Human papillomavirus type 59 is a strain that poses a high oncogenic risk. Its manifestations, as well as those of non-dangerous HPV genotypes, are non-indicative, which makes the situation especially alarming. Many people, noticing a papilloma in themselves, simply “etch” it with folk remedies, but this line of behavior is completely unsuitable for oncogenic strains and can lead to the rapid development and growth of a cancerous tumor. That is why, if you detect any abnormal growths on the body, you must first consult a doctor and conduct a histological analysis of the growth.
Human papillomavirus type 59
What is HPV type 59 in women? Today it is a fairly common disease among women. More than 80% of the fair sex are its carriers.
HPV type 59 is a virus of the Papillomaviridae family that can infect cells of the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs, as well as the rectum, with their further mutation into neoplasms that can degenerate into malignant ones. As a result of its influence, genital warts and papillomas can be found in intimate places.
Timely recognition of HPV type 59 in women will allow timely measures to be taken to treat and prevent the disease and significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer.
Symptoms
Symptoms appear very rarely. Only 10% of HPV patients clearly sense the presence of a dangerous microorganism. Moreover, the symptoms in men and women are somewhat different. The reason lies in the difference in the structure of the genital organs, as well as in the characteristics of the immunity of patients of different sexes. Women with HPV 59 experience the following:
- pain when urinating, sometimes turning into a burning sensation;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- genital warts appear in the area of the genitals and anus (with strong exposure to them, pain also occurs;
- vaginal discharge mixed with pus and sometimes blood (if the discharge was previously due to another disease, such as thrush, then a characteristic fishy smell is added to it).
There are many strains of the HPV virus, but it is easier to prevent than to treat this disease. You can familiarize yourself with several vaccines that are designed to protect against human papillomavirus, as well as prevent infection and reduce the likelihood of developing malignant tumors.
Other manifestations are quite rare. This makes diagnosis very difficult.
In men, the symptoms are slightly different:
- discharge from the head of the penis (purulent, most often odorless);
- a large reddish plaque appears on the penis, which causes great discomfort;
- there is a burning sensation when urinating;
- pain during intercourse (rare);
- condylomas and warts all over the body.
If the disease becomes acute, then representatives of both sexes experience signs of intoxication of the body due to inflammatory processes. Such signs include headache, nausea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Loss of consciousness is also possible, but it is usually associated not with HPV 59, but with a developing cancer tumor.
Another characteristic symptom of any type of HPV is decreased sexual desire. Moreover, in men this is often combined with a weakening of potency.
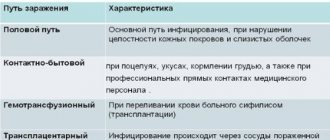
Methods of infection
Papillomaviruses are mainly transmitted sexually, that is, the main source of the virus is not blood or saliva, which many are afraid of, but particles of the affected mucous membranes or skin. Even if the neoplasms do not yet have a clearly defined shape and are not visually detectable, the presence of a pathogen in the cells is already a risk factor. For women who have promiscuous sex, the risk of contracting type 59 is quite high.
Another way of infection is the penetration of the virus in early childhood through damage to the skin and mucous membranes, as a result of which warts appear in children. One cannot fail to mention the risk of infection in medical institutions, where there is a possibility of being examined with unsterilized instruments.
In any case, if women have strong immunity, they are not afraid of papillomaviruses entering the body, even if it is HPV of high oncogenic risk, such as type 59.
Causes of the disease
The presence of HPV in a man’s body does not necessarily mean the manifestation of external symptoms.
The following factors lead to the activation of the virus:
- Excessive physical activity;
- Presence of sexually transmitted diseases;
- Malfunctions of the immune system;
- Mental fatigue, frequent stress and emotional turmoil;
- Hormonal imbalances in the body;
- The presence of bad habits, such as systematic consumption of alcohol and active smoking;
- Diabetes.
The risk of infection and activation of HPV in men increases significantly in the following cases:
- Homosexual orientation;
- Sexual contacts in the presence of damage to the genitals;
- Having a large number of sexual partners or changing them frequently;
- Beginning of active sexual activity at an early age.
Reasons for decreased immunity in women
- bad habits;
- chronic fatigue;
- lack of sleep;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- stress;
- use of antibiotics;
- infections and viruses.
A weak immune system gives impetus to the development of human papillomavirus type 59, especially in women who are at risk for the development of cancer. That is why the first point of treatment for papillomaviruses is immunotherapy.
Infection options
Human papillomavirus in patients is naturally associated with sexually transmitted diseases.
There is nothing surprising.
After all, the main way the virus spreads is sexually.
In sexual transmission, the pathogen is found in semen in men and in vaginal secretions in women.
Naturally, if you ignore basic recommendations for protected sex, it turns out to be quite easy to become infected.
A single sexual contact is enough.
Doctors emphasize that the pathogen can spread not only through classic sexual contact.
Infection can also occur if partners have unprotected anal or oral contact.
After all, the microorganism can infect not only the mucous membranes of the genital tract, but also the mucous membranes of the oropharynx and anus.
However, HPV can be transmitted from person to person not only through sexual contact.
A man can easily become infected through contact and household contact.
This happens if shared washcloths, towels, toothbrushes and other hygiene items are used, which normally should be exclusively individual.
The microorganism survives well in the environment, and therefore contact and household spread is not excluded.
HPV can also be passed from mother to child during childbirth.
The likelihood of virus penetration transplacentally is minimal.
But passing through an infected birth canal will inevitably introduce infection into the child’s body.
Moreover, not only a little girl, but also a boy can become infected.
Symptoms of HPV 59
Once in a woman’s body, the human papillomavirus may not show itself for quite a long time until factors favorable for this appear, for example:
- hormonal changes, including pregnancy;
- intrauterine devices;
- drug suppression of immunity.
The main symptoms of this type of HPV in women are:
- the presence of pointed papillomas in the area of the labia minora and majora, urethra, cervical canal, cervix;
- anemia – iron deficiency;
- constant fatigue;
- weight deficiency.
Symptoms of possible oncology in the presence of this type of virus are:
- a feeling of heaviness in the lower intestines that does not disappear after bowel movements;
- unstable stool;
- abdominal pain, flatulence;
- discomfort during defecation;
- the presence of blood in the stool.
What symptoms are observed with papillomatosis?
The main symptom is the appearance of genital warts. Unlike other infectious diseases, papillomatosis is not accompanied by fever or rash. The process of formation of neoplasms proceeds slowly, with no obvious symptoms. Often a woman discovers papillomas at the last stage of HPV 59.
Even using a condom does not exclude HPV infection. Contact with the virus-infected skin of the scrotum and pubis of a partner leads to the penetration of infection into the woman’s body.
During the formation of formations, only the appearance of itching is noted. Infection with HPV strain 59 leads to the development of condylomas on the genitals and in the anogenital area. This means that discomfort may occur during bowel movements or sexual intercourse. It is provoked by deformation of papillomas. Often a woman is unaware of the cause of the pain. As a result of a violation of the integrity of neoplasms, cancer can develop. Injury to papillomas is an indirect factor contributing to the activation of pathological processes.
With papillomatosis, the color of the formations changes. At the initial stage, they have a flesh-colored, light pink tint. As the virus develops, the color of the papillomas darkens: it becomes red, the growths acquire a bluish tint. Such changes occur during developing cancer. Additionally, an unpleasant odor appears from the woman’s genitals. There is a change in the structure of the discharge. They become abundant.
Development of HPV 59
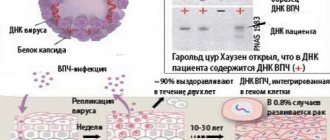
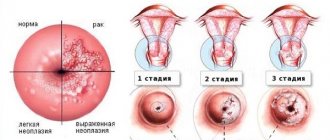
If we consider the features of the formation of this type of virus, we can distinguish 4 main stages:
- Latent. At this stage, the virus has already entered the body and has begun to develop, but has not yet manifested itself clinically. It can only be diagnosed in laboratories using DNA tests.
- The appearance of neoplasms (genital warts). After the virus has penetrated the epithelium of the affected areas, the cell's DNA is replaced with HPV DNA. As a result of such a “failure” in the program, neoplasms develop on the mucous membrane of the genital organs, in the groin and anus. Condylomas are small in size, pinkish-brown in color, and usually occur in groups.
- At the stage of dysplasia, changes occur at the cellular level, that is, the structure of the cells changes. Doctors call this condition precancerous. At this stage, it is still possible to begin treatment to avoid cancer.
- Carcinoma. Formation of cancer cells.
Development mechanism
HPV type 59, developing, overcomes 4 phases:
- Latent. The pathogen is in a “dormant” state. There are no signs of infection at all. At this stage, the pathogen is identified by testing the DNA of the virus.
- Papillomas and condylomas are formed.
- Dysplasia. Mutation processes occur in the affected cells. Papillomas are preparing for degeneration. During this period there is a chance to prevent the development of cancer.
- Carcinoma. Neoplasms transform into cancerous tumors.
In women, growths appear on the labia, urethra, vagina and cervical canal, around the anus. Growths are found on their head, neck, and arms. In addition, growths appear on the feet and face.
The dangerous infection is growing rapidly. Quite large tumors appear from small outgrowths in a matter of hours.
Basic diagnostic methods
Examination of a woman by a gynecologist
When neoplasms are detected in the intimate area, the cervix is examined first. To do this, its mucous membrane is treated with a solution of acetic acid, followed by an iodine solution. If the drugs are unevenly absorbed and a characteristic mosaic pattern is detected, the presence of papillomavirus is confirmed. Its strain and concentration are not determined by this method.
Cytological examination
To do this, the gynecologist takes a smear from the woman’s cervix or cervical canal during the examination. Laboratory testing determines the presence of cellular changes that should not normally be present. If pathologically altered cells are detected, we can talk about cervical dysplasia.
This analysis is performed using a PAP test, the results of which can be as follows:
- Grade 1: normal cell structure.
- Class 2: minor changes in individual cellular elements were detected. Possible inflammatory process. Additional tests and treatment are prescribed, after which a repeat analysis is carried out after 3 months.
- Class 3: changes in their nuclei were detected in individual cells. The results of the analysis are uncertain. To clarify the data, a histological examination and repeat cytology after 3 months are required.
- Class 4: morphological signs of malignant changes are determined; At this stage, urgent treatment is required.
- Grade 5: typical cancer cells were detected. Cervical dysplasia is confirmed. To determine the extent of tissue damage, histology is prescribed.
Diagnostics
Since the papilloma virus in women often affects the genitals and anogenital area, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- colposcopy of the cervix - assesses the condition of the tissues;
- cytological examination of a smear from the mucous membrane - infection is detected by cellular changes;
- blood and urine analysis - by changing their composition, a specialist can understand how intensively the infection is developing;
- PCR – pathogen cells are detected and its strain is determined;
- Digene test – determines the quantitative characteristics of HPV;
- biopsy and subsequent histology - reveals the presence of malignant cellular structures;
- AAT – test using acetic acid. In this way, atypical cells are identified.
Treatment of HPV 59
It is believed that it is impossible to completely recover from HPV 59, but it is possible to slow down its development and strengthen the immune system to independently fight the virus. If HPV type 59 is detected, treatment is prescribed, which usually takes place in several stages.
- removal of tumors;
- taking antiviral drugs;
- immunotherapy;
- re-testing.
Removal of condylomas is a necessary measure to eliminate discomfort in the intimate area. Performed in the following ways:
- laser destruction - removal of growths by exposure to a laser beam;
- radiosurgery – affected areas are removed under the influence of radio wave radiation without scars or scars;
- cryodestruction - removal of condylomas by freezing them with liquid nitrogen;
- chemical destruction occurs with the help of acid;
- removal of papillomas with an electric knife.
Treatment of viral infections is always accompanied by the use of antiviral drugs, which significantly increase success in the treatment of neoplasms. They are available in the form of tablets, powders, and rectal suppositories. The most common antiviral drugs are:
- Viferon;
- Cycloferon;
- Panavir;
- Groprinosin;
- Allokin-alpha.
Immunomodulators in combination with antiviral drugs make it possible to fight the virus while strengthening the immune system. As a result, even with incomplete treatment, the body has the ability to fight the pathogen on its own. There have been many cases where, after such therapy, when re-testing, HPV 59 was not detected at all. Popular immunomodulators are:
- Immunal;
- KIPferon;
- Viferon;
- Genferon;
- Cycloferon;
- Reaferon.
IMPORTANT! For successful treatment, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Only a doctor can prescribe medications, determine their dosage and duration of use.
Symptoms
External symptoms of the disease:
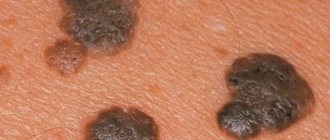
- Papilloma is a non-solid oblong growth on a stalk. The formation is colored to match the patient's skin tone. Papillomas are usually localized in the armpits, groin area, and neck.
- Condyloma acuminata is a pedunculated growth similar to a wart. The top of the new growth is porous. As it grows, the condyloma takes on a resemblance to cauliflower.
Papillomas and condylomas do not always form on visible parts of the body. They are often localized inside the reproductive organs or in the rectum .
The activation of genotype papillomavirus 59 and the development of a malignant disease are indicated by the following symptoms:
- bowel disorder (constipation or diarrhea),
- discomfort during bowel movements,
- feeling of fullness in the intestines,
- flatulence,
- pain in the intestines,
- feces with bloody inclusions.
General signs of a dangerous disease include:
- severe weight loss,
- fatigue, weakness,
- anemia.
If a person with papilloma or condyloma develops at least one dangerous sign, the likelihood that an infection with HPV genotype 59 has occurred is high. A woman needs to be urgently examined for the presence of HPV type 59 DNA, and if the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment should be started immediately.
Pregnancy and HPV 59
If papillomavirus is detected during pregnancy, then constant medical monitoring of the development of the disease is necessary. While the fetus is in the womb, it is protected from HPV. If there are growths on the cervix and genitals, a caesarean section is prescribed. If there are no neoplasms, childbirth can occur naturally. The papillomavirus does not affect conception and pregnancy in any way.
Human papillomavirus type 59 is a fairly serious disease, the treatment of which should be approached responsibly by any woman. A timely visit to a doctor will help restore health and avoid further possible problems.
How to cure HPV type 59 infection in women?
It is difficult to completely get rid of the infection, in most cases it is impossible. When infected, the condition of the body is extremely important. If immunity is weakened and cannot be increased due to external or internal factors, then the disease will continue to progress. From time to time, it is possible to suppress the activity that human papillomavirus strain 59 periodically exhibits; for this purpose, drug therapy is used.
Genital warts not only pose a risk of degeneration into malignant formations, but also cause physical discomfort and psychological problems for women.
When all the causes that provoke the development of infection are eliminated, you can count on an increase in protective forces. Then the body will fight the virus naturally, which will be facilitated by natural “killers”. Considering that it is difficult to fulfill this condition, people in most cases remain carriers of the infection. During periods of exacerbation of the disease, the following treatment methods for HPV type 59 will help eliminate symptoms and stop the development of the pathological process:
- taking medications: antiviral, immunostimulating;
- removal of condylomas.
Papillomatosis should be treated comprehensively, since by excision of excess tissue, the likelihood of developing cancer is reduced. On the other hand, taking antiviral drugs allows you to stop the pathological process. In this case, the virus is not destroyed, but its activity is inhibited. Thanks to this, the symptoms are eliminated for a certain period and the formation of papillomas stops. However, the pathological process is reactivated if immunity is not maintained. For this purpose, immunostimulating agents are taken.
When choosing a treatment method, the condition of the patient’s body is taken into account. Uncontrolled use of immunomodulatory drugs can lead to the development of autoimmune diseases. The treatment regimen is selected using the following medications:
- Genferon;
- Cycloferon;
- Viferon;
- Lavomax;
- Isoprinosine;
- Inosine Pranobex;
- Panavir, etc.
Various methods are used to remove papillomas:
- Cryodestruction - this method is widespread due to its high efficiency. This is a minimally invasive method; during the procedure, an applicator is used that delivers liquid nitrogen to the formation. Its advantage is the absence of bleeding, pain, and rapid recovery. However, it is difficult to control the level of pressure on the applicator, which increases the risk of relapse.
- Laser therapy. This is a bloodless procedure and the patient feels almost no pain. Recovery is fast.
- Radio wave exposure. This method is preferably used to remove tumors on the mucous membranes, since there are no scars left.
- Electrocoagulation. In this case, papillomas are removed with electric current. There is discomfort during the procedure, but the level of pain is minimal, and the risk of bleeding is also low.
- Surgical intervention. The method can be recommended only in cases where the papillomas have united into a single formation. Its size should be quite large (10 mm or more). Recovery is more difficult, the pain intensity is much higher than when using minimally invasive methods.
At home, growths can be removed with improvised means or pharmaceutical preparations (Ferezol, SuperClean, etc.). They have a number of disadvantages: low efficiency, a significant risk of relapse, and the likelihood of transformation of a tumor from benign to malignant.
Traditional methods of treatment
Before using traditional methods, you should know exactly what type of pathology the infection occurred.
At home it is possible to:
- increase the body's immunity,
- remove skin defect.
The use of herbs such as echinacea, nettle, and aloe helps increase immunity.
Attention! You cannot take folk remedies without a system.
Help to reduce papillomas:
- Celandine. Plant juice is dripped onto the wart every day and covered with a band-aid. Fresh warts will disappear in about ten days. It will take several weeks to remove the old ones.
- Green walnuts. They are crushed, filled with kerosene and mixed to a pulp. After applying to the papilloma, the area is covered with polyethylene for half an hour. The procedure is carried out daily, 7-10 days.
- The finished suspension - 100 g of ethyl alcohol and 5 grams of aspirin are mixed with 4 g of boric acid and 5 ml of iodine. Treat growths three times a day.
If folk remedies do not help, there is only one option left - visiting a doctor.
Features of development and stages
The 59 genotype of the virus provokes the appearance of papillomas on the skin or on its mucous membranes. The growths can have different shades and diameters. The development of the disease goes through various stages:
- The first stage is the manifestation of the virus. The disease is just beginning to develop, and there are no visible symptoms of its entry into the body. Its presence can be diagnosed only by passing certain tests;
- The second stage is the formation of condylomas. The presence of growths that have a pointed shape indicates that healthy cells are already affected by the virus. Neoplasms may appear on the skin of the genital organs or their mucous membranes. Their sizes are still small, and their shade is pink or brown;
- The third stage is the appearance of dysplasia. The cellular structure begins to change. Experts consider this condition to be precancerous. The tumor has not yet become malignant, however, in the absence of effective treatment, there is a possibility of a high oncogenic risk;
- The fourth stage is the formation of carcinoma. This is the period when condyloma is already advanced, as a result of which it becomes malignant. There is a high probability that metastases will appear in the body.