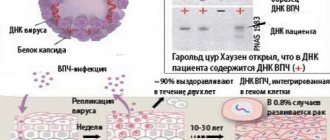
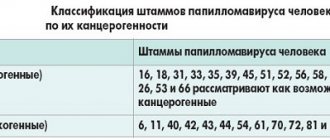
HPV type 52 belongs to a large group of human papillomaviruses. There are more than 100 different strains in this group, among which doctors distinguish non-oncogenic, low and high oncogenic viruses.
The danger of oncogenic strains for the female body lies in the fact that in the presence of provoking factors they can cause cervical cancer.
According to statistics, 70% of cases of uterine cancer are associated with the presence of papillomavirus. Strain 52 is an anogenital virus, since its localization is the genitals and anal area.
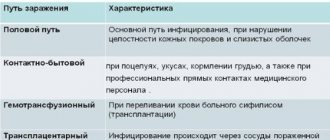
Routes of infection and development of papillomavirus
The main route of infection is unprotected sexual contact with a virus carrier. Moreover, infection can occur at the very first intimacy.
According to doctors, this occurs more often in girls who began sexual activity before the age of 16. As for the household route of transmission, it is also possible, but it does not occur so often.
Reference! In men, papillomavirus 52 strains almost never manifest themselves; a strong half of humanity are latent virus carriers.
Once in the human body, the virus has a negative effect on the epithelium of the cervical region of the uterus. It penetrates into healthy cells, changes their structure and provokes active division of the changed cells.
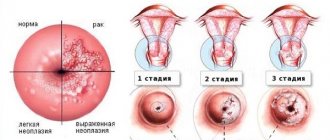
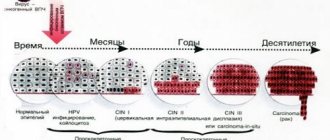
At the stage of cell degeneration, doctors can diagnose cervical dysplasia of different stages. Over time, the virus causes cells to mutate, that is, transform into cancerous ones. Thus, oncology develops, which can cover large areas and metastasize to neighboring organs.
Based on many years of observations, it was found that this entire process takes 10–20 years. This means that a young girl, having become infected with this dangerous virus, may face a dangerous disease in adulthood. However, this does not happen in all cases. In 30% of women, after diagnosis of 1st degree dysplasia, the pathological process freezes and does not develop further.
Thus, doctors say that certain conditions are necessary for the development of the virus, mainly a decrease in immunity. Therefore, the disease often does not make itself felt for a long time, and manifests itself only during menopause, when the body ages, hormonal changes and a sharp decrease in immune defense occur.
In addition, the following may be provoking factors for the activation of the virus:
- diseases of the genitourinary system of a chronic nature;
- sexually transmitted diseases;
- miscarriages and abortions;
- poor nutrition;
- presence of bad habits;
- immunodeficiencies – both congenital and acquired;
- long-term illnesses – more than 2–4 months.
Symptoms of infection
After HPV DNA enters the cavity of a healthy cell, the process of inflammation of the middle layers of the epithelium starts, but it passes without external symptoms. During this period, the so-called “root” of condyloma is formed. At the same time, capillaries degrade, which turn into vessels that feed the body of the papilloma. That is, the virus begins to parasitize. The process, unfortunately, is irreversible. I mean, if a condyloma has already appeared, then on its own it will not resolve, disappear or fall off.
Until a certain time, a girl will not even be aware of the presence of a neoplasm in her body (if it is located, for example, in the area of the cervix or rectum). This is the main difficulty in treating papillomavirus from a group of high oncogenic risk. The disease is detected already at the stage when cancer cells appear or when the woman feels discomfort, notices the presence of foreign vaginal discharge or the like.
What symptoms should you look out for? HPV 52 in women is characterized by the following symptoms:
- burning sensation in the vagina and rectum;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- sudden weight loss (relevant for rectal cancer);
- relapse of herpes (indicates activation of HPV, of which there may be several strains in the body);
- third-party vaginal discharge.
The exacerbation of the disease can be complemented by the addition of other infections, since the effectiveness of the immune system during this period is reduced.
According to the instructions of scientists, HPV 52 type predominantly occurs in women after 35 years of age, with suppression of reproductive function (when the concentration of sex hormones in the body sharply decreases). In men it is much less common (the approximate ratio is 12 to 1).
Symptoms of human papillomavirus
The clinical picture of the 52 strain virus rarely appears; they are very similar to the symptoms of other sexually transmitted infections - chlamydia, gonorrhea, and so on.
Women can observe:
- vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor and blood;
- discomfort and pain when urinating;
- the appearance of condylomas throughout the body, which can cause quite severe discomfort, especially if they occur in the anus or vagina;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse - patients complain of burning and pain;
- lack of sexual arousal;
- discomfort and heaviness in the lower back and lower abdomen.
In rare cases, nausea, fever, weakness, dizziness, and stool disorders may occur.
Features of the strain in women
Strain 52 is one of the viruses that has a high degree of oncogenicity. Clinical signs in women most often begin to appear after 40 years, when the immune system begins to work worse, however, even at a young age, the virus can become more active and manifest itself in the form of skin growths.
If condylomas are not treated in a timely manner, they can transform into malignant neoplasms and then the woman will need completely different treatment, which does not guarantee recovery.
Unfortunately, the problem lies in the fact that condylomas cannot always be identified immediately. In women, they can appear on the lining of the uterus, which means they can only be diagnosed during a gynecological examination.
Important!
Therefore, gynecologists strongly advise all women after 40 years of age to undergo regular preventive examinations.
In some cases, growths and warts may disappear on their own; as soon as the immune system is restored, the body can cope with the pathology without additional help. But with the 52nd strain of the virus, it is better not to joke and not wait for everything to go away on its own, but to seek help from a specialist.
How to prevent infection
Understanding what HPV type 52 is in women, you can guess that it is very difficult to prevent infection. Even traditional methods of contraception cannot save the situation, since here the virus is transmitted through mucous membranes, and not through sperm. And according to statistics, among women over 50 years old, about 15% are already infected with papillomavirus. But this does not mean that the disease will necessarily lead to cancer. Only in 0.1% of cases does it worsen. In other cases, the virus remains in the body, but does not manifest itself in any way.
Therefore, timely treatment (removal) of papillomas and a healthy lifestyle are the best options for preventing HPV. It is better to consult a gynecologist on this matter - he will give more specific advice.
In total, HPV type 52 is a type of papillomavirus with a high degree of degeneration into a malignant tumor. Most often it manifests itself in the form of genital warts on the mucous membrane of the genital organs, in the cervical area. If the female body fails to suppress the infection, a local area of multiple infection is formed with dozens of small (up to 1 millimeter in diameter) condylomas. Treatment of existing papillomas is only surgical. Immunotherapy is then prescribed.
Papillomavirus in men
As mentioned above, in men the papilloma virus rarely manifests itself clinically. Men of non-traditional sexual orientation and older people are at risk.
If genital warts or warts appear in the groin area or anal area, you must consult a doctor as soon as possible, who will determine the strain of the virus and prescribe the correct treatment.
If the disease is not treated, it can provoke oncological processes in the rectum and colon.
Signs that are considered dangerous:
- sudden and unjustified weight loss below normal;
- false urge to go to the toilet, frequent constipation;
- presence of blood during defecation;
- increased gas formation.
Therapy
Treatment of HPV type 52 in women is carried out with medicinal and surgical methods and should be prescribed by a specialist. Radical treatment (using a scalpel, liquid nitrogen, laser or radio wave method) is necessary in the presence of papillomas and condylomas. It is unacceptable to remove formations outside of a medical institution; this significantly increases the risk of their degeneration.
Only a doctor can determine in which case treatment is necessary. Pharmacotherapy for HPV includes:
- antiviral drugs (Reaferon, Viferon, Cycloferon);
- probiotics (Linex, Acipol);
- medications to maintain microflora in the vagina (Acilact, Gynoflor).
How to identify the disease in women
Unfortunately, most often, papillomavirus 52 strain is diagnosed in women already at the stage of dysplasia and the tendency of healthy cells to become malignant. The virus can be diagnosed in a timely manner only if a woman goes to the gynecologist once a year for the purpose of prevention and undergoes all the necessary tests.
Diagnostic measures are as follows:
- a doctor examining a woman’s history, collecting complaints and examining her in a chair using mirrors;
- colposcopy, biopsy and histology to identify cancer cells in the cervix;
- Digen test, which allows you to evaluate the characteristics of the virus;
- PAP test.
Most often, these studies are enough to determine the presence of the virus, assess its oncogenicity and determine its activity. If necessary, the patient can be referred for consultation to a proctologist, dermatovenerologist, surgeon or oncologist.
Based on the examination results, the doctor can draw the following conclusions:
- Degeneration of the mucous epithelium. In this case, to exclude the development of oncology, the woman is prescribed intensive antiviral therapy.
- The presence of malignant cells – cervical oncology.
Diagnostics
Taking an anamnesis usually does not bring results - even if there are symptoms of HPV, they still will not directly indicate the desired virus. A general blood test has approximately the same diagnostic accuracy.
Theoretically, with the help of this study it is possible to detect the causative agent of the disease, but it is simply impossible to establish its variety, much less sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. There are other diagnostic techniques for this:
- Bioseeding Biomaterial (scraping or smear) is taken from the patient, after which HPV is grown on its basis. As a result, the doctor receives an accurate diagnosis and immediately builds a treatment strategy - the type of DNA of the virus is determined.
- Daijin test. This is also a fairly accurate way to detect a virus.
- PCR.
As you can see, the most accurate result is obtained by bacteriological culture of HPV. But it’s not suitable for everyone - it’s expensive and time-consuming. Not all patients can afford such expenses, and there is no time to wait for the result, because the disease progresses continuously, the virus multiplies!
Pharmacy rapid tests for HPV provide a diagnostic accuracy of no more than 15%. It’s even a pity to spend money on this, even though they are inexpensive.
HPV is found in many biological fluids of a sick person (saliva, semen) and affects the deep layers of the skin and mucous membranes. There are two ways to detect infection with papillomavirus type 52 and determine its genotype and concentration:
- PCR diagnostics is a reliable method for determining lesions based on the study of DNA. The study determines the HPV genotype and allows timely identification of the most dangerous types of papillomavirus. The method detects infection when there is a very small presence of viral DNA molecules in the material sample.
- The hybrid capture technique is more effective than PCR diagnostics of HPV. To perform this test, a scraping is taken from the cervix. The method allows you to determine the HPV genotype and determine the concentration of the pathogen.
Sometimes signs of infection can be seen during a routine genital examination. In this case, it is necessary to do a colposcopy of the cervix and conduct tests to exclude pathology. In complex cases, a biopsy is additionally indicated, during which a piece of tissue is taken for histological examination.
Treatment, how to live, what to do
It is not possible to completely get rid of an insidious virus once it enters the body; the virus remains there until the end of a person’s life. Doctors can offer complex therapy that will blunt the activity of the virus and inhibit pathological changes in cells.
It is also possible to surgically remove tumors, which also does not remove the virus from the body, but only eliminates its clinical manifestations.
Drug treatment is based on taking drugs that help neutralize the viral agent and stop its reproduction. For this, the following drugs that have an antiviral effect are used:
- Panavir.
- Indinol.
- Cycloferon.
- Isoprinosine.
- Genferon.
- Kipferon.
As for hardware removal of papillomas, they are carried out only in a medical institution. There are several ways:
- Laser therapy . This is an almost painless removal that does not cause bleeding. The method is quite effective, so doctors most often recommend it.
- Cryodestruction . The formations are lubricated with liquid nitrogen, which leads to freezing and cell death. After some time, the growth disappears, and healthy skin remains in its place.
- Electrocoagulation . The growths are cauterized with electric current. It is performed under local anesthesia.
- Radio wave method . A painful procedure performed under local anesthesia.
If the virus is complicated by transformation into a malignant form, the papilloma is removed surgically under general or local anesthesia.
In order to help a woman normalize the functioning of the immune system, the doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- vitamin complexes;
- immunomodulators – echinacea extract, Lykopid;
- adaptogens – Ginseng, Chinese lemongrass.
As for the use of folk remedies to treat the papilloma virus, they are inappropriate. Moreover, improper treatment can provoke active growth of tumors and their spread throughout the body. However, folk remedies for increasing immunity will not be superfluous in treatment.
HPV type 52 during pregnancy
During gestation, a change in hormonal status occurs, which leads to a decrease in immunity. As a result, the papilloma virus detects its presence in a woman’s body for the first time. This situation is very dangerous for both mother and fetus, especially if the virus is diagnosed after pregnancy. Carrying a child does not allow a woman to be treated with antiviral drugs.
An acceptable measure of impact is the destruction of papillomas and condylomas. The operation is performed with utmost care under constant medical supervision. It is unacceptable to remove formations on your own, especially during this period. Pregnant women most often have condylomas removed using the laser method.
The importance of regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist
Every woman knows perfectly well how important it is to undergo regular gynecological examinations, but not all women come to them.
Such negligent attitude towards one’s own health often leads to the development of dangerous diseases, which in the initial stages of development could have been cured more easily and quickly.
The danger of papillomavirus 52 strain is as follows:
- The appearance of genital and anal warts, which can transform into malignant pathologies.
- Cervical dysplasia.
- Loss of reproductive function – infertility.
The greatest danger awaits a woman after the age of 40. This is the age when the activity of the virus increases, and benign papillomas can transform into malignant ones. Therefore, women at this age need to especially carefully monitor their health and be sure to undergo preventive examinations with a gynecologist every six months.
Treatment and prevention for men
Vaccination is used to prevent human papillomavirus disease from dangerous carcinogenic strains. The vaccine is given to girls before they become sexually active.
Usually around the age of nine. The vaccine is effective if you have time to complete the entire course before the age of 25.
The drugs are called Cervarix and Gardasil. In Europe and America, they are included in the national vaccination calendar; they can be obtained at the expense of the state.