cause of the appearance of a warty nevus is:
- genetic predisposition;
- maternal hormonal imbalances;
- improper formation of the epidermal layer.
According to:
82.5 - other unspecified anomalies of skin development.
Possible complications
If you ignore medical recommendations, regularly injure yourself, or try to self-medicate, a mole can cause:
- squamous cell skin cancer;
- bacterial eczema;
- pustular infections;
- destruction of nail plates.
The complication is provoked by ultraviolet radiation, injuries, scratches and friction. Damage to the skin around the tumor increases the risk of developing inflammatory processes, with their further spread to nearby areas. This applies to a greater extent to moles located in the armpits and groin. Due to the addition of infection, diaper rash surfaces acquire a specific pungent odor.
Moles located on open areas of the body cause serious psychological discomfort to the patient. Some forms of neoplasm cover a significant area of the skin, affect the hands and feet, and cause destruction of the nails.
Forecast
Treatment of verrucous nevus is usually performed on a benign formation. Since this disease can only in rare cases transform into a malignant form. In 80% of cases the prognosis is more than favorable.
In some cases, it is necessary to consult a doctor if the mole appeared at an advanced age, its size is large and its number has changed dramatically.
Constant damage and friction of the skin at the site of the nevus negatively affects its structure. Therefore, in order to avoid terrible consequences and complications, you must immediately consult a doctor to remove the formations.
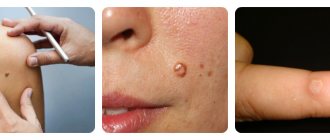
Types of warty nevus
Several criteria are used to classify warty nevi. The first of them is determined by the shape and location of the tumor. Based on this criterion, nevi are distinguished:
- lateral part of the body - shaped like the English letter S;
- middle part of the body - have a vertical, linear character;
- head and body - the shape of wide transverse stripes.
Most often, a warty nevus forms on the extremities, less often on the head. Cases of neoplasms have been recorded that cover an entire part of the body, the abdomen or the back.
According to the stage of development, these moles are as follows:
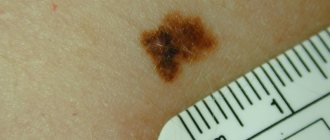
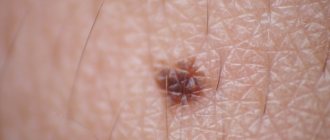
- Educational stage. The pigment spot is small, up to 1 cm in diameter. Color is brown or dark brown, less often flesh-colored.
- Stage of keratinization. The formation becomes rougher to the touch. Old cells grow on new ones, which causes the height of the growth to increase. The keratinization may be accompanied by mild itching.
- Growth stage. The size of the mole increases: its diameter reaches 3-4 cm, height - 1 cm. The shape becomes more convex and rounded, the surface becomes bumpy.
Warty nevi are linear and systemic. The first subtype is a single neoplasm that can appear on any part of the body or scalp. Linear warty nevus is small in size - up to 1 cm in diameter, with clearly defined edges, maroon or dark brown in color. Multiple cracks are visible on the surface; hair is missing.
Systemic warty nevi are less common, in 15-20% of cases. They are a cluster of formations located close to each other. Researchers describe them as a "garland" or "chain" of raised moles.
The systemic form can appear anywhere on the body, but most often forms along large blood vessels. It has a heterogeneous color, from light beige to dark brown, even black.
This accumulation has a length of up to 29 cm, the inside is dense and elastic. With age, its surface becomes more and more grainy and tortuous.
In medicine, a different classification is most often used. Warty moles are divided into 4 groups - verrucous, generalized, linear unilateral, inflammatory linear warty epidermal nevi. Let's look at them in more detail below.
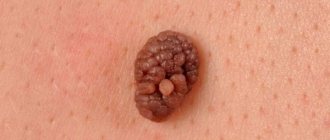
Verrucous
It is a small dark brown or yellowish-brown plaque that is located only on one area of the body. Outwardly it resembles a cluster of papillomatous or flat-topped tubercles. Rarely causes redness or inflammation.
On palpation, the warty nevus is soft to the touch. The surface is velvety, rough. Near one large tumor, several smaller ones may appear. When diagnosing, it is important to differentiate this subtype of moles from seborrheic keratosis and papillomatous melanocytic nevus.
Inflammatory linear epidermal
Linear warty inflammatory epidermal nevus is a neoplasm with an inflammatory component. It belongs to the unilateral subtypes of tumors. It can be located on the upper, lower extremities, as well as the buttocks.
The color of a linear warty inflammatory epidermal nevus is red, with pronounced scales on the surface. Often the disease is accompanied by itching and discomfort in the affected area. For this reason, the mole may be confused with ordinary psoriasis, lichen planus or linear lichen.
The inflammatory component of the neoplasm is acquired. For an accurate diagnosis, histological examination is necessary.
Linear unilateral verrucous
This subtype is characterized by unilateral spread, involving large areas of the skin. It can form on any part of the body, but is more common on the legs, arms, and torso. Externally, the formation resembles linear streaks or bundles located along Blashko's lines, and not the entire area is affected, but its individual sections.
A linear unilateral verrucous nevus can affect half of the patient's body. In this case, it grows to an impressive scale: it covers the skin, including the face, scalp, neck, back, and limbs. The boundary between healthy and affected areas is clearly defined.
In childhood, a linear unilateral warty nevus is light in color and flat in shape. As it matures, it darkens and rises above the surface. Formations located in the area of the hands and feet are more susceptible to keratinization and are harder to the touch. The surface is hairless, with the exception of rare varieties with long, thin whitish hairs.
Generalized
This form of neoplasm spreads to the scalp, torso, and limbs on both sides. It is located symmetrically, along the Blashko lines. The growths can merge into one large cluster or be located at a short distance from each other.
This form of warty nevus is one of the most widespread. It causes serious aesthetic and psychological discomfort to the patient.
Diagnostics
A person without medical education cannot independently distinguish verrucous nevus from similar ailments. Only a doctor can identify such a disease. A preliminary diagnosis is made after an external examination and questioning of the patient, but an accurate diagnosis is made only after laboratory tests. When examining a mole, the doctor pays attention to the following factors:
- Color of the neoplasm;
- Its size;
- Area of birthmark location;
- Its shape;
- The presence or absence of hair on it.
Laboratory analysis methods for moles include:
- Taking a smear from the surface of the mole. The disadvantage of this method is trauma to the neoplasm, which can lead to the degeneration of the birthmark into melanoma. But this drawback is eliminated when taking a smear from that category of patients whose nevus was already damaged before the procedure was prescribed. It is to them that doctors most often prescribe this type of laboratory analysis.
- Luminescence microscopy. This procedure involves applying a special liquid to the surface of the nevus and further examining the birthmark under a microscope. This type of laboratory analysis of a mole is considered the safest, because during the procedure the surface of the neoplasm is not damaged or injured in any way.
- Computed tomography of the tumor. The insides of the nevus are examined using x-rays, and based on what is obtained, a diagnosis is made.
- Blood test for tumor markers. The blood is examined for the presence of cancer particles.
- Histological examination. The tumor is examined under a microscope for the presence of cancer cells. This method of laboratory analysis of a nevus is considered the most informative; it is what doctors usually prescribe if they suspect malignant degeneration of a mole.
Manifestations of warty nevus in children
Wart nevus is detected mainly at birth. Cases of acquired neoplasms are rare. They are caused by the development of noticeable hyperkeratosis, leading to dark pigmentation and loosening of the skin surface.
As you grow older, the warty mole grows in proportion to the size of the body; in adulthood the pace slows down.
If the neoplasm appears at birth, it is important to explain to the child that it cannot be injured, combed, or cut. Otherwise, the mole will increase in size, become inflamed, and hurt.
Kinds
Experts distinguish several classifications of nevi. It is immediately necessary to consider the division of moles by size:
- small nevus – from 0.5 cm to 1.5 cm;
- medium nevus – up to 10 cm;
- large nevus – more than 10 cm;
- a giant pigmented formation can occupy a large area of the body (an entire limb or more), in rare cases, half of the face or neck.
Nevi vary in shape:
- Pigmented papillomatous nevus appears immediately after birth. The formation rises noticeably above the skin. In appearance it resembles a papilloma. In rare cases, papillomatous formation can be malignant.
- Blue nevus.
- Dubreuil's limited melanosis.
- Pigmented border nevus.
- Nevus Ota.
- Intradermal pigmented nevus (photo below) is a benign formation. It almost never transforms into melanoma. In most cases, this is a congenital skin defect.
- Melanocytic-dysplastic is a dangerous type of warty mole. Externally, the formation looks like a blurry spot rising above the surface of the skin.
An important factor in the appearance of this type of education is heredity. It has been scientifically proven that solarium and ultraviolet rays have a negative effect on the skin. Abuse of them can lead to malignant transformation into melanoma.
A distinctive feature of each formation is its individual structure, localization on the body and morphological characteristics. The main decisive factor is the ability to degenerate (malignancy and transformation into melanoma). Conventionally, verrucous nevus is a precancerous disease. However, some doctors classify nevi differently: melanomatous and capable of metastasis.
Treatment and removal
A congenital or acquired nevus must be shown to a doctor immediately after its discovery. He will prescribe a histological examination to determine the nature of the neoplasm and make an accurate diagnosis. The disease must be differentiated from seborrheic keratosis, acanthosis nigricans, lichen ruber, and papillomatosis.
Treatment of the disease depends on its prevalence, histological characteristics, location and other factors. Since the neoplasm most often does not pose a direct threat to the health and life of the patient, urgent therapy is not necessary. The goal of treatment is to stop the spread of the disease, improve the appearance of the skin and eliminate discomfort.
Drug therapy includes the following methods:
- taking the drug "Aevit" and "Roaccutane" - for the treatment of a common form of the disease;
- the use of corticosteroids - in the form of ointments or injections that reduce inflammation and itching;
- application of compresses based on retinoic ointment and salicylic petroleum jelly;
- cream with calcipotriol - to eliminate dryness;
- podophyllin or 5-fluorouracil - to suppress the growth of moles in the upper layers of the epidermis;
Local treatment provides a temporary effect: the appearance of the tumor improves, inflammation and itching disappear. But after stopping the use of ointment or cream, the skin will return to its original state.
Only removal of the warty nevus will allow you to get rid of the keratinized layer of the epidermis. It is performed in several ways:
- cryodestruction;
- dermabrasion;
- electrocoagulation;
- laser or radio wave method;
- surgical excision.
If the formation is not completely removed, then a relapse of the disease is likely. But overdoing it is also dangerous: it can lead to ugly scars.
Features of each method:
- Dermabrasion affects only the superficial layers of the epidermis, without penetrating into deep tissues. The method is used to eliminate small flat nevi. High risk of relapse.
- Cryodestruction can lead to swelling and the appearance of white or dark spots on the skin. Scars take a long time to heal. The method is suitable for moles of small diameter.
- Electrocoagulation and radio wave methods are used no less widely. But the accuracy and depth of removal is more difficult to control.
- Laser mole removal is the most preferred option. Small formations can be destroyed in one session, the risk of relapse is minimal.
Surgical excision removes diseased tissue in the deeper layers of the skin. It always leaves scars. There is a risk of relapse, but it is low.
How to treat?
Treatment of epidermal nevus can be either conservative or surgical. The removal procedure is complicated. Often the main goal of this process is to improve the appearance of the skin and eliminate cosmetic discomfort for the patient. If the skin lesion is extensive, multiple removal procedures may be required.
A small nevus can be completely removed in the hospital. Partial removal can provoke a recurrence of the pathology or the emergence of cancer. To improve appearance, conservative treatment is often used, including the use of ointments. The disadvantage of this therapy is that when the use of the drugs is stopped, the external symptoms return again. Corticosteroids are used to reduce itching and inflammation.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine offers dubious methods for treating warty growths: cauterization with the juice of poisonous plants, thermal and chemical effects on the growth. Not only are they ineffective, they are also dangerous: they provoke the risk of developing infections and increase the likelihood of tumor malignancy. Without a medical examination, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis, since the external signs of a mole may resemble other dermatological diseases.
Traditional medicine methods can only be used for treatment - caring for affected skin, preventing relapses. But all of them also need to be agreed upon with the attending physician.