HPV is widespread among the population; the vast majority of all men and women are infected with its various strains. Many people don't even know about it. Ignorance poses a risk to their health and facilitates transmission of the virus to sexual partners and family members.
Papillomavirus type 39 in women is dangerous due to its high degree of oncogenicity and long-term absence of symptoms, when a person can look absolutely healthy for many years and live without disturbing symptoms. Its detection and timely treatment are important conditions for preventing life-threatening pathologies.
WHAT IT IS
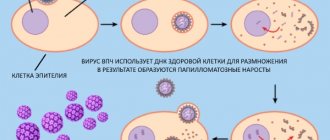
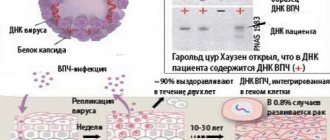
Human papillomavirus strain 39 belongs to a large group of viruses that infect epithelial cells of the surface layer of the skin, as well as the mucous membrane lining the vagina, anus, vulva, cervix, mouth, and oropharynx. Most of the HPV is neutralized by our immunity; it does not manifest itself and can disappear after 8-13 months. But in some cases, the virus can stay in the body for years, then the person becomes a carrier and can infect others.
Not all sexually transmitted HPV viruses can cause severe consequences for the body. Strains of low cancer risk in 92% of cases cause the development of genital warts, which rarely develop into cancer.
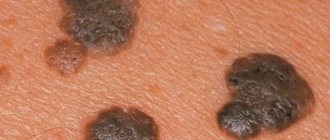
Genital warts may look like bumps or growths. They appear several weeks or even months after sexual contact with an infected partner. Low-oncogenic strains also cause the development of warts on the skin of the hands, feet or papillomas on the body and face.
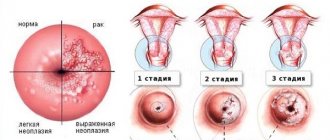
Papillomatosis caused by type 39 virus is potentially dangerous to health, since under unfavorable conditions it can lead to the development of precancerous diseases of the female genital organs and provoke the development of malignant processes in them. At first, the disease proceeds secretly.
The duration of the incubation period ranges from 3-6 months to 2 or more years. An ill woman may not experience any alarming symptoms or changes in well-being.
Subsequently, HPV type 39 in women and men manifests itself in the form of growths on the body - papillomas, genital warts on the mucous membrane, which is a predisposing factor to the development of dysplasia (a precancerous condition of the female genital organs) on the cervix. According to statistics, 95% of women diagnosed with this oncopathology were found to have highly oncogenic HPV.
It has been proven that smoking cigarettes is also a risk factor that contributes to the development of a pathogenic process in the cervix.
Prevention
Prevention of infection includes the following measures aimed at preventing the causes of virus activation:
- use contraception during promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- avoid systematic hypothermia or overheating;
- promptly treat sexually transmitted infections and chronic pathologies;
- undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist.
HPV type 39 is highly oncogenic. For a woman, the consequences of ignoring it can have a very dangerous impact on her health. Therefore, if there is any suspicion of the occurrence of this pathology, it is necessary to urgently undergo diagnostics, on the basis of which the doctor will select the appropriate treatment.
HOW CAN YOU GET INFECTED?
Men and women with active sexual lives are at risk of contracting HPV at any point in their lives if they do not take precautions. In men, the virus practically does not manifest itself, but in women, if untreated, it causes cervical dysplasia.
The human papillomavirus can be infected through household contact, sexual contact, or through contact with infected semen or vaginal secretions.
The best method of protection during sexual intercourse is a barrier method, using a condom. However, this method of contraception cannot protect against contact with other infected areas of the body. Promiscuous sexual relations and frequent changes of partners are an increased risk factor for HPV infection.
It is also possible for household infection through touch, tactile contact, household items, and hygiene products. The virus is able to live for some time in humid environments: baths, saunas, swimming pools, gyms. It can enter the body through injured skin: abrasions, scratches, cuts, as well as during shaving and hair removal.
Methods of infection with HPV type 39
A woman can become infected with HPV genotype 39 in several ways:
- through unprotected sexual contact. Although contraception does not provide a 100% guarantee of protection against various infections, the risk of contracting HPV is much less;
- contact-household method. There is a possibility of contracting the virus through household items or personal care products, but this occurs infrequently because the infection dies outside the human body;
- transmission of HPV to the child from the mother during childbirth, when the child passes through an infected cervix.
The largest percentage of infection occurs through sexual contact
The most common way of acquiring HPV 39 in women is through sexual contact, regardless of the type of sex used: vaginal, anal or oral. That is, condylomas can form not only on the genitals, but also near the anus or in the oral cavity.
Women who:
- started early sexual activity;
- often change sexual partners;
- practice anal or group sex;
- do not observe the rules of personal hygiene.
After the virus enters the body, it may not manifest itself until favorable conditions are created for its activation, which include:
- stressful situations;
- hypothermia of the body;
- prolonged vitamin deficiency;
- taking certain medications;
- disruptions in the hormonal system;
- poor environmental conditions;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- reduced immunity and some others.
A high risk of infection with strain 39 of human papillomavirus exists in the category of women who have had an artificial termination of pregnancy. In men, this type of virus does not cause serious complications, but without treatment it will continue to infect HPV type 39 sexual partners.
Symptoms of the disease
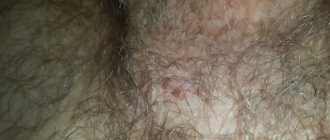
The main sign of infection with HPV type 39 is the appearance of papillomas on the genitals. In addition to the appearance of formations in some parts of the body, the patient may not feel other symptoms of the disease, as happens with other sexually transmitted diseases. Symptoms such as pain, itching or other unpleasant sensations appear if the growth is injured.
Condylomas resemble the comb of a rooster in appearance and have a pinkish tint. Their removal is necessary not only from a medical, but also from an aesthetic point of view. Papillomas can appear instantly, within a few hours after infection. If they are not treated, but a purulent process may begin in the places of formations, papillomas will continue to actively multiply, turning into malignant formations.
Diagnosis of HPV type 39
After discovering strange formations on the genitals that were not there before, you must immediately contact a gynecologist for an examination and testing. Diagnosis of HPV type 39 takes place in several steps:
- examination by a gynecologist;
- colposcopy. This procedure involves examining the vagina and cervix using a special device - a colposcope. This event allows you to detect pathogenic tissues and the area affected by the virus;
- cytological examination. To do this, a smear is taken from the patient, which is then sent for examination, which can be used to identify a malignant tumor at an early stage;
- polymerase chain reaction. As a result of studying biological material, it is possible to identify oncogenic types of HPV;
- Digen test. With its help, the DNA of the virus is determined in the presence of papillomavirus, and the type of infection is also determined;
- biopsy. If a benign formation is suspected, the doctor takes a piece of the affected tissue and sends it for tests that will show the likelihood of cancer at an early stage.
Treatment methods for HPV strain 39 in women
Both sexual partners must undergo diagnosis and treatment
If the examination results are positive and HPV type 39 was detected in the body, then the doctor selects an appropriate treatment method. It consists of several stages, which together form an effective comprehensive treatment. Combined treatment of HPV 39 includes several types of therapy:
- removal of papillomas by chemical or physical methods. The appropriate method of removal is selected by the doctor based on the location of the papilloma and its stage of development. A laser device is often used to remove HPV type 39. And if the growth is large and malignant, it is removed surgically;
- antiviral drugs and immunostimulants are prescribed. This is necessary to prevent relapses. A healthy immune system is able to independently reject the virus once and for all;
- restorative therapy. A complex of vitamins and minerals is attributed to strengthen the body after the harmful effects of the virus.
Both sexual partners should undergo diagnosis and treatment, and during the course of treatment it is not recommended to have sexual intercourse to avoid re-infection while the body is still in a weakened state. It is strictly forbidden to be treated with folk remedies if you have HPV 39 ⏤, as this will lead to irreparable consequences.
And don’t panic if you have been diagnosed with genotype 39 human papillomavirus, because this does not provide a 100% guarantee of the presence of a cancerous tumor, but only indicates that the risk of cancer is high. Timely detection of a tumor and its treatment prevents terrible consequences.
VARIETIES
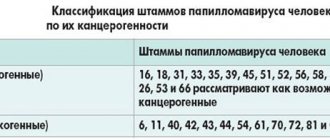
Currently, the global medical community has recorded more than 600 strains of human papillomavirus. Conventionally, they are divided into three large groups according to the ability of a viral infection to cause malignant changes in healthy cells:
- Papillomavirus of low oncogenic status - as a rule, does not cause oncogenic pathologies and does not have a harmful effect on the body.
- HPV of average oncogenic status is also considered benign, but under certain conditions (frequent bruises, injuries to papillomas, warts) can cause the growth of cancer cells.
- High oncogenic papillomavirus is the most dangerous type of virus. In advanced forms, if left untreated, it becomes the cause of cancer.
Of all the types of HPV, about 60 cause warts and papillomas on the body, and the rest are transmitted mainly through sexual contact and live in the mucous membranes of the external genitalia and the anus.
In some cases, especially in the early stages, the disease is asymptomatic and papillomas are not formed. Therefore, detection of type 39 virus is difficult; it is detected only during a gynecological examination.
HPV vaccine
Depending on the vaccine, vaccination occurs immediately against the most dangerous types of HPV. The vaccine is not live, so it is completely harmless. The types of viruses that the vaccine is effective against can cause cancer of the vagina, cervix, penis and anus.
There is evidence that vaccination also protects against a number of other oncogenic types of the virus. The vaccine cannot be used as a treatment, but only as a preventive measure.
There is no need to undergo any special examinations before vaccination. Vaccination is given to young people of both sexes aged 9 to 17 years, and women up to 26 years old. Research is being conducted on the effectiveness of vaccination among older women.
Indications:
- Prevention of cervical cancer,
- Prevention of cancer of the vagina, vulva, penis in men,
- Prevention of genital genital warts,
- Prevention of precancerous diseases,
- Prevention of laryngeal papillomatosis.
How is vaccination carried out?
The effectiveness of vaccination ranges from 95 to 100%
The vaccination is done three times. The interval between the first and second is two months, between the second and third is four months. But you can also do it according to a more dense scheme: the second one a month later and the third one two months after the second one. If all three vaccinations have been carried out within 12 months, it is successful and complete. The effectiveness of vaccination ranges from 95 to 100%.
Side effects of vaccination
In isolated cases, there was a deterioration in health in the first three days after vaccination, and a slight increase in body temperature. The vaccine injection site turns slightly red. Contraindications: Absolute: Individual intolerance to vaccine components (including aluminum or yeast). Relative: Diseases in the acute stage, including exacerbation of chronic ones. Vaccination can begin after the exacerbation has ended or the patient has been cured.
Sources:
- https://www.invitro.ru/analizes/for-doctors/554/2734/
- https://www.hpvinfo.ru/papillomavirus/infection.html
- https://www.onclinic.ru/articles/zabolevaniya/polovye_infektsii/simptomy_vpch_u_zhenshchin/
- https://www.zppp.saharniy-diabet.com/papillomy/tipy/onkogennye/39-tipa
- https://www.tiensmed.ru/news/virus_papillomy_chjelovjeka.html
SYMPTOMS
The disease is often asymptomatic. Some types of human papillomavirus cause the appearance of genital warts, flat condylomas on the external genitalia.
Other types of HPV provoke cervical cancer and other types of cancer, but do not cause the appearance of warts or other alarming symptoms. The virus of the 39th strain is characterized by the appearance of condylomas in the vagina, on the cervix, and causes dysplasia of the squamous epithelium.
Genital warts look different. They can have a sharp or flat shape, and be pink or flesh-colored. They can also be grouped into a conglomerate that resembles cauliflower in appearance. Sometimes one condyloma appears, and over time there are many of them, multiple foci are formed.
They can be small or large. They are usually located in the vagina, cervix, anus, labia majora and labia minora.
The disease is often accompanied by itching, dryness in the genital area, discharge when an infection occurs, and pain during sexual intercourse.
DIAGNOSTICS
When diagnosing the disease, self-examination can help - regularly examining your body for the appearance of warts or atypical growths. Detection of condylomas, papillomas on the arms, legs, face and genitals is a reason for examination by a doctor.
Basic diagnostic methods:
- clinical examination;
- examination and examination by a gynecologist “in the mirror”;
- colposcopy;
- biopsy, histological examination - reveals thickening of the stratum corneum;
- cytological examination of cervical smears using the PAP method to identify atypical cells;
- PCR typing – identifies HPV DNA;
- Digene screening test is a modern and highly accurate diagnostic method for identifying the maximum concentration of HPV;
The data obtained during the examination will help determine the type of pathogen, identify the type of virus and the degree of concentration in the body. Depending on the diagnostic results, treatment is prescribed.
How to distinguish from other types?
It is possible to distinguish one type of papilloma from another only after laboratory testing . To do this, it is necessary to take tissue from one of the papillomas for histological analysis. DNA testing, cytological and molecular testing may also be required. Tests for syphilis and HIV are mandatory.
Video about how tests are taken:
You can learn more about HPV tests in men from this article.
TREATMENT
It should be said that there is no radical treatment for the HPV-39 virus. Doctors can only cure the consequences of this disease - remove papillomas and condylomas, perform surgical resection of the tumor focus in the early stages of cancer development.
Drug support – immunomodulatory therapy – plays a major role in the treatment of HPV-39. At the moment, there is not a single highly specialized drug with a targeted effect on HPV-39. Medications from the interferon category are successfully used, which affect the current symptoms, but cannot prevent the risk of new infection.
To remove pathological tissues, the following is used:
- surgical resection;
- chemical cauterization of the erosive area;
- electrocoagulation;
- laser coagulation;
- cryodestruction (removal of papillomas and condylomas with liquid nitrogen).
Removal of condylomas does not guarantee that the virus has completely disappeared from the body, therefore additional drug therapy aimed at increasing general and local immunity is desirable. In some cases, the administration of antiviral drugs has a good effect.
It is important to remember that you should not try to remove or remove warts yourself - this is dangerous! The procedure can only be entrusted to a qualified medical specialist!
TRADITIONAL THERAPY
Do not underestimate traditional medicine recipes in the treatment of HPV. Herbal infusions, unique folk recipes and a balanced nutrition plan will help boost and maintain the immune system in good condition.
Indeed, according to statistics, natural immunity independently gets rid of the virus in the body within two years in 95% of cases.
Lead an active lifestyle, move a lot, eat more seasonal vegetables and fruits, include healthy proteins and fats, dried fruits, nuts and honey in your diet!
These healthy and tasty products will not only restore your well-being, but also increase resistance to diseases and improve their tolerance.