Types of fibroids
The following common types of fibroids have been found:
- Non-ossifying fibroma is a large formation on the bone surface, consisting of fleshy yellow or brown fibers mixed with blood. Teenagers and children are at risk of developing this type of fibroid. Practically does not occur in people over 30 years of age. Bone islands do not require surgical intervention, dissolving on their own, and are diagnosed only with the help of X-rays, scintigraphy and computed tomography. There are no external signs of fibroma. The growth does not cause pain or discomfort, presenting difficulties for detection and diagnosis. Does not require treatment or biopsy.
- Desmoid fibroma is a dense skin growth with a bumpy surface that lives on the skin of the back, abdominal area, limbs and chest. The diameter of the tubercle ranges from 1 mm to several centimeters. In 5% of cases it turns into cancer. To make a diagnosis, the oncologist analyzes the biopsy. The tumor is removed only if it is benign. After surgery, relapse is possible. Desmoid predominantly occurs in women. The causes of the appearance of a skin bump are unknown, but it is believed to occur as a result of trauma and skin damage.
- Odontogenic fibroma is a hard fibrous tissue that has clear boundaries and occurs in the oral cavity. It develops slowly, without causing discomfort or pain to a person. Reaching a decent size, it causes jaw deformation, pain and bloating in the oral area. The only way to get rid of the disease is surgery. The diagnostic method is x-ray.
- Chondromyxoid fibroma is a rare tumor consisting of cartilaginous tissue and multinucleated cells, and is a yellow intraosseous formation. As the disease develops, it gradually moves to the joints and spreads to the muscle tissue area. The disease is accompanied by progressive pain, swelling and hampers movement of the limbs. It can be removed by curettage, but in 25% of cases it reoccurs. Localization of formation: ribs, skull, spine, humerus and pelvic bones. Most often occurs on the tibia. Diagnosed by x-ray.
- Ameloblastic fibroma is a rare formation consisting of soft, epithelial tissue in the form of a miniature capsule and rarely develops into a cancerous tumor. The risk group includes men over 21 years of age. The tumor is localized in the oral cavity and provokes tooth loss in the area where it lives. The cyst is detected by x-ray. To avoid relapse, it is removed surgically.
- Non-osteogenic fibroma is a pathological defect that causes changes in the femur and provokes resorption of tubular bones. The presence of a bone tumor does not cause concern, but without timely treatment, a pathological bone fracture occurs. Over time, fibroids can resolve on their own.
Internal organs
This location makes it difficult to detect the tumor.
- Uterine fibrosis involves the formation of connective tissue in the muscles of the reproductive organ. A uterine tumor-like lesion does not cause cancer and is accompanied by pain and bleeding if it increases in size.
- A breast tumor is a small ball that is detected on palpation and is accompanied by noticeable progressive pain. The end result of the development of education is oncology.
- Ovarian damage does not appear at the initial stage. Reaching a substantial size, the formation brings anxiety in the form of pain in the lower abdomen, depletion of vitality, difficulty breathing, bloating and constipation.
- Pulmonary fibrosis is dangerous, affecting both respiratory organs. Accompanied by pressure on internal organs and a feeling of heaviness. A bronchial tumor is determined by the following signs: difficulty breathing, wheezing cough, hemoptysis. Precedes bronchitis, pneumonia and tuberculosis.
- Bone damage is characterized by unexpected and, at first glance, causeless fractures. The initial stage passes without symptoms. Most often occurs in children and adolescents. Does not require long-term treatment or surgery. Bone fibrosis resolves without outside medical help.
Oral lesions
- The appearance of a growth on the tongue does not pose a danger to human health and can only cause discomfort. If you try to remove the growth or cause damage, the tumor may develop into a malignant one.
- A tumor of the vocal cord and larynx affects the muscle folds of the inner mouth and vocal cords. Recognized as the most common type of fibrosis. Occurs in people who actively use their voice in their profession: speakers, teachers, artists, lecturers. The presence of a tumor negatively affects voice quality. Frequent coughing, hoarseness and difficulty breathing appear. It is detected by external examination: soft pink growths in the tonsil area are visible in the throat. Removing a tumor in the pharynx has a huge advantage: relapse after surgery is impossible.
- Maxillofacial fibroma is a single cystic formation that has a round shape and a mucous surface and is located in the jaw and oral cavity. Palpation does not bring any unpleasant sensations. It is advisable to remove the pathology to avoid transformation into a malignant tumor.
Skin damage
Soft tissue fibromatosis occurs on the skin surface and in the oral cavity. This phenomenon occurs at any age and is not determined by gender. Damage to the skin covers different areas.
Fibrosis on the face manifests itself in the form of soft or hard growths of various sizes and shapes that do not cause pain upon palpation. Facial pathology is not life-threatening and can only bring aesthetic displeasure.
Skin fibrosis affects a variety of parts of the body. The pathological phenomenon occurs in the area behind the ear of the left or right ear, on the back, on the surface of the thigh, on the chest and limbs. This includes swelling on the lip and nail. Damage to the foot and hand was repeatedly noted. Skin pathologies are characterized by having a round shape with clear boundaries and a brown or pink color.
People who have reached 40-45 years of age are at risk. The occurrence of pathology is associated with aging of the skin, heredity and the presence of diabetes mellitus. Skin fibrosis does not cause cancer, but doctors strongly do not recommend removing growths, as this leads to the reappearance of fibromatosis, which is already malignant.
Atheromas belong to skin cysts. This pathology is characterized by blockage of the sebaceous glands, causing the appearance of a residual cyst that looks like a boil or an inflamed pimple. The presence of a tumor is detected in the subcutaneous adipose tissue. The inside of the atheroma is filled with a white cheesy liquid, which is a product of the activity of the sebaceous glands and has an unpleasant odor. Both single and multiple occurrences on the skin were observed. Localization: skin of the face, head, back, genitals. Brings pain, swelling and redness during periods of inflammation. The tumor is localized in the parietal region and in the hairline area.
Fibroma on the leg under the skin treatment with folk remedies
Important! Fibroids, as a rule, do not grow into neighboring organs and vessels. Such germination is observed only in rare diffuse (aggressive) forms of fibroma.
If a benign tumor does not bother a person: it does not hurt, does not cause discomfort and does not grow at a high rate, then you can postpone a visit to the doctor. In case of negative manifestations (pain, rapid growth, etc.), you should contact a professional.
Only a qualified dermatologist should diagnose fibroids. As a rule, in addition to visual inspection and palpation, the following diagnostic techniques are used:
- scraping with cytology;
- biopsy with histological test;
- X-ray or ultrasound (if located on internal organs or if located deep).
These techniques allow not only to determine the type of tumor, but also to check its benignity. Thus, cancer can be excluded, or, conversely, cancer can be detected in time.
If fibroma is suspected in the internal organs of women, the doctor prescribes additional consultations with a gynecologist and mammologist.
The treatment strategy for fibroids largely depends on the size of the tumor. Small fibroids are treated with steroid injections , most often the drug Diprospan .
The product is injected directly into the center of the growth. Such procedures significantly reduce the size of the tumor. However, most fibroids need to be removed.
Removal of large or deep-lying skin fibromas is usually surgical .
The operation is performed under local anesthesia and takes no more than 15 minutes. Complications after such an operation are rare. The only disadvantage of surgical excision is scars (even when using cosmetic stitches).
Important! Contact qualified surgeons, as incomplete removal of skin fibroids will lead to their regrowth.
In addition, the following methods for removing skin fibroids :
- laser coagulation;
- radio wave method;
- cryodestruction;
- electrocoagulation;
- chemical method.
The most preferred methods are laser removal and radio wave coagulation.
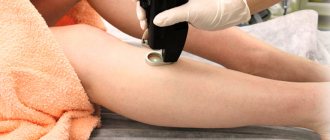
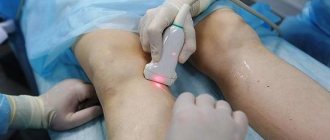
Laser coagulation – removal of fibroids with a laser beam. This method is rightfully considered one of the fastest (takes less than 15 minutes) and safest. It does not require anesthesia. The laser method eliminates bleeding and infection, and also does not leave scars. It is used to remove both large and small fibroids that have arisen in open areas (face, neck, arms, etc.).
Radio wave method - cutting fibroids with a radio knife. This is one of the most modern methods. When used, there is no bleeding, infection or scarring. The disadvantage of this method is its rather high cost.
Cryodestruction is the destruction of fibroids with liquid nitrogen or dry ice. The method is used only for removing small fibroids. Because when large tumors are removed, small white marks may remain. In addition, cryotherapy does not exclude the re-growth of fibroids in the same place.
Electrocoagulation – removal of fibroids by electric current discharges. It is used only in the treatment of small fibroids. The operation is bloodless, but leaves behind a small scar or stain.
Chemical method - removal of fibroids by burning with chemical irritants. The method is similar to cryodestruction.
Note! After removal of the tumor, an examination of its tissues is required. This is done in order to rule out cancer.
With proper and timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Resumption of fibroid growth after high-quality removal is extremely rare (in 5% of cases). Thus, modern technologies make it possible to get rid of the tumor once and for all without compromising health and beauty.
Quite often, people resort to treating fibroids with folk remedies.
These include the use of lotions, preparation of ointments, taking herbal decoctions, etc. The following “folk” procedures :
- lubricating the tumor with potato juice;
- using lotions from wood mushroom infusion (no more than 20-25 minutes a day);
- wetting fibroids with celandine juice;
- treating the growth with camphor alcohol (3 times a day);
- treatment with magnesium, or magnesium hydroxide (apply for 10 minutes a day, and then rinse thoroughly);
- lubricating the fibroid with a rub of aloe and iodine (keep the aloe leaf in the refrigerator for 3 days, then rub the leaf and leave in 100 ml of alcohol for 3 weeks, then add 10 drops of iodine to the mass).
Traditional medicine also suggests taking special drinks for skin fibroids:
- infusion of St. John's wort (1 tablespoon of St. John's wort per glass of water, leave for 4 hours, drink 3 times a day);
- freshly squeezed potato juice (1 tablespoon 3 times a day);
- infusion of oak bark (20 g of oak bark powder per glass of boiling water, leave for an hour, take three times a day);
- tincture of calendula flowers (50 g of raw material per 500 ml of alcohol, leave for 2 weeks, take 1 tablespoon three times a day);
- infusion of pine nut shells (250 g of vodka per 100 g of nuts, leave for 2 weeks, take 2 tablespoons 3 times a day);
- drink from cucumber tops (2 tablespoons of crushed raw materials per 400 ml of water, leave for 2 hours, take 20 ml 3-4 times a day).
True, the result of “folk” treatment, at best, will have to wait 2–3 months. Therefore, traditional methods should be used in combination with traditional medicine or after fibroid removal.
There is no special prevention for the appearance of fibroids. However, you can reduce the risk of tumor formation through a healthy lifestyle: playing sports, giving up bad habits, taking vitamin and mineral complexes and a balanced diet. A diet rich in dairy products, fruits, vegetables, seaweed and natural spices is believed to promote fibroid-free skin. Especially for skin patients, it is recommended to eat viburnum, apples, tomatoes and cucumbers. But salt consumption should be significantly reduced.
A fibroid is often confused with a mole, but they are not the same thing. How to identify a malignant mole is described in detail in this article.
Is fibroma a benign tumor?
Yes. Fibroma is a benign neoplasm. It consists of connective tissue, nerve cells and fat.
Which doctor should I contact?
It is worth contacting a dermatologist, since fibroma is a skin disease.
Can fibroids turn into cancer?
In isolated cases, with a rapidly growing tumor, it can, but this happens extremely rarely.
Is fibroids life-threatening?
As a rule, fibroids are not life-threatening. However, with excessive friction on clothing or with cuts, certain complications may occur: bleeding, infection, tissue necrosis, etc.
Can fibroids resolve?
Unfortunately no. At least such cases are not known to medicine. Typically, fibroids have to be removed by laser, surgery, or other means.
Summarize. Skin fibroma is a small benign tumor. It always has clear boundaries and usually resembles a pea. There are two types of fibroids: hard and soft. The main cause of fibroids is considered to be heredity. Fibroids are not dangerous: they rarely develop into cancer. However, complications can occur with injuries and friction. There are several methods for removing fibroids. A healthy lifestyle is recommended as a preventive measure.
source
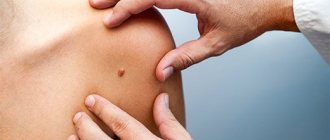
Skin fibroma is observed in people of different ages and is a rounded lump that can appear on various parts of the body under the skin. At first, it does not exceed the size of a pea, but later it tends to gradually increase. To the touch, the mobile formation can be soft or dense. Often the fibroma has a mushroom shape or stalk. In most cases, neither the structure nor the color of the skin under the tumor changes, only when the tumor enlarges, its color acquires a reddish-bluish color.
The causes of fibroids are not known for certain today. Experts believe that the appearance of such a neoplasm can be caused by a hereditary predisposition, inflammatory disease or injury. Fibroids can have complications if left untreated. This can happen as a result of injury from a razor blade or clothing items. Spontaneous twisting of the fibroid is also likely, leading to poor blood supply to the fibroid tissue.
Skin fibroids are treated through surgery. Treatment is carried out exclusively by qualified doctors in a special room. However, traditional medicine has also not ignored this problem, and can offer some means to combat this disease. A variety of tinctures and decoctions play an important role here. Also, traditional medicine often uses aloe, yarrow, wormwood, rose hips, and St. John's wort in its recipes.
Their decoctions and infusions can have a beneficial effect on the body, but the effect of their use is unlikely to be quick. To avoid unpleasant consequences, the advisability of their use should be discussed with a doctor.
To prepare the product, you need to grind and mix by volume two parts of the bark of oak branches, one part of pomegranate bark, one and a half parts of the bark of viburnum branches, pour a tablespoon of the resulting mixture with 250 ml of boiling water (in an enamel bowl), cover with a lid and for 5-7 Boil for minutes over low heat in a water bath. After this, remove the pan from the stove, let the contents brew for 45 minutes, strain, divide the resulting infusion into 3 parts and take one part at a time half an hour before meals.
This infusion is recommended by traditional medicine as a remedy for uterine fibroids. It has an astringent effect, so after using it you need to carefully monitor your intestinal function. Before using the infusion and to determine the exact dosage, you should consult your doctor.
The following recipe can help the fair sex against fibroids. You need to pick walnut leaves with a tail and fill a clay pot with them, then seal it with dough.
Next, the pot should be placed in the oven or oven to simmer for a day. Then the pot is removed and its contents are filtered. The result should be a glass of juice, which should be drunk about five times a day, one tablespoon at a time until healing.
Tincture of calendula flowers. To prepare the tincture, pour a handful of calendula flowers into half a liter of moonshine, leave for two weeks, then take the infusion three times a day, half an hour before meals, one tablespoon. Traditional medicine believes that this remedy promotes the resorption of fibroids.
For uterine fibroids, you should brew and use as tea a mixture of galangal root, five-fingered herb, yellow gentian herb, and mountain arnica flowers, crushed in a meat grinder or coffee grinder. The treatment course is about 15-20 days. If necessary, after a two-week break the course can be repeated.
Before using this product, medical consultation is required - some components of the decoction may cause allergies or other undesirable consequences.
Treatment of this disease with folk remedies can be carried out in parallel with classical treatment, but in no case replaces it. It should be remembered that each person perceives traditional medicine methods differently, and accordingly, the results will be varied. Certain traditional medicines can provoke allergies, individual intolerances or other consequences, so before starting to use them, you should definitely consult a doctor.
It must be remembered that treatment with folk remedies is a prototype of self-medication, and should be treated with caution.
7 scientific facts about the benefits of drinking water!
Plastic food containers: facts and myths!
Fibroma is a benign tumor skin formation, usually flesh-colored or light pink in color, with clear boundaries. It consists of connective or fibrous tissue and usually rises above the surface of the skin, located on a broad base or on a stalk. Does not cause pain to humans.
Fibroma in medicine is a benign neoplasm consisting of coarse fibrous bundles of connective tissue and fibroblasts. Most often, it is not life-threatening, but there are cases when fibroids grow uncontrollably, causing various problems. The tumor can develop in various places, including bones, feet, and the walls of the uterus.
There are two types of fibroids. The first of these is a hard skin fibroma. In most cases, such a neoplasm is located on a broad base, but sometimes a solid skin fibroma has a stalk. It is dense to the touch and has limited mobility. This type of fibroma can form both on the skin and...
The majority of women with uterine fibroids do not experience any symptoms and only 25% of women have clinical symptoms, which depend on the location of the tumor relative to the pelvic organs, its size, number and direction of growth of fibroid nodes. A characteristic symptom of fibroids is prolonged menstruation, turning into...
A benign tumor is a pathological neoplasm with a slow or absent rate of development. Timely treatment gives a positive prognosis - in most cases, the patient completely gets rid of the disease, and there are practically no relapses. A danger to humans is a tumor that secretly develops in the body.
source
At all times, people have paid close attention to the condition of their skin, including their feet. But sometimes various skin lumps or so-called fibroids appear on it. Such neoplasms are considered benign.
They are usually located under the top layer of skin and are dense skin structures consisting of fibrous tissue. They can be present in both singular and plural. Let's find out what it is and what treatment should be used.
Fibroids can rise above the skin or be located under it. Very often, such neoplasms are observed on the legs (inner thighs and feet). Photos of such neoplasms can be easily found on the World Wide Web or in specialized medical literature.
Fibromas are also divided according to the rate of formation into growth-limited and diffusely aggressive (they are located at a considerable depth under the skin and can involve other tissues in the process of their growth).
This type of neoplasm is wrinkled, wrinkled skin on a stalk. They are usually small, blend in color with the skin tone, or have a darker tone. Typically, such fibroid tumors are observed in men and women who have crossed the retirement age and are overweight.
You need to be especially careful with them - they can be damaged by clothing or simply shaving. They can twist themselves, which threatens poor blood supply to fibrous tissue. And this, in turn, threatens the appearance of pain, increase in size and necrosis of fibroma tissue. Such benign formations can develop into malignant ones.
This type includes dermatofibromas and plantar fibromas. The first type has a dense skin structure and can rise above the skin or be pressed into it. If you press hard on such a dermatofibroma, it will squash and form a small hole. Such fibroids do not cause pain and can be located anywhere on the body, including on the mucous membranes. Color can range from flesh-colored to red or purple. Treatment of such fibroma is simple and can often be done using gentle methods.
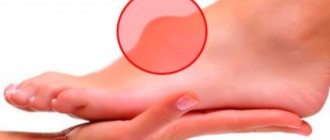
Plantar fibroma is located on the foot under the skin. This is the most unpleasant type of fibroma, since the tumor is constantly in contact with the shoe and causes pain during movement. Quite often, this kind of fibroma is not singular, but plural. This condition, naturally, causes great inconvenience to a person and requires radical treatment.
Modern medicine cannot yet give a clear definition of why fibroids occur. It is believed that the main factors for the appearance are:
- Genetic predisposition. According to medical observations, it has been established that people whose relatives have fibroids are more at risk of seeing such a tumor in themselves.
- Age. The older a person gets, the worse the connective tissues of the skin are supplied with blood. Even if the skin is slightly damaged, it may not heal properly. This creates excess skin, which eventually develops into fibroids.
- Natural photoaging of the skin.
- Hormonal changes in the body (pregnancy, menopause).
- Endocrine diseases.
- Various skin inflammations.
A separate point worth considering is how fibroids form under the skin on the leg. This type of formation often occurs in people exposed to constant physical activity and working primarily while standing. Fibroids often occur in professional athletes. In photographs of such neoplasms, dense leathery growths can be clearly seen.
Additional factors that can trigger the appearance and growth of fibroids include skin hypersensitivity and frequent injury from shoes or clothing, excessive tanning, sudden changes in temperature conditions, non-compliance with the principles of a healthy diet, liver problems and certain types of diseases (for example, tuberculosis).
To determine whether a fibroma is benign or malignant, it is necessary to conduct special studies. Usually a skin analysis is performed for histology. Naturally, it is necessary to contact a qualified specialist who will prescribe a specific treatment. It is unlikely that you will be able to make a correct diagnosis for yourself, even by looking at similar photos on the Internet.
If during a medical examination it is difficult to determine what type of fibroma it is or if it is atypical, a biopsy test is performed. To do this, a small area of skin is cut off and examined under a microscope. This is how cancer is diagnosed.
In most cases, such tumors do not cause any discomfort. But if they are a cosmetic defect or cause severe pain, then they are removed with the help of medications (injections) or surgically in an outpatient setting (during the operation, local anesthesia is usually given). Sometimes fibroids can be removed using traditional methods of treatment.
Small fibroids can be removed with certain medications. An injection is made into the center of the tumor, after which the fibroma resolves. If such treatment does not help, they resort to surgery.
The patient is given an anesthetic injection in the area where the fibroma is located, the surgeon simply removes it with a scalpel and applies a sterile occlusive dressing. For proper healing, it is necessary to further treat the wound with an antiseptic and apply dressings.
The procedure takes no more than 30 minutes, it is painless and has no contraindications. Fibroids are removed with a laser beam with certain characteristics (beam length and power). The skin is cooled by a special system, which completely eliminates pain. The laser acts directly on the fibroma without affecting adjacent areas of the skin.
After removal, the wound heals for several days and does not leave any scars or scars. The procedure can be carried out both in a clinic (if appropriate equipment is available) and in a beauty salon. Be sure to remove such tumors under the supervision of a doctor; before the operation, look at the photos in the salon before and after the operation.
This treatment is often used if there are contraindications for conventional surgery. It is most effective for excision of pedunculated fibromas, which are cut off with a radio wave scalpel. The process is bloodless and painless. In the coagulation mode, the cells of the tumor being removed are removed to the required depth and area of influence. Adjacent healthy areas of skin are not affected. The rehabilitation process takes no more than a week, the skin does not undergo scarring.
Fibroma tissue is subjected to thermal shock with the formation of a crust at the site of removal. After the wound heals, there are practically no traces left. Used for fibroids up to 2 cm in size.
Make an alcohol tincture from cedar nuts (take 100 grams of shells) and 250 milliliters of vodka. Leave for 2 weeks in a dark and cool place. Drink 2 tablespoons a day, be sure to add a little water. Divide the tincture intake 3 times. In this case, the fibroma resolves and the process of improving tissue regeneration occurs.
Pour boiling water (200 ml) over dry St. John's wort (1 tablespoon), leave for 3 hours. Filter. Divide the resulting volume of infusion into 3 equal parts and take three times a day.
Cut the leaves from the cucumber and chop them. Place a container in a water bath, putting 2 tablespoons of cucumber tops in it, filled with 400 ml of boiling water. Let stand for a quarter of an hour, strain and leave for 2 hours. To improve blood circulation, drink a tablespoon several times a day.
Let your legs never know what fibroma is! But if such a nuisance suddenly happens, then you already know what to do!
source
0
Did you like the article? Share with friends:
You may also be interested
Recipes from the people
Stye in a child: how to treat folk remedies
Barley is an acute inflammatory disease of the eye that can appear in a person of any age.
Recipes from the people
How to quickly cure barley in a child using folk remedies
Many people have encountered such a “surprise” as stye on the eye. Swelling appears on the eyelid and
Recipes from the people
Barley in a 2 year old child - folk remedies
Barley is an acute inflammatory disease of the eye that can appear in a person of any age.
Recipes from the people
Stye under the eye treatment with folk remedies
What to do if stye grows on the eyelid? How to treat stye on the eye at home
Recipes from the people
Barley initial stage treatment with folk remedies
What to do if a stye develops on the eye? It is better to treat stye on the eye with folk remedies
Recipes from the people
Stye has started, what to do, folk remedies
What to do if a stye develops on the eye? It is better to treat stye on the eye with folk remedies
Site search. Enter your query:
about the author
Hello, friends! My name is Nikolai Vakulenko. On the pages of my online magazine, I collect a variety of interesting, educational and curious information from a variety of sources, process, check and post. Information both from our sources and from foreign ones. If you see errors and inaccuracies, write about them in the comments or email me. Also, I will always answer any questions. Be healthy! Do not be ill! Take care of yourself!
Healthy
How does coding for alcoholism occur?
Interaction of the clinic, hospital, clinic and medical center with each other
Treatment of patients with alcohol and drug addiction
Take care of your eyesight - take eye vitamins!
What is hypertension in simple words
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright holders
© 2021 MDROIT.com Attention!
The information published on the site is for informational purposes only and does not constitute a recommendation for use. Be sure to consult with your doctor! Adblock detector
Causes
The causes of its occurrence have not yet been fully elucidated, but the occurrence of this disease is influenced by the following factors:
- The presence of bad habits, especially alcohol and tobacco addiction.
- Skin damage and trauma.
- Polluted urban habitat.
- Poor nutrition, especially excessive consumption of sweet, fatty, starchy and spicy foods.
- Viruses.
- Weak immunity.
- Radiation.
- Dishormonal balance.
- Excessive UV exposure.
Warning and forecast
Since the formation of fibroids is often associated with a hormonal imbalance in the body, before taking any medications that affect hormonal levels, it is necessary to consult a doctor. If fibroids are already present, it is necessary to avoid rubbing or injuring them. The main preventive measure is a healthy diet and an active lifestyle. In winter, it is worth taking vitamin complexes. It is also recommended to give up bad habits. These simple measures stabilize hormonal levels and help avoid unpleasant changes.
Diagnosis
The process of detecting formation also depends on the type and location of occurrence. Benign tumors of internal organs can be detected using X-rays, computed tomography, scintigraphy, biopsy, magnetic resonance imaging and by external examination in the case of superficial skin formations. Determining the many types of fibroids is difficult due to their asymptomatic nature and slow development. A tumor of the female reproductive system is detected by ultrasound.
During diagnosis, there is a risk of confusing a fibroma with a lipoma. How does the pathology described in the article differ from lipoma? Fibroma can consist of both soft and hard tissues. Lipoma consists of soft fibers. Lipoma does not carry the risk of cancer, while fibroma in some cases can be malignant.
Diet
Experts do not identify any special nutritional principles for the treatment of fibroids. However, if the formation of a tumor in the uterine body is diagnosed, then it is advisable to adhere to a diet that will contain foods that help increase hemoglobin. It can be liver, buckwheat, red fish, veal, cabbage, beans and others.
When fibroma is localized in the chest area, it is recommended to include foods enriched with fiber in the diet. As a rule, you need to eat more apples, beets, and seaweed.
You also need to be more careful about your drinking regime. Drink more green tea. It is better to avoid eating fatty foods.
If other organs and tissues are affected, there is no need to follow a special diet. In such cases, only proper balanced nutrition is provided.
Treatment and removal of the tumor
Surgery, oncology and dermatology are areas of medicine that contribute to the timely diagnosis, treatment and removal of fibroids. There are many professional clinics specializing in these issues. Removing fibroids is fraught with negative and dangerous consequences, requiring prior consultation with a professional doctor. Treatment of pathology depends on the type, origin and degree of complexity. Fibroma must be removed if it is malignant. Methods of treatment and tumor removal:
- Laser removal is a quick and effective way to get rid of skin defects. Removal requires a single procedure, and the recovery period lasts a maximum of 14 days. Removing a tumor with a laser is one of the safest ways to get rid of the disease. The procedure does not cause pain and does not leave scars.
- Removal of fibrosis with an electric knife is reproduced using electric current and is carried out both with and without the use of an anesthetic.
- The method of removal with an electrocoagulator is applicable to pathologies formed on the surface of the skin. The procedure involves the use of electric current to cause necrosis of fibrous tissue, resulting in the death of the skin defect. Cauterization leaves thermal burns. Coagulation is prohibited when removing malignant tumors, in the presence of herpes and somatic diseases. The wounds remaining after the procedure heal quickly without leaving marks. A light spot remains at the site where a large wart or papilloma was removed.
- Bloodless removal of fibroids by radio wave occurs using a radio knife and does not leave injuries or burns. Recommended for people with sensitive skin. Removal takes a maximum of five minutes. Recovery of the operated skin area lasts seven days.
- Laser vaporization treatment is used for diseases of the cervix and the occurrence of skin pathologies. During the procedure, the doctor adjusts the depth of the laser beam and controls its movement. This method is used in cosmetology and surgery. Laser technology does not leave spots, scars or scars after removal, unlike surgery, which leaves stitches behind. After the operation there are no complications or difficult rehabilitation period.
To prevent a new one from growing after fibroma removal, correct diagnosis and quality treatment are necessary.
Classification
The main classification of fibromas involves their division into several forms. The following forms of fibrous formations are distinguished:
- Soft fibroma - the tumor contains cellular elements with a small concentration of connective fibers. This soft tissue fibroma has the appearance of a polyp with a size ranging from 1 millimeter to 1 centimeter. Such nodes often form on the surface of the skin in the armpits, mammary glands, inguinal folds, on the neck and face.
- A dense fibroma is a tumor consisting of collagen fibers with an insignificant content of cellular fibers. Externally, the tumor looks like a mushroom with a volume of 5 mm to 10 cm.
- Desmoid fibroma - the structure of the formation is dense. The tumor often appears on the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. The tumor grows rapidly and can recur after removal.
Despite the benign nature of the tumor, if fibroma occurs in a child, you should not ignore the tumor and postpone treatment until later. It is imperative to show the baby to the doctor for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Depending on their location, there are tumors: skin, uterus, breast, ovaries and other important organs.
How dangerous is fibroma, and why can’t this disease be ignored?
The consequences of ignoring pathology are dire if the disease becomes malignant. This is the main danger of the disease. To avoid negative consequences, it is recommended to consult a doctor at the first signs of pathology. It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate or remove tissue fibrosis on your own without undergoing the appropriate studies and passing the necessary tests!
Every year, the number of people who are diagnosed with benign formations on the skin – fibromas – increases. This kind of disease can appear in both a child and an adult. Fibroma - what is it, what are its symptoms and treatment, what types of disease exist. Symptoms of a soft tissue defect are practically absent.
Conservative therapy
The possibilities for conservative correction of fibroids are significantly limited. There is a technique, the essence of which is to inject corticosteroids into the tumor tissue. Injections of beclomethasone (Diprospan) help prevent it from growing. The drug allows you to reduce the size of the fibroma, but in most cases it is not possible to do without its surgical removal.
Diet plays a certain role in the treatment of the tumor process. Patients are advised to consume more plant foods and fluids. You should limit spicy, fried and fatty foods, canned food, and dishes with chemical additives.
What is fibroma and why is it dangerous?
So, what is a fibrous formation? This is a benign node that is formed from connective tissue cells. The tumor affects different parts of the body and human organs: skin, mammary glands, uterus, ovaries, and so on. Soft tissue fibroma is a benign tumor, but if not treated in a timely manner, the tumor enters the malignant phase.
There are single or multiple (fibromatosis) lesions of connective tissue, soft and hard forms of the disease. Removal of the formation is carried out using different methods:
- surgical excision;
- cryodestruction;
- laser therapy;
- radio wave exposure.
Soft
The mild type of the disease refers to multiple tissue lesions. Appears on the face or neck, in the armpits, under the mammary glands. The neoplasm is distinguished by its color, which varies from flesh-colored to brown. A soft oncological defect looks like a round polyp on a stalk. If it is injured, pain is felt and bleeding occurs.
Solid
A solid fibrous tumor is a small tumor. It is located above the skin or mucous membrane. Often this type of disease has dimensions of no more than 1 centimeter and is formed on a spacious basis. It's not difficult to recognize her. Affects the limbs, internal organs (lungs, heart, stomach, uterus, vagina, etc.).
Diagnostics
Primary diagnostic measures are carried out by a therapist, but in addition, consultation with more specialized specialists is often required depending on the location of the tumor, for example, a gynecologist, dermatologist, pulmonologist, orthopedist, endocrinologist, dentist and other doctors.
The first stage of establishing the correct diagnosis includes:
- studying the medical history - to establish the most likely pathological etiological factor;
- collection and analysis of life history - to find out what predisposing factors could influence the development of breast fibroma or other localization;
- thorough examination and palpation of the affected area;
- a detailed survey of the patient aimed at determining the intensity of symptoms and drawing up a complete picture of the course of the disease.
Laboratory diagnostic activities involve the following:
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- blood biochemistry;
- tests to determine tumor markers;
- microscopic examination of a smear taken from the vagina or oral mucosa.
The most useful in terms of diagnostics are the following instrumental procedures:
- radiography and ultrasound of the affected area;
- CT and MRI;
- mammography and gastroscopy;
- colonoscopy and hysteroscopy;
- bronchoscopy and diagnostic laparoscopy;
- endoscopic biopsy;
- orthopantomogram and radiovisiography.
Endoscopic biopsy
Soft tissue fibroma
Tissue tumors often develop in men and women on the skin, mammary glands, and tendons. The location of such oncology of all types is very diverse. The neoplasm mainly affects the soft tissues of the arms and legs, the torso area, the face, and the neck. Often benign oncology appears in internal cavities and organs. Let's consider the main forms of tumor.
Uterus
Uterine fibroids - what is it? This type of cancer forms in the muscle tissue of the uterus. Neoplasms are divided into fibroma, myoma and fibromyoma. The first type consists of connective tissues. Myoma is an oncology formed from muscle tissue, and uterine fibroids, the symptoms and treatment of which are identical to the classical form of the disease - it is formed from connective and muscle fibers.
In most cases, a uterine tumor does not have pronounced symptoms, but sometimes its size or location gives the woman severe pain, and at times even bleeding occurs. The size of multiple nodes varies from small to extensive formations. It happens that the anomaly increases to very large sizes.
Mammary gland
Breast fibroma is detected in many women. The appearance of oncology is often closely related to hormonal changes in the female body (menstruation, menopause, childbirth). Breast fibroma is classified into two types: fibroadenoma and fibroadenomatosis. The first type is a solid ball that moves. The second one fills the mammary gland completely, which causes severe pain to the person.
Ovarian
A neoplasm of a round shape with a smooth or nodular surface, having a stalk, is an ovarian fibroma. If it is small in size, then the symptoms hardly appear. When the formation increases, it often leads to the following signs of the disease:
- severe weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- dyspnea;
- tachycardia;
- pain;
- bloating of the abdominal cavity.
Fibrous skin tumor is a benign connective tissue pathology. Formations of a soft structure are located on various parts of the body (in the folds of the groin, armpits, chest, fingers). This type of cancer is often detected in females after 40-50 years of age. A solid tumor forms in both women and men. It has a dense structure and protrudes above the surface of the skin.
Angiofibroma is a formation derived from fibroma. It consists of connective fibers, with vessels on a smooth surface. This type of benign fibrous abnormality forms as a noticeable small nodule that is flesh-colored or light brown in color. It is often diagnosed in males and females over the age of 45 years.
Lungs
Oncological diseases also affect the human lungs. Pulmonary fibroids - what is it, what are their features? A very dangerous tumor, often affecting both respiratory organs at once, and can increase in size. Occurs at any age, multiple and solitary forms of the disease are observed. At first there are no signs, but with significant growth, there is a feeling of heaviness in the chest, pressure on the sternum organs.
On the tongue
A benign tumor of the oral mucosa, consisting of connective fibers, is called oral fibroma. A neoplasm is formed on the mucous membrane of the lips, gums, palate, tongue, and inside the cheeks. It looks like a round shaped knot with a stem or large base. If a tumor on the tongue or other part of the oral cavity is often damaged, it can transform into malignant.
On the face
Facial fibroma is localized in different parts of the face, affecting people of all ages. The main symptom of the disease is the sudden appearance of a small hard or soft growth. In general, pathology on the face occurs without symptoms, unless it is receptive to touch. Often forms in/on the nose, ears, eyelids.
Uterine fibroids - malignant tumor or not
Myoma is a degeneration of myometrial cells, which leads to the formation of a chaotic plexus of smooth muscle fibers, round nodes are formed. The formation nodes can be small, single or multiple, large nodes that deform the reproductive organ. They can form on the outside of the uterus, grow towards the tissues and organs of the abdominal cavity, or form inside the cavity, on the cervix. Since the development of formation begins due to a violation of the division of one smooth muscle cell, all subsequent cells are also similar smooth muscle cells.
Video: is fibroid dangerous?
The video explains what soft tissue fibroids are and how dangerous this disease is to health and life. After watching the video, you can find out what types of tumors exist and how to deal with them. Such useful information will allow you to identify the disease in time and undergo examination by a doctor who will prescribe the optimal therapy.
Breast fibroadenoma is a very common benign breast disease.
This pathology is diagnosed mainly during a woman’s reproductive age, but sometimes it can also occur during menopause.
For a long time, fibroadenoma may not bother a woman in any way, and if a woman does not examine the mammary gland on her own and irregularly visits a mammologist, the pathology may not be diagnosed immediately.
Such a negligent attitude towards one’s own health is dangerous because advanced fibroadenoma can lead to various complications, including the development of oncology.
Associated symptoms
During a self-examination of the mammary gland, a woman may find multiple or single lumps in the upper part of the gland.
This neoplasm has a characteristic structure and shape. A single tumor is a spherical elastic compaction with a smooth surface. The neoplasm easily changes its position, since it has no connection with other tissues.
The clinical picture, as a rule, is not clearly expressed, and indirect signs of the disease are:
- weight loss with normal appetite;
- weight gain;
- vision problems;
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle.
Such signs may have various hormonal disorders, which are the causes of the formation of fibroadenoma.
As for the leaf-shaped form of pathology, it has more pronounced symptoms:
- the size of the mammary gland increases;
- the shape of the breast changes;
- pain is possible, which intensifies before the onset of menstruation.
What is it formed from?
The exact reasons for which fibroadenopathy develops are currently unknown. Experts say that the increased effect of female sex hormones provokes focal growth of glandular and connective tissue.
Factors that can trigger the development of the disease:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Hormonal disorders in thyroid dysfunction, diabetes, obesity.
- Factors related to the reproductive system (late or too early childbirth, lack of lactation, frequent cycle disorders, abortion);
- Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, liver, gall bladder.
- Uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives.
- Stress, smoking, alcohol abuse.
What is the danger of neoplasms?
Fibroadenoma itself is not dangerous to the health and life of a woman. However, this does not apply to all its forms.
In addition, the active growth of the tumor can lead to an increase in the size of the mammary gland, which, in turn, will provoke:
- an increase in the size of the mammary gland and its asymmetry . This phenomenon leaves a negative imprint on the psychological state of a woman, and therefore requires surgical correction;
- the occurrence of pain symptoms in the sternum . Large tumors can put pressure on nerve endings, leading to pain and discomfort;
- deterioration of the mammary glands . By pinching blood and lymphatic vessels, fibroadenoma can contribute to malnutrition of the mammary gland tissue, which will negatively affect the health of the breast.
However, the greatest danger of fibroadenoma is its possible degeneration into oncology.
Fortunately, this does not happen often, but the possibility cannot be completely discounted. Most often, the leaf-shaped form of the pathology becomes malignant, so such fibroadenoma is removed immediately after diagnosis, even if its size is small.
The danger of fibroadenoma during pregnancy is that the tumor can begin to grow rapidly.
It is known that while carrying a baby, significant hormonal changes occur in a woman’s body, and the hormonal balance is disrupted. This gives impetus to the growth of the tumor, and can also provoke transformation into a malignant process.
Mammologists recommend planning a pregnancy and undergoing a thorough examination to remove the tumor before conception.
Even if the fibroadenoma is surgically removed, recurrence of the disease cannot be ruled out. Relapses occur especially often if the factors that provoke the disease are not eliminated. Therefore, it is very important not only to remove the tumor, but also to treat ailments that provoked hormonal imbalance.
Symptoms of fibroid degeneration into cancer
- Vaginal examination.
- Rectal examination.
- Cytological examination or biopsy.
- Diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity.
- Diagnostic curettage of the cervical canal.
- Ultrasound.
- Lymphography.
- Ileocavagraphy.
- CT.
- MRI.
- Lymphangiography.
In some cases, sarcoma forms inside a fibroid node. When fibroids turn into cancer, the signs of a malignant tumor appear as follows:
- Pain.
- Bleeding.
- Profuse leucorrhoea.
These three symptoms indicate signs of fibroid degeneration into a malignant tumor. Leucorrhoea with uterine sarcoma can be watery and profuse, blood-stained, mucous, and foul-smelling. The fetid odor and putrid nature of vaginal discharge indicate late stages of cancer. Bleeding becomes prolonged and profuse, and pain intensifies. Pain and spotting appear in a young woman after sexual intercourse or physical activity, after douching, or examination by a doctor - this may indicate the development of a malignant process in the cervix or body of the uterus.
If a woman experiences spotting after menopause, this most often indicates the development of uterine cancer. The spread of epithelial cancer cells often occurs through the lymphatic system, so tumor metastases are found in the obturator, pericervical, periuterine, common, external and internal iliac lymph nodes. The inguinal and peri-aortic lymph nodes are much less commonly affected. In most cases, cervical carcinoma affects the vaginal tissue. Uterine cancer spreads more slowly than cervical cancer.
If signs of tumor development appear, the doctor refers the patient to tests that help to quickly determine the nature of the disease. Ileocavagraphy and lymphography help determine the degree of damage to the lymph nodes and the degree of tumor metastasis. Using MRI and CT, a malignant neoplasm is diagnosed, blood circulation, tumor size, and tumor invasion into neighboring organs and tissues are assessed. The doctor prescribes a biopsy of the tumor and additional blood tests. After a complete examination, a treatment plan is developed, which will depend on the size, stage of tumor development, the patient’s age, and concomitant diseases.
Treatment methods
Surgery to remove fibroadenoma is the only way to completely get rid of the pathology. However, in some cases, doctors choose observational tactics or recommend hormonal treatment.
If the tumor reaches 2 cm in diameter, the question of surgical intervention arises.
Without surgery, it is possible to slow down the growth of the tumor, which makes it possible to postpone surgery to a later date.
For this, a woman is prescribed the following groups of medications:
- synthetic hormones;
- vitamin complexes;
- if necessary, anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antiestrogens;
- herbal medicines;
- oral contraceptives;
- gestagens.
If such treatment does not lead to positive results within six months, it is canceled and surgical intervention is prescribed.
There are two main surgical methods for removing fibroadenoma:
- enucleation - removal of the tumor itself, without affecting surrounding tissues;
- resection - sectoral or complete - in this case the neoplasm is removed along with part of the breast tissue or the mammary gland is removed completely. Most often, sectoral resection is performed; radical methods are resorted to in the development of oncological processes.
As for other methods of tumor removal, they are as follows:
- laser removal – removal is carried out without anesthesia, after treatment there are no scars left on the skin;
- removal using radio frequencies - a tiny incision is made in the mammary gland, where a radio knife is inserted and the tumor is removed;
- cryoablation – freezing the tumor with liquid nitrogen. This is the most popular procedure for removing breast fibroadenoma.
Patient reviews
Ksenia, Minsk: After a planned visit to the gynecologist, I was diagnosed with as many as 4 fibroadenomas. One large one had to be removed, I constantly monitor the rest, lead a healthy lifestyle and try to prevent their increase.
Inna, Krasnodar: Removal of fibroadenoma is a non-scary and uncomplicated operation that completely relieved me of the problem. After a few years, only a small, almost invisible scar reminds of the fears experienced.